Amniotic fluid rate by week. The index of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid) is most accurately determined by ultrasound
Most of the time that the child spends in the mother's womb, he stays under the protection of the placenta, or, as it is also called, the amniotic sac. Amnion constantly produces amniotic fluid, in which the baby will remain until the very moment of his birth. Such a liquid protects the baby from bacteria and viruses, creates favorable conditions for its development, allows it to stay warm and comfortable during the most important and crucial months of its life.
The temperature of the amniotic fluid is maintained by the body at a constant level and is about 37 ° C, provided that the woman is healthy. As for the amount of fluid, this indicator is constantly changing and directly depends on what week of pregnancy the expectant mother is in. It is also worth noting that the larger the baby becomes in the womb, the more fluid the amnion produces. The rate of amniotic fluid during pregnancy is 1-2 liters at 36 weeks of the term, but in the following days this figure may decrease slightly, because during preparation for childbirth, the body begins to actively remove fluid.
Among the constituents of the amniotic fluid, you can find a wide variety of components, for example, proteins and carbohydrates, hormones and enzymes, fats and salts, various vitamins and glucose. The amniotic fluid also contains oxygen, carbon dioxide, immunoglobulin, baby's waste products and many other substances. The composition of the liquid is always unstable and changes at least every 3 hours. In addition, the composition of the waters also depends on the duration of pregnancy, because at different periods of development, the baby needs different substances.
Why amniotic fluid is needed
The role of amniotic fluid in the growth and development of the fetus is difficult to overestimate, because thanks to the many functions that this substance performs, the child is not only under constant protection, but also has the opportunity to be born. We will tell you more about the functions of the amniotic fluid below:
- One of the purposes of amniotic fluid is the metabolism between maternal and child organisms. Those components that are required by the baby for his development and maintenance of vital activity come to him precisely through the amniotic fluid. Processed food, excreted from a tiny organism, also first enters the amniotic fluid, and only then is completely removed from the woman's body. Waste products that enter the liquid also include the upper scales of the epidermis, particles of primordial lubricant, baby hairs and components of the mother's blood.
- The second important function of the amniotic fluid is its ability to protect the unborn baby from all kinds of harmful factors in the surrounding world. Due to the constant temperature of the waters, the child in the womb will not be able to freeze, moreover, he is not afraid of physical influences such as blows, squeezes, pressure. Amniotic fluid eliminates the risk of squeezing the umbilical cord, gives the baby the ability to move freely in the mother's belly.
- The female body also made sure that the amniotic fluid is always absolutely sterile. Due to the fact that viruses, bacteria and other pathogens do not penetrate them, the baby is reliably protected from diseases. Sterility is mainly maintained due to the constant renewal of the composition of the liquid, which occurs at least every 3 hours.
- The amniotic fluid not only helps the baby to grow and develop in a safe environment, but also directly participates in the process of delivery. First, the so-called anterior waters, by their pressure on the uterus, ensure a better opening of its cervix. Secondly, while the baby is trying to be born, the amniotic fluid protects him until the very moment of birth. Thirdly, during the passage of the child through the birth canal, water plays the role of lubrication, facilitating this process.
In addition to the above useful functions, amniotic fluid also has important diagnostic value. Having carried out certain analyzes of waters, the doctor can find out a lot of necessary information regarding the health of the child and the characteristics of his development. Thanks to diagnostics, it is possible not only to establish the sex of the baby and his blood group, but also to obtain information about possible hereditary diseases or other deviations, the development of which can be prevented even at the stage of pregnancy.
Volume, composition, degree of transparency, color and consistency - all these parameters of amniotic fluid can be found using the necessary analyzes. In addition, in the case of some pathologies, when emergency delivery is required, with the help of such a diagnosis, it is possible to establish the degree of the child's readiness for birth. Based on the data obtained, a decision is made to use special medical equipment to support the life of the baby for a certain period.

Pathology of amniotic fluid
Low water during pregnancy
The condition when there is little amniotic fluid during pregnancy is called oligohydramnios. This pathology can occur if the amnion produces less fluid than is excreted from the body. It should be said that such a disease is not so common and accounts for no more than 1% of cases in the total number of pregnancies. Low water is a serious problem that requires attention and timely treatment. If this phenomenon is not eliminated, certain complications may arise:
- First, the pressure of the amniotic fluid on the uterine canal is significantly reduced, which, in turn, leads to difficulties in the delivery process.
- Secondly, oligohydramnios is fraught with complications such as premature birth. A child born prematurely will need special medical care.
- Low water is also dangerous because the baby is not able to move normally, which increases the risk of breech presentation of the fetus.
- A very frequent companion of this pathology is hypoxia - a lack of oxygen necessary for the child. The consequences of hypoxia are growth retardation and fetal abnormalities.
As a rule, it is not possible to notice such a pathology on your own, since oligohydramnios has almost no symptoms that are palpable physically. Occasionally, a woman with a similar problem may feel minor pain in the abdomen, but often this manifestation is simply absent. It is possible to identify the disease with the help of ultrasound, which is why the timely delivery of tests and the passage of scheduled ultrasounds are so important for a pregnant woman.
If it is possible to detect oligohydramnios before 28 weeks, examination of the body of the expectant mother will make it possible to find out the cause of the pathology and, if possible, eliminate it. So that the child does not suffer from a lack of oxygen, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible - this will allow the gas exchange and uteroplacental blood flow to be established. In the process of therapy, the doctor monitors the baby's condition and sometimes, in case of emergency, prescribes an early caesarean section.
Let's take a closer look at what are the causes of oligohydramnios during pregnancy:
- the presence of hypertension in the expectant mother;
- significant overweight of a pregnant woman;
- infections and inflammatory diseases;
- abnormalities in the development of the placenta;
- inflammation in the pelvic area;
- polycystic kidney disease of the fetus, anomalies in the development of its genitourinary system.

Polyhydramnios during pregnancy
About as rare as low water, the opposite pathology can also occur - polyhydramnios. This problem occurs in 1-1.5% of pregnant women and represents an excess of amniotic fluid relative to the norm.
