Low frequency impulse waves. Low frequency pulse therapy. Invention patent of the Russian Federation ru2164424
INVENTION
Patent of the Russian Federation RU2164424
Inventor Name:
Name of the patentee:
Konoplev Sergey Petrovich, Konopleva Tatyana Petrovna
Correspondence address:
103489, Moscow, Zelenograd, PO Box 34, NPP "Alice"
Start date of the patent:
28.06.1999
The invention relates to medical technology, namely to low-frequency electromagnetic therapy for treatment various diseases, harmonizing the work of organs and increasing the body's defenses.
At correct application and it is very effective when applied. However, it cannot be taken out of context. complex therapy, which should not be considered as a treatment. Majority physical procedures have similar effects and depending on the parameters, some of them may be dominant. Main effects: analgesic, muscle relaxation, trophic and anti-edema.
Electric currents used in therapy are conventionally divided into three main groups: galvanic current, constant current pulse and alternating current. Galvanic current Galvanic current is a constant current. It is mainly used for iontophoresis, or its trophic stimulation effect is used. The big disadvantage of galvanic current is the risk of chemical damage to the tissue under the electrodes. Damage can be caused hydrochloric acid which occurs under the anode or the soda layer that occurs under the cathode.
DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
The invention relates to medical equipment, namely to low-frequency electromagnetic therapy, and can be used to influence the human body with a weak low-frequency modulated electro magnetic field for the treatment of various diseases, harmonizing the work of organs and increasing the body's defenses.
Similar types of tissue damage can occur with any direct current. Direct currents should not be used in patients with metal implants! Nowadays, this current is often replaced by galvanic intermittent current. This current has the same effects, but because of the interruption of the initially constant intensity at 8 kHz, it is better tolerated by patients. It is especially suitable for iontophoresis.
Pulsed direct current Pulsed direct current has a variable intensity, but only one polarity. The basic shape of the pulse can be changed. Depending on the frequency and intensity used, it has stimulating, trophic and analgesic effects. In general, variable direct currents involve the same risks as galvanic currents and therefore require careful monitoring of the procedure. Pay attention to the correlation between the applied intensity and the duration of the application.
The technical result is the ability to provide impact for treatment various bodies and body systems. The method of electromagnetic therapy includes exposure to biologically active points and biologically active zones with a pulsed electromagnetic field with a strength of 0.1 V / m2. In this case, electromagnetic pulses are in the form of radio pulses with a packet repetition rate of 0.1 - 100 Hz, a discrete of 0.01 Hz and a carrier frequency of 10 - 15 kHz. The device contains an antenna device, a power supply, a control keyboard, a liquid crystal display, a device for matching with an antenna, a stabilizer whose input is connected to a power source, a microprocessor controller, outputs connected to a control keyboard, a liquid crystal display for displaying the parameters of a treatment program being executed and to a device for matching with antenna device. In this case, the microprocessor controller is made with the ability to memorize up to 1000 treatment programs and form pulses at the output with a repetition rate of 0.1 - 100 Hz, modulated with a frequency of 10 - 15 kHz. Each program includes up to 20 frequencies with an operating time of 1 - 4000 s. The essence of the invention is to induce resonance in organs and systems with the help of a weak electromagnetic field and thereby harmonize the work of the body.
The main effect is stimulation, which is important, especially below the cathode. The shape of the main pulse can again change - rectangular, triangular and harmonic sinusoidal, exponential or combined. It can be alternating, symmetrical, or asymmetrical. Therefore, this current also allows for long-term applications. It can even be used for patients with metal implants. Usage alternating current in contact electrotherapy implies much less stress on the tissue under the electrode.
This technical solution is a logical continuation of work in the field of low-frequency relaxation therapy (LRT), based on exposure to short electrical impulses(from 0.1 to 100 ms) with a current from 0.1 to 100 mA through electrodes to biologically active points (BAP) of the human body or to biologically active zones of the human body (BAZ). In most cases, BAPs coincide with the classical points of acupuncture (acupuncture) of various schools of traditional oriental medicine.
