Elbow pain after exertion. Causes of knee pain. Exercise knee pain
To the beginning active pursuits sports or fitness we come with different natural inclinations, physical capabilities, and sometimes with existing diseases or a tendency to them.
In order for training to strengthen health, and not vice versa, an individual selection of loads is necessary. But even under this condition, you can often hear complaints of joint pain.
And more often than others, the biggest and most difficult of them hurts - the knee. Why knees hurt after exercise - what to do and how to treat? What caused this pain, is it possible to get rid of it and how? Let's figure it out together.
The common talk that training through pain is the norm dangerous delusion. Especially if it becomes regular or persistent and gets worse from session to session. Causes of knee pain after leg workout and possible options getting rid of suffering is several.
1. Overtraining
If you regularly experience sports overload and at the same time still eat irrationally, you cannot avoid deepening degenerative-dystrophic processes in the most vulnerable joint of our body - the knee. Indeed, although it is a unique movable structure that can withstand the weight of our body and the load during movement, its capabilities are not endless. Internal inflammation of the muscle and connective tissue of the joint can, with a careless attitude, end in complete destruction of cartilage and bone deformation.
If the pain is regular, after each workout: 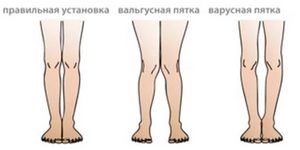
- Apply cold to your knees for 10-15 minutes, it will prevent soft tissue swelling. The procedure can be repeated several times a day.
- Lying on your back, raise your legs above the level of your heart, placing a roller under your aching knees. This will relieve the swelling of the joint.
- In the morning, use anesthetic and warming ointments and gels to relieve pain symptoms and activate blood circulation.
If the pain lasts more than two days, it makes sense to take a number to the orthopedist.
Important! Performance strength exercises inevitably injures the knee, but healthy person it soon recovers completely. But overtraining - along with such factors as age, heredity, infectious and inflammatory diseases, metabolic disorders, improper nutrition- reduces the ability to recover. AND pathological changes, gradually accumulating in tissues, can develop into a chronic disease, accompanied by constant pain.
2. Age-related changes in tissues
Statistics are stubborn things, and they show that after 30 years people suffer from knee injuries at times more often. The reason is simple - the body decreases collagen production. it natural process, and you can't argue with nature.
 It is possible to recommend from time to time to take courses of gelatin and collagen-containing preparations to restore cartilage, strengthen ligaments and bones, and reduce joint pain.
It is possible to recommend from time to time to take courses of gelatin and collagen-containing preparations to restore cartilage, strengthen ligaments and bones, and reduce joint pain.
Periodically take courses of physiotherapy (electrophoresis, amplipulse, massage, etc.). All this, as you understand, should be supervised by an experienced and proven physician.
5. Overweight
It should be remembered: every extra kilogram of body fat responds to the knee joint by 6 times the load.
Get busy with your physical fitness, check out.
Watch your diet, but don't overdo it. In pursuit of weight loss, you can inadvertently "rob" your body for the vitamins and minerals it needs.
6. Incorrectly performed exercises
Traumatic tension and pain appear if:

- strength exercises are excessive and stress the knee joints in excess of the physical fitness human;
- the athlete distributes the load ineptly, while friction under the kneecap increases and causes pain;
- exercise technique in gym is wrong, for example, the typical habit of standing up with a weight to fully extend the knees multiplies the traumatic pressure on them.
To determine the cause, do brief analysis: at what point in the workout, during which exercise your knees began to bother you. Consider technique and weight - make adjustments as needed or look for alternative exercises with less stress on the joint.
Be sure to familiarize yourself with the correct technique for performing traumatic exercises such as:
Also, if your knees ache after training all the time:
- Exclude from training "hopping" exercises, where both feet come off the floor - jumping, running, aerobic exercise on the platform.
- Try to choose and perform exercises with less weight, but higher amplitude - this will improve the cellular nutrition of the joint and repair damaged structures.
7. Incorrectly fitted shoes
If you perform dynamic exercises in shoes of poor quality orthopedic or not your size, the position of the foot will be incorrect, and the distribution of the load will be uneven.
Choose the right athletic shoes.
8. Genetic defects or diseases of the musculoskeletal system
The former include, for example, flat feet. It causes the kneecap to rotate inward as it moves, which causes pain.
The onset of the development of diseases can be given by injuries not treated in the past, complications after infectious diseases... An example is arthritis and arthrosis.
