Prevention of premature birth. Premature birth - causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention. Premature birth test
Description:
Termination of pregnancy between the 21st and 37th weeks is considered preterm labor. At the same time, a viable, but premature baby is born. Up to 25% of women do not carry pregnancy, of these cases, 5-10% are premature births.
Premature birth is dangerous for the mother and fetus, since it causes serious complications (perinatal morbidity and mortality, internal hemorrhages, etc.)
Symptoms:
A woman may notice the appearance of pulling pains in the lower abdomen and in the lower back. The pains are sometimes cramping in nature, i.e. we can talk about the beginning of the contractions. In some cases, childbirth begins with the outflow of amniotic fluid or with the discharge of a mucous plug. In any of these cases, urgent hospitalization in a maternity hospital is required.
Causes of occurrence:
Primarily an infection. Normally, the uterine cavity is sterile. Any inflammatory process makes the wall of the uterus defective, so pregnancy continues as long as the wall of the uterus can stretch, and then the body tries to get rid of the embryo.
That is why it is not necessary to spare money, time and effort for examination for the presence of infection. Every woman - ideally even before pregnancy - should be examined for infectious diseases, especially those that are often asymptomatic (carriage of chlamydial, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, toxoplasma infection, herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus). Special attention should be paid to women with a history of chronic and acute inflammation of the uterine appendages and endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterine body), intrauterine interventions (abortion, diagnostic curettage), as well as cases of spontaneous abortion. In the presence of an inflammatory process, it naturally needs to be cured. The drugs and procedures selected by the doctor will help expel the infection from the body even before conception. If, for some reason, the necessary tests were not done before conception, then when diagnosing pregnancy, you should definitely undergo an appropriate medical examination, and in the future you should not neglect regular examinations. The sooner the presence of microbes in a woman's body that can cause premature birth or potentially dangerous to the fetus is revealed, the better. Modern medicine has a significant arsenal of tools in order to reduce the risk and infection of the fetus.
The second common cause of premature birth is ICN (isthmus - "isthmus", the place where the body of the uterus passes into the cervix, cervix - "uterus"), that is, the inferiority of the muscular layer of the cervix, which, during a normal pregnancy, plays the role of a kind of sphincter (retaining ring ), which does not allow the embryo to "leave" the uterine cavity. ICI is congenital (very rare) and acquired. What can cause the development of ICI? The reasons are quite commonplace: injuries of the isthmus and cervix during abortion, especially when the first pregnancy is interrupted, deep ruptures of the cervix in previous births (this can happen, for example, during childbirth with a large fetus, the imposition of obstetric forceps), gross forcible expansion of the cervical canal during diagnostic manipulations in the uterine cavity (hysteroscopy, i.e. examination of the uterine cavity using a special device - a hysteroscope; endometrial scraping), that is, any injury to the muscular layer of the cervix.
Very often, ICI is formed with hyperandrogenism - an increased content of male sex hormones in the blood, which are produced in the adrenal glands of the mother, and later, of the fetus.
Infections and ischemic-cervical insufficiency are the main, but not the only factors that cause premature birth. Often, endocrinopathies lead to premature birth - mild dysfunctions of the endocrine glands - the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, pituitary gland (with gross violations, women, as a rule, cannot get pregnant on their own).
Also, premature birth can occur when the uterus is overstretched, caused by multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, and a large fetus.
Heavy physical work, a chronic stressful situation at work or at home, any acute infectious disease (influenza, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, especially with an increase in body temperature, etc.) can also provoke an abortion.
Treatment:
For treatment are prescribed:
With a premature onset of contractions, first of all, tocolytic (that is, reducing the tone of the uterus) drugs are prescribed - partusisten, ginipral. First, these drugs are administered intravenously, and when the contractions stop, it is possible to switch to tablet forms. These medications are usually taken before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Magnesia sulfate, a 10% solution of ethyl alcohol and some other drugs are also used as agents that reduce the tone of the uterus.
At the second stage of treatment, they try to eliminate the very cause of premature birth. When an infection is detected, antibacterial drugs are prescribed (depending on the type of infection), sedative (that is, calming) therapy - in order to break the vicious circle: the fear of losing a child is added to the objective factors that increase the tone of the uterus, which, in turn, further increases the tone uterus.
