French cure for stomach ulcers. Treatment of stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcers with tablets, medications, preparations. Other drug subgroups
A stomach ulcer is a chronic disease. With it, the appearance of ulcerative defects in the gastric mucosa occurs. The main risk group for this disease is men 20-50 years old. The disease is characterized by frequent relapses, the peak of which falls on spring-autumn period... What medicines to use for stomach ulcers will be best told by a gastroenterologist.
Recommendations for next dose for stomach ulcers and duodenum... Eliminate symptoms quickly. A suitable therapeutic response can be obtained with doses of 10 mg, so individual doses will be considered. If treatment with Losek 20 mg daily has not resulted in symptom control within four weeks, more research is recommended. Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: In these patients, doses will be individualized and treated according to clinical indications.
If the daily dose exceeds 80 mg, it should be divided and administered twice a day. Renal impairment: No dose adjustment is required in patients with impaired renal function. Elderly: No dose adjustment is required for the elderly. Children: Children have limited experience with Losek. Take 10 mg gastro-resistant tablet Take 20 mg gastro-resistant tablet.
The cause of the disease is an imbalance between the mechanisms of protection of the stomach and aggressive factors from outside. Exists whole list factors that can lead to it:
- various chronic diseases Gastrointestinal tract;
- poor nutrition;
- long-term use of ulcer-forming drugs;
- long-term smoking;
- frequent alcohol consumption;
- stressogenicity;
- genetic inclinations.
Stomach ulcer treatment options

Each 10 mg tablet contains 10 mg of rabeprazole sodium, corresponding to 9.42 mg of rabeprazole. Excipients listed in section 1. Adults and the elderly. Active duodenal ulcer, active benign stomach ulcer. The recommended dose of Paretta is 20 mg per day.
Some patients with active duodenal ulcer disease may require a dose of 10 mg per day. In most patients, an active duodenal ulcer heals within 2-4 weeks, and few may need to take the medication for another 4 weeks. An active benign stomach ulcer usually lasts 6 weeks, but some patients may take another 6 weeks.
Looking at each specific case, the doctor can suggest to the patient:
- diet therapy, which includes proper nutrition;
- drug treatment, implying drugs against stomach ulcers;
- remedial gymnastics;
- surgical intervention;
- minimally invasive procedures.
The vast majority of patients are treated at home. Only patients who have a strong pain syndrome, complication, or they have no effect from outpatient treatment.
Erotic or optic gastroesophageal reflux disease. The recommended daily dose is 20 mg. The medicine should be taken within 4-8 weeks. Long-term treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Symptomatic treatment of moderate to severe gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The recommended dose of the parasite in patients without esophagitis is 10 mg once daily. If the symptoms of the disease do not completely disappear within a four-week period, the patient should be further investigated. If the symptoms of the disease disappear during treatment, the medicine can be used as needed in case of subsequent symptoms.
Treatment with drugs

Tablets for stomach ulcers can be roughly divided into three groups:
Treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. The recommended starting dose for adults is 60 mg once daily. The dose can be increased to 120 mg per day, depending on the individual needs of the patient. Dosages up to 100 mg per day can be taken once a day. 120 mg may need to be divided and taken twice 60 mg twice daily. Treatment should be continued as long as it is clinically needed.
Within 7 days it is recommended to use following methods... Take a desk 20 mg, 500 mg clarithromycin and 1 g amoxicillin twice a day. In cases where only one steamed is to be taken daily, it should be taken in the morning before meals. Although it was not noticed that food or daytime will interfere with the effectiveness of rabeprazole sodium, but patients with this dosage are generally better.
- drugs from the antibiotic group;
- drugs that block histamine receptors;
- drugs that inhibit the proton pump.
In addition, any medicine for stomach ulcers for complementary therapy, can be classified additionally:
- propyne-like agents;
- means for neutralizing stomach acid;
- drugs that promote mucosal healing;
- metabolism enhancers;
- drugs to protect the gastric mucosa;
- drugs that relieve spasmodic pain;
- drugs that inhibit vomiting;
- drugs that enhance immunity;
- Pain relievers;
- Ganglion blocking drugs.
Together with two other anti-infectious agents, you must take it twice a day. Patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Patients with hepatic or renal impairment do not need to change the dose. Chapter 4. Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the excipients. It is contraindicated in pregnant or breastfeeding women.
The relaxation symptoms caused by the Paré effects do not indicate that the stomach or esophagus is not malignant tumors and therefore it is necessary to investigate whether it is present before treatment. The attending physicians constantly monitor the patients who are being treated continuously.