In the first case, the destruction of cartilage occurs, which performs a shock-absorbing function and ensures the sliding of the components of the joint. Its consequences are gradually increasing chronic pain in the knee up to disability, joint deformity. At first, the knee swells, the skin around it turns red, hurts.
But arthrosis begins with a crunch, morning numbness and limited knee action, progresses up to a change in the shape of the leg.
If you find yourself with similar symptoms, do not delay, start treatment.
Find out 7 more reasons from the video:
What does it mean if your knee is swollen after exercise?
Swelling and pain when flexing is a symptom common to several pathologies. This could be:
- injury;
- exacerbation of arthritis or arthrosis;
- joint inflammation.
In addition to the fact that the knee is swollen, it can turn red and hurt when pressed. The nature of the pain also varies - aching, cutting, pulling, and it can appear immediately after training, at night or in the morning, at rest or in motion. You may also have a fever - locally or throughout your body. These are all symptoms that you will need to describe during a visit to the doctor for correct diagnosis.
Take care of your knees in a timely manner
Even if your knee joints do not bother you at all, you need to take preventive measures so that this does not happen as long as possible. Even if your knees just crunch a lot after bending training, this is already a reason to think. And if they are already sick, then even more so.
For prevention, you should load yourself gradually without jerks, taking into account the level of physical fitness and state of health, the "second wind" of beginners is not a reason to overload.
Don't forget about medical examinations with the repetition of the same discomfort and about proper nutrition... Eat foods high in minerals and vitamins, after all, with sweat, salts, trace elements, as well as water, necessary for joints, are excreted from the body. Lots of fruits and vegetables, meat, fish and dairy products, as well 1.5-2 liters of water a day - and your knees will thank you with a long and trouble-free service.
Knee pain on exertion is currently one of the most common clinical disorders of the functional activity of the musculoskeletal system. As a rule, the main reason for the occurrence of such a phenomenon as knee pain is everyday physical activity, which is sometimes unnecessary and can aggravate a person's quality of life.
Most often, knee pain signals a bruise, a fractured meniscus, or a sprain. People retirement age, have complaints of pain in the knee during exertion, for example, when climbing stairs, and in the process of normal upright posture or descent, pain does not occur.
Knee pain during exercise is related to how the load itself is acting on the joint. When climbing the stairs, the muscles of the thigh are in tension, while the joint itself is unbending. When descending, the knee joint, on the contrary, unbends, and the load on it is reduced.
What is the reason for knee pain?
For example, when moving up the stairs, the patella or patella begins to exert pressure on the surface of the joint. In the normal state, the joint without special labor copes with this pressure. In the event of surface damage, this pressure is painful. And the further the process of knee joint disease goes, the more often it occurs knee pain on exertion.
What to do if knee pain occurs during exercise?
Regular or temporary knee pain during exertion is usually a signal of the development of a disease of the knee joint (for example, gonarthrosis). Therefore, do not hesitate to visit your doctor if you develop knee pain during exertion.
How can knee pain be avoided?
Anatomically, the knee joint is considered the largest with a very complex structure, therefore it is often prone to sports injuries and other diseases characteristic of this joint.
You can have a beneficial effect on the joint through a number of very common measures. Today our life goes on in an incredible rush, where one way or another we are subject to both mental and physical stress. On first appearance knee pain on exertion start to be more attentive to your body. If your schedule includes sports training, you need to reduce the intensity, but in no case stop moving regularly. Joint overload is also exerted by the presence excess weight, from which it is necessary to get rid of it as much as possible, otherwise the disease will progress due to excessive load on the joint. Through targeted training and regular mobility, weakened joints are stabilized and strengthened, which significantly reduces knee pain during exertion.
Tips for Preventing Exercise Knee Pain in Everyday Life
- Try to do your work in a standing position as much as possible, as this is more active than a sitting position. In addition, you will strengthen the muscles of the legs.
- If possible, alternate continuous sitting in the workplace with leg stretching exercises to prevent shortening of muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
- Instead of using the elevator, take the stairs, this will strengthen the leg muscles and promote slimness.
- Take a walk at a walking pace. Movement is, in principle, very important for building muscles, and especially for the knee joint.
- Avoid too abrupt, chaotic movements. Stand up slowly, keep your posture and do not squat.
Knee pain on exertion
To clarify the diagnosis, complex diagnostics are prescribed (ultrasound, X-ray, CT, scintigraphy). Arthroscopy is also performed for diagnostic purposes. To complimentary diagnostic methods include lab tests. The cost of a complex diagnostics package is about € 600 - € 800.