With the development of ICI for up to 28 weeks of pregnancy, "tightening" sutures are applied to the cervix, which prevent the ovum from "falling out" from the uterus. Sutures are applied under short-term intravenous anesthesia, while drugs are used that have a minimal effect on the child.
For a period of more than 28 weeks with a defective cervix, a special supporting Golgi ring is inserted into the vagina: it, without narrowing the cervix, holds the presenting part of the fetus, not allowing it to press on the cervix. Moreover, if the contractions have stopped, further opening of the cervix does not occur.
The complex of treatment always includes the hormonal drug dexamethasone (micro doses of this hormone are prescribed, so that side effects are practically excluded). Its action is aimed not at preventing premature birth, but at stimulating the "maturation" of the lungs in a child (so that he can breathe on his own if he is born prematurely).
A woman must always comply with bed rest, and in a hospital setting. In the diet, it is better to avoid irritating, spicy, fatty, indigestible food.
The situation is more difficult with premature rupture of amniotic fluid. At a gestation period of up to 34 weeks, if it was possible to suppress labor activity, the condition of the woman and the fetus is normal, there is no increase in body temperature, there are no inflammatory changes in the blood, it is possible to preserve and prolong pregnancy with the obligatory prescription of antibacterial drugs to prevent infectious complications. (The fact is that the discharge of water indicates a violation of the integrity of the fetal bladder. This means that the vagina is now communicating with the uterine cavity, that is, the path of infection is open, and the use of antibacterial drugs is a vital measure.)
Despite the current medical equipment capable of saving the life of a premature baby weighing only 500 g, the diagnosis of the threat of premature birth instills fear in every pregnant woman. What threatens such a condition for a future woman in labor, is there a chance to prevent this variant of events and what you need to know about premature birth - the main topic of this article.
According to the international classification, delivery is called premature between 22 and 38 gestational weeks. A few years ago, such a diagnosis was announced only after 28 weeks, since before that time the woman had a miscarriage and the baby died, because it was impossible to save him.
The outdated classification recognized premature birth from 28 to 37 weeks (the weight of the crumbs was more than 1 kg). If the child was born sooner, his weight was equal to 0.5-1.5 kg and he lived or lived for more than 7 days, such a case was also counted as a premature delivery. In all other cases, late miscarriage occurred.
Now modern equipment allows you to take care of tiny babies weighing 500 g or more. For this, special boxes are used that play the role of the mother's body. But not all medical institutions have the necessary equipment and medicines. And nursing a premature baby is not cheap, so it is not always possible to save a newborn weighing less than 1 kg.
Depending on the gestational age, the threat of premature birth (code 060 for microbial 10) is:
- early labor process - starts at 22-27 gestational weeks; the fruit weighs from 0.5 to 1 kg;
- early premature birth - 28-33 weeks, the weight of the baby is close to 2 kg;
- full-fledged premature birth - gestational period 34-37 weeks; the child is already mature enough for a full life, his weight is about 2.5 kg.
Threat of premature birth and weeks of pregnancy
In order to dispel at least a little the fears of women about preterm birth, you can cite optimistic statistics on delivery at different stages of gestation. Less than 9% of all births are premature. And the fact that 8 out of 100 women in labor could not deliver the baby before the end of pregnancy cannot but inspire hope.
Of this number of preterm births, 7% occur between 22 and 28 weeks. Of course, it is very difficult to care for such babies and not everyone cares for them. But the prompt work of neonatologists and the presence of specialized equipment gives a chance to save a newborn.
About 30% of babies are born between 27 and 33 weeks of age. They are distinguished by high survival rates and quickly catch up with their peers who were born on time. But they are still unable to breathe fully and therefore need expensive treatment.
More than 60% of early births occur after 34 gestational weeks. Newborn crumbs are quite a bit lagging behind in weight, but their body works fully outside the womb. The survival rate of such children is close to 100%.

The threat of premature birth - causes
Creates unfavorable conditions for the further bearing of the fetus, and then the threat of premature birth, many factors. Sometimes this happens for unknown reasons, and sometimes it is possible to accurately identify and eliminate the provoking factor.
Consider the causes of the pathological course of pregnancy known to medicine:
- Endocrine diseases. There are several chronic disorders that can trigger premature delivery. This is an imbalance of female hormones, diabetes, hypo- or hyperthyroidism.
