Krasnoyarsk State Medical Academy Department of Restorative Medicine and Balneology IPO Impulse currents of low and medium frequency. Definition
Krasnoyarsk State medical Academy Department of Restorative Medicine and Balneology IPO Impulse currents low and medium frequency. Determination of impulse currents. Electrosleep, electroanalgesia, electrical stimulation, diadynamic therapy Head. department, MD, professor S.V. Klemenkov Teacher: doctor the highest category, candidate medical sciences Karachintseva Natalia Vladimirovna



Healing effects: Hypnotic Sedative antispasmodic secretory Indications: Diseases of the nervous system (reactive and asthenic states, disturbed night sleep, logoneurosis), neurasthenia, diseases cardiovascular systems (atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels in the initial stage, ischemic heart disease, exertional angina FC III, hypertension Stage III), peptic ulcer stomach and duodenum, bronchial asthma, neurodermatitis, eczema, enuresis.
![]()
Physical characteristic (parameters): For electrosleep, rectangular current pulses with a frequency of Hz and a duration of 0.20.5 ms are used. The impulse current usually does not exceed mA. The pulse repetition rate is selected taking into account the patient's condition. Low-frequency pulses (5-20 Hz) are used with increased excitation of the central nervous system, and higher (Hz) - with its depression. The efficiency of the impulse effect increases when the constant component of the applied electric current is turned on.

Apparatus Electroson-4T, EGASS and an apparatus for ES therapy are used for electrosleep procedures.They allow one to act with impulse currents with different ratios of impulse and direct current (constant component). The pulse currents generated by these devices can be discretely varied in frequency and amplitude.


Dosage The strength of the impulse current supplied to the patient is dosed according to the patient's sensation of light tingling, tapping or painless vibration. The severity of such sensations increases when the constant component is turned on, which leads to an increase in the amount of electricity passing through the patient's tissues. The maximum permissible current during electrical sleep procedures should not exceed 8 mA. It is increased until the patient appears feeling light painless vibration under the electrodes.

(continued) The duration of the treatment carried out every other day or daily is 2040 minutes; the course of treatment is 1520 procedures. If necessary, a second course of electrosleep is prescribed after 23 months. In children, electrosleep can be used from 3-5 years old. It is carried out at low frequencies, less amperage and shorter duration.
![]()
Transcranial electroanalgesia is a method of neurotropic therapy based on the impact on the central nervous system patient with impulse currents rectangular with a frequency from up to 2000 Hz with variable and constant duty cycle.

Transcranial electroanalgesia is considered as a method with pronounced sedative, tranquilizing and analgesic effects. When it is accepted, it is believed that the sedative effect is more pronounced at frequencies up to Hz, tranquilizing at, anesthetic above 1000 Hz.

The mechanism of action is based on the selective stimulation of the structures of the endogenous opioid system of the brain stem by impulse currents. The release of antinociceptive mediators (endorphins and enkephalins), blockade of nociceptive impulses at the level of the medulla oblongata and thalamus, as well as the activation of the segmental portal mechanism of pain control provide the main therapeutic effects... In patients, emotional stress, fear disappear, the skin turns pink, warmth is felt in the limbs, muscle relaxation occurs, pain decreases.

(continued) Resulting restructuring energy balance bioelectrical processes in the brain in the form of a decrease in slow-wave activity and stabilization of the a-rhythm favorably affects the activity of the vasomotor and respiratory centers, as well as the suprasegmental structures of the autonomic nervous system. This is accompanied by the normalization of hemodynamics, stimulation of trophic-regenerative processes, and an increase in the general resistance of the organism.

Apparatus Two types of apparatuses are used: 1. Transair and Etrans-1,2,3 generating rectangular pulses with voltage up to 10 V, frequency Hz and duration 3.54.0 ms; 2. LENAR and Bi-LENAR, generating rectangular pulses with voltage up to 20 V, frequency Hz and duration 0.150.5 ms. The design of all devices provides for the use of an additional component of the galvanic current, while both the ratio of the pulse and direct current, and the frequency and duration of the pulses can be changed.

METHOD The treatment is carried out according to the frontal-occipital technique. The bifurcated cathode is placed in the superciliary region, the bifurcated anode is placed under the mastoid. 3x3 or 4x4 cm pads under electrodes are wetted warm water or 2% sodium bicarbonate solution. - Having set the necessary parameters of the procedure (frequency, pulse duration, duty cycle), initially include an additional constant component until a tingling sensation or light heat under the electrodes. Then the amplitude of the impulse current is gradually increased until the patient has a painless vibration under the electrodes.

average value pulse current to achieve a sedative effect - 0.8-1.2 mA, for pain relief the maximum current tolerated by the patient (up to 3 mA). It is generally accepted that analgesia increases with the inclusion of an additional constant component of the acting current in a ratio of 5: 1-2: 1, and the sedative effect increases in a variable duty cycle. The duration of exposure is from 20 to 40 minutes (for acute pain). The course of treatment 1015 daily procedures.

Contraindications: sharp painsdue to pathology internal organs (myocardial infarction, angina attack, renal, hepatic and intestinal colic and others), progressive organic diseases of the nervous system, epilepsy, thalamic pain, closed craniocerebral trauma, cardiac arrhythmias, damage to the skin in the places where the electrodes are applied, as well as individual current intolerance.

Diadynamic therapy is an electrotherapy method in which the patient's body is exposed to low-frequency half-sinusoidal impulse currents (with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz), supplied separately, in various combinationsmodulated and in intermittent mode.

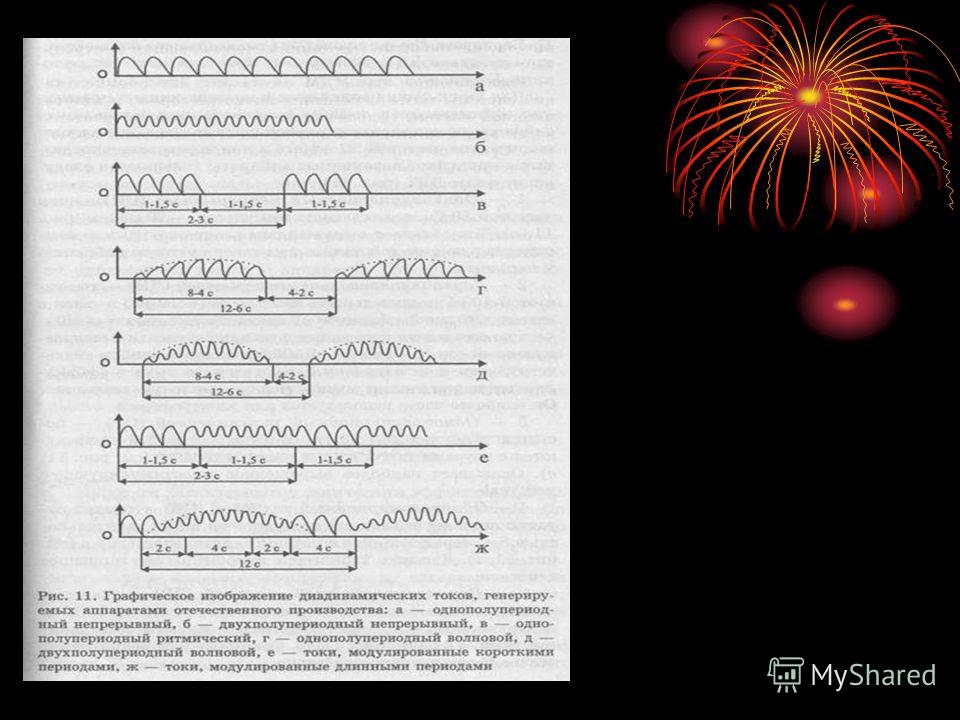
Description DDT Half-wave continuous (OH) - Current with a frequency of 50 Hz, pulse duration - 20 ms. Irritant and myostimulating effect, causes large vibration in the patient. Full-wave continuous (DN) - current with a frequency of 100 Hz, pulse duration -10 ms. Analgesic and vasoactive effect, causing fine diffuse vibration. Half-wave rhythmic (OP) - current pulses with a frequency of 50 Hz, duration 1.5 s alternating with pauses of 1.5 s. Myostimulating action.
![]()
(continuation) Half-wave wave (ОВ) - smoothly increasing and decreasing current with a frequency of 50 Hz, duration 8 s, alternating with pauses of 4 s. Neuromyostimulating action. Full-wave wave (DW) - smoothly increasing and decreasing current with a frequency of 100 Hz, a duration of 8 s, alternating with pauses of 4 s. Neurotrophic and vasoactive action. Short period (CP) - alternation of currents with a frequency of 50 Hz and 100 Hz with a series duration of 1, 5 s. Neuromyostimulating and analgesic action Long period (DP) - alternating current

Continuation With a frequency of 50 Hz, a pulse duration of 4 s and a smoothly increasing and decreasing current of 100 Hz with a duration of 8 s. Analgesic, vasoactive and trophic effect. One-half-wave shortened wave current (OB) - smoothly increasing and decreasing OH current with a duration of 4 s, alternating with pauses with a duration of 2 s. Full-wave shortened wave current (LW) is a smoothly increasing and decreasing BP current with a duration of 4 s, alternating with pauses of 2 s duration.

Physiological and therapeutic effects of DDT The most characteristic clinical effect of DDT (especially DP and CP) is anesthetic. It is caused by a number of factors. According to Bernard himself, the coming adaptation of peripheral receptors, including pain receptors, to DDT leads to an increase in the pain perception threshold and, consequently, to a decrease in pain.

Continued Irritation by given current a large number receptors leads to the appearance of a rhythmically ordered stream of impulses, which leads to the formation of a dominant focus of excitation in the cerebral cortex, which suppresses the pain dominant. There is an increase in the release of endorphins, an increase in the activity of enzymes that destroy the main mediators of pain (histaminase, acetylcholine esterase). At the same time, under the influence of DDT, edema resorption occurs in tissues, trophism and blood circulation normalize, and hypoxia decreases. DDT reduces increased muscle tone and breaks the vicious circle: pain - increase muscle tone - pain.

Continuation of -DDT actively affects the blood supply to tissues. With the transverse arrangement of the electrodes, there is an improvement in capillary blood flow, a decrease in the tone of spasmodic vessels, with a longitudinal increase in the blood flow velocity by 23 times. -In addition, DDT stimulates collateral blood circulation, increases the number of functioning capillaries. -Installed positive influence DDT for cleansing and healing purulent wounds, ulcers, pressure sores, reparative tissue regeneration, inflammatory process in tissues.

Equipment. Technique and methodology For diadynamic therapy, the devices "SNIM-1", "Model-717", "Radius-01", DTGE-70-01, "Tonus-1", "Tonus-2", "Diadinamik DD5A" and others are used. The question of the type of currents, their combination and duration of application is decided in accordance with the therapeutic objectives and nature pathological process.

Continuation Pain syndromes are treated according to the scheme: DN (DV) - 1 - 2 min, CP 3 - 4, DP 1 - 2 min. If pain is localized under both electrodes, the polarity is reversed in the middle of the exposure. Sequential impact on several fields is allowed. In case of severe pain, the procedures can be performed 23 times a day with an interval of 4-5 hours. The course of treatment is 6-10 daily procedures. After a day break, a second course of treatment may be prescribed. It is advisable to prescribe the second and third courses of treatment only in the presence of positive dynamics in the patient's condition.

Continuation For electrical stimulation, the currents of OB and DW are used, less often - OR. The electrodes are placed in the area of \u200b\u200bthe motor points of the affected nerves and muscles. The current is applied until the contractions of average force are obtained for 2-3 minutes 3 times with an interval of 1-2 minutes. Due to the limited parameters of the current, electrical stimulation is carried out mainly in peripheral paresis with not sharply expressed qualitative and quantitative violations of muscle electrical excitability. The course of treatment of daily procedures.

Indications for DDT are acute pain syndromes with damage to the peripheral nervous system (neurological manifestations of osteochondrosis of the spine, neuralgia, mono- and polyneuropathy, ganglionitis, plexitis), diseases and damage to the musculoskeletal system (myositis, periarthritis, epicondylitis, arthrosis, bruises, stiffness in the joints after injuries and surgical interventions and others), digestive organs (gastritis, colitis, biliary dyskinesia) and respiration (bronchial asthma), chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages, algomenorrhea, urinary retention and incontinence, enuresis, impotence, prostatitis, initial stages arterial hypertension and obliterating diseases of the vessels of the extremities, migraine, Quincke's edema, diseases of the ENT organs (laryngitis, otitis, sinusitis, rhinitis, paresis of the vocal cords), periodontal disease, itchy dermatoses, etc.

Contraindications individual current intolerance acute inflammatory processes bleeding tendency frequent vascular crises, high blood pressure the presence of unfixed bone fragments in fractures acute intra-articular injuries generalized eczema Thrombophlebitis, urinary and cholelithiasis, and general contraindications for physiotherapy.