In the presence of moderate damage to joints, cartilage and menisci, arthroscopy is usually indicated for the patient. Thanks to the optical arthroscope, it is possible to examine the cavity of the knee, as well as the patella, without significant damage. A 3cm incision is required to insert the arthroscope into the body. The video system transmits the image to the screen, and a special computer analyzes the information and draws up a visual report on the condition of the knee cavity, which the doctor receives in digital form.
If there is a meniscus rupture, a meniscectomy is prescribed. This operation allows you to remove damaged fragments of the meniscus, stabilize and restore the amortization capacity of the intact part of the meniscus. Menisco-capsular connection in this case remains intact. Arthroscopic meniscectomy is also performed at the Friedrichshafen Clinic. This is an endoscopic procedure that, unlike conventional meniscectomy, allows for partial meniscectomy, i.e. remove only the non-functional part of the meniscus. In addition, in the course of such treatment, lavage and cleaning of the articular surface are carried out, which is the prevention of the development of arthrosis. Depending on the extent of the meniscus damage, the cost of such an operation is about € 3.000 - € 6.000.
If in your case preventive measures it's too late to accept knee pain on exertion does not allow to live and work in peace, contact our clinic for help. Experienced rheumatologists will conduct a thorough diagnosis, perform X-rays and select individual plan treatment.
The sooner treatment for the knee joint is prescribed, the easier and more effective it will be to eliminate the problem causing the pain.
We are looking forward to your visit!
Regular physical activity in the gym or in ordinary life sometimes lead to discomfort in the knees. When knees begin to hurt during exertion, this can greatly bother a person, but it is better not to self-medicate, since first you need to find out the exact cause of the discomfort that has arisen. There are a lot of disorders and diseases in which pain in the knee joint appears under stress, but we will try to consider the main ones.
What causes pain?
Discomfort with pain after exertion of different nature and the intensity forces people to seek medical attention. An experienced orthopedist or traumatologist, based on complaints, can diagnose and determine what caused the pain in the knees. In people who are involved in active sports or are experiencing stress in everyday life, pain can be caused by a number of reasons:
- damage to the ligaments caused by stretching (the pain is especially strong when stretching at the end of the workout, but it can also appear in the process if the loads are serious);
- dislocations of the joint, accompanied by damage to the cartilage, tears of the ligaments and even damage to the bones (with such injuries, pain in the knees due to stress is strikingly strong and persists even after the joint is fixed);
- muscle strain or fatigue of the ligaments (pain appears after exertion and does not disappear for a long time);
- damage to cartilage tissue and bone fractures (in these situations, the knee joint hurts during exertion and even during normal walking, and you can also hear the characteristic ones);
- bruises (because of them, the pain is sometimes quite strong, and additionally there is swelling and hematoma).
If you do not play sports or generally lead a sedentary lifestyle, knee pain after exertion may have completely different causes. Sometimes it is a matter of thinning of cartilaginous tissue, excessive or too little fluid production in the synovial bags, as well as in inflammatory processes.
How are the causes of pain diagnosed?
When knees hurt and it is caused by physical. loads, important role plays professional diagnostics... It is required for the appointment of a timely and correct treatment, which will prevent the development of complications. Doctors to determine violations, causing pain, the following tests are prescribed:
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- blood and sometimes urine tests;
- visual inspection;
- tissue biopsy;
- puncture of the contents of the synovial bag.
There are other specialized techniques for diagnosing knee pain from exertion, which depend on patient complaints. The information obtained allows you to determine the course of therapy.
Methods for treating disorders
The exact course of treatment at 45 degrees and other physical activity depends on the cause. There are a lot of diseases, so self-medication is unacceptable - it can be very harmful. The main thing is not to postpone a visit to the doctor in situations such as:
- knee pains do not subside for a long time;
- their intensity gradually increases;
- pain appears suddenly even after insignificant exertion;
- the knee is reddened;
- the sensitivity of this part of the leg has changed;
- the knee is noticeably deformed.
In each case, the doctor will treat sore knees differently. The most common techniques are:
- minimizing or completely eliminating any activity (a fixation bandage may be required to secure the knee joint);
- warm compresses or, which will improve blood microcirculation;
- using a bandage or elastic bandages to stabilize the knee;
- thorough and prolonged warm-up of the knees before training or just physical activity;
- sometimes cold compresses are useful if the pain is acute, but the duration of their application should not exceed a quarter of an hour;
- taking medications (in case of inflammatory processes, special drugs are needed, including restorative ones);
- surgical operations.