The main role is assigned to antisecretory drugs that should be drunk with stomach ulcers, taking into account the following factors:
- the size of the ulcerative defects;
- their number;
- their depth;
- location;
- position of the gastroduodenal mucosa;
- background ailments.
Picked up with the help of a doctor best medicine from stomach ulcers for your specific case painful sensations should pass fairly quickly, within a few days. However, you cannot stop drinking the drugs, since the ulcers are not healed.
Children Do not treat Paret, so they should not be given this medication. Gastric acid secretion from rabeprazole sodium salt is significantly and steadily decreased, so use of this product in conjunction with others may occur medicines absorption depending on the interaction with gastric acid. Studies have shown that together with the sodium salt of rabeprazole using ketoconazole or itraconazole, the following antifungal plasma concentrations are decreased.
Thus, the use of these drugs together with Pariet, in some patients, monitoring may be required to determine if there is no need to adjust the dose. Clinical trials have been used in addition to liquid antacids, no significant interaction was observed.
Of all possible options top scores gives a diagram consisting of two stages.
1) The duration of the first stage is seven days. On these days, the patient must take an antibiotic complex, the name of the drugs may vary, these may be:
- clarithromycin - considered the main and most effective remedy from an ulcer;
- amoxicillin - absorbed almost completely, can be used more than twice a day;
- metronidazole is a synthetic analogue of azimycin, the action of which is to destroy the DNA of bacteria;
- tetracycline - stops protein synthesis by bacterial cells, as a result of which they die off.
In addition to antibiotics, drugs that inhibit the proton pump are prescribed. Examples are:
Whether rabeprazole is safe to treat in pregnant women is unknown. Studies have shown that the drug does not reduce fertility in rats and rabbits, does not cause damage to the fetus, but rats slightly penetrate the placenta. Pregnant women Parieta is contraindicated.
Is rabeprazole sodium salt excreted in the body? breast milk... Studies in nursing mothers have not been conducted. With milk, rats are excreted from the body. Breastfeeding women should not use Parieta. According to the pharmacodynamics of the drug and side effects, it can be argued that the ability to control or operate the mechanisms of Pariet should not interfere. However, if the presence of drowsiness worsens alertness should be avoided in order to drive and use machines.
- lansoprazole - accelerates the exchange of hydrogen protons;
- omeprazole - reduces the activity of enzymes;
- rabeprazole - in addition to inhibition, it negatively affects the main causative agent of the ulcer;
- esomeprazole is an analogue of omeprzole, the actions are very similar.
The goal of the first stage is to fight the pathogen bacteria, in more than 90 percent of cases this is successful.
Observed side effects were transient and mild to moderate. The most common side effects are headache, diarrhea and nausea. More often than isolated cases, reports of adverse reactions by organ system class and frequency are listed below. Data on these side effects that have been obtained from clinical trials as well as the post-marketing period of the drug. However, all adverse reactions reported to the company in clinical trials are only such side effects Headache, diarrhea, abdominal pain, asthenia, flatulence, rash and dry mouth have been associated with the use of Pariet tablets.

2) The second stage lasts twice as long - fourteen days. Previously taken antibiotics and PPIs are supplemented with drugs that block histamine receptors, this list includes:
Metabolism and Eating Disorders Anorexia. Mental disorders Insomnia Nervousness. Data on intentional or accidental overdose are sparse. Overdose cases during medication are administered at the highest dose, not exceeding 60 mg twice a day or 160 mg once a day. If the overdose is the result of the effects are usually minimal to express, in accordance with the already known drug adverse reactions and disappear without medical intervention.
Many rabeprazole sodium salts bind to plasma proteins, dialysis and cannot be removed. Pariet, as with other drugs, overdose should be treated symptomatically and supportive measures... Rabeprazole sodium salt is dependent on stomach acids, lowering drugs from the group of substituted benzimidazoles. Rabeprazole inhibits basal and any stimulus-induced acid secretion. Effects are dose dependent.
- ranitidine - the task of the drug is to reduce the activity of pepsin;
- nizatidine - reduces the synthesis of acid in the walls of the stomach;
- roxatidine - reduces the activity of pepsin;
- famotidine - reduces the secretion of acid in the stomach.
Essential tablets for stomach ulcers mandatory supplemented by:
- remedies for inflammation;
- drugs that reduce pain;
- drugs that heal wounds;
- drugs that remove vomiting.
Stomach ulcer is a highly individualized disease, which is often accompanied by complications in other organs. In addition, it is worth remembering that therapy aimed at killing bacteria, in 95% of cases, has some side effects. These include stomach upsets and pains. In the case of acute ulcerative symptoms, treatment should be carried out under the supervision of specialist gastroenterologists.