Polyhydramnios is of two types:
- Chronic polyhydramnios is characterized by the fact that the amount of amniotic fluid arrives gradually. If the pregnant woman is healthy and feeling normal, the doctor may prescribe diuretics for her - special medications that are responsible for removing fluid from the body. In addition, the doctor prescribes adherence to a certain diet, which involves reducing the amount of salt in the diet. It is important to adhere to all the doctor's recommendations, because polyhydramnios can turn into unpleasant consequences. An overly enlarged uterus oppresses other organs, disrupting their work. In addition, polyhydramnios sometimes causes circulatory disorders in the female body, it complicates labor and can cause profuse bleeding after childbirth.
- The second type of polyhydramnios is acute. It is characterized by a sudden increase in amniotic fluid that occurs over several hours. As a rule, such a disease makes itself felt with the following symptoms: abdominal pain, severe edema, shortness of breath. With such a pathology, a woman needs hospitalization. While in hospital, the pregnant woman adheres to bed rest, which makes it possible to reduce the risk of premature birth. If acute polyhydramnios is characterized by the incessant flow of water and threatens the health of a woman and her baby, abdominal amniocentesis can be used as a remedy for the problem. In the process of such an operation, the placenta is pierced and excess fluid is removed.
Among the causes of pathology are the following:
- diabetes mellitus in a pregnant woman;
- conflict between rhesus blood of mother and baby;
- carrying twins;
- the child has genetic diseases;
- getting the infection to the fetus in utero;
- disruption of the fetal bladder, which manifests itself in the excessive production of amniotic fluid even in the early stages of pregnancy.

Leakage of amniotic fluid during pregnancy
Another pathology of amniotic fluid is leakage. This condition is characterized by the appearance of abundant liquid discharge from the female genital tract. The amniotic fluid is distinguished from ordinary secretions by transparency, colorlessness, a very liquid consistency, and no odor. Often, leakage of amniotic fluid during pregnancy does not manifest itself with any symptoms, except for the aforementioned discharge. But the expectant mother may not pay attention to such manifestations, because during pregnancy, abundant vaginal discharge is the norm.
In the event that a woman suspects a similar pathology in herself, she should immediately get an appointment with a doctor. The specialist will prescribe tests that will determine the nature and origin of the discharge, after which the leakage of water can be refuted or confirmed. By the way, in pharmacies you can find special tests with which such an analysis is carried out independently. But it is recommended to use this method only if it is absolutely impossible to consult a doctor for some reason. In addition, if the test gives a positive result, the pregnant woman will somehow have to go to the hospital for inpatient treatment.
If a similar phenomenon makes itself felt after 36 weeks of the term, doctors can stimulate childbirth, and the baby will be born prematurely for only 1 week. If the leakage of water happened in the early stages, the woman needs hospitalization in order to maintain the pregnancy for the maximum possible period. Strict bed rest should be observed during hospitalization. In some cases, when the term is too short and it is not possible to maintain the pregnancy for a long time, the situation is fraught with abortion.
The most common causes of amniotic fluid leakage are infections of the genital tract. To avoid such a risk, it is very important to monitor your health, observe the rules of personal hygiene, engage only in safe sex and periodically get tested for the presence of pathogenic flora in the vagina.

Amniotic fluid is green
Clarity, colorlessness, odorlessness and liquid consistency are characteristics of normal amniotic fluid. Slightly cloudy amniotic fluid during pregnancy can be observed at the very end of the term and is also considered the norm, since their appearance is due to the presence of epidermal scales and flakes of lubricant entering the fluid from the baby's body. But in the event that the amniotic fluid has acquired a greenish tint, we can talk about pathology. The green color of the amniotic fluid is often caused by particles of original feces, which the baby secretes if he does not have enough oxygen. Hypoxia is considered one of the most dangerous conditions of the fetus, because it not only interferes with the normal development of a small organism, but sometimes becomes the cause of irreparable consequences.
Possible reasons why amniotic fluid can turn green are described below:
- If during the entire pregnancy the waters were normal and turned greenish already during childbirth, very often this can be the cause of stress for the baby. Experiencing childbirth, the baby sometimes secretes meconium, due to which the liquid acquires a characteristic shade.
- As mentioned above, the cause of this pathology during pregnancy can be such a dangerous condition as fetal hypoxia. It is sometimes caused by over-term pregnancy. If the baby is in the womb for too long, the amniotic fluid becomes old and does not function properly. Because of this, the baby is experiencing a lack of oxygen.
- Sometimes a greenish tint to the amniotic fluid indicates infection. This happens if the expectant mother has had a cold, flu, bronchitis, has had an infection of the genitourinary system or any other inflammatory disease.
- Very rarely, genetic diseases of the fetus can be the cause of the abnormal shade of amniotic fluid.
Green waters can be hazardous to babies if they swallow contaminated fluids. If such a phenomenon was found late in pregnancy, the woman may be prescribed a caesarean section. If such a pathology is detected in the early stages, you should first identify the causes of the condition and take measures to eliminate them. Since the amniotic fluid is often updated, it will be enough to eliminate the causes of the appearance of the pathology in order to correct the situation.
In the event that the pregnant woman has lost green waters, the process of delivery should be started as soon as possible in order to eliminate the risk of oxygen starvation and the associated consequences.

Tests of amniotic fluid during pregnancy
There are several ways to assess the state of amniotic fluid during pregnancy, the simplest of which is ultrasound. This procedure does not harm the health of the woman and her fetus, but is the least informative. With the help of ultrasound, you can only visually determine the transparency of the liquid and establish its amount. For more detailed information, other studies are being carried out, which we will consider in more detail:
- Amniocentesis is a complex procedure in which fluid is drawn directly from the amniotic fluid. To do this, a woman's belly is pierced with a special tool and a small amount of amniotic fluid is pulled out. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia. Then this material is sent to research, where immunological, biochemical, cytological and hormonal analyzes are performed. Depending on the location of the amniotic fluid, doctors determine the puncture site, and during the procedure, an ultrasound device is used. Amniocentesis is performed if there is a conflict between the blood rhesus of the mother and the child, as well as if there are suspicions of chromosomal pathologies, hypoxia, and genetic diseases. Such an analysis is also carried out when the age of the future woman in labor exceeds 40 years, as well as in the case when it becomes necessary to determine the maturity of the child's lungs. Amniocentesis is not used if a woman has any inflammation in her body, if a pregnant woman suffers from pathologies in the development of the uterus or from diseases of the genitourinary system. If there is a threat of miscarriage, the procedure should also be abandoned.