- Untreated sexually transmitted infections in a woman (for example, chlamydia, gonorrhea, ureaplasmosis, herpes) are often the culprits of unscheduled childbirth. And even if the woman's condition was stabilized, the risk of infection of the fetus and the formation of defects in it remains.
- Gynecological diseases during gestation. Cervical erosion, vulvovaginitis, endometriosis, adenomatosis, salpingitis and other pathologies create conditions for premature birth with an unfavorable outcome for a woman.
- Infections (for example, acute ARVI, viral hepatosis, carious teeth) are the source of a dangerous infection that disrupts the normal course of pregnancy.
- Progesterone deficiency. Lack of progesterone (a female hormone) causes miscarriage. The situation can be corrected by the regular reception of Utrozhestan with the threat of premature birth.
- Abnormal structure of the uterus. Congenital malformations, neoplasms, adhesions and physical deformity of the uterus caused by surgery most often provoke uterine contraction, as well as insufficiency of the cervical canal. A woman rarely manages to deliver a baby even up to 17 weeks, because under the weight of the fetus, the cervix opens and a miscarriage occurs.
- Non-infectious somatic diseases (for example, heart disease, deficiency of vitamins and amino acids, failure of the kidneys, liver, etc.). They cause depletion of the body and disrupt the course of pregnancy.
- Abnormal fetal development. Breakdowns at the genetic level and all kinds of defects often end in miscarriage in the first trimester. In some cases, the body decides to get rid of the defective fetus at a later date, and the woman starts labor. Most often, the threat of premature birth is created between 22 and 28 weeks.
- Complicated gestation. Multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, gestosis, abnormal fetal position and other conditions that aggravate pregnancy can pose a threat of premature birth.
- Improper behavior of a pregnant woman. Drinking alcohol, smoking, lifting weights, stress, inadequate sleep are frequent provocateurs of the threat of early childbirth.
Important! Any trauma in the abdomen can lead to the threat of premature birth. Therefore, a woman should be especially careful not to allow falls, bumps and other physical influences on the abdomen.

The first signs of a threat of premature birth
The clinical manifestations of the threat of premature birth at first are somewhat similar to the symptoms of miscarriage. If you turn to an obstetrician-gynecologist in time, the outcome is safe. Most often, a woman is sent to a hospital for conservation. It is difficult to predict how long you will have to lie with the threat of premature birth. There are times when the condition stabilizes and the woman is discharged, and it also happens that she remains in the hospital until the very birth.
If the first signs are ignored, the amniotic fluid flows out and the woman begins labor. In this situation, it remains only to wait for the birth of the baby and provide him with the help necessary for salvation.
To prevent unscheduled delivery, you should pay attention to the following symptoms of a threat of premature birth:
- Threatening premature birth can be recognized by barely perceptible pain below the navel, a feeling of heaviness or contraction in the uterus, a change in the motor activity of the fetus, and strange discharge (mucus with blood). Contacting a doctor and following his recommendations allows you to stop the pathological process. When the cervix is dilated or ischemic-cervical inferiority is diagnosed, a ring is placed on a woman with the threat of premature birth.
- Beginning premature labor. The symptomatic picture is much brighter. A woman notices severe pain in the lower back, cramping painful sensations appear in the lower abdomen. Discharge of the mucous plug, the outpouring of water, the development of bleeding is possible. The uterus usually softens and is already open. If, with the threat of premature birth, timely treatment is prescribed, there is a chance to postpone labor for a while.
- Started premature birth process. If the process of childbirth has begun, it can no longer be slowed down. And no injections with the threat of premature birth can prevent the early birth of a baby. A woman experiences all the symptoms of childbirth: severe pain, contractions, attempts.

The threat of premature birth: what to do?
At the appearance of the slightest symptoms of a threat of premature birth, a woman should consult a doctor. Timely care can save your baby's life. After all, even a few extra days spent in the womb can be decisive.
It is very dangerous to go to the hospital on your own. Any shaking on the road can aggravate the situation, so it is better to wait for the ambulance to arrive. It is also important that the woman is brought to a department that specializes in premature babies. If the threat is not eliminated, the child will have every chance to survive.
After calling an ambulance, you can take a sedative - a valerian pill or motherwort tincture. Two Nosh-pa tablets will not hurt either. Before the arrival of the doctors, it is better to be in a supine position and try not to worry.