"Chapter 1. Medicinal use direct electric current Chapter 2. Therapeutic use of low frequency impulse currents Chapter 3. Therapeutic use of medium and high alternating current ... "
- [Page 2] -
Assess the effect of impulse currents on the patient's body.
To study the principles of operation of the devices "Electroson-5", "LENAR", "Tonus-3", "Mioritm".
INFORMATION BLOCK
Impulse exposure techniques physical factors - the most adequate stimuli for the body, and in case of impaired functions, their therapeutic effect is most effective. The main advantages of pulsed physiotherapy techniques:Selectivity of action;
The possibility of a deeper impact;
Specificity;
Lack of quick adaptation of tissues to a physical factor;
Therapeutic effect with the least stress on the body.
Impulse currents consist of rhythmically repetitive short-term changes in electrical voltage or current. Possibility of using pulsed current for stimulating effect on various bodies, tissues and systems of the body is based on the nature of electrical impulses that mimic the physiological effect of nerve impulses and cause a response similar to natural excitement. The action of the electric current is based on the movement of charged particles (ions of tissue electrolytes), as a result of which the usual composition of ions on both sides of the cell membrane changes and the cell develops physiological processescausing excitement.
Excitability can be judged by the least strength of the stimulus required for the occurrence of a reflex reaction, or by the threshold current strength, or by the threshold potential shift sufficient for the emergence of an action potential. Speaking of excitability, they use concepts such as rheobase and chronaxia. These concepts were introduced into physiology in 1909 by L. Lapik, who studied the smallest (threshold) effect of excitable tissues and determined the relationship between the strength of the current and the duration of its action. Rheobase (from the Greek "rheos" - flow, flow and "basis" - course, movement; base) is the smallest DC electric current that causes excitation in living tissues with a sufficient duration of action. Rheobase, like chronaxia, makes it possible to assess the excitability of tissues and organs by the threshold strength of irritation and the duration of its action. Rheobase corresponds to the threshold of irritation and is expressed in volts or milliamperes.
The reobase value can be calculated using the formula:
I \u003d a / t + b, where I is the current strength, t is the duration of its action, and, b are constants determined by the properties of the tissue.
Chronaxia (from the Greek "chronos" - time and "axia" - price, measure) - least time the action of a direct electric current of a doubled threshold force (doubled rheobase), which causes tissue excitation. As established experimentally, the magnitude of the stimulus causing excitation in the tissues is inversely proportional to the duration of its action, which is graphically expressed by hyperbole (Fig. 6).
Changes in the functional state of cells, tissues and organs under the influence of an external electrical stimulus are called electrical stimulation. Within the limits of electrical stimulation, electrodiagnostics and electrotherapy are distinguished. In electrodiagnostics, the body's response to electrical stimulation by impulse currents is examined. Determined that irritating effect a single current pulse depends on the steepness of its leading edge rise, the duration and amplitude of the pulse. The steepness of the rise of the front of a single pulse determines the acceleration of ions as they move. In addition, the effect of alternating electric current on the body depends significantly on its frequency. At a low pulse frequency (about 50-100 Hz), the displacement of ions is sufficient to irritate the cell. At medium frequencies, the irritating effect of the current decreases. At a sufficiently high frequency (of the order of hundreds of kilohertz), the magnitude of the displacement of ions becomes commensurate with the magnitude of their displacement during thermal motion, which no longer causes a noticeable change in their concentration and does not have an irritating effect.
The value of the threshold amplitude determines the maximum instantaneous displacement of ions and depends on the pulse duration. This connection is described by the Weiss-Lapik equation (see Fig. 6).
Each point of the curve in Fig. 6 and the points above the curve correspond to impulses that cause tissue irritation. Extremely short-term impulses do not have an irritating effect (the displacement of ions is commensurate with the amplitude of oscillations during thermal motion). With rather long pulses, the irritating effect of the current becomes independent of the duration. Pulse parameters that provide an optimal response to irritation are used for therapeutic electrical stimulation. Modern development electronics provides the ability to obtain pulse currents with any required parameters. In modern devices, pulses of various shapes are used, with a duration from tens of milliseconds to several seconds, with a repetition rate from fractions of a Hertz to ten thousand Hertz.
Figure: 6. Curve of electrical excitability of muscle (Weiss-Lapik).
Electrosleep Electrosleep is a method of neurotropic nonpharmacological action on the central nervous system with a constant impulse current of a rectangular configuration, low frequency (1-160 Hz) and low strength (10 mA). The method is harmless, lack of toxic effects, allergic reactions, addiction and cumulation.
It is believed that the mechanism of action of electrosleep is based on the direct effect of current on the structures of the brain. The impulse current, penetrating into the brain through the openings of the orbits, spreads through the vascular and cerebrospinal fluid spaces and reaches the sensitive nuclei of the cranial nerves, pituitary gland, hypothalamus, reticular formation and other structures. The reflex mechanism of action of electrosleep is associated with the effect of low-strength direct current pulses on the receptors of the reflexogenic zone: the skin of the eye sockets and upper eyelid... In a reflex arc, irritation is transmitted to the subcortical formations, the cerebral cortex, causing the effect of protective inhibition. In the mechanism therapeutic action Electrosleep plays an essential role in the ability of nerve cells in the brain to assimilate a certain rhythm of impulse current.
By acting on the structures of the limbic system, electrosleep restores disturbances in the emotional, vegetative and humoral balance in the body.
Thus, the mechanism of action consists of the direct and reflex influence of current impulses on the cerebral cortex and subcortical formations.
Impulse current is a weak stimulus that has a monotonous rhythmic effect on such brain structures as the hypothalamus and reticular formation. Synchronization of impulses with biorhythms of the central nervous system causes inhibition of the latter and leads to the onset of sleep. Electrosleep has an analgesic, hypotensive effect, has a sedative and trophic effect.
The electrosleep procedure has two phases. The first is inhibitory, associated with stimulation of the subcortical formations by impulse current and manifested by drowsiness, drowsiness, sleep, decreased pulse, breathing, decreased blood pressure and bioelectric activity of the brain. This is followed by the disinhibition phase, associated with an increase in the functional activity of the brain, self-regulation systems and manifested by increased efficiency and improved mood.
Electrosleep has a calming effect on the body, induces sleep that is close to physiological. Under the influence of electrosleep, conditioned reflex activity decreases, respiration and pulse are reduced, small arteries expand, blood pressure decreases; the analgesic effect is manifested. In patients with neuroses, emotional stress and neurotic reactions weaken. Electrosleep is widely used in psychiatric practice; at the same time, the disappearance of anxiety and sedation are noted.
Indications for the appointment of electrosleep in patients with chronic ischemic disease heart (IHD) and postinfarction cardiosclerosis:
Cardialgia;
Feeling of fear of death;
Insufficient effectiveness of sedatives and hypnotics.
Electrosleep effects:
- & nbsp– & nbsp–
stimulating;
relieves mental and physical fatigue.
Apparatus and general instructions on the performance of procedures For carrying out procedures for electrical sleep use generators of voltage pulses of constant polarity and rectangular configuration with a certain duration and adjustable frequency: "Electroson-4T" and "Electroson-5".
The procedures are carried out in a quiet, darkened room with a comfortable temperature.
The patient lies on a couch in comfortable position... The technique is retromastoidal.
Eye electrodes with wetted hydrophilic pads 1 cm thick are placed on closed eyelids and connected to the cathode; occipital electrodes are fixed on the mastoid processes temporal bones and attached to the anode. The strength of the current is dosed according to a slight tingling sensation or painless vibration felt by the patient. When unpleasant sensations in the area where the electrodes are applied, the strength of the supplied current should be reduced, usually not exceeding 8-10 mA. The pulse frequency is selected depending on the functional state of the patient. In diseases caused by the development of organic, degenerative processes in the vessels and nervous tissue of the brain, the effect occurs if an impulse frequency of 5-20 Hz is used, and with functional disorders CNS - 60-100 Hz. Simultaneously with electrophoresis, electrophoresis of medicinal substances can be performed. Procedures lasting from 30-40 to 60-90 minutes, depending on the nature of the pathological process, are carried out daily or every other day; the course of treatment includes 10-20 exposures.
Indications for treatment:
- & nbsp– & nbsp–
Hypertonic disease;
Ischemic heart disease (coronary insufficiency of the 1st degree);
Obliterating vascular diseases of the extremities;
Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels in the initial period;
Bronchial asthma;
Rheumatoid arthritis in the presence of neurasthenia or psychasthenia;
Pain syndrome;
Phantom pain;
Post-traumatic encephalopathy (in the absence of arachnoiditis);
Schizophrenia during asthenization after active drug treatment;
Diencephalic syndrome;
Neurodermatitis;
Toxicosis of pregnancy;
Preparing pregnant women for childbirth;
Menstrual dysfunction;
Premenstrual and climacteric syndrome;
Meteotropic reactions;
Logoneurosis;
Stressful states and prolonged emotional stress.
Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
Inflammatory and degenerative eye diseases;
Retinal disinsertion;
High degree of myopia;
Dermatitis of the facial skin;
- & nbsp– & nbsp–
Post-traumatic arachnoiditis;
The presence of metal objects in the tissues of the brain and eyeball.
Transcranial electroanalgesia Transcranial electroanalgesia is a method of neurotropic therapy based on the impact on the central nervous system of pulsed currents of rectangular configuration with a frequency of 60 Hz with variable and constant duty cycle.
The therapeutic effect is based on the selective excitation of the endogenous opioid system of the brain stem by impulse currents of low frequency. Pulse currents change the bioelectrical activity of the brain, which leads to a change in the activity of the vasomotor center and is manifested by the normalization of systemic hemodynamics. In addition, the release of endogenous opioid peptides into the bloodstream activates regenerative reparative processes in the inflammation focus.
Transcranial electroanalgesia is a method with pronounced sedative (at a frequency of up to 200-300 Hz), tranquilizing (at 800-900 Hz) and analgesic (above 1000 Hz) effects.
Apparatus and general instructions for performing the procedures For carrying out the procedures of transcranial electroanalgesia, devices are used that generate rectangular pulses with voltage up to 10 V with a frequency of 60-100 Hz, duration 3.5-4 ms: "TRANSAIR", "Etrans-1, -2, - 3 "- and voltage up to 20 V with a frequency of 150-2000 Hz (" LENAR "," Bi-LENAR "). The strength of the analgesic effect increases with the inclusion of an additional constant component of the electric current. The optimal ratio of direct and impulse current is 5: 1-2: 1.
During the procedure, the patient lies on the couch in a comfortable position.
A fronto-mastoid technique is used: a bifurcated cathode with gaskets moistened with warm water or 2% sodium bicarbonate solution is installed in the region of the brow arches, and a bifurcated anode is placed under the mastoid processes. After choosing the parameters of transcranial electroanalgesia (frequency, duration, duty cycle and amplitude of the constant component), the amplitude of the output voltage is gradually increased until the patient develops a tingling sensation and light heat under the electrodes. The duration of exposure is 20-40 minutes. The course of treatment includes 10-12 procedures.
For transcerebral electroanalgesia, sinusoidal modulated currents with the following parameters are also used:
The duration of half periods is 1: 1.5;
Variable mode;
Modulation depth 75%;
- & nbsp– & nbsp–
The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes. The procedures are carried out daily, the course of treatment includes 10-12 manipulations. During the procedure, an electronic rubber half mask from the electric sleep apparatus is used, replacing the plug with a plug device for the Amplipulse series apparatus.
Indications for treatment:
Neuralgia of the cranial nerves;
Pain due to vertebral pathology;
Phantom pain;
Vegetodystonia;
Exertional angina pectoris of I and II functional class;
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
Neurasthenia;
Neurodermatitis;
Overwork;
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome;
Sleep disturbance;
Meteopathic reactions. Contraindications:
General contraindications to physiotherapy;
Current intolerance;
Acute pains of visceral origin (angina pectoris attack, myocardial infarction, renal colic, childbirth);
Closed brain injuries;
Diencephalic syndrome;
Thalamic syndrome;
Violation of the rhythm of the heart;
Damage to the skin where the electrodes are applied.
Therapeutic techniques In case of stage I and II hypertension and coronary artery disease for electrical sleep, an orbital-retromastoidal technique is used using a rectangular pulse current with a frequency of 5-20 Hz, lasting from 30 minutes to 1 hour, daily. The course of treatment consists of 12-15 procedures.
Transcranial electrotranquilization is performed according to the frontorethromastoidal technique using a rectangular pulse current with a frequency of 1000 Hz, lasting 30-45 minutes daily. The course of treatment consists of 12-15 procedures.
With stable hypertension, electrosleep is used using a rectangular pulse current with a frequency of 100 Hz (the first 5-6 procedures); then they switch to 10 Hz. The duration of the procedures is 30-45 minutes. The course of treatment includes 10-12 daily procedures.
With diencephalic syndrome and neuroses, electrosleep is used using a rectangular pulse current with a frequency of 10 Hz for a duration of 30 minutes to 1 hour, every other day. The course of treatment consists of 10-12 procedures.
Transcranial electrotranquilization is carried out according to the frontorethromastoidal technique using a rectangular pulse current with a frequency of 1000 Hz and a duration of 30-40 minutes. The course of treatment includes 12-15 daily procedures.
In traumatic encephalopathy, electrosleep is used according to the ophthalmic-retromastoidal technique using a rectangular pulse current with a frequency of 10 Hz lasting from 30 minutes to 1 hour, every other day. The course of treatment includes 10-12 procedures.
Short-pulse electroanalgesia Short-pulse electroanalgesia (percutaneous electroneurostimulation) impact on the painful focus with very short (20-500 μs) current pulses, followed by bursts of 20-100 pulses with a frequency of 2 to 400 Hz.
The duration and repetition rate of current pulses used for short-pulse electroanalgesia are very similar to the corresponding parameters of pulses of thick myelinated Ap fibers. In this regard, the flow of rhythmic ordered afferentation, created during the procedure, excites the neurons of the gelatinous substance of the posterior horns spinal cord and blocks the conduct of nocigenic information at their level. Excitation of the interneurons of the posterior horns of the spinal cord leads to the release of opioid peptides in them. The analgesic effect is enhanced by an electric impulse effect on the paravertebral zones and areas of reflected pain.
Fibrillation of smooth muscles of arterioles and superficial muscles of the skin caused by electrical impulses, activates the processes of utilization of algogenic substances (bradykinin) and mediators (acetylcholine, histamine), released during the development of pain syndrome. Strengthening local blood flow activates local metabolic processes and local protective properties fabrics. Along with this, perineural edema decreases and depressed tactile sensitivity is restored in areas of local pain.
Apparatus and general instructions for performing procedures
For the procedures, the devices "Delta-101 (-102, -103)", "ElimanBion", "Neuron", "Impulse-4" and others are used. During the procedures, electrodes are applied and fixed in the projection area of \u200b\u200bthe pain focus. According to the principle of their placement, peripheral electroanalgesia is distinguished, when the electrodes are placed in areas of pain, points of exit of the corresponding nerves or their projection, as well as in reflexogenic zones, and segmental electroanalgesia, in which the electrodes are placed in the region of paravertebral points at the level of the corresponding spinal segment. Two types of short-pulse electroanalgesia are most often used. In the first case, current pulses with a frequency of 40-400 Hz with a force of up to 5-10 mA are used, causing rapid (2-5 minutes) analgesia of the corresponding metamer, which lasts at least 1-1.5 hours. When exposed to biologically active points (BAP) use current pulses up to 15-30 mA, supplied with a frequency of 2-12 Hz. Hypoalgesia develops in 15-20 minutes and captures, in addition to the area of \u200b\u200bimpact, and neighboring metameres.
The parameters of impulse currents are dosed in terms of amplitude, repetition rate and duty cycle, taking into account the stage of pain syndrome development. Along with this, the appearance of a feeling of hypoalgesia in the patient is taken into account. During the procedure, the patient should not have pronounced muscle fibrillation in the area where the electrodes are located. The exposure time is 20-30 minutes; procedures are carried out up to 3-4 times a day.
The duration of the course depends on the effectiveness of pain relief.
Indications for treatment are pain syndromes in patients with diseases of the nervous system (radiculitis, neuritis, neuralgia, phantom pain) and musculoskeletal system (epicondylitis, arthritis, bursitis, sprains, sports injury, bone fractures).
Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
General contraindications to physiotherapy;
Acute pains of visceral origin (angina pectoris attack, myocardial infarction, renal colic, labor pains);
Diseases of the membranes of the brain (encephalitis and arachnoiditis);
- & nbsp– & nbsp–
Psychogenic and ischemic pain;
Acute purulent inflammatory process;
Thrombophlebitis;
Acute dermatoses;
The presence of metal fragments in the affected area.
Diadynamic therapy Diadynamic therapy (DDT) is an electrotherapy method based on exposure to a low-frequency pulsed current of a constant direction of a half-sinusoidal shape with an exponential trailing edge of 50 and 100 Hz in various combinations.
DDT has an analgesic effect. The analgesic effect of DDT is due to processes developing at the level of the spinal cord and brain.
Irritation by a rhythmic impulse current of a large number of nerve endings leads to the appearance of a rhythmically ordered flow of afferent impulses. This flow blocks the passage of pain impulses at the level of the gelatinous substance of the spinal cord. The analgesic effect of DDT is also facilitated by reflex excitation of the endorphin systems of the spinal cord, resorption of edema and reduction of compression of the nerve trunks, normalization of trophic processes and blood circulation, elimination of tissue hypoxia.
The direct effect of DDT on body tissues differs little from the effect of galvanic current. The reaction of individual organs, their systems and the organism as a whole is due to the impulsive nature of the supplied current, which changes the ratio of ion concentrations at the surface of cell membranes, inside cells and in intercellular spaces. As a result of changing ionic composition and electric polarization, the dispersion colloidal solutions cells and the permeability of cell membranes, the intensity of metabolic processes and tissue excitability increase. These changes are more pronounced at the cathode. Local changes in tissues, as well as the direct action of the current on receptors, cause the development of segmental reactions. In the foreground is hyperemia under the electrodes, caused by vasodilation and increased blood flow. In addition, when exposed to DDT, reactions caused by current pulses develop.
Due to the changing concentration of ions at the surface of cell membranes, the dispersion of cytoplasmic proteins changes and functional state cells and tissues. When rapid changes concentration of ions, the muscle fiber is reduced (at a low current strength, it is strained). This is accompanied by an increase in blood flow to excited fibers (and to any other working organ) and an intensification of metabolic processes.
Blood circulation also increases in areas of the body innervated from the same segment of the spinal cord, including the symmetrical region. At the same time, blood flow to the affected area, as well as venous outflow, increases, the resorption capacity of the mucous membranes of the cavities (pleural, synovial, peritoneal) improves.
Under the influence of DDT, the tone of the great vessels is normalized and collateral circulation is improved. DDT affects the functions of the stomach (secretory, excretory and motor), improves the secretory function of the pancreas, stimulates the production of glucocorticoids by the adrenal cortex.
Diadynamic currents are obtained by single- and full-wave rectification of alternating mains current with a frequency of 50 Hz. In order to reduce adaptation to influences and increase the effectiveness of treatment, several types of current have been proposed, representing a sequential alternation of currents with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz or an alternation of the latter with pauses.
Half-wave continuous (OH) half-sine current with a frequency of 50 Hz has a pronounced irritating and myostimulating properties, up to tetanic muscle contraction; causes a large, unpleasant vibration.
Full-wave continuous (DN) half-sinusoidal current with a frequency of 100 Hz has a pronounced analgesic and vasoactive property, causes fibrillar muscle twitching, small diffuse vibration.