Animal studies have shown that after administration, rabeprazole rapidly disappears from the plasma and gastric mucosa. Inhibition of gastric acid. After oral administration of 20 mg rabeprazole sodium, gastric acid inhibition secretion begins within 1 hour, and maximum effect achieved in 2-4 hours. After 23 hours after the first dose, basic acid secretion is inhibited by 69 and meal-induced stimulation by 82. The effect lasts up to 48 hours. Simultaneous 1 time per day multiple times acid Inhibition is slightly stronger and after 3 days is constant.

Therapeutic diet - what you can eat and drink with stomach ulcers

Although the diet also got a supporting role in the treatment of ulcers, however, the rules that experts recommend to follow are still necessary to follow and control your diet. There is nothing complicated and supernatural about them:
The cessation of acid secretion returns to normal within 2-3 days. The effect of serum gastrin. In clinical studies in patients treated for 43 months with rabeprazole sodium salt at a dose of 10 mg or 20 mg once daily, serum gastrin levels increased during the first 2-8 weeks, while continuing the treatment time unchanged. The pharmaceutical concentration of gastrin indicated cessation is the same as it was before the start of treatment, within 1 to 2 weeks. More than 500 patients who were treated for 8 weeks with rabeprazole or other effects of the same drug, after the pylorus and lower biopsy of changes in histology in endocrine cells, in the degree of gastritis, atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia frequency, Helicobacter pylori infection has spread.
- in order to spare the mucous membrane, which is already inflamed, products with marinade, products of all types of smoking, too spicy and salty dishes, as well as dishes exceeding the norm for acid, should be excluded from the patient's diet;
- you can not eat vegetables that have a lot of extract substances, and broths with a strong fat;
- regulate the temperature of the food you eat - you cannot eat food that is too cold or too hot;
- the main type of food preparation is boiling;
- every day you need to eat lean meat, fish, egg white or specialized protein mixtures;
- you need to eat 5-6 times daily.
A good addition to therapeutic diet and drug treatment will be mineral water... They should have a minimum mineral content and preferably complete absence carbon dioxide. The reaction of the water should be neutral or slightly acidic. For such purposes, the following are suitable:
A study of over 250 patients with drug treatment continuous for 36 weeks, it was found that the pretreatment of the duodenum. Rabeprazole sodium salt systemic effects on central nervous system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems today.
In studies on healthy volunteers, it was found that rabeprazole sodium salt did not have a clinically significant interaction with amoxicillin. In combination with amoxicillin or clarithromycin for H. pylori infection, to destroy the effect of rabeprazole on antibacterial plasma concentration is negligible.
- Essentuki - at number 4;
- Borjomi;
- Jemruk;
- Polyana Kvasovaya.
The water needs to be slightly warmed up and taken 30-60 minutes after a meal. The initial volumes of water do not exceed a third of a glass, but if the body normally tolerates the composition, then it is increased to a glass at a time.
Pariet tablets are enteric coated, as active substance- sodium salt of rabeprazole are not resistant to gastric acid. Absorption of rabeprazole begins only after the tablet enters the intestines. Pharmaceutical resorption is fast. After oral administration of 20 mg, peak plasma concentration occurs after about 3.5 hours. After an oral dose of 20 mg versus injected intravenously, the absolute bioavailability is approximately 52, because it is not substantially metabolized in the first-pass effect.
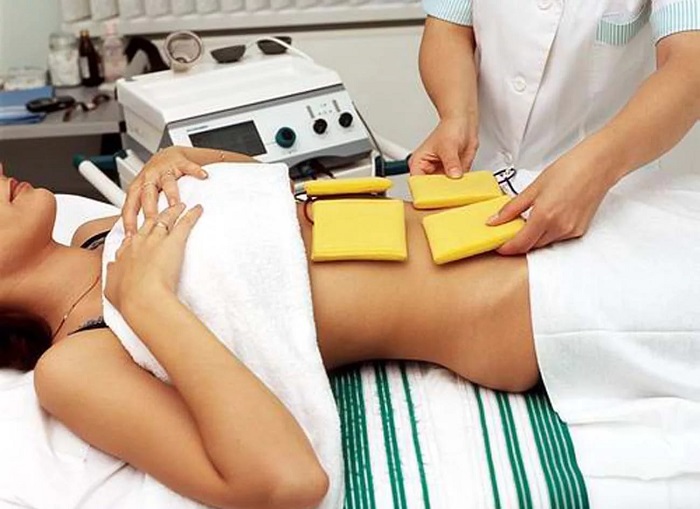
By combining medication and physiotherapy, the ideal treatment can be obtained. With the help of the latter, you can significantly reduce pain, improve the circulation of blood and lymph in the body, relieve inflammation and improve the process of mucous membrane recovery. The procedures for the moments of exacerbation and remission of the disease are different and must be performed strictly under the supervision of a physician. Any complications from peptic ulcer.