After contacting an obstetrician-gynecologist, it is important to adhere to all recommendations and take the prescribed medications if there is a threat of premature birth. Any frivolity on the part of a woman can end in the loss of a child.
The support of relatives and the atmosphere in the family is especially important. It has long been proven that stress, moral violence at home, unreasonable experiences play an important role in the development of the threat of premature birth. Therefore, you need to take a responsible attitude to your psychological state and, if there is a need, ask for help from a specialist.

Treatment of the threat of premature birth
Therapy of the threat of early delivery is aimed at stopping and delaying the onset of labor. A woman is always hospitalized, and if there is still time to carry out preserving measures, drug treatment is prescribed. As a rule, it consists of a dropper with the threat of premature birth to reduce the uterine tone, sedatives and restorative drugs.
- Drug treatment involves tocolysis in women. This treatment consists in suppressing the contractile activity of the uterus, which allows you to temporarily suspend labor activity. First of all, a woman is injected intravenously with magnesium with the threat of premature birth. It quickly relaxes the smooth muscles of the body of the uterus, relieves soreness, and stops pathological contractions. This treatment is shown only at the initial stages of the development of the threat.
- They also use beta-adrenergic agonists, which also prevent premature birth. Ginipral, Fenoterol, Salbutamol are used with great success to stop the threat of premature birth.
- To enhance the effect of the latter, calcium channel blockers are prescribed. They are taken 30-40 minutes before the intravenous administration of adrenergic agonists. The most effective blocker is considered to be Nifedipine when there is a threat of premature birth. It is used only in the most critical period of pregnancy and is canceled after stabilization of the state. And Ginipral is transferred from intravenous administration to oral administration and is taken up to 36-38 gestational weeks.
Important! The formation of the threat of premature birth between 25 and 34 weeks involves the introduction of glucocorticoids, which help the respiratory system of the fetus to form more quickly. In order for a full-fledged opening of the alveoli of the lungs to occur in a premature baby, Dexamethasone is used with the threat of premature birth.
- Additionally, sedative therapy is carried out to stabilize the psycho-emotional background of a pregnant woman. The drugs allowed during pregnancy are Oxazepam and Diazepam.
- If a rapid growth of prostaglandins causing fetal rejection is diagnosed, a course of Indomethacin in the form of rectal suppositories is carried out from 14 to 32 weeks.
- Special attention is paid to the cause of this pathology. So, if the threat of premature birth is provoked by an infection, antibiotic therapy is performed. The use of antibiotics is also important when the water is draining up to 33 gestational weeks. This helps to protect the baby from infection. After 34 weeks, labor does not stop when the water leaves.
- If a woman has an isthmic-cervical inferiority of the cervical canal of the uterus, suturing is performed for up to 28 weeks under local lightened anesthesia. This helps prevent cervical dilatation and fetal prolapse. At a later gestational age, a Golgi ring is attached to the cervix.
Important! Even if a woman has a successful pregnancy, the threat of premature birth, although negligible, still exists. Therefore, it is important to know the first signs of such a pathology.

How to prevent premature birth
Not a single woman is insured against unscheduled childbirth, so no one canceled the prevention. Good preparation of your body before conception and correct behavior after pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of such a pregnancy outcome.
What do we have to do:
- Complete a comprehensive examination. At this stage, it is necessary to identify and cure chronic diseases, eliminate abnormal features of the uterus, treat genital infections.
- Timely visit the antenatal clinic and register. It is important to immediately discuss with the gynecologist the existing health problems, to provide the results of the examination at the planning stage.
- Avoid contact with sick people during pregnancy.
- Reduce or completely eliminate excessive physical activity, as well as isolate yourself from stressful situations.
- Complete all tests according to the pregnancy schedule.
- Monitor your well-being, and if you suspect, immediately consult a doctor.
Compliance with these simple rules allows you to reduce the chance of a threat of premature birth at any time.

As much as you would like to postpone the moment of hospitalization, remember that you are risking not only your own health, but also the life of your unborn baby. Don't ignore dangerous symptoms and don't be afraid to seek help. Doctors will do everything depending on them to keep your pregnancy. And you just have to follow their assignments unquestioningly.