One-half rhythmic (RR) current, the transmissions of which alternate with pauses of equal duration (1.5 s), has the most pronounced myostimulating effect during the transmission of current, combined with a period of complete muscle relaxation during the pause.
Short-period modulated current (CP) is a sequential combination of OH and DN currents following equal bursts (1.5 s). The alternation significantly reduces the adaptation to the impact. This current first has a neuromyostimulating effect, and after 1-2 minutes - an analgesic effect; makes the patient feel the alternation of a large and soft gentle vibration.
Modulated current long period (DP), - simultaneous combination of OH current transmissions with a duration of 4 s and a DN current with a duration of 8 s. The neuromyostimulating effect of such currents decreases, but the analgesic, vasodilating and trophic effects gradually increase. The patient's sensations are similar to those in the previous exposure regime.
One-half-wave wave (OF) current is a series of half-wave current pulses with an amplitude that increases from zero to a maximum value for 2 s, remains at this level for 4 s, and then decreases to zero for 2 s.
Total duration sending a pulse of 8 s, the duration of the entire period is 12 s.
Full-wave wave (DW) current is a series of full-wave current pulses with an amplitude that changes in the same way as the OF current. The total duration of the period is also 12 s.
Diadynamic current has an injecting ability, which leads to its use in techniques drug electrophoresis (diadynamophoresis). Yielding galvanic current by the amount of medicinal substance, it contributes to its deeper penetration, often potentiating its action.
It is best to prescribe diadynamophoresis when pain prevails.
Apparatus and general instructions on the performance of procedures To carry out DDT procedures, devices are used that generate pulses of different duration, frequency and shape with varying duration pauses between messages, such as "Tonus-1 (-2, -3)", "SNIM-1", "Diadynamic DD-5A", etc.
During DDT procedure hydrophilic electrode pads required size moistened with warm tap water, wring out, metal plates are placed in the pockets of the gaskets or on top of them. Cup electrodes are placed in the area of \u200b\u200bthe most pronounced pain sensations and during the procedure they are held by the hand on the handle of the electric holder. An electrode is placed on the painful point, connected to the negative pole of the apparatus - the cathode; another electrode of the same area is placed next to the first at a distance equal to its diameter or more. With electrodes of different areas, a smaller electrode (active) is placed on the painful point, the larger (indifferent) is placed at a considerable distance (in the proximal part of the nerve trunk or limb). With DDT, water can be used as an active electrode on the area of \u200b\u200bsmall joints of the hand or foot: it is filled into a glass or ebonite bath and the bath is connected to the negative pole of the apparatus through a carbon electrode.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, the stage of the disease, the patient's reactivity (the property of the tissue to differentially respond to the action of an external stimulus; in in this case - the action of a physiotherapeutic factor or changes in the internal environment of the body), individual characteristics organism and the therapeutic tasks to be solved, one or another type of DDT, as well as their combination, is used. To reduce addiction and gradually increase the intensity of exposure, 2-3 types of DDT current are used on the same part of the body.
The current strength is selected individually, taking into account subjective feelings patient (slight tingling, burning, feeling of electrode slipping, vibration, intermittent compression or contraction of muscles in the area of \u200b\u200bexposure). With DDT of pain syndrome, the current strength is selected so that the patient feels a pronounced painless vibration (from 2-5 to 15-30 mA). During the procedure, addiction to the action of DDT is noted; this must be taken into account and, if necessary, the intensity of the impact must be increased.
The duration of the procedure is 4-6 minutes in one area, the total exposure time is 15-20 minutes. The course of treatment includes 5-10 daily procedures.
Indications for treatment:
Neurological manifestations of osteochondrosis of the spine with pain syndromes (lumbago, radiculitis, radicular syndrome), motor and vascularotrophic disorders;
Neuralgia, migraine;
Diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system, myositis, arthrosis, periarthritis;
Diseases of the digestive system (peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer, pancreatitis);
Chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterine appendages;
Hypertension in initial stages... Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
General contraindications to physiotherapy;
Acute inflammatory processes (purulent);
Thrombophlebitis;
Non-fixed fractures;
- & nbsp– & nbsp–
Hemorrhage in the cavity and tissue;
Tears of muscles and ligaments.
Therapeutic techniques Diadynamic therapy in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia Small round electrodes are used. One electrode (cathode) is placed at the exit site of one of the branches of the trigeminal nerve, the second - in the area of \u200b\u200bpain irradiation.
Impact with current DN 20-30 s, and then with current KP for 1-2 minutes. The current strength is gradually increased until the patient feels a pronounced painless vibration; the course of treatment includes up to six daily procedures.
Diadynamic therapy in the treatment of migraine
The position of the patient is lying on the side. They act with round electrodes on a hand holder. The cathode is installed 2 cm behind the corner lower jaw on the area of \u200b\u200bthe upper cervical sympathetic node, the anode - 2 cm higher. The electrodes are placed perpendicular to the neck surface. Apply current DN for 3 min; the current strength is gradually increased until the patient feels a pronounced vibration.
The impact is carried out from two sides. The course consists of 4-6 daily procedures.
Diadynamic therapy for headaches associated with an hypotensive state, atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels (according to V.V. Sinitsin) The position of the patient is lying on his side. Use small double electrodes on a hand-held holder. The electrodes are placed in the temporal region (at the level of the eyebrow) so that the temporal artery is in the interelectrode space. The KP current is applied for 1-3 minutes, followed by a change in polarity for 1-2 minutes. During one procedure, the right and left temporal arteries are acted upon alternately.
The procedures are carried out daily or every other day, the course of treatment consists of 10-12 procedures.
Diadynamic therapy on the gallbladder area The plate electrodes are positioned as follows: an active electrode (cathode) with an area of \u200b\u200b40-50 cm2 is placed on the projection area of \u200b\u200bthe gallbladder in front, the second electrode (anode) with a size of 100-120 cm2 is placed transversely on the back.
OV is used in a constant or variable mode of operation (in the latter, the duration of the period is 10-12 s, the rise time of the leading edge and the fall of the trailing edge is 2-3 s each). The current strength is increased until pronounced contractions of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall begin under the electrodes. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes daily or every other day, the course of treatment consists of 10-12 procedures.
Diadynamic therapy for the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
Electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b200-300 cm2 are placed on the abdominal wall (cathode) and in the lumbosacral region (anode). DDT parameters: OV-current in continuous operation; the current strength is increased until pronounced contractions of the abdominal wall appear, the exposure time is 10-12 minutes. The course of treatment includes up to 15 procedures.
Diadynamic therapy for the perineal region
Electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b40-70 cm2 are positioned as follows:
Above the pubic joint (anode) and on the perineum (cathode);
Above the pubic articulation and on the perineal area under the scrotum (the polarity depends on the purpose of exposure);
Above the symphysis pubis (cathode) and on the lumbosacral spine (anode).
DDT parameters: half-wave current in alternating mode of operation, period duration 4-6 s. Syncope rhythm can be used with alternating operation. With good tolerance, the current is increased until the patient feels a pronounced vibration. The duration of the procedure is up to 10 minutes daily or every other day, the course of treatment includes up to 12-15 procedures.
The effect of diadynamic therapy on a woman's genitals Electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b120-150 cm2 are placed transversely over the pubic joint and in the sacral region. DDT parameters: DN with polarity reversal - 1 min;
CP - 2-3 minutes, DP - 2-3 minutes. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day. The course of treatment consists of 8-10 procedures.
Diadynamic therapy for diseases of the shoulder joint Plate electrodes are placed transversely on the anterior and posterior surfaces of the joint (the cathode is at the site of pain projection).
DDT parameters: DV (or DN) - 2-3 minutes, CP - 2-3 minutes, DP - 3 minutes In case of pain under both electrodes in the middle of exposure to each type of current, the polarity is reversed. The strength of the current is increased until the patient feels a pronounced painless vibration. 8-10 procedures are prescribed for the course, carried out daily or every other day.
Diadynamic therapy for bruised or sprained joint ligaments
Round electrodes are placed on both sides of the joint at the most painful points. Impact with the current of the DN for 1 min, and then - KP for 2 min in the forward and reverse directions. The current strength is increased until the patient feels the most pronounced vibration. The procedures are carried out daily. The course of treatment consists of 5-7 procedures.
Electrostimulation
Electrical stimulation is a method of therapeutic action with impulse currents of low and high frequency, used to restore the activity of organs and tissues that have lost their normal function, as well as to change the functional state of muscles and nerves. Separate impulses are applied; series, consisting of several impulses, as well as rhythmic impulses alternating with a certain frequency.
The nature of the reaction caused depends on:
Intensity, configuration and duration of electrical impulses;
The functional state of the neuromuscular apparatus. These factors, closely related to each other, form the basis of electrodiagnostics, allowing you to select the optimal parameters of the pulse current for electrical stimulation.
Electrical stimulation supports muscle contractility, enhances blood circulation and metabolic processes in tissues, and prevents the development of atrophy and contractures. Procedures carried out in the correct rhythm and with an appropriate current strength create a stream of nerve impulses that enter the central nervous system, which in turn contributes to recovery motor functions.
Indications
Electrostimulation is most widely used in the treatment of diseases of the nerves and muscles. These diseases include various paresis and paralysis of skeletal muscles, both flaccid, caused by disorders of the peripheral nervous system and spinal cord (neuritis, the consequences of poliomyelitis and spinal injuries with spinal cord damage), and spastic, post-stroke. Electrical stimulation is indicated for aphonia due to paresis of the muscles of the larynx, paretic state of the respiratory muscles and diaphragm. It is also used for muscle atrophy, both primary, which developed as a result of injuries of peripheral nerves and spinal cord, and secondary, which arose as a result of prolonged immobilization of the limbs in connection with fractures and osteoplastic operations. Electrical stimulation is indicated for atonic states of smooth muscles of internal organs (stomach, intestines, bladder). The method is used for atonic bleeding, to prevent postoperative phlebothrombosis, to prevent complications during prolonged physical inactivity, to improve the fitness of athletes.
Electrical stimulation is widely used in cardiology. A single high voltage electrical discharge (up to 6 kV), the so-called defibrillation, is able to restore the functioning of a stopped heart and bring a patient with myocardial infarction out of a state of clinical death. An implantable miniature device (pacemaker), which supplies rhythmic impulses to the patient's heart muscle, provides long-term effective work heart when blocking its pathways.
Contraindications
Contraindications include:
Gallstone and kidney stone disease;
Acute purulent processes in the organs abdominal;
Spastic state of the muscles.
Electrical stimulation of mimic muscles is contraindicated with an increase in their excitability, as well as with early signs contractures. Electrical stimulation of the muscles of the extremities is contraindicated in case of ankylosis of the joints, dislocations before their reduction, fractures of bones before their consolidation.
General instructions for performing procedures
Electrostimulation procedures are dosed individually according to the strength of the irritating current. During the procedure, the patient should experience intense, visible, but painless muscle contractions. The patient should not experience any discomfort. Lack of muscle contractions or painful sensations indicate wrong location electrodes or the inadequacy of the applied current.
The duration of the procedure is individual and depends on the severity of the pathological process, the number of affected muscles and the method of treatment.
In physiotherapy, electrical stimulation is used mainly to act on damaged nerves and muscles, as well as on the smooth muscles of the walls of internal organs.
Electrodiagnostics Electrodiagnostics is a method that allows you to determine the functional state of the peripheral neuromuscular apparatus using some forms of current.
When a nerve or muscle is irritated by a current, their bioelectric activity changes and spike responses are formed. By changing the rhythm of stimulation, one can detect a gradual transition from single contractions to dentate tetanus (when the muscle has time to partially relax and contract again under the action of the next current impulse), and then to full tetanus (when the muscle does not relax at all due to the frequent repetition of current impulses). These reactions of the neuromuscular apparatus when irritated by constant and impulse currents formed the basis of classical electrodiagnostics and electrical stimulation.
The main task of electrodiagnostics is to determine the quantitative and qualitative changes reactions of muscles and nerves to irritation with tetanizing and intermittent direct current. Repeated electrodiagnostic studies allow to establish the dynamics of the pathological process (restoration or deepening of the lesion), assess the effectiveness of treatment and obtain the necessary information for prognosis. In addition, the correct assessment of the state of the electrical excitability of the neuromuscular apparatus allows you to select the optimal parameters of the current for electrical stimulation.
Electrical stimulation maintains contractility and muscle tone, improves blood circulation and metabolism in the affected muscles, slows down their atrophy, and restores high lability of the neuromuscular apparatus. During electrical stimulation, on the basis of electrodiagnostic data, the shape of the pulse current, the pulse repetition rate are selected and their amplitude is adjusted. At the same time, pronounced painless rhythmic muscle contractions are achieved. The duration of the impulses used is 1-1000 ms. The current strength for the muscles of the hand and face is 3-5 mA, and for the muscles of the shoulder, lower leg and thigh - 10-15 mA. The main criterion for the adequacy of obtaining an isolated painless muscle contraction of the maximum size when exposed to a current of minimal force.
Apparatus and general instructions on the performance of procedures For carrying out electrodiagnostics, the "Neuropulse" apparatus is used. When electrodiagnostics are used:
Intermittent direct current with a rectangular pulse duration of 0.1 s (with manual interruption);
Tetanizing current with triangular pulses, frequency 100 Hz and pulse duration 1-2 ms;
Pulse current of rectangular shape and pulse current of exponential shape with pulse frequency adjustable in the range of 0.5-1200 Hz and pulse duration adjustable in the range of 0.02-300 ms.
The study of electrical excitability is carried out in a warm, well-lit room. The muscles of the study area and the healthy (symmetrical) side should be as relaxed as possible. When carrying out electrodiagnostics, one of the electrodes (guide, with an area of \u200b\u200b100-150 cm2) with a moistened hydrophilic pad is placed on the sternum or spine and connected to the anode of the apparatus. The second electrode, previously covered with a hydrophilic cloth, is periodically moistened with water. In the process of electrodiagnostics, the reference electrode is placed on the motor point of the nerve or muscle under investigation. These points correspond to the projection of the nerves in the place of their most superficial location or the places where the motor nerve enters the muscles. Based special studies R. Erb in late XIX in. compiled tables showing the typical location of motor points, where muscles contract at the lowest amperage.
For myoneurostimulation, the devices "Miorhythm", "Stimul-1" are used. For insignificantly expressed lesions of nerves and muscles, devices for DDT and amplipulse therapy (in a straightened mode) are also used for electrical stimulation.
Internal organs are stimulated using the Endoton-1 apparatus.
The Stimul-1 device generates three types of pulse currents. For electrostimulation with this device, plate electrodes with hydrophilic pads of various areas are used, as well as strip electrodes of a special design. In addition, electrodes on a handle with a push-button breaker are used. The location of the points is noted by the doctor during the electrodiagnostics.
For electrical stimulation of nerves and muscles with severe pathological changes a bipolar technique is used, in which two equal-sized electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b6 cm2 are positioned as follows: one electrode (cathode) - at the motor point, the other (anode) - in the area of \u200b\u200btransition of the muscle to the tendon, in the distal section. In the bipolar technique, both electrodes are placed along the stimulated muscle and fixed with a bandage so that muscle contraction is unobstructed and visible.
During electrical stimulation, the patient should not experience unpleasant pain sensations;
after muscle contraction, its rest is necessary. The greater the degree of muscle damage, the less frequent contractions are caused (from 1 to 12 contractions per minute), the longer the rest after each contraction. As muscle movement is restored, the frequency of contractions gradually increases. With active stimulation, when the current is turned on simultaneously with the patient's attempt to make a volitional muscle contraction, the number and duration of impulses are regulated by a manual modulator.
The current strength is regulated during the procedure, achieving pronounced painless muscle contractions. The current strength varies depending on the muscle group - from 3-5 mA to 10-15 mA. The duration of the procedure and the course of electrical muscle stimulation depends on the nature of the muscle damage and its severity. The procedures are carried out 1-2 times a day or every other day. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures.
Indications for electrical stimulation:
Flaccid paresis and paralysis associated with nerve injury, specific or non-specific inflammation of the nerve, toxic damage nerve, degenerative dystrophic diseases of the spine;
Central paresis and paralysis associated with the disorder cerebral circulation;
Muscle atrophy with prolonged physical inactivity, immobilization dressings;
Hysterical paresis and paralysis;
Postoperative intestinal paresis, various dyskinesias of the stomach, intestines, biliary and urinary tract, ureteral stones;
Muscle stimulation to improve peripheral arterial and venous circulation and lymph flow;
Increase and strengthen muscle mass athletes. Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
General contraindications to physiotherapy;
Acute inflammatory processes;
Contracture of facial muscles;
Bleeding (other than dysfunctional uterine);
Bone fractures before immobilization;
Dislocation of joints before reduction;
Ankylosis of the joints;
Bone fractures before their consolidation;
Cholelithiasis;
Thrombophlebitis;
Condition after acute disturbance cerebral circulation (first 5-15 days);
Suture of a nerve, a vessel during the first month after surgery;
Spastic paresis and paralysis;
Violations heart rate (atrial fibrillation, polytopic extrasystole).
MEDICINAL APPLICATION OF AC MEDIUM AND
HIGH FREQUENCY
MOTIVATION
For the correct appointment of physiotherapeutic procedures, it is necessary to have a holistic understanding of the mechanism of action of medium and high frequency alternating currents on the human body.PURPOSE OF THE LESSON
Learn to use amplipulse therapy, fluctuation, interference therapy, ultraton therapy, darsonvalization techniques for the treatment of various diseases.TARGETED ACTIVITIES
Understand the essence of the physiological action of medium and high frequency alternating current. Be able to:Determine indications and contraindications for the use of alternating currents of medium and high frequency;
Choose an adequate type of therapeutic effect;
Independently appoint procedures;
Assess the effect of alternating currents on the patient's body.
To study the principles of operation of the devices "Amplipulse-4 (-5)", "AIT-50Ch", "ASB-2-1", "Iskra", "Ultraton".
Information block
AMPLIPULSE THERAPY
Amplipulse therapy is an electrotherapy method based on exposure to alternating sinusoidal currents with a frequency of 5000 Hz, modulated low frequencies in the range of 10-150 Hz. The depth of their amplitude modulation varies within the frequency range of the biopotentials of nerve and muscle cells. As a result of modulation, a series of current pulses are formed, separated from each other by gaps with zero amplitude. There are five types of sinusoidal modulated currents (CMT).The first type of work (I PP, constant modulation, PM) is the modulation of the current of the fundamental (carrier) frequency by currents of a fixed frequency (in the range of 10-150 Hz) and modulation depth. The strength of the exciting effect increases with decreasing modulation frequency and increasing its depth.
The second kind of work (II RR, pause-pauses, PP) is a combination of carrier-frequency current pulses modulated with a certain frequency, with pauses. The duration of the current pulses and pauses varies within 1-6 s. This mode provides a pronounced contrast of the effect of SMT against the background of pauses and has the most pronounced neuromyostimulating properties.