- Amnioscopy is another method for determining the state of the amniotic fluid. During the procedure, the doctor inserts an amnioscope into the cervix and examines the lower pole of the placenta and amniotic fluid. With the help of the procedure, you can establish the amount of amniotic fluid, examine its color and identify the presence of hypoxia in the fetus.

Amniotic fluid during pregnancy. Video
The amniotic index is an indicator that characterizes the amount of amniotic fluid during pregnancy. Amniotic fluid is also called amniotic fluid: the liquid natural environment provides the baby with everything necessary for the formation of strong immunity from birth. Its volume is of great diagnostic value when examining a woman during pregnancy.
The biological environment surrounding the fetus in the mother's womb is multifunctional - the child cannot survive without it. This is what amniotic fluid is remarkable for:
- "Feeds" the growing organism. In terms of energy value, amniotic fluid can be called an ideal breeding ground for the fetus at all stages of its development. For some time after conception, useful substances from the amniotic fluid enter the body of the embryo, simply being absorbed through its cells. When the fetus grows up, he himself regularly swallows the surrounding fluid in small portions;
- protects the fetus from the mechanical influence of the world on the other side of the mother's belly - pressure and shocks coming from the outside are not terrible for the baby;
- protects the fetus from developing infection. The amniotic fluid is rich in immunoglobulins that help keep your baby healthy. In addition, 100% closure of the fetal bladder and constant renewal of amniotic fluid provide the baby with a sterile environment for a safe existence;
- provides the child with complete freedom of action in the uterine cavity;
- mutes harsh sounds from the outside world.
Main characteristics of amniotic fluid
As pregnancy progresses, the quantitative and qualitative indicators of amniotic fluid are constantly changing. Deviations of these figures from the norm are of great importance for doctors - on the basis of this information, one can assume the presence or absence of certain pathologies in the expectant mother. Timely diagnosis can reduce the risk for a woman and her baby even before childbirth or, in extreme cases, after the baby is born.
The amniotic fluid index (AFI) is an indicator that reflects how much amniotic fluid fills the fetal bladder at a given stage of pregnancy.
In addition, experts take into account other characteristics of the natural liquid environment in which the fetus develops:
- Color and transparency. Normally, the amniotic fluid is colorless or slightly yellowish. This liquid is quite transparent, and the presence in it of a certain amount of fragments of the skin and hair of the fetus is not a deviation from the norm.
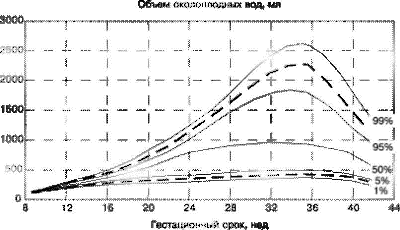
- Quantity. The volume of amniotic fluid is determined by the gestational age, so when they talk about this indicator, the trimester of pregnancy must be taken into account. For example, the norm of the amniotic index at 22 weeks of an "interesting" position is 145 ml and this is the average. The lower limit reaches 89 ml and the upper limit reaches 235 ml. the volume of water increases by 40 - 45 ml every day up to 32 weeks. When the AFI reaches its highest value (144 ml at 32 weeks), the amount of fluid begins to gradually decrease. A few days before the birth of the baby, the indicators of amniotic fluid fluctuate between 0.5 - 1.500 ml.
- The presence of hormones.
- Biochemical and cytological indicators of the composition.

Diagnosis of amniotic fluid
Analysis of amniotic fluid using ultrasound allows you to diagnose two common abnormalities during pregnancy - oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios, as well as take timely measures to eliminate them. During an ultrasound scan, the specialist will determine the amniotic fluid index and establish the frequency of the vertical pocket. If the indicators exceed the normal limits or, conversely, less than them, the conclusion indicates polyhydramnios or low water.
What is a vertical pocket and what is its size for? The vertical pocket is the longest section of free water that lies between the baby and the anterior abdominal wall. It is undesirable for the limbs or umbilical cord of the fetus to be located in this area. The permissible length of the vertical pocket is 5 - 8 cm.
Amniotic index rate during pregnancy
To assess the volume of amniotic fluid using the amniotic fluid index, the gynecologist will divide the belly of the expectant mother into 4 sections, drawing two conditional perpendicular lines that intersect in the navel. Then, in each of the four zones, he will determine the index of the largest vertical pocket. The final index value is calculated by adding up the values of all pockets.
The rate of the amniotic index is calculated by week, starting from a period of 16 weeks. With an increase in the gestational age, the AFI indicators will also increase: the highest indicator will be at 32 weeks - 77 - 169 ml. Amniotic index rates are shown in the table.

If the AFI indicators do not coincide with the specific periods of pregnancy, the expectant mother is diagnosed with oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios.
Deviation during pregnancy: oligohydramnios
This pathology accompanies the bearing of a child quite often. The amniotic index with oligohydramnios is slightly or significantly underestimated. Moderate oligohydramnios is diagnosed when the volume of amniotic fluid differs slightly from the normal AFI. The situation can be corrected with the help of a special diet and adjusting the daily routine, then the amount of water will soon return to normal and will not affect the child's health in any way.
Malnutrition is considered pronounced if the amniotic fluid index during pregnancy is significantly less than the standard indicator. In this case, the pregnant woman is urgently sent to the hospital - the likelihood of developing complications of the child is too high. Severe lack of water can cause underdevelopment of vital organs and systems, significant curvature of the skeleton.