For these types of currents, the capacitive component of the skin resistance is involved, and due to this, these currents are very well tolerated by patients. In general: short pulse width improves subjective perception, zero mean prevents chemical damage to tissue, frequency and amplitude are responsible for the desired therapeutic effect.
Therefore, in addition to suppressing chemical tissue damage, the risk of electrical tissue damage is also minimized. As their names suggest, these currents are designed to stimulate nerve roots or nerve fibers. Their main uses are to relieve pain, inhibit itching, etc. their mechanism of action is most often explained by the so-called gate pain theory. In addition to treating pain, these currents can also be used effectively in electro-gymnastics.
Known devices for searching for BAPs, measuring the resistance of BAPs and BAZs (by the Nakatani-Ryodoraku method, by the method of Dr. R. Voll, etc.) and contact action on BAPs and BAZs with needles, electric pulses, microwave, EHF radiation, light and laser radiation of various ranges from UV to IR. In addition, these devices are combined with each other and are different names- electrotherapy, EHF-therapy, microwave-therapy, percutaneous stimulators, laser puncture, etc.
Interference has similar effects as low frequency currents, although it is carried by higher frequency currents and does not place much stress on the tissue under the electrode. The carrier frequency of the channels is 5 to 10 kHz. The higher this frequency, the better it is tolerated by the patient. The advantage of four-pole interference is deep targeting of the treated surface and reduced stress on the surface skin.
Therefore, more than high values intensity than for a bipolar application. Therefore, two electrodes are sufficient for its application. The absolute values of the intensity that can be achieved are lower than for classical interference, and at the same time, the stress on the skin surface is higher than for classical interference. Its advantage is that it can be applied with a point electrode and therefore can be effectively used in combination with therapeutic ultrasound.
Common to these devices is the introduction of energy into BAP and BAZ in various forms and through them a therapeutic effect on the human body.
The closest analogue is a device for generating a magnetic field with a duplicated system and an anti-jamming device (FRG patent N 4238745, MKH 5 A 61 N 1/16, 2/04, 1994). The device is designed for magnetic therapy with a strong local magnetic field, and then a weak magnetic field distributed over the surface. The description has the property of the matrix to create a strong concentrated magnetic field on a short time and a weak uniform field on long time... The coils are driven by current generators. A strong concentrated magnetic field creates an excess of energy in organs and systems, which is dangerous in cancer.
This means that the placement of individual electrodes is much easier - i.e. they no longer need to form a perfect cross. The effect of these currents is very diffuse, deep and delicate. In the direction of this dipole, the field modulation reaches 100%, in other directions it is almost zero. You can manually rotate this dipole and thus precisely target the desired therapy effect on the treated tissue or allow it to rotate automatically.
Pain is a multifactorial phenomenon, and research shows that different types of pain respond to several physiotherapy, i.e. also electrotherapeutic procedures. There are several mechanisms by which the analgesic effect of electrotherapy is achieved - in addition to the well-known theory of gate pain, an increase in the production of endogenous opioids is also supported. The analgesic effect is also confirmed by the trophic effects of the flowing current.
The technical result obtained during the implementation of the invention is treatment of various organs and systems of the body with a weak electromagnetic field with a frequency of 10 to 15 kHz, modulated with a frequency in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz with a discretion of 0.01 Hz, selected according to the methods of doctors R. Voll, F. Kramer, O. Klauss, O. Kollmer, Paul-Schmidt and others.
Over time, muscle relaxation removes muscle hypertension and therefore also pain of myofascial origin. Since the analgesic effect of electrotherapy is fundamental and widespread in practice, it should be described in more detail. Pain is usually simply defined as an unpleasant meaning and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. We usually distinguish between acute and chronic pain. Acute pain is short-lived. This is caused by mechanical damage tissue or disease, occurs immediately after the painful stimulus and disappears after its termination.
This technical result is achieved due to the fact that with the help of a weak electromagnetic field in organs and systems, resonance is caused and thereby the work of the body is harmonized. This is necessary in order not to force the organs to perform functions that are not characteristic of them.