The third type of work (III PP, carrier-frequency, PN) is a combination of current pulses modulated at a certain frequency with unmodulated current pulses with a frequency of 5 kHz. The duration of the current pulses varies within 1-6 s.
The stimulating effect of SMT with this combination is less pronounced than with II PP, but the analgesic effect begins to manifest itself.
The fourth type of work (IV RR, moving frequencies, IF) is the alternation of current pulses with different modulation frequencies: in one of the messages, the modulation frequency is constant (150 Hz), in the other, the modulation frequency is selected from the range of 10-150 Hz. In this case, CMTs give the greatest analgesic effect, increasing with a decrease in the difference between the frequency of 150 Hz and the selected modulation frequency.
Similar works:
Journal of Siberian Federal University. Engineering & Technologies 3 (2009 2) 250-277 ~~~ UDC 541.182.023.4 + 546.57 + 621.315.592 + 541.121 + 543.7 The use of silver (review) L.T. Denisova, N.V. Belousov, V.M. Denisov, V.V. Ivanov Siberian Federal University, Russia 660041, Krasnoyarsk, pr. Svobodny, 79 Received 16.09.2009, received in revised form 06.10.2009, accepted 20.10.2009 A review of works devoted to the application, from ancient times to the present, is carried out. Analysis done ... "
“General doctrine of tumors Relevance of the topic A tumor, or blastoma, is an atypical neoplasm of tissue, which differs from other forms of growth (regeneration, hyperplasia, proliferation, metaplasia) in a number of basic biological properties (see below). A tumor can arise in any tissue, any organ and develop both in humans and in many animals and plants. The field of medicine that studies the causes, mechanisms of development and clinical manifestations tumors, as well as developing methods for their diagnosis, ... "
"St. Petersburg State University, Department of Ichthyology and Hydrobiology. MATERIALS of the VIII scientific seminar" Readings in memory of K.M.Deryugin "St. Petersburg The collection contains materials of the 8th annual scientific seminar" Readings in memory of K.M.Deryugin ", which was held at the department Ichthyology and Hydrobiology of St. Petersburg State University December 2, 2005. The book is of interest to hydrobiologists, ecologists, zoologists and specialists in the history of science. Editor: M. V. Katolikova © Department of Ichthyology and Hydrobiology ... "
“SUPERECOTOXICANTS, SUPRAMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS, ZONOSES, HYDROAUSTIC INSTRUMENT, ARTIFICIAL STURGEON BREEDING, GEOINFORMATIONAL MAPPING Object of study is the biological diversity of ecosystems of the coast and water area of \u200b\u200bthe Middle Caspian. Objectives of the work - Creation of technologies, methods and tools for monitoring biodiversity ... "
"Vladimir State University, Vladimir region., Murom, st. Orlovskaya, 23 E-mail: mas [email protected] Biological adaptation as a basis social work IN modern society important role plays the phenomenon of human biological adaptation, which further determines the need to harmonize human interaction and ... "
Samarskaya Luka: problems of regional and global ecology. Samarskaya Luka. 2009. - T. 18, No. 1. - S. 188-201. UDC 581.5 + 581.9 DEVELOPMENT OF HYDROBOTANIC RESEARCHES IN THE MIDDLE VOLGA REGION © 2009 V.V. Solovyova1, S.V. Saxonov2, S.A. Senator2, N.V. Koneva2 * Volga State Social and Humanitarian Academy, Samara (Russia) Institute of Ecology of the Volga Basin, Russian Academy of Sciences, Togliatti (Russia) [email protected] Received February 17, 2009 Review of the state of knowledge of coastal water and water ... "
«2014 Geographical Bulletin 2 (29) Ecology and Nature Management 4. Balamirzoev MA, Mirzoev EM-R., Adzhiev AM, Mufaradzhev KG. Soils of Dagestan. Environmental aspects their rational use. Makhachkala: State Institution “Dagest. book publishing house ”, 2008. 336 p. 5. Woodward D.B. The influence of ecotourism activities on the microbiological composition of soils // Proceedings of the II International. scientific-practical conf. " Actual problems ecology and nature management in Kazakhstan and adjacent territories ”, 23-24 October. 2007, ... "
"N.V. Lagutkin SMART FARMING Penza, 2013 UDC 631 Reviewers: Lysenko Yu. N., Doctor of Agricultural Sciences, Honored Worker of Agricultural of the Russian Federation Makhonin I.A., Professor of RAE, Ph.D. Volgograd GAU Lagutkin N.V. K56 Reasonable agriculture. / N.V. Lagutkin - Penza, 2013 .-- 116 p. I express my gratitude to the scientists of the Penza Scientific Research Institute agriculture PER. Kirasirov, N.A. Kuryatnikova for the great work on carrying out industrial experiments on the fields of TNV "Pugachevskoe", the results of which ... "
LECTURE 1. History of the development of microbiology. The subject and objectives of sanitation and hygiene. Microbiology is the science of microorganisms. The object of the study of microbiology is microorganisms - organisms with sizes within 0.1 mm. These include protozoa, unicellular algae, microscopic fungi, bacteria, viruses (slide 1.4). Microorganisms are ubiquitous in nature. Due to their small size, their number in 1 g of substance can be millions and billions of cells. Basic ... "
“Ecosystems, their optimization and protection. 2012. Issue. 7, pp. 114–125. UDC 547.9 + 591.5 + 581.524.1 + 582.26 / 27 + 582.232 + 551.46: 574.5 + 632.9 MASS SPECIES OF CYANOBACTERIA AND MICROALGAE IN ECOSYSTEMS: INTERSPECIFIC RELATIONSHIPS AND THE SOUTHERN BRANCH OF THE KO-EVOESLUISOV National University agrotechnological university ", Simferopol, [email protected] Considered current situation in the Azov-Black Sea basin concerning ... "
Biology (magistracy) Key dates of history November 5, 1804 By the Charter of the Kazan Imperial University, the following departments were created: Natural history and botany, Anatomy, physiology and forensic medicine. November 15, 1930 Creation of an independent Medical Institute March 15, 1933 The Faculty of Biology was created. eighteen..."
“.00.08 -“ ”2012 NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA. ., .., .., ... 2012.1-, [email protected] www.zhesc.sci.am 2012.31-: 035 ,. The topic of the thesis was approved by the Yerevan State ... "
"K.M.Deryugin" St. Petersburg St. Petersburg State University Faculty of Biology and Soil Science Department of Ichthyology and Hydrobiology MATERIALS of the X scientific seminar "Readings in memory of K.M.Deryugin" St. Petersburg The collection contains materials of the 10th annual scientific seminar " Readings in memory of K.M.Deryugin ", which took place at the department ..."
“Literature of the Russian Academy of Sciences This research was carried out with the financial support of the Russian Foundation for the Humanities (Project No. 01-03-00332a) CONTENTS Introduction. CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS: EVOLUTION, DEVELOPMENT, PROGRESS, ANTIPROGRESS Chapter I. FACTORS OF SOCIOCULTURAL EVOLUTION. § 1. Demographic factor § 2. Spontaneous changes in the natural environment .. § 3 .... "
"Coolant. 628.315.2.1 ol zhazba ynda YELZHASOV ABYLAY ARALBAILY Saryndy courts of biology tazartu process zhkteme aryly zhetildiru 05.23.04 - Sumen zhabdytau, sewerage, su orlaryn oraudyl rylysty zhymerysym candidates .Stbaev atynday azalty technicians of the university_inde oryndaldy ylymi zhetekshiler: technique yymdaryn doctors, professor Myrzakhmetov M.M, because I.
“Ecosystems, their optimization and protection. 2012. Issue. 7, pp. 229–242. Geoecology UDC 546.4: 591.148: 593.8 EFFECT OF HEAVY METALS ON BEROE OVATA LIGHT (CTENOPHORA: BEROIDA) OV Mashukova, Yu. N. Tokarev Institute of Biology of the Southern Seas A.O. Kovalevsky NAS of Ukraine, Sevastopol, [email protected], [email protected] The variability of the amplitude-time characteristics of the bioluminescence of the comb jelly Beroe ovata Mayer, 1912, depending on the toxicity of the heavy metal, its ... "
"PLAN of laboratory studies in microbiology for 3rd year students of the pediatric faculty for the fall semester of the 2014-2015 academic year LESSON 1 Topic: Methods of microbiological diagnosis of diseases caused by staphylococci, streptococci, neisseria. Staphylococcus, taxonomy, general characteristics, factors of pathogenicity. Diseases of staphylococcal nature, features of pathogenesis, immunity. Methods for microbiological diagnosis of staphylococcal infections. Material for research in ... "
“From the decision of the Board of the Accounts Chamber of the Russian Federation dated July 17, 2014 No. 36K (982)“ On the results of the control measure “Checking compliance with customs and tariff regulation measures, organizing customs control in order to ensure the completeness of customs payments in respect of aquatic biological resources, products from them, ships and equipment for their extraction and processing, transported across the customs border Russian Federation (Customs Union) in 2013 and expired ... ”write to us, we will delete it within 1-2 business days.
Myoneuroelectrostimulation is an effect on muscles and nerve endings with physiological currents of different parameters. Essentially, this is electrotherapy.
To more accessible and understandable display this difficult topic for perception - we tried our best to exclude cumbersome professional terms from the field of physics and medicine / while writing this article /.
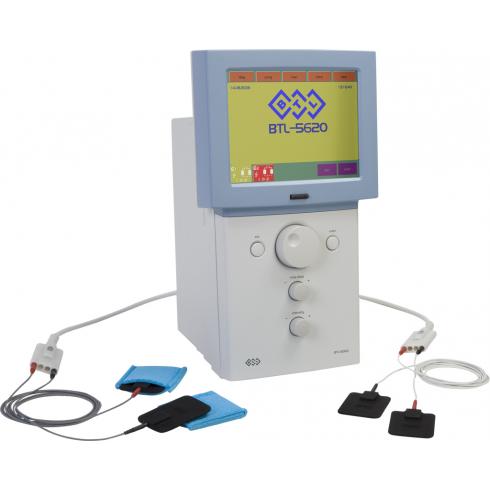
 Electrotherapy - these are all methods of treatment using electric current. Used for treatment electricity low, medium and high frequency. In our clinic of Dr. Starish, in Odessa, electrotherapy is represented by devices of the BTL-5000 series. This is a device of the latest generation, self-testing, with a multi-stage protection system, which allows accurately, up to milliamperes, to dose the current strength and duration of treatment, therefore, in our clinic, electrotherapy is absolutely safe and effective.
Electrotherapy - these are all methods of treatment using electric current. Used for treatment electricity low, medium and high frequency. In our clinic of Dr. Starish, in Odessa, electrotherapy is represented by devices of the BTL-5000 series. This is a device of the latest generation, self-testing, with a multi-stage protection system, which allows accurately, up to milliamperes, to dose the current strength and duration of treatment, therefore, in our clinic, electrotherapy is absolutely safe and effective.
There are currents :
low, medium and high frequency and they are used for various purposes. Electrotherapy applications depend on the frequency of the current.
Low frequency current
We use low frequency currents as remedy for the purpose of electrical stimulation - a method of influencing weakened muscles. And this is very  important for diseases of the spine, which is kept upright thanks to. Electrical stimulation causes repetitive, involuntary muscle contractions, which strengthens them and prevents the development of atrophy. In fact, this is "exercise for the lazy." A person lies, dreams, and the apparatus "shakes" the muscles, the muscles work. This is especially true when the muscles of the back are spasmodic on one side, visually shortened, and on the other side they are stretched, overstretched, like a bowstring. This is one example that is quite illustrative.
important for diseases of the spine, which is kept upright thanks to. Electrical stimulation causes repetitive, involuntary muscle contractions, which strengthens them and prevents the development of atrophy. In fact, this is "exercise for the lazy." A person lies, dreams, and the apparatus "shakes" the muscles, the muscles work. This is especially true when the muscles of the back are spasmodic on one side, visually shortened, and on the other side they are stretched, overstretched, like a bowstring. This is one example that is quite illustrative.
There is such a pathology of the spine - instability of the vertebrae,  occurs, as a rule, in the cervical spine, at a young and middle age. We can say that this is a “tumbler syndrome”, when, when turning the head, the vertebrae are displaced relative to each other, causing mechanical compression of the vertebral artery (). Here you cannot do without passive muscle pumping, without electrical stimulation. Because for any physical. exercise, we will cause additional displacement of the vertebrae and further deterioration of the patient's condition.
occurs, as a rule, in the cervical spine, at a young and middle age. We can say that this is a “tumbler syndrome”, when, when turning the head, the vertebrae are displaced relative to each other, causing mechanical compression of the vertebral artery (). Here you cannot do without passive muscle pumping, without electrical stimulation. Because for any physical. exercise, we will cause additional displacement of the vertebrae and further deterioration of the patient's condition.
Perhaps another example - in case of - problems with the disc - when the disc has "sat down", worn out, excellent results are obtained by stimulating the muscles of that part of the spine where there is a problem. The muscle works, blood supply, nutrition improves, venous congestion goes away, respectively, pit rushes to the diseased disc.  substances. The diseased disc, one might say, gets a breath of fresh air.
substances. The diseased disc, one might say, gets a breath of fresh air.
direct current of low frequency is amplified if the gasket under the electrode is moistened with a solution
a medicinal substance that is injected into the tissue through the skin by current and has its inherent positive action on the patient's body. The advantages of this effect are that in the right place locally, the body receives the required concentration of the drug. This method is called medicinal electrophoresis.
Indications for the use of electrotherapy low frequency current:
- neuralgia, lumbago, radiculitis, sciatica
- arthrosis-arthritis
- scoliosis
- discopathy, disc herniation
Average frequency current
Medium-frequency electrotherapy is an interference of two-frequency alternating current. This method is also called interference therapy. we ![]() we use in combination with. The method is called - Wind farm — vacuum electrical stimulation
... Difference from: none vectorscanning the pain site. The impact with IES is distributed evenly over the entire area of \u200b\u200bexposure - this is what is called - 4-pole interferential therapy.
we use in combination with. The method is called - Wind farm — vacuum electrical stimulation
... Difference from: none vectorscanning the pain site. The impact with IES is distributed evenly over the entire area of \u200b\u200bexposure - this is what is called - 4-pole interferential therapy.
During the procedure, 4 electrodes are applied to the patient's body (for cross-flow of current) with vacuum suction cups. The strength of the current is recruited so that the patient feels a light, pleasant tickling like "goose bumps". The medium frequency current acts somewhat stronger in terms of anesthetic effect than the low frequency current, but to a lesser extent it works as a "muscle trainer". With its application, an analgesic (pain-relieving) effect is achieved faster, blood circulation becomes more intense. This method is also used to irritate body tissues. Indications to use this method treatment - muscle pain, pain caused by degenerative diseases of the spine, pain in the shoulder, knee joints, bruises, injuries, dislocations, sprains, as well as poorly healing bone fractures.
High frequency current
Treatment with high frequency current in our clinic is presented darsonval.
Few people know that this method of treatment is named after the genius Frenchman D * Arsonval. In 1892, the physiologist Jacques Arsene D * Arsonval applied a high voltage transformer in physiological research and introduced it into medical practice... The method of treatment was named - darsonvalization.
Now Darsonval is widely used in cosmetic medicine and not only ... For those dedicated to the secrets of physics, physiology and anatomy - Darsonval - how high-frequency current pulses acting through the receptor apparatus of the skin and mucous membranes affect the autonomic system, promote expansion peripheral vessels, improve trophism (nutrition) of tissues, reduce increased tone smooth muscles, reduce pain. Thus, there is an improvement cellular respiration, the activity of the nervous and endocrine system, microcirculation improves (condition of capillaries). All this leads to rapid reduction inflammatory and traumatic processes, creating conditions for tissue renewal, reducing pain, partial resorption of salt conglomerates in the joints. Recommended for, with, with, and myositis, with alopecia, acne…
Contraindications to electrotherapy:
- the presence of a pacemaker, implant, other metal objects, plates in the patient's body;
- myocardial infarction;
- epilepsy;
- pregnancy;
- increased body temperature;
- the presence of neoplasms;
- the presence of background (precancerous) diseases in gynecology (not recommended for the area of \u200b\u200bthe uterus and appendages, as well as the mammary glands)
- renal failure;
- postoperative condition;
- stones in the biliary or urinary tract.
CHAPTER 3 MEDICAL USE OF MEDIUM AND HIGH FREQUENCY AC
MOTIVATION
For the correct appointment of physiotherapeutic procedures, it is necessary to have a holistic understanding of the mechanism of action of alternating currents of medium and high frequency on the human body.
PURPOSE OF THE LESSON
Learn to use amplipulse therapy, fluctuation, interference therapy, ultraton therapy, darsonvalization techniques for the treatment of various diseases.
TARGETED ACTIVITIES
Understand the essence of the physiological action of medium and high frequency alternating current. Be able to:
Determine indications and contraindications for the use of alternating currents of medium and high frequency;
Choose an adequate type of therapeutic effect;
Independently appoint procedures;
Assess the effect of alternating currents on the patient's body.
To study the principles of operation of the devices "Amplipulse-4 (-5)", "AIT-50Ch", "ASB-2-1", "Iskra", "Ultraton".
Information block
AMPLIPULSE THERAPY
Amplipulse therapy is an electrotherapy method based on exposure to alternating sinusoidal currents with a frequency of 5000 Hz, modulated by low frequencies in the range of 10-150 Hz. The depth of their amplitude modulation varies within the frequency range of the biopotentials of nerve and muscle cells. As a result of modulation, a series of current pulses are formed, separated from each other by gaps with zero amplitude. There are five types of sinusoidal modulated currents (CMT).
The first type of work (I PP, constant modulation, PM) is the modulation of the current of the fundamental (carrier) frequency by currents of a fixed frequency (in the range of 10-150 Hz) and modulation depth. The strength of the exciting effect increases with decreasing modulation frequency and increasing its depth.
The second kind of work (II RR, pause-pauses, PP) is a combination of carrier-frequency current pulses modulated with a certain frequency, with pauses. The duration of the current pulses and pauses varies within 1-6 s. This mode provides a pronounced contrast of the effect of SMT against the background of pauses and has the most pronounced neuromyostimulating properties.
The third type of work (III PP, carrier-frequency, PN) is a combination of current pulses modulated at a certain frequency with unmodulated current pulses with a frequency of 5 kHz. The duration of the current pulses varies within 1-6 s. The stimulating effect of SMT with this combination is less pronounced than with II PP, but the analgesic effect begins to manifest itself.
The fourth type of work (IV RR, moving frequencies, IF) is the alternation of current pulses with different modulation frequencies: in one of the messages, the modulation frequency is constant (150 Hz), in the other, the modulation frequency is selected from the range of 10-150 Hz. In this case, CMTs give the greatest analgesic effect, increasing with a decrease in the difference between the frequency of 150 Hz and the selected modulation frequency.
The fifth kind of work (V PP, intermittent frequencies-pause, PPP) is a combination of alternating current pulses with different modulation frequencies in the range of 10-150 Hz and pauses between
them. This mode provides a weakly pronounced contrast of the effect of SMT against the background of pauses and has a mild neurostimulating and trophic effect. The action of the CMT is diverse. Amplipulse therapy has a pronounced analgesic effect. Its mechanisms are the same as in DDT, however, due to poor adaptation to SMT, they are characterized by a more effective blockade of pain impulses and a more stable dominant. SMTs also have a ganglion-blocking effect, which explains their analgesic effect in sympathetic disorders. In addition, amplipulse therapy leads to the normalization of central and peripheral hemodynamics, improves blood supply to tissues, and increases the tone of the cerebral, spinal and peripheral arteries. This effect develops reflexively due to the exciting effect of the current on the sensitive and autonomic nerve fibers, as well as as a result of blood flow to the muscles, which contract under the influence of CMT. Along with the increasing blood flow in the affected area, the venous outflow from it, as well as the lymph outflow, increase. Depending on the technique used, it is possible to achieve an increase in blood circulation in any organs and tissues.
Hemodynamic shifts are accompanied by an increase in local temperature in the area of \u200b\u200bexposure, activation of metabolic and diffusion processes. Depending on the parameters and method of application of the effects of CMT, they affect the tone and contractility of muscles, which is used not only for pathology of the neuromuscular system (paresis, paralysis), but also for various pathologies of internal organs (restoration motor activity fallopian tubes in tubal infertility, correction of the pancreas, increased tone of the atonic gallbladder with non-calculous cholecystitis).
Amplipulse-4 (-5) devices are used to carry out amplipulse therapy procedures. During the procedure, the same electrodes are used as for DDT. Plate electrodes with hydrophilic pads 1 cm thick are used. When performing the procedures, it should be borne in mind that the muscles in the affected area should be as relaxed as possible, and the size of the electrodes should correspond to the area of \u200b\u200bpain or pathological focus. After establishing the area of \u200b\u200bpain
points, one electrode is applied to the skin in the projection zone of pain, and the second is applied nearby (at a distance equal to the diameter of the first electrode) or on the opposite side (transversely). The electrodes, equipped with gaskets, pre-moistened with warm water and wrung out, are fixed with a rubber bandage, sandbags or the patient's body weight (if he lies on the electrodes). When using round electrodes on hand-held electrodes, the procedure nurse fixes them with the hand. The use of strip electrodes is possible.