In the latter case, the patient is placed in a hospital, where he will be examined and treated until complete regeneration of the diseased joints that hurt after exertion.

Can you protect yourself from pain?
You should be aware that any disorder is easier to prevent than to cure. The knees are often injured when playing sports. Thanks to the simplest measures, you can have a beneficial effect on the joint, preventing the spread of pain during physical exertion.
At the first unpleasant sensations and mild pain after exertion, you need to listen to the body. Try to lower the intensity of your workout, but don't stop moving. Activity for mild joint pain is a must! if you have overweight on the body, you need to get rid of them as soon as possible so that excessive stress on the joints does not contribute to the progression of the disorder.
Targeted training and regular mobility help stabilize and strengthen sore joints, resulting in pain relief. To avoid knee pain during exercise, follow these guidelines:
- Try to stand and walk more if you have a sedentary job. It is important to keep your leg muscles in good shape.
- If possible, alternate continuous sitting with leg stretching exercises to avoid shortening of muscles and ligaments.
- Stop using the elevator and walk up the steps.
- Walk more and have easy jogging.
- Avoid chaotic and abrupt movements. You need to get up slowly, control your posture and not squat down.
Recall that you need to start treatment immediately if your knee hurts during physical exertion. Inaction will only make the situation worse and worsen your health.
The ankle joint is the pivot point of the human skeleton. It is he who accounts for most of the load when walking and any other movements. Pain in the ankle joint can occur both against the background of various injuries and as a result of the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
The ankle is responsible for movement in the limbs and maintaining balance. The joint is quite complex, it consists of many bone, tendon, muscle elements, which are in close interaction with each other. Therefore, in the event of pain in the ankle, it is recommended to contact an osteopath as soon as possible in order to understand the causes of the disorders that have arisen and choose effective treatment.
The main causes of ankle pain
Ankle arthritis is an inflammatory process that occurs against the background of injuries, infections, degenerative and destructive changes in other joints. The leading symptom is arthralgia - joint pain that appears as a result of irritation of the neuroreceptors of the synovium.
Ankle fracture - trauma to hard and soft tissues that occurs when the foot is turned sharply outward or inward. When injured, the person feels severe pain... Swelling builds up soft tissue the ankles become hyperemic, hot to the touch, the movements of the injured leg are sharply limited.
Achilles tendonitis is an inflammation that occurs with regular exertion, microtraumatization of the tendon tissue, due to the development of arthritis. Appears constant pain in the ankle joint, the temperature rises locally, moderate swelling is observed. Tendinitis occurs predominantly in athletes and people who constantly overload the ankle, especially when they professional activity associated with monotonous movements.
Tunnel syndrome - damage to blood vessels, nerve formations of the ankle as a result of its excessive compression. Pathology occurs with tendovaginitis, trauma to the ankle, arthrosis, diabetes mellitus.
Subluxations, dislocations - often cause pain in the ankle joint and limited mobility. If you suspect such injuries, you should consult a specialist, carry out X-ray diagnostics and start treatment as soon as possible.
Deforming arthrosis - degenerative changes in the articular structures of the ankle. This systemic pathology leads to deformation, destruction of the joint, the appearance of severe pain syndrome.
Gout is a chronic disease characterized by the deposition of uric acid salts in joint tissues, which leads to deformities and the formation of characteristic gouty nodules. The diagnosis is confirmed during X-ray diagnostics and upon receipt of the results of the study of the synovial fluid.
Ankle Pain Treatment Principles
Timely treatment of pain in the ankle joint will help to avoid the development of complications, quickly relieve a painful attack, restore physical activity... V acute period analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. Correctly selected drug therapy and the observance of physical rest allows you to avoid further trauma and an increase in the symptoms of the disease. To find an effective treatment, it is necessary to conduct an examination, collect anamnesis, and schedule an examination.
Finding out the causes of pain in the ankle joint, determining the severity inflammatory process, the specialist selects the medical tactics. Studying the nature of the pain attack plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis. As a result of dislocation, fracture, sprains of the ligaments, pain occurs in the ankle joint when walking, running and other physical activities. On examination, swelling is noticeable, the surrounding tissues are hyperemic. The patient can usually tell the exact time and cause of the pain. If they progress chronic diseases joints (arthritis, arthrosis, gout), then pain syndrome can develop at rest, sometimes even without external changes fabrics.