In addition, lack of water threatens the child with a number of other complications, including:
- developmental delay;
- fusion of the fetus with the fetal membrane;
- hypoxia;
- underweight at birth;
- drying out of the child's skin due to lack of water;
- intrauterine fetal death.
When a significantly underestimated AFI was found over a long period (30-34 weeks), serious pathologies of the child's development are most likely already present, therefore, the question of artificial termination of pregnancy is often raised, since treatment, unfortunately, will not bring positive results.
Why oligohydramnios develops
There are many factors that directly or indirectly affect the development of oligohydramnios during pregnancy. Let's list the most likely ones:
- insufficient development of the membranes;
- reduced water production;
- abnormalities in the development of the child (problems with the kidneys and skeleton);
- high blood pressure in a pregnant woman;
- bacterial infections that have penetrated the amniotic fluid;
- pregnancy with twins or triplets;
- uneven maturation of the placenta;
- overburdening;
- impaired metabolism in a pregnant woman;
- excess weight of the expectant mother.

Signs of pathology
Low water does not manifest itself to such an extent that the pregnant woman immediately suspects that something was wrong - the clinical picture of the deviation in this case is blurred. With severe lack of water, a woman may suffer from weakness, dry mouth, and frequent nausea. Sometimes the expectant mother feels pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies when the baby moves.
During a diagnostic study of a pregnant woman with oligohydramnios, the doctor will certainly note that the patient's uterus is too small for the current gestational age, and the fetal movement is significantly constrained. An ultrasound scan is used to confirm the diagnosis.
Specificity of treatment of oligohydramnios
Correction of oligohydramnios begins with an assessment of the test results - this is the only way a doctor can establish the cause of what happened, determine the degree of the disease and the condition of the child. Only then can a treatment plan be developed.
If pregnancy proceeds against the background of obesity and impaired metabolism in a woman, she is prescribed a special sparing diet, healthier nutrition, vitamin therapy and drugs that stimulate the blood supply to the membranes of the placenta. Moderate polyhydramnios can be treated on an outpatient basis, therapy of severe pathology is carried out exclusively in stationary conditions.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, physical activity and physical activity are minimized; in most cases, a woman is shown bed rest. During the treatment of oligohydramnios, the expectant mother will often do ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound - these procedures will help to notice unwanted metamorphoses in the body of the mother and her child in time. When, as a result of an ultrasound examination, it turns out that at 33 weeks (and later) the AFI values are too low, and the child, meanwhile, is ready to be born, the doctor will most likely decide on an early birth.
Low water during pregnancy. Video
Deviation during pregnancy: polyhydramnios
With polyhydramnios, the IAI indicators are significantly overestimated. About 1% of pregnant women face such a problem when more amniotic fluid appears than necessary. The deviation can only be detected by ultrasound examination. Statistics say that a third of pregnancies from 1% end in miscarriages.
The reasons for the development of polyhydramnios
Doctors find it difficult to say exactly what underlies the pathology, but they still identified the main risk groups. Here are the diseases in which there is a high likelihood of developing polyhydramnios:
- chromosomal breakdowns;
- chronic diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- all stages of diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of infectious origin;
- diseases of the genitourinary system;
- Rh-conflict between a pregnant woman and a fetus;
- TORCH infections;
- kidney disease;
- severe anemia;
- severe toxicosis;
- multiple pregnancy;
- anomalies of intrauterine development of the child.

Forms of pathology
Depending on the rate of development, polyhydramnios is acute and chronic.
The acute form of the deviation develops very rapidly - literally within a few hours. This is a very serious problem, since its consequences are irreversible: the fetus either dies in the second trimester of pregnancy, or survives, but is born with severe developmental disabilities.
The chronic form of polyhydramnios does not develop immediately, therefore, with timely diagnosis, doctors have time to intervene in this process and save the child. Often, the deviation does not make itself felt in any way, and the expectant mother needs to very carefully monitor her well-being in order to go to the hospital with the slightest suspicious symptoms.

You can suspect the development of pathology by the following signs:
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- "Stone" in the lower abdomen;
- general weakness, rapid fatigability;
- swelling in the legs;
- dyspnea;
- fast heart rate;
- the appearance of a huge number of stretch marks on the skin;
- big belly (more than 110 - 120 cm in volume);
- enlargement of the uterus prematurely;
- persistent constipation.
Only a timely response to what is happening and competent treatment will help a woman to inform her baby.
The danger of polyhydramnios
A pathological condition can threaten a pregnant woman and her child with the following problems:
- Miscarriage or artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Extremely severe toxicosis in late pregnancy.
- Fetoplacental insufficiency, due to which the full development of the child is impossible.
- Massive bleeding.
- Placental abruption. As a result of her premature aging, the child is deprived of nutrients and vital oxygen.
- Premature birth. This is very dangerous, since not all premature babies are able to fight for life.
- Insufficient labor activity or its complete absence.
For a child, the consequences of polyhydramnios are no less dangerous. Here's what can happen due to this pathology:
- The fetus will not be positioned correctly in the uterus, because of which the natural delivery will have to be replaced with a caesarean section.
- Entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord, which can lead to its death.
- Acute hypoxia of the child.
- Development of heart and central nervous system abnormalities.
- Infectious diseases of the fetus.

Features of the treatment of polyhydramnios during pregnancy
To improve the condition of the expectant mother with polyhydramnios, doctors will first of all conduct a comprehensive examination of her - it is necessary to establish and eliminate the cause of what happened.
In parallel with the main course of treatment, the patient is prescribed a multivitamin preparation with mandatory vitamins C, E and a group of B vitamins in its composition, preparations containing magnesium, diuretic drugs and, possibly, some antibacterial drug of a broad spectrum of action. Usually, with a chronic course of polyhydramnios, the child can be saved.
Every woman who is preparing to become a mother should at least in general terms understand what the amniotic index means during pregnancy. Often it is this kind of ignorance that prevents pregnant women from realizing how important it is to be on the lookout for a baby. Even the smallest suspicious symptoms in your well-being cannot be ignored, because behind them there may be a serious illness that threatens the well-being of the mother and baby. With the help of modern diagnostic procedures, doctors have a chance to detect and eliminate the problem in time, and the determination and assessment of the amniotic fluid index during pregnancy is one of them.