Amplipulse therapy procedures are dosed according to current density, duration of its transmissions, frequency and depth of modulation. In this case, the current density does not exceed 0.1 mA / cm 2. You should also take into account the patient's sensations, who normally feel a mild painless vibration under both electrodes. The duration of exposure is 20-25 minutes. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day; 8-10 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
SMT-phoresis is carried out using I PP in a rectified mode, with a modulation frequency of 150 Hz and its depth of 75-100%. The duration of the procedures is 10-15 minutes daily or every other day. When operating in a straightened mode, vibration under the cathode is more pronounced.
Indications for treatment:
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system with pain syndrome (neuralgia, radicular pain of various levels, neuromyositis);
Diseases of the nervous system with movement disorders in the form of central and peripheral paresis;
Diseases of the autonomic nervous system with neurotrophic and vascular disorders;
Atherosclerotic obliteration of the vessels of the extremities, chronic lymphostasis of the legs, post-traumatic edema and pain syndrome;
Hypertension I, IIA and IIB stages;
IHD functional class I and II;
Diseases of the respiratory system (chronic bronchitis, protracted exacerbations of chronic pneumonia, mild to moderate bronchial asthma);
Diseases of the digestive system ( chronic gastritis with secretory insufficiency, gastric ulcer and
duodenum in the phase of exacerbation and incomplete remission, functional disorders of the pancreas, hypotonic and hypokinetic disorders of the biliary tract and gallbladder in the absence of stones, dyskinetic constipation, reflux esophagitis);
Violation of fat metabolism of an exogenous constitutional nature;
Diabetes;
Rheumatoid arthritis with minimal and medium process activity, arthrosis;
Periarthritis;
Chronic inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
Impotence, chronic prostatitis;
Nocturnal urinary incontinence in children;
Urolithiasis disease;
Inflammatory and dystrophic diseases of the anterior and posterior parts of the eyes.
Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
Non-fixed bone fractures;
Fresh hemarthrosis;
Cholelithiasis.
Healing techniques
The impact of CMT is carried out using several types of work. The main scheme of exposure: for 3-5 min, alternating mode, III PP, modulation frequency 100 Hz, its depth 75%, burst duration 2-3 s. Then V PP, frequency 70 Hz, modulation depth 75-100%, burst duration 3 s are applied for the same time. The more pronounced the pain syndrome, the more the frequency of current modulations in III PP increases (they act for 3-5 minutes). On the contrary, at IV RR, the frequency difference is small, the duration of the messages is 1-2 s, the exposure time is limited to 3-4 minutes. With a decrease in pain syndrome by the 3-4th procedure, the modulation frequency is reduced to 30-60 Hz, and its depth is increased to 50-75%. In case of mild pain with muscle atrophy, the affected tissues are affected by II PP, and then I PP for 3-5 minutes.
Exposure to a sinusoidal modulated current on the colon area
In the first case, two ltlastinch electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b80-100 cm 2, connected to one pole of the apparatus, are placed on the ascending and descending parts of the large intestine. An electrode with an area of \u200b\u200b160-200 cm 2 is placed on the lumbar region and connected to the second pole of the apparatus. The shape of the current is sinusoidal, II PP, modulation frequency 10-30 Hz, its depth 100%, duration of "send-pause" 5-6 s, current strength 30-40 mA (until visible contraction of the muscles of the abdominal wall). The duration of exposure is 10-15 minutes, the course of treatment consists of 10-12 daily procedures.
In the second case, plate electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b120-150 cm 2 are placed on the region of the ascending and descending parts of the intestine. Modulated sinusoidal current, II RR, modulation frequency 20-30 Hz, its depth 100%, “send-pause” duration 4-5 s, current 30-40 mA (until visible contraction of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall). The duration of exposure is 5-10 minutes, the course of treatment includes 10-15 procedures.
Exposure to a sinusoidal modulated current on the gallbladder region
The plate electrodes are positioned as follows: an active electrode (cathode) with an area of \u200b\u200b40-50 cm 2 is placed on the projection area of \u200b\u200bthe gallbladder in front, the second electrode (anode) with a size of 100-120 cm 2 is placed transversely on the back. SMT parameters: II PP, modulation frequency 20-50 Hz, its depth 100%, “send-pause” duration 2-3 s. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes, the course of treatment includes up to 15 daily procedures.
Impact of a sinusoidal modulated current on the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall
Electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b200-300 cm 2 are placed on the abdominal wall (cathode) and in the lumbosacral region (anode). SMT parameters: II PP, modulation frequency 30-50 Hz, its depth 75-100%, “send-pause” duration 2-3 sec.
Exposure to a sinusoidal modulated current on the perineum
Electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b40-70 cm 2 are placed in one of the following ways:
Above the pubic joint (anode) and on the perineum (cathode);
Above the pubic articulation and on the perineal area under the scrotum (the polarity depends on the purpose of exposure);
Above the symphysis pubis (cathode) and on the lumbosacral spine (anode).
SMT parameters: II PP, modulation frequency 30-70 Hz, its depth 50-100%, “send-pause” duration 2-3 sec. The current is increased until the patient feels vibration under the electrodes. The duration of the procedure is up to 10 minutes, the course of treatment includes up to 12 daily procedures.
The effect of a sinusoidal modulated current on a woman's genitals
With the stimulating vaginal technique, a special metal electrode is inserted into the patient's vagina while she is lying on her back. A second plate electrode with an area of \u200b\u200b80-100 cm 2 is placed above the pubic joint. SMT parameters: II PP, modulation frequency 10 Hz, its depth 100%, “send-pause” duration 5 s. The current is increased until the woman feels vibration under the electrodes (15-20 mA). The exposure time is 15 minutes, the course of treatment consists of 10-12 daily procedures.
Otherwise, electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b120-150 cm 2 are placed transversely: above the pubic articulation and in the sacral region. SMT parameters: half-sine modulated current, I PP, modulation frequency 150 Hz, its depth 50-75%, exposure duration - 2 minutes with forward and reverse polarity. Then use IV PP. The modulation frequency is 60-80 Hz, its depth is 50-75%, the “send-pause” duration is 2-3 s. The duration of exposure is 3-5 minutes in direct and reverse polarity, 8-10 daily procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Impact of a sinusoidal modulated current on the hip joint
One electrode measuring 10x12 cm is placed in the outer region of the buttock behind the greater trochanter, the second electrode 12x16 cm in size is placed on the front surface of the thigh in its upper third. SMT parameters: I, IV PP 5-10 min and III PP 5-10 min, modulation frequency 30-100 Hz, its depth 50-75%, duration of current pulses 4-5 s. The current strength is gradually increased until pronounced, but not painful sensations vibration. Up to 12-15 procedures are prescribed for the course, carried out daily or every other day.
Impact of sinusoidal modulated current on the bladder area
One 8x12 cm electrode is placed on the lower part of the abdominal wall above the pubic articulation, the other,
measuring 10x12 cm, - on the sacral region. CMT parameters: I, II PP, modulation frequency 20-30 Hz, its depth 100%, “send-pause” duration - 5 s each. The strength of the current is brought to the appearance of distinct contractions of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. The duration of the procedures is 10-12 minutes, the course of treatment includes up to 10-12 daily procedures.
Exposure to a sinusoidal modulated current on various parts of the hand
The electrodes are placed in one of the following ways:
On the projection of the radial nerve along the outer projection of the shoulder - an electrode measuring 3x3 cm, on the inner surface of the shoulder - 4x10 cm;
In the area of \u200b\u200bthe middle and ulnar nerves along inner surface shoulder - an electrode measuring 4x10 cm, on the outer surface of the shoulder - 6x12 cm;
Two identical electrodes 4x10 cm in size are placed on the area of \u200b\u200bthe external and internal condyles of the shoulder;
On the inner and outer surfaces of the wrist joint, two identical electrodes measuring 4x5 cm are placed.
If the hand is damaged, it is immersed in a bath of water, where one of the electrodes is lowered. The second electrode in the form of a cuff 6-8 cm wide is applied to the outer surface of the shoulder. SMT parameters: I, IV PP 3-6 min and III PP 3-6 min, modulation frequency 30-100 Hz, its depth 50-75%, burst duration 2-4 s. The current strength is gradually increased until a feeling of painless vibration appears. Up to 10-12 procedures are prescribed for the course, carried out daily or every other day.
Exposure to a sinusoidal modulated current on painful areas in the shoulder girdle
The electrodes are positioned as follows:
Electrodes measuring 4x8 cm are applied to the area of \u200b\u200bpalpable pain in the paravertebral areas at the level of the spinous processes of the lower cervical and upper thoracic spine;
On the projection of the trapezius muscle, one electrode is placed along its upper edge, the second parallel to the first, at a distance of at least 6 cm with the size of the electrodes 15x8 cm;
On the base of the lateral surface of the neck and the outer surface of the shoulder joint, 6x10 cm electrodes are placed in parallel;
On the anterior and posterior surfaces of the shoulder joint, 8x10 cm electrodes are placed one against the other.
SMT parameters: I, III PP 3-5 min and IV PP 3-5 min, modulation frequency 30-100 Hz, its depth 25-75%, duration of current pulses in a period of 2-4 s. The current strength is gradually increased until the appearance of pronounced, but not painful, vibration sensations. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day. Up to 12 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Interference therapy
Interference therapy - method medicinal use interference currents. These currents are not introduced into the body from the outside - they are formed endogenously inside organs and tissues as a result of the superposition (interference) of two sinusoidal currents of medium frequency. One of these currents is injected into the body with a constant frequency (for example, 5000 Hz), the frequency of the other varies in the range of 4900-5000 Hz. The frequency of the resulting endogenous current exactly corresponds to the difference between the two crossing currents, i.e. can vary between 1 and 100 Hz.
Improvement of peripheral blood circulation plays a leading role in the therapeutic effect of interference currents. It manifests itself in the normalization of the pathologically altered tone of the main arteries and the capillary bed, in an increase in the number of active collaterals, and in the improvement of microcirculation. In the mechanism of expansion of peripheral vessels, the suppression of the sympathetic link of the autonomic nervous system by interference currents and the increased release of vasoactive substances that change the lumen and, accordingly, the tone of the vessels during the procedure are of major importance. Interference currents cause muscle contractions, providing a kind of massaging effect, as a result of which it is possible to improve peripheral blood circulation and lymph drainage. Stimulation of blood circulation leads to a local increase in body temperature, an improvement in the supply of oxygen to tissues, rapid removal toxic metabolic products, activation of the reticuloendothelial system. With interference therapy, the pH of the tissues shifts to the alkaline side, which contributes to the relief of the inflammatory process.
Excitation by interference currents of myelinated conductors of Ap fibers leads to peripheral block
de-impulses from a painful focus (according to the principle of a portal block), and also inhibits the impulse activity of non-myelinated conductors of pain sensitivity (C-fibers) and autonomic ganglia. The delocalization of the pain dominant and the activation of opioid peptides carried out in the antinociceptive system of the brain stem by the interference current are less effective than the diadynamic current and SMT. Due to the peculiarities of the method, the interference of the initial currents occurs in a wide zone of the interelectrode space, which makes it possible to increase the area of \u200b\u200binfluence on the internal organs.
The interference current stimulates the differentiation of osteoblasts, fibroclasia of granulation tissue and the regeneration of the conductors of the peripheral nervous system. The significant disadvantages of this method include the rapid adaptation of the body to the interference current, which requires constant variation in the beat frequency.
Apparatus and general instructions for performing procedures
For the procedures, devices that generate sinusoidal currents of medium frequency are used: "AIT-50-Ch", "Interferentspulse", "Endomed". The design of the devices provides the ability to automatically apply the interference current of different frequencies.
To carry out the procedure of interference therapy, two or three pairs of electrodes are applied to the patient's skin so that the lines of force of the electromagnetic fields created by each pair of electrodes intersect in the area of \u200b\u200bthe pathological focus. Depending on the localization of the pathological focus, each pair of electrodes is placed either transversely or longitudinally. Diagonally located electrodes are connected to one circuit.
Depending on the size of the area to be affected, either conductive plate electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b2 to 300 cm 2 with thin (up to 0.5 cm) hydrophilic spacers or vacuum cup electrodes with a pressure of up to (1-2) x104 Pa are used.
When choosing the frequency of the interference current, one should take into account the differences in the action of currents of different frequencies. The analgesic and antispasmodic effect is most pronounced at a frequency of 90-100 Hz; reducing the frequency to 25-50 Hz enhances the neurostimulating effect; frequency 1-10 Hz increases the tone of the sympathetic nervous
systems, and an increase in the frequency of current beatings reduces it; a rhythmically variable interference current in the range of 1-5 Hz causes periodic muscle contraction and excitation of autonomic nerve fibers. That is why a current with a frequency of 0-10 Hz is used to influence the smooth muscles of internal organs, a current with a frequency of 0-10 Hz is used, to influence skeletal muscles - 20-50 Hz, for the treatment of vegetalgia and pain syndromes - 70-100 Hz. The strength of the current in pairs of electrodes depends on their area and the individual sensitivity of the patient and can reach 40-50 mA. During the procedure, the current strength is gradually increased until the patient feels a clearly pronounced painless vibration in the interference zone of the initial current. The duration of the procedures is 5-15 minutes (in the acute phase of the disease) or 15-30 minutes (in the chronic phase), 10-12 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment, carried out daily or every other day. Indications for interference therapy:
Various pain syndromes associated with irritation of the conductors pain sensitivity and vegetative fibers (vegetalgia, radiculopathy, neuralgia);
Diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system (bruises, ligament ruptures, bone fractures after immobilization of bone fragments);
Degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the joints (cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis with radicular and reflexotonic syndrome, periarthrosis of the shoulder scapula);
Diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, dyskinesia of the digestive system);
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs (adnexitis, parametritis);
Hypertension stage I-II;
Raynaud's disease;
Obliterating endarteritis. Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
General contraindications to physiotherapy;
Acute inflammation and infectious diseases;
Fresh hemarthrosis and intra-articular fractures;
Fractures with non-immobilized bone fragments;
Gallstone and urolithiasis;
Thrombophlebitis and phlebothrombosis;
Traumatic arachnoiditis with liquorodynamic disorders;
Glaucoma;
Multiple sclerosis;
Pregnancy (fetal area).
Healing techniques
Effects on the spine
The position of the patient is lying on his stomach. Plate electrodes 5x10 cm in size are placed paravertebrally in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine so that both medium-frequency currents intersect in the affected area: one electrode of the first pair is placed to the right of the spine, the other - to the left, below the first; the electrodes of the second pair are placed to the right and left of the spine opposite the first pair. The current frequency is 70-100 Hz. The strength of the current is increased until the patient feels a fine vibration under the electrodes. The exposure time is 10-20 minutes, the course of treatment consists of 8-10 procedures.
Effects on the abdominal and pelvic organs
The position of the patient is lying. The plate electrodes are placed transversely: one electrode of the first pair is on the abdominal wall, the other is on the back on the right; the electrodes of the second pair are positioned in the same way: one is on the abdominal wall on the right, the other is on the back on the left. With this arrangement of the electrodes, the zone of interference of currents falls on the organ to be affected: the stomach, gall bladder, intestines, ureter, bladder, uterus.
Current parameters:
The frequency of hypomotor dyskinesia and atony is 0-10 Hz. The strength of the current is increased until the patient feels vibration deep in the tissues. The duration of the procedure is 10-20 minutes, the course of treatment consists of 10-12 daily procedures;
With hypermotor dyskinesia, the frequency is 70-100 Hz. The strength of the current is increased until the patient feels a slight vibration in the affected area. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes, the course of treatment consists of 10-12 daily procedures.
Impact on the shoulder joint
The position of the patient is lying or sitting. Rectangular plate electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b40-50 cm 2 are placed on
the front and back surfaces of the shoulder joint. One electrode of the first pair is in the front, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe trapezius muscle, the second is in the back on the deltoid muscle. The electrodes of the second pair are placed opposite the electrodes of the first pair in front and behind the shoulder joint. Current frequency 100 Hz (at strong restriction mobility 0-10 Hz). The current is increased until the patient feels a painless vibration. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. The course of treatment includes 10-12 procedures.
Impact on the elbow (knee) joint
The position of the patient is lying. Two rectangular electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b50-80 cm 2 are positioned as follows: the first - on the outer surface of the lower third of the shoulder (thigh), the second - on the inner surface of the upper third of the forearm (lower leg). Two other electrodes of equal size are positioned as follows: the first is on the inner surface of the shoulder (thigh), the second is on the outer surface of the forearm (lower leg). Frequency 100 Hz (with severe limitation of mobility 0-10 Hz). The current is increased until the patient feels a moderate vibration. The duration of the procedure is 8-12 minutes. The course of treatment consists of 8-15 procedures.
Fluctuorization
Fluctuorization is an electrotherapy method based on the use of low-strength alternating current (3 mA / cm 2) and low voltage (up to 100 V) with a spontaneously changing frequency in the range of 100-2000 Hz and amplitude.
Used alternating current causes excitation of cutaneous efferents belonging mainly to thin myelinated fibers (Aδ-type) and unmyelinated C-fibers. The resulting asynchronous afferent streams suppress impulses from the painful focus, causing analgesia. Reaching the posterior horns of the spinal cord, these afferent streams also stimulate segmental reflex reactions, which are manifested in increased regional blood flow and activation of trophic processes in tissues. Due to the parabiosis of the sensitive nerve conductors, with prolonged exposure, the increase in the excitability of the nerve conductors is replaced by its suppression.
The fluctuating current intensely irritates the proprio- and interoreceptors, which is accompanied by painless synchronous
reduction of myofibrils. At the same time, a slight increase in tissue temperature is noted, hyperemia appears, which activates metabolism in tissues, increases the intensity of phagocytosis, enzymatic activity; promotes the resorption of toxic substances from the focus of inflammation, enhances cellular immunogenesis. When exposed to a purulent inflammatory focus, fluctuorization limits the spread of the process and causes its reverse development. The postoperative use of currents promotes the rapid rejection of necrotic tissues, wound cleansing, accelerated regeneration, the rate of formation of granulation tissue and epithelization of the wound surface increases.
Apparatus and general instructions for performing procedures
Fluctuorization procedures are performed on the ASB-2 (-1) and FS-100 (dental) apparatus. The device for fluctuating forms three forms of fluctuating current:
Bipolar symmetric fluctuating current - continuously following pulses of the same amplitude, chaotically changing in polarity and frequency;
Bipolar asymmetrical fluctuating current - continuously following impulses of unequal amplitude, mainly negative polarity, chaotically changing in frequency;
Unipolar symmetric fluctuating current - continuously following, chaotically changing in frequency, monopolar pulses (this form of current can be used for fluctuophoresis of medicinal substances).
Fluctuorization procedures are carried out with contact application of electrodes. One electrode (smaller area) is located in the projection area of \u200b\u200bthe pathological focus, the second (up to 80 cm 2) - on the opposite body surface. Longitudinal arrangement of electrodes is also possible. When dosing the current, the subjective feelings of the patient and objective indicators are taken into account:
With low-intensity exposure (current density less than 1 mA / cm 2), the patient feels a slight vibration and tingling sensation;
Exposure to medium intensity (current density up to 2 mA / cm 2) causes slight twitching of the superficial muscles);