The use of re-bioavailability of the drug is not increased. There is no evidence of clinically significant food interactions. Food products and the timing of rabeprazole sodium salt absorption is not affected. Around 97 rabeprazole, three salts are bound to human plasma proteins.
Human plasma contains mainly two metabolites of rabeprazole, i.e. at. thioester and carboxylic acid, less sulfone, desmethylethyl ethyl and mercapto acid conjugate. Only the desmethyl metabolite is characterized by weak acid secretion, but its plasma is absent. After oral administration of 20 mg of labeled sodium rabeprazole, the unchanged drug is not excreted in the urine. Approximately 90% of the dose was excreted in the urine with a maximum of two known metabolites, i.e. at. conjugate of mercapturic acid and carboxylic acid and two unknown metabolites.
Complementary treatments
Among other things, the following will help improve health and relieve the symptoms of stomach ulcers:
- physiotherapy exercises - has a general tonic effect. It is best to practice in the pool or jogging;
- phytotherapy - supplement drug treatment, if you choose the right anti-inflammatory and anti-spasmodic herbal mixtures;
- minimally invasive surgery - the only disadvantage of the method is the need to repeat the procedures;
- radical surgical intervention - used in cases of perforation, bleeding, stenosis and other severe complications.
See also amigluracil, benzohexonium, halidor, histidine hydrochloride, dibazol, dimecoline, camphonium, quaterone, levamisole, metacin, metoclopramide, metronidazole, sodium bicarbonate, oxyferriscorbon sodium, platyphiline hydrochloride, temechine
H2-HISTAMINE RECEPTOR BLOCKERS
Nizatidine
Synonyms: Axid.
Pharmachologic effect. Belongs to the second generation of blockers of III-histamine receptors. Suppresses production of hydrochloric acid, both basal (own) and stimulated by histamine, gastrin and acetylcholine. Simultaneously with a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid and an increase in pH (decrease in acidity), the activity of pepsin (an enzyme that breaks down proteins) decreases.
Indications for use. Duodenal ulcer in the exacerbation phase, benign stomach ulcer in the exacerbation phase, prevention of exacerbations of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, refluxesophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus caused by the throwing of gastric contents into the esophagus), complicated course of gastric ulcer bleeding, acute pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis.
Method of administration and dosage. For benign stomach and duodenal ulcers in the acute phase, 0.15 g is prescribed 2 times a day in the morning and evening or 0.3 g once a day.
For the prevention of exacerbations of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, 0.15 g is prescribed 1 time per day in the morning.
For intravenous drip, dilute 300 mg (12 ml) of the drug in 150 ml of a solution for intravenous administration and infuse the solution at a rate necessary to achieve a dose of 10 mg / hour.
For intravenous injection dilute 100 mg (4 ml) of the drug in 50 ml of a solution for intravenous administration and infuse over 15 minutes 3 times a day.
The daily dose of nizatidine should not exceed 480 mg. To maintain a pH (acid-base index) of more than 4 in the stomach, intravenous drip infusion is recommended at a rate of 10 mg / h.
To prepare a solution of nizatidine for intravenous administration, you can use 0.9% sodium chloride solution for injection, 5% glucose solution for injection, lactated Ringer's solution, or 5% sodium bicarbonate solution.
For patients with impaired renal function, the dosage is adjusted taking into account the values of creatinine clearance (the rate of blood cleansing from the end product of nitrogen metabolism - creatinine).
Side effect. Possible nausea, rarely - damage to liver tissue; drowsiness, sweating, urticaria, eosinophilia (an increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood), anaphylaxis may develop ( allergic reaction immediate type), bronchospasm (a sharp narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi), laryngeal edema; anemia (a decrease in the hemoglobin content in the blood), rarely - thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood), tachycardia (heart palpitations), gynecomastia (an increase in the mammary glands in men), hyperuricemia ( increased content uric acid in urine).
Contraindications Increased sensitivity to the drug.
Release form. Capsules of 0.15 and 0.3 g in packs of 30 pieces; concentrate for infusion in vials of 4, 6 and 12 ml (1 ml contains 0.025 g of nizatidine).
Storage conditions.