After the inflammatory process subsides, physiotherapy, classes physiotherapy exercises, gymnastic exercises. Motor mode it is necessary to expand gradually, giving a dosed load on the recovering joint. Treatment and rehabilitation should be supervised experienced professionals... It is important to comply with all medical advice, spare the damaged joint, avoid alcohol, excessively spicy foods.
Treatment of ankle pain with osteopathy
Modern osteopathy has great potential, allowing using special techniques and techniques to eliminate pain in the ankle joint, influencing not only the symptoms of the disease, but also the causes of its occurrence. The osteopath by his actions activates the defense mechanisms aimed at self-healing and recovery of the patient. The blood begins to circulate more actively through the tissues, the nutrition of all increases damaged structures that contributes to the extinction acute symptoms and normalization of the patient's well-being.

results osteopathic treatment ankle pain:
quick relief of a painful attack;
restoration of nutrition and blood circulation of the articular structures;
increased range of motion;
acceleration of the regeneration of damaged soft, hard tissues;
reduction of puffiness, hyperemia, discomfort;
restoration of innervation, return of sensitivity;
slowing down the deformation of the joints against the background of systemic diseases.
In the second step, blood tests are done. They are shown to the patient if the doctor suspects the autoimmune nature of arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
The third stage includes an MRI scan to determine the intervertebral hernia (which can give pain with a projection into the joint area) and some other diseases. Also, MRI is indispensable if it is impossible to explain the nature of the pain syndrome using the available data of objective research.
In general, when diagnosing the causes of pain in the hip joint area, the following sequence is recommended:
Physical examination and radiography of the hip joints and sacral spine (all patients).
A blood test for markers of inflammation: ESR, CRP, rheumatoid factor (for patients with coxarthrosis under 50 years of age and with minimal changes on the radiograph).
MRI of the hip joints and lumbosacral spine (for patients who, according to the results of the previous stages, could not find out the cause of the disease).
Diagnostic blockade of the hip joint and lumbosacral spine to exclude ex juvantibus in patients with an unexplained cause according to the results of previous studies (Vakulenko V.M., 2008).
Pain in the hip joints from the point of view of an osteopath
Since the range of problems in which the hip joint hurts is quite wide, osteopathic diagnostics is one of the leading methods at the first stage of the examination. The further fate of the patient, the need for narrow, expensive examinations and the general direction of the diagnostic search depend on how carefully the doctor conducts the examination. The wrong message in the first step can lead to months of walking in circles without any improvement.
Osteopathic diagnostics for pain in hip joints implies not only a classic examination according to orthopedic principles, but also specific diagnostic tests characteristic of osteopathy.
The mobility of the head is clarified in detail femur, angles of displacement, muscles and ligaments involved, their tone and functional state that cannot be detected using instrumental methods (MRI, X-ray). It is imperative to diagnose associated injuries of those organs that could be affected by changes in the hip joints.
After the cause of the pain has been clarified with absolute accuracy (not only in the general words "arthrosis", "neuritis", "disc herniation", "tendonitis", etc., but also with a functional osteopathic diagnosis), the osteopath prescribes treatment that is most appropriate for the individual situation the patient.
Under no circumstances will an osteopathic doctor insist on the use of exclusively osteopathic manual techniques if the patient has indications for surgery and other types surgical treatment... However, in many cases, these unpleasant procedures can be avoided by working out the problem with non-drug osteopathic remedies.
After a successful operation (9 if necessary), osteopathy helps the patient to fully recover, get rid of residual pain and undergo full rehabilitation as soon as possible, and return to normal life as soon as possible.
The more experience the osteopathic doctor has in treating joint problems and his qualifications, the more likely a favorable outcome for the patient. Our clinic employs only certified specialists with extensive experience under the guidance of leading doctors of osteopathy and teachers of osteopathic schools in Russia: RVSHOM, SPb MAPO.

Wrist pain - main causes and treatment
Despite its apparent simplicity, the wrist is a complex complex joint with many small items... Subtle damage to any component of the articular complex can lead to the fact that the wrist is sore for a long time and does not respond to standard therapy protocols.
From an osteopathic point of view, the treatment of wrist pain should begin with an accurate diagnosis of its cause: which tendon or bone has deviated from its place, how far, which adjacent tissues are affected, etc.
Subluxation of the extensor ulnar tendon
The extensor ulnar muscle of the wrist passes in the sixth canal of the dorsum of the forearm, where it is held in the ulnar groove by the fibrous sheath. With a subluxation of the tendon, this sheath breaks. The mechanism of injury usually includes flick palm up, bending or abducting the palm to the side.