Amniotic fluid (low water and polyhydramnios)
Amniotic fluid is a liquid biologically active medium that fills the cavity of the fetal bladder formed by the membranes, surrounds the fetus during its development in the maternal body and is a product of secretory activity amnion(embryonic membrane).
The intensive exchange of amniotic fluid and the complexity of the chemical composition, along with the placenta, ensure the normal intrauterine development of the fetus. Changes in the composition and quantity of amniotic fluid not only reflect organic and functional disorders of the feto-placental complex, but also accompany pathological processes in the mother and fetus.
Despite the great interest shown in the study of amniotic fluid, the mechanism and source of their formation are still not entirely clear. According to some authors, the first portion of amniotic fluid is the result of secretion chorion(i.e. the outer embryo membrane that surrounds the embryo and is formed at the initial stages of gestation), as evidenced by their visualization at the 3rd week of pregnancy. Starting from the 5th week, amniotic fluid is included in the amniotic fluid, the amount of which progressively increases. Until the 13-14th week of pregnancy, amniotic fluid is the result of secretion of the amniotic membrane.
According to modern concepts, in the II trimester of pregnancy, the main component of amniotic fluid is the maternal plasma transudate, which penetrates the placenta. It is also known that, starting from the II trimester, amniotic fluid is partially replenished with fetal urine. The cells of the amnion, the umbilical cord, and the lungs of the fetus are also involved in the formation of amniotic fluid. From the 16th week of intrauterine development, a general increase in the amount of amniotic fluid occurs due to a slightly greater excretion of fluid through the kidneys and lungs compared to their swallowing by the fetus.
In the third trimester, fetal diuresis has a certain value in the formation of amniotic fluid and by the end of pregnancy is 500-600 ml per day. At the same time, resorption of amniotic fluid occurs at the same time, part is absorbed by the fetus (up to 400 ml of amniotic fluid), part enters the body of the pregnant woman through the membranes. The main amount of fluid is removed from the amniotic cavity by the paraplacental route.
Amniotic fluid, containing metabolic products, flows through the amnion wall, intercellular spaces and blood vessels of the smooth chorion into the decidua parietalis and from it into the venous system of the pregnant woman. Amniotic fluid is completely renewed every 3 hours. Their amount depends on the gestational age and ranges from 300 ml to 1.5 liters. So, according to S. Campbell, K. Liz (2004), at 10 weeks. the volume of amniotic fluid is 30 ml, at the 20th week - 300 ml, at the 30th week - 600 ml, at the 38th week - 1000 ml, at the 40th week - 800 ml, at the 42nd week - 350 ml. The decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid during prolongation has not yet been clearly explained.
Amniotic fluid has a number of critical functions that ensure the normal development of the fetus:
- protection of the fetus from mechanical damage;
creating conditions for fetal movements and preventing limb contractures;
prevention of adhesions between the fetus and the amnion;
creating conditions for the development of the fetal lungs, when the fluid moves in two directions in the fetal bronchioles (the absence of amniotic fluid in the second trimester of pregnancy leads to lung hypoplasia).
Malnutrition... The amount of amniotic fluid less than 500 ml is called oligohydramnios or oligohydramnios, and their complete absence is called anhydramnios. According to modern literature data, the prevalence of water scarcity ranges from 0.3 to 5.5%. With congenital malformations of the fetus, this condition occurs 10 times more often. The widespread introduction of the ultrasound method of prenatal diagnostics into clinical practice has increased the detectability of oligohydramnios during pregnancy.
Usually low water is explained:
- insufficient development of the epithelium lining the amniotic membrane, or damage to its secretory function;
according to some authors, oligohydramnios occurs against the background of hypertension, and the frequency of development and the severity of oligohydramnios depend on the duration of the course of vascular pathology and the degree of its compensation; with hypertension, oligohydramnios is often combined with fetal malnutrition;
the causes of low water can be infectious-inflammatory extragenital and gynecological diseases of the mother - 40%, metabolic disorders (obesity of the III degree) - 19.6%, placental insufficiency and anomalies of the urinary system in the fetus.
- early oligohydramnios - diagnosed by ultrasound in the period from 18 to 24 weeks; it is due to the functional failure of the membranes;
- late oligohydramnios - diagnosed by ultrasound after 24 - 26 weeks, when oligohydramnios occurs due to hydrorhea due to partial rupture of the membranes.
According to E.N. Kondratyeva(1999), a decrease in the volume of amniotic fluid at different stages of pregnancy is due to three pathogenetic options:
- parietal membranitis, which is characterized by inflammatory changes in the membranes (chorioamnionitis, chorioamniodeciduitis, choriodeciduitis) with extensive necrosis of the amniotic epithelium; in 74% of cases, this form of oligohydramnios develops against the background of infectious and inflammatory diseases of the mother and in 25% of cases it is combined with placental insufficiency and the syndrome of fetal growth retardation that has developed against them;
- atrophic lesion of the decidua, which is characterized by a predominant lesion of the decidua with the relative safety of the amniotic epithelium, compact layer and cytotrophoblast (CT); this form of oligohydramnios often develops against the background of maternal vascular pathology, as well as metabolic disorders and is combined with placental insufficiency and FGR in 46% of cases;
- a dysontogenetic form of changes in the membranes, which is characterized by the absence of inflammatory changes in the presence of a significant number of atrophic villi in the CT layer; this form of oligohydramnios often develops against the background of infectious and inflammatory diseases, transferred immediately before conception and in the first trimester of pregnancy, and is characterized by the most frequent combination of oligohydramnios with placental insufficiency (86%) and fetal malformations (54%).