The passive electrical properties of biological tissues are characterized by impedance (impedance), the value of which is determined by the capacitive and active conductivity with the corresponding tissue inductance. Active component of electrical conductivity on low frequencies ah is mainly due to the amount and electrolyte composition intercellular fluid, and at high frequencies an additional contribution is made by the electrical conductivity of the cells. Since the resistive resistance of cells is connected in series with the capacity of the cell membrane, the phenomenon of frequency dispersion of the electrical conductivity of biological tissues is observed. Possessing high dielectric properties and extremely small thickness, bilayer lipid membranes are characterized by high specific electrical capacity. The large value of the charging capacity of membranes, and, consequently, the capacitive properties of biological tissues are due to the significant polarization capacity of the membrane dielectric, which depends on its relative permittivity. At high frequencies, the polarization mechanisms are turned off with a slowdown in the relaxation time, therefore, with an increase in frequency, the tissue capacity should decrease, as well as with an increase in the dielectric constant.
Intensity acute pain depends on the intensity of stimulation. On the other hand, chronic pain is long-term or recurrent. Its intensity does not depend on the intensity of stimulation; emotions play a role. Currently, the generally accepted theory of pain perception is based on the assumption that there is a special sensory system that transmits information from pain receptors to the central nervous system through pre-formed special neural pathways.
However, the process is actually much more complex, and interested parties can learn about it from the literature available. To understand the effects of electrotherapy, it is important to understand, in particular, the modulating factors that affect the perception and transmission of pain stimulus: the first important factor modulation is described by the so-called pain gate theory. It is based on the assumption that; the neural mechanism in the posterior medullary horns acts as a small gateway that passes through a limited number of nerve impulses from the peripheral afferent fibers to the central nervous system, depending on how open it is.
At low frequencies, the impedance of tissues is determined mainly by their resistive properties. This area includes tissues with high electrical conductivity (nerve tissue). The mid-frequency region includes tissues, the electrical properties of which are determined by both resistive and capacitive properties (parenchymal organs). In the high-frequency region, the electrical properties of tissues are of a capacitive nature (membranes, lipids). Slow polarization mechanisms in this frequency range can lead to significant dielectric losses in tissues (heating).
Stimulation of certain specific fibers can modulate the degree of opening or closing of the pain gate and therefore also increase or decrease the transmission of nociceptive information. It is assumed that a similar gate system will exist at the level of the Thalamus. Another important modulation factor is described by the theory of neuromodulation, which is based on the analgesic effect of certain substances belonging to the group of so-called neuromodulators. Especially endorphins and enkephalins. These substances are produced in the central nervous system and, according to the aforementioned theory, they are critical, especially for the subjective perception of pain.
Thus, living cell can be represented as an oscillatory circuit with capacitance and resistance, and the capacity (membrane) is determined by free radical reactions and the antioxidant defense system, and the resistance is determined by enzymatic oxidation.
An oscillating circuit has such a property as inductance - the ability to excite electricity in another circuit or a closed conductor due to its magnetic moment. Generation of pulses of an electromagnetic field from units to tens of Hz is characteristic feature normal functioning of various human organs.
In any case, the analgesic effect of electrotherapy is most commonly used. Then correctly determine the diagnosis, or at least a preliminary hypothesis, and only then intervene against the pain. Very often, the source of these complaints is far from the place where the pain is projected.
This method is effective especially for acute and segmental localized pain. To achieve both of the above mechanisms in combination for pain relief use "modular modulation". Carrier frequency should be about 100 Hz, pulse frequency up to 10 Hz.
In the form of an oscillatory circuit, one can imagine not only a cell, but also more high levels organization of living matter: tissues and organs with different predominance of glucose oxidation pathways, organ systems and the whole organism as an induced equilibrium system of oscillatory circuits. An organ such as the liver contains both pathways of glucose oxidation in equal proportions, which makes it key in the system for regulating the body's capacity and inductance.
Pulse modulated currents lead to an accumulated analgesic effect. Muscle relaxation and antispasmodic effect. Especially after post-urographic examination showed that the general administration of so-called muscle relaxants has a negative long-term effect on body posture. The ability to accurately target the hypertensive muscle was considered a particularly valuable benefit of muscle relaxation procedures. General application muscle relaxants primarily affect the phasic muscles that are already weakened due to layer syndrome.