Patients with such an injury complain of pain in the wrist on the dorsum, clicking sounds when rotating the hand (supination and pronation), edema or swelling. Routine radiographs usually do not provide any information, on MRI you can see damage to the fibrous membrane of the tendon and its displacement from its place.
Treatment of acute subluxation should be carried out with a mandatory period of immobilization of the wrist using splints or elastic materials. Rehabilitation measures can be started after 6 weeks, when the rupture of the tendon sheath has healed.
Stenosing synovitis
 With stenosing synovitis of the ulnar extensor of the wrist, pain is observed from the back side, with synovitis of the flexor - from the palmar side of the wrist. It is not very common, but the likelihood should be considered in the diagnosis of wrist pain.
With stenosing synovitis of the ulnar extensor of the wrist, pain is observed from the back side, with synovitis of the flexor - from the palmar side of the wrist. It is not very common, but the likelihood should be considered in the diagnosis of wrist pain.
With stenosing synovitis, patients complain of diffuse pain throughout the wrist, swelling of the back of the wrist. Many of the patients are athletes whose activity involves frequent repetitive wrist movement. Symptoms can be reproduced by asking the patient to resist pressure on the back of the hand. MRI helps in making the diagnosis.
Conservative treatment of synovitis includes removing the load on the wrist joint, bandaging or splinting (depending on the severity), cold compresses, injections of anti-inflammatory drugs in the wrist area, and NSAIDs. Osteopathy can be a good addition to shorten the rehabilitation period.
Arthrosis-arthritis of the radioulnar joint
Can be seen as pure arthritis inflammatory nature(for example, in rheumatoid arthritis) and degenerative changes with the development of chronic arthrosis. The causes of arthrosis can be frequent repetitive trauma, the consequences of acute trauma (fractures, dislocations, etc.).
In arthrosis-arthritis of the radioulnar joint, pain in the wrist usually appears during rotational movements of the hand (supination-pronation), as well as when the hand is squeezed with the other hand. On radiographs, you can see the narrowing of the joint space, osteophytes (bone outgrowths), subchondral cysts. With clear radiographs, CT and MRI help to identify the lesion.
Osteopathy treatment is possible in the absence of clear signs acute autoimmune process, rheumatoid arthritis, acute injuries. In other cases, soft tissue techniques can significantly improve the condition of the joint.
Damage to triangular fibrous cartilage
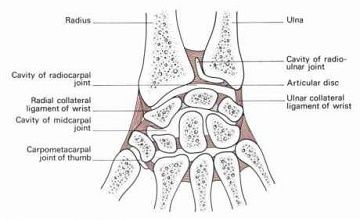
 Triangular fibrous cartilage connects the radius to the styloid process of the ulna and has great importance for movement in the wrist joint and its stability. TPC lesions can be traumatic and degenerative.
Triangular fibrous cartilage connects the radius to the styloid process of the ulna and has great importance for movement in the wrist joint and its stability. TPC lesions can be traumatic and degenerative.
Traumatic injuries of TPC occur with sharp twisting movements of the hand, stretching of the wrist, with a large axial load (falling on outstretched hand). They can appear both independently and in combination with arm fractures and dislocations.
Degenerative changes are usually the result of chronic stress trauma to the wrist. Patients with TPC trauma usually complain of pain and clicking when moving the hand, degenerative changes may be asymptomatic.
Treatment also includes splinting and anti-inflammatory drugs. If they are ineffective, they resort to arthroscopic operations to suture the lesions. Osteopathy can be effectively applied in the form soft techniques at almost any stage.
Fractures, dislocations and joint instability
Wrist pain can be a symptom of a dislocation or fracture of almost any of the bones in the carpal articular complex. On radiographs or CT scan, you can find:
- displacement (subluxation) of the head of the ulna (pain arises from the palmar side);
- fractures and cracks of the ulna and radius, styloid process;
- fractures of the wrist bones: scaphoid, triangular, hooked, etc.
- subluxation, fracture of the pisiform bone;
- lunar-triangular or mid-carpal instability and so on.
All fractures are treated in traumatology by reduction and immobilization. Osteopathy can significantly help at the stage of recovery, relieve pain and swelling, and improve joint trophism. Minor subluxations can also be successfully corrected in an osteopathic session, but serious ones should be treated in traumatology with anesthesia.