Analysis of the course of pregnancy and childbirth in pregnant women with oligohydramnios, carried out by various authors, revealed a number of severe complications:
- the number of cases of threatened miscarriages and premature birth ranges from 36 to 48.8%;
- weakness of labor activity - a frequent complication of the course of labor with oligohydramnios (9.6%); some authors associate the appearance of primary weakness in labor with the formation of a flat bladder in childbirth and a violation of the processes of retraction and distraction of the muscle fiber of the cervix;
- with low water, bleeding is much more often observed due to residues in the uterine cavity of the membranes and placental tissue - in 4% of cases;
- an increase in the number of cases of bleeding during childbirth leads to an increase in such surgical interventions as manual and instrumental examination of the walls of the uterine cavity - in 12.6%;
- an increase in the number of ruptures of the cervix with a reduced amount of amniotic fluid - in 24% of women in labor.
Most authors note an increase in the number of cases of congenital malformations of the fetus (from 17 to 13%) during pregnancy complicated by oligohydramnios (R. Romero et al., 1994; N. Damato et al., 1993). An insufficient amount of amniotic fluid in the second trimester of pregnancy leads to the development of fetal lung hypoplasia. Severe oligohydramnios limits the motor activity of the fetus and is often complicated by joint contractures and anomalies of the facial skeleton. With a pronounced lack of water between the skin of the fetus and the amnion, adhesions are formed, which acquire the character of strands or threads. By linking individual parts of the placenta, umbilical cord and parts of the fetus, amniotic constrictions can lead to a variety of fetal abnormalities (deformities or amputation of limbs or fingers).
Polyhydramnios- one of the forms of obstetric pathology associated with excessive accumulation of amniotic fluid in the amniotic cavity (more than 2 liters). This pathology occurs in 0.13 - 3% of cases. The focusing of the attention of specialists in ultrasound diagnostics to this problem is due to the fact that echography is the most accurate method for diagnosing polyhydramnios and under echographic control, monitoring and treatment of pregnant women with this pathology is carried out.
Polyhydramnios can be acute or chronic. Acute polyhydramnios is extremely rare and, as a rule, occurs at 16 - 27 weeks of gestation, more often observed in monozygous twins, infectious diseases, especially viral ones. Chronic polyhydramnios is more common. It is usually first diagnosed in the third trimester of pregnancy and has a more blurred clinical picture. The number of cases of chronic polyhydramnios ranges from 0.17 to 2.8%.
Causes of polyhydramnios not fully disclosed. However, the pathological conditions of the pregnant woman and the fetus, in which polyhydramnios are observed, have already been quite clearly defined. The analysis of numerous literature data made it possible to identify the following possible causes of polyhydramnios:
- maternal reasons:
- isoimmunization;
- diabetes;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
Placental causes:
- chorionangioma;
- "placenta surrounded by a roller";
Fruit reasons:
- multiple pregnancy;
- fetal-fetal transfusion syndrome;
- congenital malformations of the fetus;
- chromosomal abnormalities and hereditary diseases;
Idiopathic polyhydramnios ( ! the frequency of idiopathic polyhydramnios is the lower, the more extensive and thorough the examination was carried out in the antenatal period).
The most accurate diagnosis of polyhydramnios can be made during an ultrasound scan. Polyhydramnios is characterized by the presence of large echo-negative spaces in the uterine cavity. In this case, as a rule, there is an increased motor activity of the fetus, its limbs, internal organs, and the umbilical cord are better visualized. With moderately expressed polyhydramnios, the size of the vertical "pocket" is 8 - 18 cm, with pronounced polyhydramnios, this indicator exceeds 18 cm. AFI with polyhydramnios is more than 24.
In 1984, P. Chamberlain et al.... the following ultrasound options for the amount of amniotic fluid were presented, depending on the depth of their pocket:
- pocket depth of waters<1,0 см - маловодие;
- 1 - 2 cm - reduced (borderline) amount of water;
- > 2.0 cm, but<8,0 см - нормальное количество вод;
- > 8.0 cm - polyhydramnios.
- moderate - pocket depth 8.0 - 11.0 cm;
- average - 12 - 15 cm;
- heavy - 16 cm and more.
Amniotic fluid begins to form at 5-6 weeks, and its volume changes during pregnancy.
If at 5-6 weeks the volume of amniotic fluid is about 5 ml, then at 38 weeks this volume is about 1 liter, and at 40 weeks about 600 ml.
In this article, we will consider what the amniotic fluid consists of, what they are for, what methods are there for the study of amniotic fluid. We will also analyze the common pathologies of amniotic fluid.
Why amniotic fluid is needed
Amniotic fluid plays a critical role in the development and protection of the baby throughout pregnancy and c.
- protection of the fetus from mechanical damage;
- creating conditions for fetal movement and preventing limb contractures;
- adhesion prevention;
- the presence of amniotic fluid prevents compression of the umbilical cord;
- amniotic fluid creates the necessary "purified" environment for the baby, protects the fetus from infections. The amniotic fluid volume is renewed every 3 hours, and thus, this environment always remains "fresh";
- creating conditions for the development of the lungs of the fetus;
- fetal nutrition;
- the baby "throws" all the products of processing into the amniotic fluid, and this makes it possible to remove these products through the excretory system of the mother, thereby cleansing the child's body;
- when it’s time for childbirth, the amniotic fluid weighs on the cervix, forcing it to open. During childbirth, the amniotic fluid makes it easier for the baby to move through the birth canal.
What amniotic fluid is made of
Throughout pregnancy, the composition and volume of amniotic fluid changes. The composition includes: scales of the epidermis, vellus hair and primordial lubricant of the fetus, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, enzymes, vitamins, glucose, hormones and waste products of the fetus.
Amniotic fluid, main indicators
Amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid is produced by the amnion (fetal bladder) throughout pregnancy. But the amount (volume) of water is not the same at different times. The largest volume of amniotic fluid is at about 36 weeks, and is about 1-1.5 liters. By the amount of amniotic fluid, conditions such as polyhydramnios and low water are diagnosed. The amount of water is determined by. The approximate norms for the volume of amniotic fluid (depending on the duration of pregnancy) are shown in the diagram below.