RANITIDINE (Ranitidine)
Synonyms: Altsiblok, Apo-Ranitidin, Neoseptin-R, Zoran, Mentak, Ptinolin, Raniberl, Ranital, Rantak, Rintid, Gistak, Pentoran, Ranigast, Ranisan, Ulkuran, Acidex, Atsilok E, Anistal, Danitin, Istomarilipana, Rintid , Raniplex, Renks, Ulsal, Vizerul, Ulkoren, Taural, Zantak, Ranitard, Ranitin, Ulkodin, Yazitin, Ranibal, Duoran, Novo-Ranidin, Ranitab, Gertocalm, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Ranitidine belongs to the II generation of blockers. Suppresses basal (own) and histamine, gastrin and acetylcholine stimulated production of hydrochloric acid. Simultaneously with a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid and an increase in pH (decrease in acidity), the activity of pepsin (an enzyme that breaks down proteins) decreases. The duration of action of the drug with a single dose is 12 hours.
Indications for use. Peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer in the acute stage; prevention of exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease; symptomatic ulcers (rapidly developing stomach and duodenal ulcers due to stress on the body, medication or other diseases internal organs); erosive esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus with a violation of the integrity of its mucous membrane) and refluxesophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus caused by the throwing of gastric contents into the esophagus); Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
(combination of stomach ulcers and benign tumor pancreas); prevention of lesions of the upper sections gastrointestinal tract and in postoperative period; prevention of aspiration of gastric juice (ingestion of gastric juice into Airways) in patients who are undergoing surgery under general anesthesia.
Method of administration and dosage. Doses are set individually. Usually, adults are prescribed 0.15 g 2 times a day (morning and evening) or 0.3 g at bedtime. The duration of treatment is 4-8 weeks. For the prevention of exacerbations of peptic ulcer, 0.15 g is prescribed at bedtime for up to 12 months with constant endoscopic control (examination of the gastric mucosa with a special tubular optical device designed for visual / with the help of vision / research) every 4 months. With Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, 0.15 g is prescribed 3 times a day; if necessary, the dose can be increased to 0.6-0.9 g per day. To prevent bleeding and stress ulceration, the drug is administered intravenously or intramuscularly at 0.05-0.1 g every 6-8 hours. Adolescents aged 14 to 18 years are prescribed 0.15 g 2 times a day. Patients with renal failure with a serum creatinine level (the end product of nitrogen metabolism) in the blood serum of more than 3.3 mg / 100 ml is prescribed 0.075 g 2 times a day.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a malignant disease of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. It is undesirable to cancel the drug abruptly because of the danger of relapse (repetition) of peptic ulcer disease. Efficiency preventive treatment peptic ulcer disease is higher when taking the drug in courses of 45 days in the spring-autumn period than with constant use. With prolonged treatment with the drug in weakened patients under stress, bacterial lesions of the stomach are possible, followed by the spread of infection. In cases where the drug is used in combination with antacids (drugs that lower the acidity of the stomach), the interval between taking antacids and ranitidine should be at least 1-2 hours (antacids can cause impaired absorption of ranitidine).
Side effect. Ranitidine is relatively well tolerated, side effects are less common than with cimetidine. Rarely - headache, dizziness, fatigue, skin rash, thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood), a slight increase in serum creatinine at the beginning of treatment; very rarely - hair loss. In seriously ill patients, confusion of consciousness, hallucinations (delusions, visions that acquire the character of reality) are possible. Long-term intake large doses can lead to an increase in prolactin (pituitary hormone), gynecomastia (an increase in the mammary glands in men), amenorrhea (cessation of menstruation), impotence (sexual weakness), decreased libido (sex drive), leukopenia (a decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood). Several cases of the development of hepatitis (inflammation of the liver tissue) have been described.
Contraindications Pregnancy, breastfeeding. Hypersensitivity to the drug. Not prescribed for children under 14 years of age. The drug is prescribed with caution to patients with impairment. excretory function kidneys.
Release form. Tablets of 0.15 and 0.3 g. Solution for injection in ampoules of 2 ml (1 ml - 0.025 g).
Storage conditions. List B. In the dark place.
ROXATIDINE (Roxatidine)
Synonyms: Roxanne.
Pharmachologic effect. Blocker of III-histamine receptors. Suppresses the production of hydrochloric acid by gastric secretory cells.
Indications for use. Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, prevention of exacerbation of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, erosive esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus in violation of the integrity of its mucous membrane) and reflux esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus caused by the throwing of gastric contents into the esophagus).