The circulatory system itself is also a cascade of closed conductors from the capillary loops to the large and pulmonary circulation. Different impedance of venous and arterial blood creates conditions for the mutual influence of organs on each other. The electrical properties of blood are determined by the amount of hemoglobin, oxygen and other cyclic compounds in it, the protein-electrolyte composition, as well as the blood flow rate.
Thus, the electromagnetic field, considered within the framework of classical electrodynamics, can integrate the work of the whole organism, creating and maintaining the specialization of various tissues. And the circulatory system is the mediator through which regulation is carried out. The ancient Chinese qi energy circulating in the blood becomes quite real, having its physical equivalent.
Only later, or when a stronger dose is applied, will the tonic muscles also be affected. This effect lasts for several weeks and has a very negative effect on the stiffness of the spine even after the acute complaint has subsided. Treatments with a muscle relaxant effect include a therapeutic ultrasound procedure, 2-pole interference with a loop frequency of 100-200 Hz, 4-pole interference currents and high-voltage therapy in the same frequency modulation. For small superficial muscles, especially on the arms, paraffin wax can be used.
Favorable side effect muscle relaxation is also an analgesic effect. The trophic effect is caused by hyperemia. Galvanization is generally recommended. The trophic hyperemic effect is also usually associated with an analgesic effect. Practically associated with hyperemia, vascular eutonization and increased capillary permeability. Therefore, a therapy called trophism is also antioxidant.
Acupuncture is based on the philosophy of ancient Chinese medicine, which considers the body as a whole, in which each part is subordinate to this whole, and the whole depends on each part.
The qi energy, divided into yang and yin in their constant interaction and dynamic equilibrium, fully corresponds to the described integration based on the electromagnetic field of the oscillatory circuit, if qi is replaced by inductance, and yang and yin are represented as capacitance and resistor. Then biologically active points (BAT) are additional sources regulation of energy in the form of a coil-nerve around the core-vessel, in which electromotive force will be generated when the nerve is excited or weaken when the excitation is removed from the nerve and vice versa.
Opponents of physical therapy tend to refer to its effects as a placebo. Creation control group almost out of the question. The afferent system processes all data, including visual, auditory, tactile and other analyzing impulses. Since a small stimulus is very often sufficient to divert the body from the existing functional balance and use its enormous capacity for self-realization, the body itself helps.
A "useless" patient is often only invited to a test exam after about ten procedures and "hopefully it will be better." The attending physician should know the answers to the following questions: what is the cause of the complaints, that is, usually the pain? Whether the defect is functional or organic. Where did the defect begin - where is the key area? Based on these responses, the physician must select the type, location, intensity, frequency, and total number of procedures. Also in relation to them - the date of the examination for the patient.
Electroacupuncture diagnostics according to Voll allows you to assess the degree of balance in the vibrational circuits of various organs and tissues. The constant current and voltage given by the apparatus during diagnostic testing of meridian points do not exceed physiological ones. Thus, we introduce electromagnetic interference into the living oscillatory circuit, which normally should not disturb its equilibrium, and the arrow of the device should be in the middle of the scale.
The increased inductance of the organ will give higher numbers when measured. And the slowdown in oxidative processes is low. Square-law measurements show dominance of inductance nervous system over other tissues, since in this case they are a capacitance in comparison with the resistive properties of the nervous tissue. Obtaining low numbers indicates a decrease in the inductance of the nervous tissue (imbalance in its oscillatory circuit) or an increased blood inductance for any reason. The fall of the arrow indicates a large self-induction, that is, going out of control of the body.
Electromagnetic vibrations existing inside the living organism itself are only partially dependent on vibrations existing outside the organism. Although the natural oscillations of the body are excited by the oscillations of external EMF, they are then formed in the body again in a specific form. Each organ and each cell has its own specific spectrum of vibrations, its own specific characteristics of these vibrations (form and type, as well as frequency). The maintenance of these oscillations depends on the "quality factor" of the resonator of a cell, organ, tissue or organism as a whole. If the "quality factor" of the resonator is broken or absent, incoherent, inadequate, pathological electromagnetic oscillations may occur. In the case when the mechanism of self-regulation and healing existing in the body is not able to destruct these fluctuations, a disease arises.