Amniotic fluid color
Normally, the amniotic fluid is colorless, odorless, colorless, transparent, sometimes (a variant of the norm) may be slightly whitish. It is also normal to have a small amount of white flakes. The color of the amniotic fluid becomes clear when water is poured out, or when water is leaking. The presence of "flakes" can be seen on the ultrasound. When the amniotic fluid flows out or leaks, dangerous symptoms are:
- unpleasant smell of waters and their green color. Green "color" indicates oxygen starvation of the fetus, and requires urgent delivery (). Green waters come from the fact that during oxygen starvation, the child secretes original feces (meconium) into the water and it paints the water in a characteristic color.
- bright yellow color, - indicates the development of the Rh conflict, or the incompatibility of the mother and child by blood groups. Requires urgent therapy in a hospital setting.
- red color - indicates the onset of bleeding (due to premature placental abruption or for other reasons). Urgent hospitalization of the pregnant woman is required, and, as a rule, urgent delivery.
At the onset of labor, the amniotic fluid may have bloody streaks (mostly transparent). This is a variant of the norm, since when the cervix is dilated, micro-ruptures can occur.
Biochemical, cytological and hormonal composition of amniotic fluid
The composition changes during pregnancy, and experts can draw conclusions about the condition of the fetus, as well as the work of the mother-placenta-fetus system, by the composition of the amniotic fluid. Also, according to these indicators, various genetic pathologies can be diagnosed. For the analysis, amniotic fluid is needed, it is carried out using the amniocentesis procedure.
Transparency of amniotic fluid
A small amount of flakes in the amniotic fluid is considered normal. These "flakes" begin to be seen on ultrasound from about the middle of the second trimester. By the end of pregnancy, their number is growing. These are particles of the skin of the fetus, elements of the original lubricant.
Amniotic fluid, research methods
Ultrasound. During an ultrasound scan, the specialist can check the transparency and volume of the amniotic fluid. The presence of a large amount of flakes in the waters (in the third trimester) can be a symptom of fetal hypoxia. According to the results of ultrasound, the index of amniotic fluid is also calculated and such pathologies of the amount of amniotic fluid as polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios are diagnosed.
Amnioscopy. During the amnioscopy procedure, the amniotic fluid is examined visually using an amnioscope. Amnioscopy makes it possible to assess the color of the amniotic fluid, as well as to determine the composition of impurities (meconium, grease, flakes, sometimes blood). During the examination, an amnioscope is inserted into the cervix. The procedure is performed without anesthesia, on a gynecological chair. Amnioscopy is performed on the whole.
Indications for amnioscopy: fetal prolongation, chronic fetal hypoxia.
Contraindications to amnioscopy: inflammation in the cervix,.
Amniocentesis.The procedure for the study of amniotic fluid, in which the fetal bladder is pierced and 20-25 ml of amniotic fluid is taken for analysis. With such a sampling of material, hormonal, biochemical and cytological analysis of amniotic fluid can be performed. An indication for such a study may be suspicion (by ultrasound) of genetic abnormalities of the fetus. The puncture site is determined based on the ultrasound results (the largest "free" pocket of amniotic fluid, without umbilical cord loops).
Of the listed research methods, ultrasound and amnioscopy are not invasive methods (without a puncture), but amniocentesis is an invasive method.
Amniotic fluid, pathology
By the volume of amniotic fluid, such pathologies are diagnosed.
- Polyhydramnios is a pathology of amniotic fluid, during which the amniotic fluid exceeds the norm in volume. In domestic medical practice, a volume of 1.5 liters is considered the norm (with a normal full-term pregnancy). In foreign practice, - 2 liters. Polyhydramnios can be acute or chronic (depending on the course and growth of symptoms). You can read in detail about the consequences, symptoms, diagnosis and causes of this pathology in the article.
- Low water is a pathology of amniotic fluid, in which the volume of amniotic fluid (with advanced pregnancy) is lower than 500 ml (in domestic medical practice), and less than 300 ml in foreign practice.Distinguish between moderate and severe lack of water. To make a diagnosis (according to ultrasound), the doctor calculates the so-called "amniotic fluid index", AFI. According to the timing of occurrence, oligohydramnios can occur in the first, and in the second, and in the third trimester. You can read in detail about the consequences, symptoms, diagnosis and causes of this pathology in the article.
During pregnancy, the baby in the tummy bathes in the amniotic fluid. In addition to being so comfortable for the baby, and thanks to the waters, he can move, they perform several more important functions:
Water acts as a shock absorber and protects the fetus from external influences (shock and shock);
The liquid protects the umbilical cord from compression between the fetus and the walls of the uterus;
The lower pole of the fetal bladder, in which the so-called anterior waters (that is, located in front of the fetal head) are located, participates in labor, performing the function of a hydraulic wedge and facilitating the opening of the cervix;
The presence of amniotic fluid makes contractions less painful for both the mother and the fetus.
In the formation and maintenance of the amount of amniotic fluid (amniotic fluid), the fetal surface of the placenta and fetal membranes, which can secrete and absorb water, take part, as well as the fetus itself, which swallows amniotic fluid and excretes urine. Thus, the waters are constantly being renewed. A complete exchange of amniotic fluid is carried out approximately every 3 hours.
Normally, the amount of amniotic fluid is 600-1500 ml. The maximum amount is determined at 37-38 weeks, then it decreases slightly. With low water, the amount of amniotic fluid is less than 500 ml, with polyhydramnios - more than 1.5-2 liters. Low water is extremely rare, polyhydramnios - more often.
Causes of polyhydramnios and low water:
The reasons for polyhydramnios can be:
Infection (both sexually transmitted diseases and chronic infection in the mother's body);
Fetal malformations and chromosomal abnormalities of the fetus (most often with polyhydramnios, defects of the nervous and digestive systems are detected);
Diabetes mellitus in the mother;
Rh-conflict pregnancy;
Feto-placental insufficiency;
Low water can occur when:
Postterm pregnancy;
Infectious process;
Fetal malformations (with low water more often there are malformations of the excretory system and the kidneys of the fetus);
Chronic hypoxia and fetal growth retardation, since at the same time it secretes little urine;
Hypertension in the mother;
Feto-placental insufficiency;
Smoking during pregnancy;
When low water is detected, it is imperative to exclude a violation of the integrity of the fetal bladder and leakage of amniotic fluid.