At high intensity (current density up to 3 mA / cm 2), the patient experiences pronounced muscle twitching in the affected area.
The duration of the procedures is from 7 to 20 minutes. For the course of treatment, from 3 to 15 procedures are prescribed, carried out daily or every other day.
Indications for fluctuating:
Diseases of the peripheral nervous system with pain syndrome (for example, neuralgia, osteochondrosis with radicular and reflex-tonic syndrome, neuromyositis);
Dental diseases and pain after tooth extraction;
Acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of surface tissues, including purulent (abscess, phlegmon, periodontal disease).
Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
General contraindications to physiotherapy;
Acute infectious diseases;
Thrombotic diseases;
Vibration disease;
Meniere's syndrome.
Healing techniques
Fluctuorization of the temporomandibular joint
The position of the patient is sitting. The method of exposure is transverse. An external 3x4 cm plate electrode is applied to the skin in the area of \u200b\u200bthe affected joint. The second electrode (oral with an active apical surface), fixed on a plastic spatula, is inserted into the patient's wide open mouth behind the eighth upper tooth, providing contact with the mucous membrane behind the molar triangle. Apply the first form of current at a low-medium dose for 10-12 minutes. The course of treatment includes 10-12 daily procedures.
Fluctuorization on facial muscles
The position of the patient is sitting. An indifferent electrode (anode) with an area of \u200b\u200b100 cm 2 is applied to cervical spine. An active electrode (cathode) with a 1 cm 2 breaker is placed on the motor point of the affected muscle. Apply the third form of current at a density sufficient for the appearance of muscle contraction. The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a week for 10 minutes. From each motor point, 5 to 15 contractions are caused. 10-12 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Fluctuorization on the trigeminal nerve area
The position of the patient is sitting or lying. The built-in active electrode (each with an area of \u200b\u200b1 cm 2) is applied to the skin in the projection area of \u200b\u200bthe upper orbital, lower orbital or chin foramen (the point of exit of the branches of the trigeminal nerve). An indifferent electrode with an area of \u200b\u200b3 cm 2 is placed 0.5 cm in front of the tragus of the affected side of the ear. Apply the first form of current at a low-medium dose for 5-6 minutes. The course of treatment includes 10-12 daily procedures. Affect only damaged nerve branches.
Fluctuorization on the sciatic nerve area
The patient is placed on his stomach. Two identical electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b50-60 cm 2 are placed as follows: the first is applied to the lumbosacral region, the second to the projection area of \u200b\u200bpain along the sciatic nerve (posterior surface of the thigh, popliteal fossa, posterior surface of the leg). Apply the first form of current in a small dose for 10 minutes daily. 10-12 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Fluctuorization of the lumbosacral region
The position of the patient is lying on his stomach. Two electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b50-60 cm 2 are placed on the lumbosacral region to the right and left of the spinal column. Apply the first form of current in a low-medium dose for 10 minutes daily. The course of treatment consists of 10-12 procedures.
Fluctuorization of the pelvic organs
The position of the patient is lying. Electrodes with an area of \u200b\u200b100 cm 2 are applied transversely to the anterior abdominal wall and the lumbosacral region. Apply the first form of current in a low-medium dose. In the treatment of gynecological diseases, an anode is applied to the anterior abdominal wall and a third form of current is used in a small dose. The duration of the procedures is 10-15 minutes. Up to 15 daily procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Fluctuorization of the focus of inflammation within the subcutaneous tissue
The patient is placed in a comfortable position. Two electrodes of the same area are placed above and below the inflammatory focus. If there is an incision, the electrodes are placed at its ends. The size of the electrodes exceeds the size of the inflammatory focus. Apply the first form of current, during the first 3-5 days - daily, then
can be done every other day. If the focus is not opened, then a small and medium dose is prescribed; when the focus is opened, a large dose is used for 10-12 minutes. The course of treatment consists of 5-10 procedures.
Darsonvalization
Darsonvalization - healing method, based on the impact of high-frequency alternating impulse current of high voltage and low strength. The method is named after its creator, the French physiologist and physicist d'Arsonval.
One of the most characteristic effects of local darsonvalization is a vegetative-vascular reaction, accompanied by increased microcirculation, dilation of arterioles and capillaries, elimination of vascular spasms, and changes in vascular permeability. At the same time, the activity of the venous system improves: the tone of the walls of the veins increases, the venous stasis decreases, and the venous outflow increases.
Under the influence of a spark discharge, foci of micronecrosis appear in the skin, which is accompanied by the stimulation of phagocytosis and the release of biologically active substances and mediators, and then their inhibitors. The products of protein breakdown entering the bloodstream stimulate the humoral link of immunity, metabolic and trophic-regenerative processes. A spark discharge, as well as ozone and nitrogen oxides formed in the near-electrode space, are capable of causing a bacteriostatic and bactericidal effect.
Local darsonvalization increases skin turgor and elasticity, stimulates the proliferative activity of germ cells hair follicle, enhances hair growth, prevents the development of wrinkles and hair loss. The method is also characterized by an antispastic effect, which is manifested in the cessation of vasospasm and sphincters and in the reduction of pain caused by spasm.
Apparatus and general instructions for performing procedures
For local darsonvalization, the Iskra-1 and Iskra-2 apparatus are used, complete with a set of vacuum glass electrodes.
Two methods of exposure are used - contact and remote. With the contact technique, the electrode is firmly pressed against the skin and mucous membrane, while a quiet spark discharge is formed, which causes a weak sensation of warmth in the patient.
The vacuum electrode is easily, without pressure, moved in circular or linear movements over the skin of the affected area, dried and powdered with talcum powder. With the remote technique, the vacuum electrode is moved over the area of \u200b\u200bthe pathological focus with an air gap of 0.5-0.7 cm, and a spark discharge occurs between the electrode and the patient's skin. The strength of the discharge depends on the applied impact power. With the remote method, the most pronounced irritating and cauterizing effect of darsonvalization. With rectal and vaginal techniques, the vacuum electrode is stably left in the cavity during the entire procedure, while the patient feels a slight warmth. The duration of the procedures is 5-10 minutes; the course of treatment includes 5-10 procedures carried out daily or every other day. Indications:
Functional disorders of the nervous system;
Cardialgia;
Neuralgia of the peripheral nerves;
Varicose veins of the extremities and small pelvis;
Trophic skin diseases;
Paradontosis;
Trophic ulcers;
Chronic diseases of organs and tissues;
Hair loss. Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
Healing techniques
Darsonvalization of the scalp
The position of the patient is sitting. Before the procedure, metal hairpins are removed from the hair, the hair is combed. The method of the procedure is contact. The comb electrode is slowly and smoothly moved along the scalp from the forehead to the back of the head. The exposure is carried out at low power for 5-10 minutes daily or every other day, 15-20 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Darsonvalization of the face
The position of the patient is sitting or lying. The technique is contact or remote. Mushroom electrode slow in a circular motion move along the skin of the face from the scalp
head to chin and nose to ears. Power of exposure according to indications, duration of exposure 5-10 minutes. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day, the course of treatment consists of 15-20 procedures. Darsonvalization of the gums
The position of the patient is lying or sitting. Contact technique. The gingival electrode is slowly moved along the outer surface of the gums, first in the upper and then in the lower jaw, without touching the teeth. The power of exposure is determined according to indications, the duration of the procedure is up to 10 minutes. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day, the course of treatment consists of 15-20 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the external auditory canal
The position of the patient is lying on the side or sitting. Earrings and clips are removed from the earlobes. Contact technique. Pulling back auricle up and back, a cone-shaped electrode is inserted into the external auditory canal 1-1.5 cm and left there until the end of the procedure. The exposure is carried out at low power for 5 minutes for each ear. The course of treatment includes 15-20 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the collar zone
The position of the patient is sitting. The technique is remote, with a small gap. The mushroom electrode is moved along the surface of the neck, shoulder girdle, upper back to Th VI, supra- and subclavian regions. The exposure is carried out daily or every other day at an average power for 10-12 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the heart area
The patient's position is supine. The method of the procedure is contact. The mushroom electrode is moved around the heart, bypassing the nipple. The exposure is carried out daily or every other day at an average power for 3-10 minutes. The course of treatment consists of 10-15 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the breast
The patient's position is supine. The method of the procedure is contact. A large mushroom electrode is moved over the breast surface, bypassing the nipple and halo. The exposure is carried out daily or every other day at low-medium power for 10 minutes. The course of treatment consists of 12-15 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the rectum
Before the procedure, the patient needs to cleanse the intestines. The position of the patient is lying on the side with bent legs.
The method of the procedure is contact. A rectal cylindrical electrode, lubricated with sterile petroleum jelly, is introduced with a rotary motion to a depth of 4-6 cm and fixed. The power is increased until the patient feels a slight warmth. The duration of the procedure is up to 8-10 minutes. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day; the course of treatment includes up to 15 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the vagina
The patient's position is lying on the back with legs apart and bent. A vaginal electrode, lubricated with sterile petroleum jelly, is inserted to a depth of 8-12 cm and fixed. The power is increased until the patient feels a slight warmth. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes, 10-15 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment.
Darsonvalization of the perineum
The patient's position is supine with hips bent and apart. The mushroom electrode is moved along the inner surface of the thighs and perineum. The exposure is carried out daily or every other day at medium-high power for 10-15 minutes. The course of treatment consists of 12-15 procedures.
Darsonvalization of the lower limb
The position of the patient is lying. The mushroom electrode is moved along the thigh to the knee joint or foot, the power is average, the duration of the procedure is 8-10 minutes daily or every other day, 12-15 procedures are prescribed for the course of treatment. Darsonvalization in case of skin damage (wound, ulcer)The position of the patient depends on the localization of the wound surface. The technique is remote, with a gap of 3-6 mm. First, for 3-5 minutes, they affect healthy tissues (within 5-10 cm) around the lesion, then 1-3 minutes directly at the lesion. You can carry out the procedure through a gauze bandage. The exposure is carried out daily at low-medium power. The course of treatment includes 10-15 procedures.
Ultraton therapy
Ultraton therapy - exposure to medicinal purposes high-frequency (22 kHz) sinusoidal alternating current of high voltage (3-5 kV) with power up to 10 W. Ultraton therapy causes a pronounced vegetative-vascular reaction, manifested in the expansion of capillaries and arterioles, an increase in venous tone, a slight increase in local body temperature, an improvement in blood and lymph
treatment. The procedure has a beneficial effect on metabolism, improves tissue trophism and enhances regeneration processes. Similar to darsonvalization, ultraton therapy has an antispastic and bactericidal effect. With intraorgan effects, the activity of the genital organs is stimulated, hemodynamics in the vascular basin of the small pelvis are normalized, and the functional state is improved urinary tract and urodynamics.
Compared with darsonvalization, ultraton therapy has a more pronounced anti-inflammatory, heat-generating and analgesic effect, causes more active and prolonged hyperemia, but is accompanied by less antispastic and irritating effect.
Apparatus and general instructions for performing procedures
For the procedures, the devices "Ultraton-1", "Ultraton-2", "Ultraton-APM", equipped with a set of glass electrodes, are used. Metal spiral rods are located inside the electrodes, their cavity is filled with an inert gas neon under a pressure of 13.3-20 hPa. The impacts are carried out according to a labile and stable method. After the electrode is installed over the area of \u200b\u200bthe pathological focus, the device is turned on and its output power is increased. As the power increases, the brightness of the red glow of the gas inside the electrode increases, but the main reference point is correct dosage a moderate warmth felt by the patient. The duration of procedures is up to 5 minutes per field and does not exceed 10-15 minutes per procedure. Influences are carried out most often daily, the course of treatment includes up to 12-15 procedures.
Ultraton therapy is indicated for the following diseases:
Neurological:
❖ neuralgia and neuropathy;
❖ consequences of traumatic brain injury;
Surgical:
❖ infected wounds;
❖ trophic ulcers;
❖ infiltrates;
❖ obliterating vascular diseases;
❖ adhesive processes;
Dermatological:
❖ eczema;
❖ neurodermatitis;
❖ acne;
❖ furunculosis;
❖ purulent alopecia;
Gynecological:
❖ chronic inflammatory processes;
❖ violation menstrual cycle;
❖ erosion of the cervix;
Urological:
❖ inflammatory diseases urinary tract;
❖ prostatitis;
Dental:
❖ periostitis;
❖ alveolitis;
❖ abscess;
❖ gingivitis;
❖ periodontal disease. Contraindications:
Current intolerance;
General contraindications to physiotherapy.
Therapeutic techniques are similar to those of darsonvalization.
As you know, alternating current used for industrial and domestic purposes has 50 oscillations per second. The number of oscillations of the alternating high-frequency current reaches hundreds of thousands and millions per second.
High frequency current is characterized by the number of oscillations per second and the length of the electromagnetic wave. There is a simple relationship between the wavelength and the frequency of the current: the higher the frequency of the current, the shorter the wavelength.
By length, electromagnetic waves are divided into long - 3000 m and more, medium - from 3000 to 200 m, intermediate - from 200 to 50 m, short - from 50 to 10 m and ultrashort - less than 10 m.
High-frequency currents are obtained using special generators, spark and lamp. At the heart of any high-frequency generator is an oscillatory circuit. The oscillating circuit consists of an electrical capacitance (a capacitor, denoted by the letter C) and a self-induction coil, otherwise an inductor (denoted by L), which is a wire spiral.
If a charge is imparted to the capacitor of the oscillatory circuit, then an electric field arises between its plates (Fig. 29, 1). The capacitor begins to discharge through self-induction; when the discharge current passes through self-induction, an electromagnetic field arises around it due to the current energy (Fig. 29, 2). When the capacitor is completely discharged, the current should stop; but as the current weakens, the energy of the electromagnetic field stored in self-induction is transferred back into the current of the same direction. As a result, the capacitor will be charged again, although the sign of the charge on the capacitor plates will be reversed (Fig. 29, 3). Having received a charge, the capacitor again begins to discharge through self-induction, but the capacitor discharge current will be in the opposite direction (Fig. 29, 4). The passage of current through self-induction will again be accompanied by the appearance of an electromagnetic field, the energy of which, as the discharge current weakens, will be converted into the energy of the induced current of the same direction. The capacitor plates will be charged again, and their charge will be of the same sign as at the beginning (Fig. 29, 5).
The energy stored now in the capacitor will be less than the initial one, since part of it was spent on overcoming the ohmic resistance of the circuit.
Going first in one direction, and then in the opposite direction, the capacitor discharge current makes one oscillation.
Having received a charge again, although less than the initial one, the capacitor will again begin to discharge through self-induction. With each oscillation, the amplitude of the current will decrease. This will continue until all the energy stored in the capacitor is consumed to overcome the ohmic resistance of the circuit. A group of damped oscillations arises.
So that the oscillations in the oscillatory circuit do not stop, it is necessary to periodically supply the capacitor with a supply of energy.
DARSONVALIZATION
For the first time, high-frequency currents were used for therapeutic purposes in the form of darsonvalization.
Darsonvalization is the treatment of high frequency electrical and electromagnetic waves.
This method of treatment was proposed by the famous French physiologist and physicist d'Arsonval in 1892 and named after him.
Currents d "Arsonval are separate groups of sharply damped high frequency oscillations (Fig. 30). When applied locally, their voltage reaches a significant value - 20,000 V and above; general application a high-frequency electromagnetic field is used, formed by currents d "Arsonval.
Physiological action
The physiological action of Arsonval currents is mainly based on reflex phenomena. Acting on the receptors of the skin or mucous membrane, Arsonval currents cause corresponding segmental reflex reactions, simultaneously exerting a local effect on tissues.
With the local application of currents d "Arsonval, if the contact between the skin and the electrode is loose, a stream of small sparks jumps from the electrode to the skin and irritation occurs: the patient experiences light tingling sensations, the skin turns red. The latter depends on the vasodilatation that occurs after a preliminary short-term narrowing of them.
Thermal properties of currents d "Arsonval s full force they cannot manifest themselves due to the small value of the current, reaching only a few milliamperes when applied topically.
If you move the electrode away from the body, then under the influence of high voltage near the electrode ionization of air molecules occurs, its conductivity increases, and a quiet discharge occurs on the patient's body, which he feels like a light breeze.
By lowering the sensitivity of nerve endings, currents d "Arsonval have an analgesic effect.
The anti-spastic effect inherent in the currents of d "Arsonval helps to stop the spasm of blood vessels and sphincters and reduces pain caused by spasms.
The trophic effect of Arsonval's currents on the skin and deep organs occurs as a result of hyperemia. There is also an increase in tissue metabolism. local application currents d "Arsonval accelerates the maturation of granulation tissue.
With general darsonvalization of low intensity, a high-frequency electromagnetic field induces such weak high-frequency currents in the patient's body that they are not felt by the patient.
With general darsonvalization, an increase in metabolism occurs; there is a calming effect on the nervous system; in sick hypertension blood pressure may decrease, hot flashes to the head, tinnitus, dizziness decrease.
Equipment
There are two types of apparatus for obtaining currents d "Arsonval: portable (portable) and stationary.
The portable apparatus d "Arsonval" (Fig. 31) looks like a small box with a removable lid.
The device panel contains:
- 1) output terminal; one end of a rubber-insulated wire is attached to it; an ebonite handle with an electrode inserted into it comes to its other end;
- 2) switch;
- 3) handle of the spark gap regulator;
- 4) knob of the voltage regulator in the patient's circuit;
- 5) two sockets for screwing a pin into one of them when the device is switched on from a network of 120 or 220 V.
According to the principle diagram, the portable apparatus of Arsonval is a high-frequency spark generator with two oscillatory circuits, with a vibrator similar to an induction coil breaker. big number turns of wire, as a result of which the voltage on its contact rises sharply, reaching, as mentioned above, 20,000 V. The self-inductions of both circuits are placed in a round cardboard box and embedded in paraffin. Voltage regulation is carried out by a rheostat placed in the first oscillatory circuit.
The self-induction circuits in some types of portable devices d "Arsonval are enclosed in a thick plastic handle filled with paraffin; connecting wires fit to the handle at one end, and an electrode is inserted at the other. Voltage adjustment is made using a slider on the handle, which is moved along the self-induction loops. You can also find previously produced portable devices d "Arsonval, in which spark arresters, and sometimes a vibrator, are placed on the panel of the device.
Portable apparatus d "Arsonval" - low power (25-30 W) and are usually used to affect a small area of \u200b\u200bthe body, which is why they are often called "local d" Arsonval ".
The oscillatory circuits of the Arsonval apparatus were tuned to a frequency of 100,000 vibrations per second, which corresponds to an electromagnetic wavelength of 3000 m.
The stationary apparatus of d "Arsonval" serves for both local and general darsonvalization. appearance (Fig. 32) the stationary apparatus d "Arsonval" ("big d" Arsonval "), previously produced by the EMA plant, is a white wooden cabinet on the lid of which the Uden resonator rises - a part of the self-induction of the first oscillatory circuit and all the self-induction of the second oscillatory circuit, wound on a cardboard frame.