The specific reactions of the human body to the effect of an artificial electromagnetic field (EMF) were detected only when switching to ultra-weak intensities of low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz of EMF (when the field intensity induced inside the body was significantly less than 0.1 V / cm ).
It should be noted that at an external field strength of the order of 10 V / m, it is practically impossible to experimentally measure the values of the field induced inside the body. They were obtained by calculation and ranged from 10-8 to 10-7 V / m. The presence of the body's reaction to such low field strengths does not contradict the generally accepted physical assessments based on the signal-to-noise ratio. Indeed, since the control physiological processes is carried out using super slow waves, i.e. processes with a bandwidth of the order of 1 Hz, then with a specific resistance of nerve tissues of R300 Ohm / cm, the intensity of thermal noise is Ush10-9 V / cm, i.e. an order of magnitude lower than the above values of tension.
When comparing the effects of artificial and natural low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz EMF on a person, it should also be taken into account that the effect of artificial EMF is short-term, its duration is significant less life human; the impact of natural EMF is carried out continuously throughout life. In this regard, it can be expected that to obtain therapeutic effect when exposed to artificial EMF, its intensity should be higher.
To explain the effect of exposure to low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz of EMF on a person, it was assumed that the receptors on the EMF can be the meridian systems and acupuncture points (TA). Since all known hypotheses about the role of TA were limited to an abstract theoretical consideration of their purpose, to test this assumption, experimental studies were carried out in order to detect low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz of electrical signals in the areas of cutaneous TA projections. The search for such signals was carried out on the basis of the following considerations.
In accordance with the principle of antenna reciprocity, any structure that receives EMF is also capable of emitting EMF in the same frequency range. Therefore, the aim of the study was to detect electrical signals in the areas of cutaneous projections of TA in the range of low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz.
During experimental research in these zones, low-frequency electrical signals were found with maximum values of amplitudes at a number of discrete frequencies in the range from units to tens of Hz. In addition, weak low-frequency radiation in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz of EMF was recorded over the surface of the body in these zones, which also had a discrete spectrum in the range of up to tens of Hz. It was found that when the sensor is displaced from the TA zone, the amplitudes of the received signals sharply decrease; the spatial distribution of signals in the TA zone is anisotropic. In neutral areas of the body, the observed signals had a noise character and their amplitude was 5-10 times less than in the TA zones.
The obtained experimental data can be reasonably considered a confirmation that the receptors-receivers of electromagnetic fields in the frequency range from units to tens of Hz are TA and the system of meridians. Naturally, for effective reception low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz EMF, the biological object should have a lot of receptors, spaced across its body to the maximum possible distance... It is these requirements that are observed in the TA meridian structures in all living organisms. Therefore, it can be assumed that the TA meridian structures are systems of discrete receiving elements. Each such discrete structure is associated with one or another functional system organism and provides independent reception of synchronizing low frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz EMF.
A strong oscillation of systems with weakly suppressed natural oscillations in the event that they are excited by relatively weak external forces with a frequency that is equal or almost equal to the natural frequency of the system is called resonance. The essence of the invention is to induce resonance in organs and systems with the help of a weak electromagnetic field and thereby harmonize the work of the body. This is necessary in order not to force the organs to perform functions that are not characteristic of them. Thus, we avoid the effect of overdose. Since organ diseases can be caused different reasons, then it is necessary to use for treatment different systems organism, i.e. sets of frequencies. Thus, the treatment program should consist of a set of frequencies, each of which acts in advance. set time causing resonance in the necessary organs and systems. Low-frequency electromagnetic therapy causes resonance phenomena, but at the same time the energy introduced into the body is so small that there is no overdose effect, and this is especially important for the treatment of cancer patients.