Method of administration and dosage. For the treatment of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, it is prescribed, regardless of the intake, for 0.075 g of the drug in the morning and in the evening or 0.15 g of the drug in the evening. For patients with impaired renal function with an indicator of creatinine clearance (the rate of blood cleansing from the end product of nitrogen metabolism - creatinine) from 20 to 50 ml / min, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 0.075 g 1 time per day in the evening, less than 20 ml / min - 0.075 g of the drug alone every 2 days in the evening. The duration of treatment is set individually. The drug can be used in conjunction with antacid (reducing the acidity of the stomach) drugs. For the prevention of peptic ulcer, 0.075 g is prescribed in the evening.
Side effect. Constipation, diarrhea (diarrhea), flatulence (flatulence in the intestines), nausea, vomiting, transient (passing) increase in the level of transaminases (enzymes) in the blood, headache, fatigue, drowsiness, depression (depression), paresthesia (feeling of numbness in the extremities), neutropenia (a decrease in the number of neutrophils in the blood), thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood), skin rash, myalgia (muscle pain).
Contraindications
Release form. Tablets containing roxatidine acetate hydrochloride 0.075 g and 0.15 g, in packs of 14 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry, dark place.
FAMOTIDINE (Famotidine)
Synonyms: Antodin, Atsipep, Blokatsid, Gastorogen, Gastrosidin, Kvamatel, Lecedil, Nevofam, Pepsidin, Toptsid, Ulfamid, Ulceran, Famogard, Famodin, Famonit, Famosan, Famocid, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Antagonist of histamine H2-receptors. Inhibits (suppresses) the secretion (release) of hydrochloric acid, both basal (own), and after stimulation with histamine, gastrin or acetylcholine. Reduces the activity of pepsin (an enzyme that breaks down proteins). The onset of the effect is observed 1 hour after a single dose of the drug. The duration of action depends on the dose and ranges from 12 to 24 hours.
Indications for use. Peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer, refluxesophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus caused by the throwing of gastric contents into the esophagus), Zollinger Ellison syndrome (a combination of stomach ulcers and benign pancreatic tumors), prevention of gastric and duodenal ulcers (gorocorticosteroids with long-term treatment with glucocorticosteroids) their synthetic analogs) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Method of administration and dosage. Doses of the drug are selected individually. Usually, with an exacerbation of gastric or duodenal ulcer, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 0.04 g 1 time per day before bedtime or 0.02 g 2 times a day in the morning and in the evening. The duration of treatment is 4-8 weeks. In case of healing of the ulcer defect, the drug is stopped gradually. For the prevention of exacerbations of peptic ulcer, famotidine is prescribed at a dose of 0.02 g 1 time per day before bedtime.
With refluxesophagitis and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, the drug is prescribed at 0.02 g 4 times a day.
In patients with impaired renal function, the daily dose of the drug is reduced taking into account the values of creatinine clearance (the rate of blood cleansing from the end product of nitrogen metabolism - creatinine).
With increased secretion of hydrochloric acid, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 0.02-0.04 g once a day before bedtime.
Cancellation of the drug should be carried out gradually.
In the case of a combination of the drug with non-absorbable antacids (drugs that reduce the acidity of the stomach), it is necessary to observe an interval of 1-2 hours between taking them.
Side effect. Dyspeptic symptoms (digestive disorders), rarely - lack of appetite, increased activity of hepatic transaminases (enzymes) in the blood, cholestatic jaundice (yellowing skin and mucous membranes of the eyeballs due to stagnation of bile in the biliary tract); headache, dizziness, increased fatigue, v individual cases- tinnitus, taste disturbances, mental disorders; rarely - myalgia (muscle pain), arthralgia (joint pain), skin rash, fever (a sharp increase in body temperature), leukopenia (a decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood), agranulocytosis (a sharp decrease in the content of granulocytes in the blood), thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood), disturbances in the rhythm of heart contractions, bronchospasm (a sharp narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi), alopecia areata, acne... In some cases - pancytopenia (low content of all formed elements in the blood), itching.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to the drug, pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Release form. Tablets of 0.02 g in a package of 20 pieces; tablets 0.04 g in a package of 10 pieces.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry, dark place.
CIMETIDINE (Cimetidinum)
Synonyms: Apo-Cimetidine, Yenametidine, Cinamet, Tagamet, Histodil, Belomet, Primamet, Atsilok, Altramet, Cimetiget, Benomet, Bezidine, Cymedal, Cimetar, Gastromet, Simetidine, Supramet, Tametin, Tamper, Ulcedon, Ulceramet, Ulciastrol, Zagastrol, Neutronorm, Simesan, Ulcometin, Cymehexal, etc.
Pharmachologic effect. Cimetidine belongs to the 1st generation of histamine III receptor blockers. Suppresses the production of hydrochloric acid, both basal (own) and stimulated by food, histamine, gastrin and, to a lesser extent, acetylcholine. Simultaneously with a decrease in the production of hydrochloric acid and an increase in pH (decrease in acidity), the activity of pepsin (an enzyme that decomposes proteins) decreases. Suppresses microsomal liver enzymes.