Video "What is the reason for the development of the threat of premature birth"
Yes, in fact, just as well as timely. A woman may notice the appearance of pulling pains in the lower abdomen and in the lower back. The pains are sometimes cramping in nature, i.e. we can talk about the beginning contractions. In some cases, labor begins with outpouring of amniotic fluid or with discharge of mucous plug ... In any of these cases, urgent hospitalization in a maternity hospital is required.
What could be the cause of premature birth?
First of all infection 2 ... Normally, the uterine cavity is sterile. Any inflammatory process makes the wall of the uterus defective, so pregnancy continues as long as the wall of the uterus can stretch, and then the body tries to get rid of the embryo.
That is why it is not necessary to spare money, time and effort for examination for the presence of infection. Every woman - ideally even before pregnancy - should be examined for infectious diseases, especially those that are often asymptomatic (carriage of chlamydial, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, toxoplasma infection, herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus). Special attention should be paid to women with a history of chronic and acute inflammation of the uterine appendages and endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterine body), intrauterine interventions (abortion, diagnostic curettage), as well as cases of spontaneous abortion. In the presence of an inflammatory process, it naturally needs to be cured. The drugs and procedures selected by the doctor will help expel the infection from the body even before conception. If, for some reason, the necessary tests were not done before conception, then when diagnosing pregnancy, you should definitely undergo an appropriate medical examination, and in the future you should not neglect regular examinations. The sooner the presence of microbes in a woman's body that can cause premature birth or potentially harmful to the fetus, so much the better. Modern medicine has a significant arsenal of tools in order to reduce the risk of miscarriage and fetal infection.
The second common cause of premature birth is ischemic-cervical insufficiency , ICN (isthmus - "isthmus", the place of transition of the body of the uterus to the cervix, cervix - "uterus"), that is, the inferiority of the muscular layer of the cervix, which, during a normal pregnancy, plays the role of a kind of sphincter (holding ring) that does not allow the embryo " leave the uterine cavity. ICI is congenital (very rare) and acquired. What can cause the development of ICI? The reasons are quite commonplace: injuries of the isthmus and cervix during abortion, especially when the first pregnancy is interrupted, deep ruptures of the cervix in previous births (this can happen, for example, during childbirth with a large fetus, the imposition of obstetric forceps), gross forcible expansion of the cervical canal during diagnostic manipulations in the uterine cavity (hysteroscopy, i.e. examination of the uterine cavity using a special device - a hysteroscope; endometrial scraping), that is, any injury to the muscular layer of the cervix.
Very often, ICI is formed with hyperandrogenism - an increased content of male sex hormones in the blood, which are produced in the adrenal glands of the mother, and later, of the fetus.
Infections and ischemic-cervical insufficiency are the main, but not the only factors that determine premature birth... Often to premature birth lead endocrinopathies - mild dysfunctions of the endocrine glands - the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, pituitary gland (with gross violations, women, as a rule, cannot get pregnant on their own).
Also premature birth can occur when overdistension of the uterus caused by multiple pregnancies, polyhydramnios, large fetuses.
Hard physical work , chronic stressful situation at work or at home, any acute infectious disease (flu, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, especially with an increase in body temperature, etc.) can also provoke abortion.
What to do if premature birth has begun?
If alarming symptoms appear: abdominal pain, leakage of amniotic fluid, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Only in the hospital can doctors choose the right tactics for each specific case.
Before the arrival of the ambulance team, you can drink 2 no-shpa tablets or, if a woman is taking Ginipral, an additional tablet of this drug.
As a rule, in the hospital, they try to preserve the pregnancy, since every day spent in the womb increases the child's chances of survival.
What are doctors doing to stop preterm labor?
At premature onset of contractions first of all, tocolytic (that is, reducing the tone of the uterus) drugs are prescribed - partusisten, ginipral. First, these drugs are administered intravenously, and when the contractions stop, it is possible to switch to tablet forms. These medications are usually taken before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Magnesia sulfate, a 10% solution of ethyl alcohol and some other drugs are also used as agents that reduce the tone of the uterus.
At the second stage of treatment, they try to eliminate the very cause. premature birth... When an infection is detected, antibacterial drugs are prescribed (depending on the type of infection), sedative (that is, calming) therapy - in order to break the vicious circle: the fear of losing a child is added to the objective factors that increase the tone of the uterus, which, in turn, further increases the tone uterus.