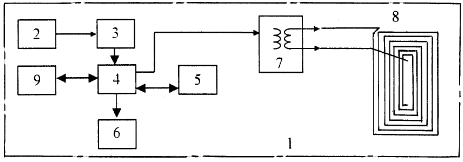
The block diagram shown in the drawing reflects that the device consists of a housing 1, in which a power source (battery) 2 is connected through a stabilizer 3 to a microprocessor controller 4. The microprocessor controller 4 is connected to a control keyboard 5, an LCD indicator 6, a computer interface unit 9 and a matching device 7. The matching device is connected to the antenna device 8.
The low-frequency electromagnetic therapy device works as follows.
A person from the control keyboard 5 turns on the device and on the keyboard or on the computer through the interface unit with the computer 9 dials the treatment program. (The program can consist of one or several frequencies in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz. For each frequency, a time is set in the range from 1 to 4000 s). Microprocessor controller 4 memorizes the entered program. (The number of programs that the microprocessor controller 4 memorizes and stores, from 1 to 1000). After that, it directs the antenna device 8 to the biologically active zone and starts the execution of the treatment program. Microprocessor controller 4, executing a given program, generates radio pulse packets (in the range from 0.1 to 100 Hz) filled with an audio frequency. These packets of radio pulses are fed to the matching device 7 and through it to the antenna device 8. In this case, the liquid crystal display 6 displays the parameters of the running program of the microprocessor controller 4. At the end of the specified program, the device will automatically turn off. Treatment is based on resonance phenomena, and not on forcing organs to perform functions that are not inherent to them. That is why it is impossible to overdose or exacerbate the disease with electromagnetic therapy devices. If the introduced frequency causes resonance, then the body needs it and there is a therapeutic effect. If there is no resonance, then there is no healing effect. And as a consequence of this, it is impossible to harm this device.
This method has passed clinical trials at the Central Military Clinical Red Banner Hospital. P.V. Mandryk, at the State Research Center for Preventive Medicine, in Moscow medical academy them. Sechenov, in the Department of Radiation Medicine of the Moscow Research Institute of Diagnostics and Surgery of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, in the Research Center "Ultramed" (Moscow). Examples are given below for a better understanding of the method for electromagnetic therapy.
Example 1. Patient V., Zelenograd, filed a complaint about varicose veins veins. Prior to that, she had been unsuccessfully treated for many years. Carried out laser therapy, chemotherapy, etc. The legs are swollen. Ulcers up to 8 cm deep. Treatment for this way for electromagnetic therapy. The patient was exposed to a pulsed electromagnetic field with a strength of 0.1 V / m2. In this case, the carrier frequency is 10 kHz. The impact was carried out locally on the legs. The program consisted of the following frequencies: 10 Hz - 600 s, 33.5 Hz - 300 s, 94 Hz - 300 s, 85 Hz - 300 s, 46.5 Hz - 300 s, 99.5 Hz - 300 s. The treatment was carried out once a day before going to bed, and after the session the patient went to bed without getting up. Within two weeks, the swelling subsided, the ulcers healed and she was able to put on her boots. No relapse of the disease was observed for three years.
Example 2. Patient I., 65 years old, Voronezh, filed a complaint about bronchial asthma... He had an aggravation every spring and autumn during the period of rains and dampness for many years. The treatment was carried out according to this method for electromagnetic therapy. The patient was exposed to a pulsed electromagnetic field with a strength of 0.1 V / m2 with a given repetition rate of radio pulse packets with a step of 0.01 Hz. In this case, the carrier frequency is 12 kHz. The impact was carried out on the whole organism. The program consisted of the following frequencies: 0.9 Hz - 300 s, 4.0 Hz - 300 s, 8.0 Hz - 300 s, 9.45 Hz - 300 s, 82 Hz - 300 s, 82 Hz - 300 s. The first session was held at 5 pm in April. In the morning next day repeated and during the day three more sessions were carried out. By the evening, the exacerbation ended and in the fall, no recurrence was recorded.
Example 3.
Patient K., 55 years old, Zelenograd, complained of hypertension. Constant medication to normalize blood pressure. Individual frequencies for regulation were selected for treatment. After that, he began to constantly carry the device with him. As soon as the pressure starts to rise, he turns on the program and the pressure returns to normal. For three and a half years, no pills have been used and the state of health is normal.