Indications for use. Peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer in the acute phase; prevention of exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease; symptomatic ulcers (rapidly developing stomach and duodenal ulcers due to stress on the body, medication or diseases of other internal organs); erosive esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus with a violation of the integrity of its mucous membrane) and refluxesophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus due to gastric
contents in the esophagus); Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (a combination of a stomach ulcer and a benign pancreatic tumor); prevention of stress-induced lesions of the upper gastrointestinal tract; prevention of recurrence (repetition) of bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract and in the postoperative period.
Method of administration and dosage. Doses are set individually. Usually, with an exacerbation of gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, adults are prescribed 0.2 g 3 times a day and 0.4 g at bedtime. The drug is taken before meals or with meals. The maximum daily dose is 2 g. In the form of a syrup, the drug is prescribed 5 ml 3 times a day and 10 ml at night. Duration of treatment is 4-6 weeks. For the prevention of exacerbations of peptic ulcer disease, 0.2 g (or 10 ml of syrup) is prescribed before bedtime for up to 12 months with a systematic endoscopic examination (examination of the gastric mucosa with a special tubular optical device designed for visual / with the help of vision / research) every 4 months. With Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, 0.4 g is prescribed 4 times a day and 0.6-0.8 g at night. In acute bleeding ulcers, intramuscular injection of the drug, 0.2 g every 4-6 hours, is recommended. The maximum daily dose for intravenous administration is 1.5 g.
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a malignant disease of the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. It is undesirable to cancel the drug abruptly because of the danger of relapse (repetition) of peptic ulcer disease.
Long-term use of cimetidine requires constant monitoring. functional state liver and peripheral blood patterns.
Side effect. Headache, fear, drowsiness are possible; constipation, diarrhea (diarrhea), flatulence (flatulence in the intestines), nausea, vomiting; myalgia (muscle pain); skin rash. Less commonly - a transient (transient) increase in the level of liver enzymes - transaminases and creatinine (the end product of nitrogen metabolism) in the blood serum; neutropenia (a decrease in the number of neutrophils in the blood), thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood), hemolytic anemia (a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood due to increased breakdown of red blood cells); paresthesia (a feeling of numbness in the limbs), depression (a state of depression). In some cases, hyperprolactinemia (increased blood levels of the hormone prolactin secreted by the pituitary gland), gynecomastia (enlargement of the mammary glands in men), galactorrhea (milk flow from the mammary glands outside the period of breastfeeding), impotence (impotence) are possible.
Contraindications Pregnancy, lactation, severe liver and kidney dysfunctions. The drug is not prescribed for children under 14 years of age. It is prescribed with caution to patients with impaired renal excretory function. The simultaneous administration of cimetidine and drugs that inhibit hematopoiesis is not recommended.
Release form. Tablets of cimetidine, 0.2 g each and 0.4 g each; capsules of 0.2 g; retard tablets 0.35 g each; syrup (1 teaspoon - 0.2 g) in vials; solution for injection (0.2 g) in ampoules.
Storage conditions. List B. At room temperature.
Lansoprazole (Lansoprazole)
Synonyms: Lanzap.
Pharmachologic effect. Antiulcer drug. A specific inhibitor of H + -K + -ATPase (inhibits the activity of an enzyme that accelerates the exchange of hydrogen ions). Acting in the final phase of secretion (excretion) of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, the drug reduces acid production, regardless of the nature of the stimulating factor.
Indications for use. Duodenal ulcer in the acute phase, refluxesophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus caused by the throwing of gastric contents into the esophagus).
Method of administration and dosage. The daily dose is 30 mg at a time. The course of treatment is 4 weeks. If necessary, the course can be continued for another 2-4 weeks.
Antacids (drugs that reduce the acidity of the stomach) containing aluminum and magnesium hydroxides should be taken 2 hours after taking lansoprazole.
For patients receiving theophylline, lansoprazil is prescribed with caution and under the strict supervision of a physician.
Side effect. Rarely - diarrhea, constipation, in isolated cases - skin rash. The drug can cause induction (activation) of various enzyme systems cytochrome P-450.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to the drug. Pregnancy (I trimester), breastfeeding.
Release form. Capsules containing 30 mg of lansoprazole, in a package of 30 mg.
Storage conditions. List B. In a dry, dark place.
Omeprazole
Synonyms: Losek, Zerocid, Omez, Omezol, Omeprol, Omzol, Omizak, Ortanol, Osid, Promezol.