Other causes of wrist pain
- Vascular necrosis of the scaphoid or lunate bones of the wrist (Kienbeck's disease). Should be ruled out for chronic wrist pain in the absence of visible trauma. Necrosis occurs due to impaired blood flow in these wrist bones for unclear reasons. Surgical treatment.
- Enchondroma, ulna, or wrist osteoma are very rare. Enchondromas are often asymptomatic and can be detected on x-rays. However, in some cases, the patient may be concerned about pain in the area of the tumor.
- Soft tissue ganglion cysts in the wrist can compress blood vessels or nerves and cause pain.
- Ulnar artery thrombosis can result from trauma. The pain appears at night and with repetitive hand movements, the blood supply to which is disrupted. Treatment requires surgical restoration of blood flow through the artery.
- Infringement of the ulnar nerve can occur as a result of activity associated with strong squeezing of objects with the hand (sticks, oars, canes, etc.). Pain in the wrist is rare, usually manifested by numbness in the little finger and impaired mobility of the IV-V fingers.
Wrist pain and osteopathy
Sometimes wrist pain does not go away even after surgery, and arm function deteriorates over time. Osteopathy helps not only to reduce pain, but in many cases to eliminate the cause - joint subluxation, tendon displacement, muscle tone disorder. Neural techniques help to speed up the recovery of damaged nerves, release them from the pinched canal, and improve the condition of nerve fibers. Fascial methods of treatment can significantly improve the function of the ligaments and fascia in the wrist area, and neutralize the consequences of injuries. As auxiliary osteopathic methods can be used for almost any cause of pain in the arm.
The knee is a large joint with a complex structure. The pain that occurs in this joint can indicate the presence of a wide variety of pathologies, it can appear after excessive stress or talk about some kind of abnormality in the body.
In view of such a variety of reasons for the occurrence of discomfort in the knees, it is necessary to be able to distinguish in which case you need to quickly apply for medical help and when treatment can be done at home.
Factors of occurrence and symptoms
Knee pain can be quite varied, as an injury can damage any bones, tendons, cartilage, ligaments or other structures that make up the joint. To pick up the right way treatment, it is important to understand the manifestations and understand which doctor you need to seek help from.
A common cause of pain is chronic illness. The patient will not be able to independently diagnose such a pathology.
However, such diseases have characteristic symptoms, thanks to which one can suspect them of initial stage development, so that there is no subsequent progression of pathology.
Arthrosis and arthritis
After forty years, knee pain in 30% of cases may appear due to the presence of arthrosis. In this case, discomfort often occurs in both legs at the same time.
The factors behind this condition lie in:
- a variety of bone tumors and other injuries that occur after exercise;
- age-related changes;
- intra-articular disorders in cartilage and bones.
At first, the joint practically does not hurt, and severe discomfort appears only occasionally. But over time, other signs appear:
- limited mobility;
- stiffness in the knee, resulting sutra;
- crackle that appears during movement.
Moreover, pain in the patella can be reminiscent of itself when a person climbs stairs, when getting up from a chair and moving short distances.
In this case, as a result of the progression of the disease, deformation of the knees occurs. But when a person is resting, pain is almost not felt, therefore, at night he can sleep peacefully.
Arthritis refers to a group of diseases characterized by pain, swelling and inflammation in the knees. Most people often develop osteoarthritis.
At the beginning of the disease, the joints rub against each other while walking, resulting in discomfort. The reasons for the appearance of osteoarthritis lie in the decrease in the amount and decrease in the quality of the intra-articular substance, which is necessary to lubricate the structure of the knee.
Usually, early development the disease appears after frequent joint damage or due to excess weight... TO characteristic manifestations diseases other than painful sensations, arising in the process of movement, includes swelling, and at an advanced stage, the patient cannot lean on the sore leg or even just stand. Moreover, the intensity of symptoms increases gradually, it can take months and years.
The next most common type of arthritis is rheumatoid arthritis. Basically, it develops if there is a failure in the immune processes. But the factors behind the appearance of this disease have not yet been identified.
With this type of arthritis, in addition to the knee joints, other joints are also affected, as a rule, on the hands. In this case, the pain can go from large joints to small ones.
And during an exacerbation, the patient feels strong pain even in lung time touching the affected area.
At initial symptoms arthritis, you must immediately consult a doctor, since if appropriate treatment is not carried out, then the person will become disabled.
Gout and Becker's cyst
Gouty arthritis occurs due to chronic excess in human body uric acid. When an attack of illness occurs in the knees, sharp pain and redness.