The treatment was carried out according to this method for electromagnetic therapy. The patient was exposed to a pulsed electromagnetic field with a strength of 0.1 V / m2 with a given repetition rate of radio pulse packets with a step of 0.01 Hz. In this case, the carrier frequency is 15 kHz. The impact was carried out on the whole organism. The program consisted of the following frequencies: 3.3 Hz - 300 s, 6.0 Hz - 300 s, 9.2 Hz - 300 s, 9.4 Hz - 300 s, 9.5 Hz - 300 s, 62.5 Hz - 300 p.
Prostatitis is successfully treated with this method. For the treatment of prostatitis, a set of programs has been developed, which consists of the following programs:
1. Prostate 2.6 + 4.0-4.9 + 9.4 + 19.5 + 51 + 51.5 + 57 Hz for 300 s per frequency.
2. Regulation of the functions of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal-gonads system: 4.0 + 4.9 + 5.5 + 9.4 Hz for 300 s per frequency.
3. Energy program: 10 + 12.5 + 19 Hz for 300 s per frequency (known as "Active Protection Device").
4. Arthritis - arthrosis: 1.2 + 1.6 + 9.2 + 9.6 + 95.5 + 96.5 + 100 Hz for 300 s per frequency.
5. Testicle, testis: 14 + 4.5 + 51 Hz for 300 s per frequency.
6. Weakening of potency: 4.5 + 14 + 15.5 + 55 + 55.5 + 57 + 49.5 Hz for 300 25 s per frequency.
7. Local circulatory disorders: 50 + 58 + 85.5 Hz for 300 s per frequency.
This set of programs has been tested in medical center"Andromed", Voronezh. Within six months, 135 people with similar problems were treated. The experiment showed 85% cure.
Thus, this method of electromagnetic therapy and the device of electromagnetic therapy with their implementation made it possible to ensure the harmonization of the work of human organs and systems due to resonance phenomena caused in the body at given frequencies, and thereby expand the possibilities of their application and automate the treatment process.
Industrial applicability
This invention can be used to influence the human body with a weak low-frequency modulated electromagnetic field for the treatment of various diseases, harmonizing the work of organs and increasing the body's defenses.
SOURCES OF INFORMATION
1. Samokhin A.V. Gotovsky Yu.V. Electropuncture diagnostics and therapy by the method of R. Voll. - M .: IMEDIS, 1995 .-- 447 p.
2. Kramer F. Textbook on electroacupuncture. T. 1. - M .: IMEDIS, 1995 .-- 189 p.
3. German patent N 4238745, MKI 5 A 61 N 1/16, 2/04 1994.
CLAIM
1. A method of electromagnetic therapy, including exposure to a pulsed electromagnetic field with a strength of 0.1 V / m2, characterized in that the effect on biological active points and biologically active zones of the human body is carried out, with a repetition rate of radio pulse packets of 0.1 - 100 Hz and a discrete 0.01 Hz, and the carrier frequency of the electromagnetic field is in the range from 10 to 15 kHz.
2. A device for electromagnetic therapy, containing an antenna device and a power source, characterized in that a control keyboard, a liquid crystal display, an antenna matching device, a stabilizer whose input is connected to a power source, a microprocessor controller with outputs connected to a control keyboard, are introduced into it, a liquid crystal display for displaying the parameters of the treatment program being executed and to a device for matching with an antenna device, the output of which is connected to the antenna, while the microprocessor controller is configured to store in memory up to 1000 treatment programs, in each program up to 20 frequencies with an operating time of 1 - 4000 s , and form pulses with a repetition rate of 0.1 - 100 Hz, modulated with a frequency of 10 - 15 kHz.
3. The device according to claim 2, characterized in that a computer and a computer interface unit connected to the controller are inserted into it.
In medical practice, 3 different kinds impulse currents.
1. Pulse current rectangular (formerly it was called the Leduc current) with a pulse duration of 0.1 to 1 ms and a frequency of 10 to 100 Hz.