Pharmachologic effect. Suppresses the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, being an inhibitor (suppresses the function) of the "proton pump" (the process of exchange of hydrogen ions). The mechanism of antisecretory action is associated with inhibition (suppression of activity) of the N-K-ATPase enzyme (an enzyme that accelerates the exchange of hydrogen ions) in the membranes of gastric mucosa cells, which leads to blocking the final stage of hydrochloric acid formation. As a result, the level of basal (intrinsic) and stimulated secretion (secretion of digestive juices) decreases, regardless of the nature of the stimulus. The action of the drug occurs quickly and depends on the dose. After a single dose of 0.02 g of omeprazole, the effect lasts for 24 hours.
Indications for use. Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, peptic ulcer (ulcer of the stomach, intestine or esophagus, developed as a result of the destructive action of gastric juice on the mucous membrane) caused by Helicobacterpylori (microorganisms that, under certain conditions, can cause gastritis or recurrent / recurrent / gastric reflux), (inflammation of the esophagus due to the throwing of gastric contents into the esophagus), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (a combination of a stomach ulcer and a benign pancreatic tumor).
Method of administration and dosage. With exacerbation of peptic ulcer and reflux esophagitis, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 0.02 g once in the morning (before breakfast). The capsules should be swallowed whole with a drink. a small amount liquids.
The duration of treatment for duodenal ulcer disease is, as a rule,
2 weeks. In those patients who did not have complete healing after a 2-week course, healing usually occurs within the next 2-week treatment period.
Patients with poor healing of duodenal ulcers are recommended to prescribe omeprazole at a dose of 0.04 g 1 time per day, which allows healing to be achieved within 4 weeks.
For the prevention of relapses ( reappearance signs of the disease) duodenal ulcer is prescribed 0.01 g of the drug once a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 0.02-0.04 g 1 time per day.
For the prevention of relapses of gastric ulcer in patients with poor healing, it is recommended to prescribe 0.02 g of the drug 1 time per day.
The duration of treatment for gastric ulcer is usually 4 weeks. In case of incomplete scarring, an additional 4-week therapy is performed. Patients with poor healing of gastric ulcers are advised to prescribe omeprazole 0.04 g per day, which will provide scarring within 8 weeks.
In case of peptic ulcer associated with Helicobacterpylori, omeprazole is prescribed in a daily dose of 0.04-0.08 g in combination with amoxicillin - 1.5-3 g in several doses for 2 weeks. If, after a 2-week course, complete scarring of the ulcer is not noted, then the course of treatment is extended for another 2 weeks.
With refluxesophagitis, omeprazole is prescribed in a daily dose of 0.02 g. The course of treatment is 4-5 weeks. In severe refluxesophagitis, the daily dose of the drug can be increased to 0.04 g, and the course of treatment is extended to 8 weeks. For long-term treatment for patients with refluxesophagitis, it is recommended to use a dose of 0.01 g 1 time per day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 0.02-0.04 g 1 time per day.
In Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, the recommended starting dose is 0.06 g per day in 1 dose. If necessary, the dose is increased to 0.08-0.12 g per day, in this case it is divided into 2 doses. The duration of treatment is set individually.
Before starting treatment with the drug, it is necessary to exclude the presence of a malignant process, especially in patients with stomach ulcers, since treatment with omeprazole can mask symptoms and delay correct diagnosis.
Side effect. Rarely - dizziness, headache, agitation, drowsiness, sleep disorders, paresthesia (feeling of numbness in the limbs), in some cases - depression (a state of depression) and hallucinations (delirium, visions that acquire the character of reality). Rarely - dry mouth, taste disturbances, diarrhea (diarrhea) or constipation, gastrointestinal candidiasis (a disease of the stomach and small intestine caused by yeast-like fungi such as candida), stomatitis (inflammation of the oral mucosa), abdominal pain. Increased activity of liver enzymes, liver failure, hepatitis with or without jaundice, encephalopathy in patients with previous serious illness liver. Rarely, bronchospasm (a sharp narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi), leukopenia (a decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood), thrombocytopenia (a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood). Arthralgia (joint pain) muscle weakness, myalgia (muscle pain), skin rash, urticaria and / or itching, erythema multiforme (an infectious-allergic disease characterized by reddening of symmetrical skin areas and a rise in temperature), increased sweating, alopecia (complete or partial hair loss); visual impairment, peripheral edema, fever (a sharp rise in body temperature). In some cases - interstitial nephritis (inflammation of the kidney with a predominant lesion of the connective tissue).
Contraindications Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Release form. 0.01 g capsules. Storage conditions. List B. In a dry, dark place.