In principle, the stationary apparatus for darsonvalization is a high-frequency spark generator with two spark arresters and two oscillating circuits. On the panel of the device, in addition to the Uden resonator, there is a switch, a voltage regulator for local darsonvalization and terminals.
With local darsonvalization, a wire from a handle with an electrode is connected to the output terminal of the Uden resonator.
With general darsonvalization, the jumper is removed from the second terminal, which entails the disconnection of the second oscillatory circuit and part of the first oscillatory circuit - only spark arresters and capacitors remain from it.
The ends of the solenoid cage winding are connected to the first and second terminals.
The solenoid cage (Fig. 33) is a wooden frame with coils of copper tape, with a door for the patient's passage.

A patient placed inside the solenoid (sitting on a chair) is exposed to the electromagnetic field generated by the passage of high-frequency currents through the solenoid turns. The presence of a field can be detected by holding a neon lamp to the turns of the solenoid, which starts to glow.
Technique and technique of darsonvalization
Local darsonvalization is carried out using glass vacuum capacitor electrodes. They are called vacuum because air is pumped out of them. When a high voltage is applied to the electrode, it begins to glow with a pinkish-violet light; the glow intensity of the electrode increases with increasing voltage on the electrode.
The name of the capacitor is given to the electrode because when it is applied to the body, a capacitor appears, one of which is the patient's body, the second is the rarefied air inside the electrode, and the dielectric is glass.
Glass electrodes can also be filled with graphite powder to form capacitor graphite electrodes.
Capacitor electrodes can be different shape... So, for example, to influence the surface skin use the "fungus"; when darsonvalization of the scalp - "comb"; rectum - with a cone-shaped electrode, etc. (Fig. 34).
After application, the electrodes are washed with warm water and wiped with a cotton swab with alcohol.
With local darsonvalization of the skin, the electrode is led along the skin surface (Fig. 35). To make the electrode easier to slide over the skin, it is first sprinkled with talcum powder.