At the same time, the local body temperature rises, and the joints become overly sensitive, which is felt even after the slightest touch to them.
If proper treatment is not carried out, then this condition can last for several weeks. But with the right therapy painful symptoms may disappear within a few days.
- This is an inflammation of the ligaments located in the popliteal fossa. This phenomenon is noticeable visually, it is a dense formation. It is worth noting that the cyst is visible only when the knee is unbent, and during flexion it decreases or becomes completely invisible. The appearance of a tumor is associated with factors such as:
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- trauma to the menisci;
- damage to the cartilage tissue in the joint;
- osteoarthritis;
- joint injury.
At the beginning of the development of the disease, pain occurs infrequently. However, with a gradual increase in the size of the cyst, its intensity increases, the foot in the affected leg becomes numb and it becomes difficult to bend the fingers. All this happens due to the compression of the nerve endings located under the knee.
Pain after exercise, dislocation and sprain
After intense exertion, knee pain can appear at any age. This happens because of a single over-stimulation of the knee and after a constant load such as movement or pressure.
Dislocations are often common among professional dancers and athletes. After all, it is during these types of activities that the knees have to experience tremendous stress.
With injuries of this kind, the knee is significantly deformed and swollen. The main manifestations of dislocation include:
- inability to move your leg;
- strong and sharp pain(it even hurts a person to stand);
- painful to move the leg at minimum distances.
In some cases, the knee can be adjusted on its own: back to the mechanism of the old injury. However, in order to control all manipulations, it is advisable to seek medical help. But it is worth noting that in case of dislocation with rupture or damage to the ligaments, an operation is necessary.
- Another reason due to which pain in the knee joint may appear. As a rule, the reasons for this phenomenon lie in ordinary situations:
- after falling to one knee;
- direct blow to the knee joint;
- unsuccessful turn of the leg with force (this is a common phenomenon for people involved in great sports).
Compared to dislocation, stretching causes swelling and pain after touching the affected area. In addition, it hurts a person to move a leg, and sometimes a characteristic crackling sound is heard when moving a limb. After a few hours, swelling and bruising appear.
It is worth noting that when stretching, ice compresses can be applied to the injured area, but only after the incident.
And, for example, a day after the fall, there is no point in performing such a procedure.
Meniscus injury and vascular pain
For damage to a part of the meniscus or its rupture, one unsuccessful turn or squat is enough. With such an injury, the patient cannot fully straighten his leg. In such a situation, you should immediately consult a traumatologist.
But sometimes the damage goes away by itself, without the help of a doctor after 5-7 days. However, it should be noted that trauma to the meniscus is a serious phenomenon, since repeated infringements can cause arthrosis. Unfortunately, in this case, even removing the meniscus surgically turns out to be ineffectual.
Vascular knee pain occurs due to poor circulation. This phenomenon is diagnosed in about 5-10% of people who go to doctors with complaints of knee discomfort.
With vascular pain, the joint does not swell and remains mobile. Usually, discomfort in the joints occur due to:
- long stay in the cold;
- colds;
- physical activity;
- a sharp change in the weather.
As a rule, conditions of this kind are characteristic of adolescents, since during intensive growth bone tissue, their vessels do not have time to develop rapidly.
But after 18 years, the stabbing pain significantly decreases, however, in some cases, such discomfort accompanies a person for many years.
Examination for knee discomfort
If the knee hurts, then to establish an accurate diagnosis, you need to conduct an extensive examination, which begins with palpation and questioning the patient. Further, taking into account the described symptoms, the doctor conducts additional research, consisting of:
- and computed tomography;
- radiography;
- ultrasound examination;
- general and biochemical analysis blood;
- puncture of the joint or puncture biopsy of the bone (for this purpose, a little intra-articular fluid is taken for examination).
Treatment
In the event of pain in the knee joint, there is no single method of therapy. The treatment regimen directly depends on the factors of the appearance of uncomfortable sensations.
And in each a separate case is necessary individual approach... But there is simple rules which must be adhered to if in knee joints painful sensations appear:
- Wear elastic bandage or bandage;
- Use medicines anti-inflammatory effect;
- Apply special ointments that have a warming effect and apply hot compresses to the affected area, if recommended by the attending physician.
- Always warm up before sports training or direct load on the joint.
- Reduce the intensity of the load to such an extent that the discomfort is completely absent.
Whatever the pain in the knee, it is very serious symptom that cannot be neglected. Because the damage can be something more significant than a simple sprain.