This type of current is used to treat electrosleep. In this case, the bifurcated electrode in the form of glasses is placed on closed eyes and connect it to the cathode of the apparatus, the second bifurcated electrode is placed in the area of the mastoid processes and connect it to the anode of the apparatus; the current strength in the amplitude value is 8-15 ma, the pulse frequency is from 10 to 80 Hz, their duration is 0.2-0.3 msec. The procedures are usually carried out every other day (every day) after breakfast, in the supine position of the patient, in a darkened room, in silence. The duration of the procedure at the first exposure is 15-20 minutes, followed by its increase to 1-2 hours (after the patient falls asleep, the current may be turned off); for a course of treatment 12-20 procedures.
2. Current with pulses of pointed triangular shape(tetanizing current, formerly faradic current); the duration of an individual pulse is 1-17g ms, the frequency is 100 Hz.
3. Exponential current with pulses a slowly rising and more rapidly falling shape of the curve (formerly the Lapik current) with a pulse duration of 3 to 60 ms and a frequency of 8 to 80 Hz.
When treating impulse currents the periods of exposure alternate with the periods of rest of the irritated muscles: in this case, the amplitude of the impulses in each period of exposure smoothly increases from zero to the maximum value and then also smoothly decreases to zero.
When using a tetanizing current or an exponential current for electro-gymnastics (depending on the results of an electrodiagnostic study), electrodes are placed on the motor points of the muscles.
When acting on striated muscles, conventional electrodes are used for galvanization with an area of 4-6 cm2, and when acting on large muscle groups - with an area of 50-100-200 cm2.
The strength of the current in the amplitude value of the impulse is selected such as to obtain visible muscle contractions without at the same time causing the patient unpleasant sensations, usually up to 10-15 ma. Procedures lasting from 15 to 30 minutes are carried out every other day (daily), a total of 15-20 procedures for a course of treatment.
4. Diadynamic currents introduced into medical practice P. Bernard, are of the following types:
A) single-ended fixed current with a frequency of 50 Hz;
B) fixed push-pull current with a frequency of 100 Hz;
C) short-period current, when a single-cycle current with a period duration of 1 sec alternates with a push-pull current of the same period duration;
D) current long period, when a single-cycle current with a period duration of 3 "/ g sec alternates with a push-pull current with a period duration of 6r sec.
The patient is supplied with current by two round or plate electrodes using a damp pad. Procedures from 4 to 8-10 minutes with a current strength of 3-15 mA are carried out daily (every other day), distributing this duration to various types of current used; in total for a course of treatment from 6 to 10 procedures.
5. Interference currents (Nemec currents) are obtained by superimposing a sinusoidal current of constant frequency (4000 Hz) on a sinusoidal current of varying frequency in the range of 3900-4000 and 3990-4000 Hz. When a current of one frequency is superimposed on a current of another frequency, modulations can occur either with a constant or with a rhythmically varying frequency (in the range from 0 to 100 or from 0 to 10 Hz) with a period of 15 seconds.
To supply current to the patient, two separate pairs of electrodes are used, usually used in galvanization. With the help of each pair of electrodes, a sinusoidal current of various frequencies is supplied (for example, 3900 and 4000 or 3990 and 4000 Hz). The electrodes, depending on the site of exposure (usually with an area of 50-200 cm2), are placed in pairs on the skin in the soft tissue area so that the target is located at the intersection of the current lines of force from both pairs of electrodes (mutually perpendicular or diagonally).
Procedures with a current strength of 5-25 mA lasting 10-30 minutes are carried out every other day (daily), for a course of treatment 12-20 procedures.
6. Sinusoidal modulated current is a sinusoidal current with a frequency of 5000 Hz, modulated by sinusoidal oscillations of low frequency (in the range from 10 to 150 Hz). To reduce the adaptation of the organism to such influences, currents are used, modulated by continuously alternating frequencies (in 150 Hz I within 10 + 150 Hz) with separate adjustment of their duration within l-5 seconds; it is also possible to alternate modulated current oscillations with pauses, as well as modulated and unmodulated oscillations.
For procedures in