The duration of the procedure for local darsonvalization is 5-10 minutes; procedures are carried out daily or every other day; the number of procedures, depending on the disease, is from 5 to 25.
With stable darsonvalization for cracks anus or hemorrhoids, a cone-shaped electrode, lubricated with petroleum jelly, is inserted into the anus (the patient must come to the procedures prepared: the rectum must be emptied of the contents with a small enema); the patient is in a lateral position with an extended lower leg and bent in knee joint Other. To prevent the electrode from jumping out, the handle of the electric holder is fixed with a bandage to the thighs and between the sandbags.
Treatment is carried out daily. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. The number of procedures for cracked anus is 6-10, for hemorrhoids - 25-30.
If the electrode is moved away from the skin, then stronger sparks jump from its surface, which cause pain and can cause burns. This is used to burn small warts using an electrode with a metal tip.
For exposure to effluvia (quiet discharge), an electrode is used in the form of a disk with sharp points, mounted on an insulating handle; it is either led above the skin surface at a distance of 3-5 cm, or suspended on a special holder. Procedures daily or every other day for 5-10-15 minutes.
With general darsonvalization, they use, as mentioned above, a cage (solenoid). The procedures are carried out daily, their duration is 20 minutes. The course is 12-20 procedures.
General indications and contraindications for treatment with currents d "Arsonval
Arsonval's currents in the form of a local procedure are indicated for cardiac neuroses, frostbites of I and II degrees, dry eczema, skin paresthesia (itching), neuralgia, hair loss, hysteria, trophic ulcers and wounds, cracks in the anus, hemorrhoids.
General darsonvalization is indicated for neurotic conditions, climacteric disorders, and the initial form of hypertension.
Contraindications are malignant neoplasms and a tendency to bleed.