Often the reasons that caused high or low water are more dangerous than the “wrong” amount of water itself, therefore, a thorough examination is always carried out to identify the cause.
Clinic of low and polyhydramnios
With polyhydramnios the size of the abdomen increases. Because of this, stretch marks occur more often, the venous pattern on the abdomen is enhanced. During examination, the doctor hardly probes parts of the fetus, the heartbeat is not heard clearly. The fetus easily changes its position (unstable position of the fetus). A woman with severe polyhydramnios may feel difficulty breathing, heaviness, increased heart rate.
With polyhydramnios, an abnormal position of the fetus is often observed: transverse or oblique position, or breech presentation. Excessive free movement of the fetus in a large amount of fluid can lead to entanglement of the umbilical cord around the neck or trunk of the fetus. Due to the strong stretching of the membranes, premature rupture of amniotic fluid and premature birth are more common. Due to the strong stretching of the uterus, its contractile activity worsens, which can lead to weakness of labor. In severe cases, when there is a lot of water, due to the pressure of the enlarged uterus on the lungs and difficulty in breathing, the mother may experience hypoxia (lack of oxygen in the blood), which causes or aggravates fetal hypoxia.
With little water the size of the abdomen lags behind the norm. The motor activity of the fetus may decrease, as the baby is "cramped". Sometimes fetal movements can hurt a woman.
With oligohydramnios, a complication such as compression of the umbilical cord between the fetus and the walls of the uterus can occur, which can lead to acute oxygen deficiency and fetal death. Since with a small amount of water, the fetus is more clamped in the uterus and its movement is difficult, the newborn often has a curvature of the spine, problems with the hip joints, torticollis, clubfoot. If oligohydramnios appears already in the second trimester of pregnancy, intrauterine fetal death often occurs.
The lower pole of the fetal bladder with oligohydramnios is flat and cannot perform its function as a hydraulic wedge during childbirth; on the contrary, it delays the advancement of the head, therefore, there is a weakness in labor.
 Usually, the amount of amniotic fluid is determined by ultrasound.
According to ultrasound, such indicators as the vertical pocket (VK) and the amniotic fluid index (AFI) are determined. The vertical pocket is the maximum area of free fluid between the fetus and the anterior abdominal wall. Normally, it is 5-8 cm. AFI is a more accurate indicator, it is the sum of the values of vertical pockets in four quadrants of the uterus (the uterus is conventionally divided into 4 parts, and the maximum vertical pocket is measured in each). The norms of this index are different for each gestational age (may differ slightly on different devices). On average, the AFI is normally 5-24 cm.
Usually, the amount of amniotic fluid is determined by ultrasound.
According to ultrasound, such indicators as the vertical pocket (VK) and the amniotic fluid index (AFI) are determined. The vertical pocket is the maximum area of free fluid between the fetus and the anterior abdominal wall. Normally, it is 5-8 cm. AFI is a more accurate indicator, it is the sum of the values of vertical pockets in four quadrants of the uterus (the uterus is conventionally divided into 4 parts, and the maximum vertical pocket is measured in each). The norms of this index are different for each gestational age (may differ slightly on different devices). On average, the AFI is normally 5-24 cm.
VK and IAZH are not 100% methods for diagnosing high and low water. Sometimes errors are possible.
Since both polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios can be signs of fetal abnormalities, the anatomy of the fetus is especially carefully studied by ultrasound. If, in addition to the "wrong" amount of water, some other signs of chromosomal abnormalities are detected, the woman is sent for cordocentesis - a blood test from the umbilical cord, in which the genotype of the fetus is determined.
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause that caused the change in the amount of water. Usually, complex therapy of fetal-placental insufficiency is carried out, since both with oligohydramnios and with polyhydramnios, it almost always takes place.
If an infection is detected, antibiotic treatment is prescribed. With this pathology, antibiotic treatment can be prescribed, even if no infection has been detected (which often causes bewilderment among expectant mothers). The fact is that it is impossible to examine for all existing microorganisms, and if the doctor does not see any other causes of polyhydramnios, treatment is carried out against infection, since this is the most common cause of polyhydramnios.
If fetal malformations that are incompatible with life are detected before 28 weeks, the woman is offered an abortion.
If other causes are identified (increased pressure in the mother, diabetes mellitus, Rh-conflict, etc.), the underlying disease is treated.
An increase or decrease in the fluid you drink does not affect the amount of amniotic fluid.
Delivery
By themselves, high and low water are not indications for a cesarean section. If the fetus does not suffer and the position of the fetus is correct (longitudinal position, cephalic presentation), childbirth is carried out through the natural birth canal.
In childbirth, both with oligohydramnios and with polyhydramnios, amniotomy (instrumental opening of the fetal bladder) is indicated. With low water, the lower pole of the fetal bladder is opened, since its membranes are pulled over the head of the fetus and delay its progress (flat fetal bladder), with polyhydramnios, a large amount of fluid stretches the uterus and interferes with its contractile activity, therefore, part of the water must be released. With polyhydramnios, amniotomy should be performed carefully, water is released a little, otherwise, with a sharp outflow of water, there may be complications such as prolapse of the umbilical cord, arms or legs of the fetus or placental abruption.
Even despite the performed amniotomy, with polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios, there is often a weakness of labor and protracted labor, so you have to resort to stimulation of labor, and if the stimulation is ineffective - to a caesarean section.
With polyhydramnios, due to poor contraction of the uterus, the risk of bleeding in the postpartum period is increased. For prevention, reducing drugs (oxytocin, methylergometrine) are prescribed.
Early delivery is resorted to in cases of impaired fetal condition according to ultrasound, CTG and Doppler and the ineffectiveness of the therapy for several days.
As they say, everything is good in moderation. And amniotic fluid is no exception. Therefore, if their quantity is "wrong", it is imperative to undergo examination and treatment.