With the development of ICI for up to 28 weeks of pregnancy, tightening sutures are applied to the cervix, which prevent the ovum from falling out of the uterus. Sutures are applied under short-term intravenous anesthesia, while drugs are used that have a minimal effect on the child.
For a period of more than 28 weeks with a defective cervix, a special supporting Golgi ring is inserted into the vagina: it, without narrowing the cervix, holds the presenting part of the fetus, not allowing it to press on the cervix. Moreover, if the contractions have stopped, further opening of the cervix does not occur.
The complex of treatment always includes the hormonal drug dexamethasone (micro doses of this hormone are prescribed, so that side effects are practically excluded). Its action is not aimed at preventing premature birth, but to stimulate the "maturation" of the lungs in the child (so that he was able to breathe on his own, if he is still born prematurely).
A woman must always comply with bed rest, and in a hospital setting. In the diet, it is better to avoid irritating, spicy, fatty, indigestible food.
The situation is more difficult with premature rupture of amniotic fluid... At a gestation period of up to 34 weeks, if it was possible to suppress labor activity, the condition of the woman and the fetus is normal, there is no increase in body temperature, there are no inflammatory changes in the blood, it is possible to preserve and prolong pregnancy with the obligatory prescription of antibacterial drugs to prevent infectious complications. (The fact is that the discharge of water indicates a violation of the integrity of the fetal bladder. This means that the vagina is now communicating with the uterine cavity, that is, the path of infection is open, and the use of antibacterial drugs is a vital measure.)
.jpg)
Do doctors always try to stop preterm labor?
No not always.
There are situations requiring early delivery due to the threatening condition of the woman. In severe forms of late toxicosis (gestosis), chronic diseases of internal organs, doctors often causepremature birth to save the life of both mother and fetus.
For a period of more than 34 weeks, with the outpouring of water, pregnancy also does not persist, but they try to very gently and carefully carry out childbirth.
What happens to a woman after a premature birth?
During the postpartum period 3 at premature birth, as a rule, is no different from that after timely delivery. It happens that a woman is detained in a maternity hospital for longer than the prescribed period, but this is due in most cases to the condition of the child, and not of the woman herself.
To all women after premature birth it is advisable to undergo a comprehensive examination, including tests for the presence of infectious diseases and the carriage of infectious agents, a study of the hormonal status. With ICI, it is necessary to perform hysterosalpingography (X-ray examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes after the introduction of a radiopaque substance into their cavities); in case of severe somatic diseases - to be examined by the appropriate specialists. Naturally, if violations are detected, you need to undergo a course of treatment.
During subsequent pregnancies, hospitalization in the maternity hospital in the so-called "critical time" is desirable. The greatest concern is the term of termination of the previous pregnancy. In addition, the following are considered critical periods: the first 2-3 weeks (fixation of the ovum in the uterine mucosa); 4-12 weeks (placenta formation); 18-22 weeks (intensive increase in the volume of the uterus); days corresponding to menstruation.
What happens to a baby after a premature birth? 4
At present, it is possible to nurture children whose body weight at birth is more than 1 kilogram, but, unfortunately, such small babies survive only in 50% of cases. Sometimes children weighing from 500 to 1000 grams are nursed, but this happens extremely rarely, in addition, it is a very, very expensive process. It is easier for pediatricians to care for children born with a weight of more than 1500 grams, since all their organs are more "mature".
At the second stage of nursing premature babies, they are often sent to children's hospitals.
1 Premature birth is usually reported after 28 weeks of gestation. Spontaneous abortion from conception to 28 weeks is called spontaneous abortion (miscarriage). For details on the threat of termination of pregnancy, see: A. Koroleva, "The threat of termination of pregnancy" / №1-2001.
2 For more information on infectious diseases see: J. Mirzoyan; S. Gonchar.
3 On the course of the postpartum period, see N. Brovkina's article "The Fourth Trimester" in this issue of the journal.
4 The subject of this article is premature birth, therefore literally a few lines are devoted here to nursing premature babies. A detailed material on the methods of nursing premature and low birth weight babies will be published in one of the next issues of our magazine.
In our country, threatening premature birth is an indication for hospitalization.
If it is possible to prolong pregnancy, treatment should be directed, on the one hand, to suppress the contractile activity of the uterus, and on the other, to induce the maturation of fetal lung tissue (at 28-34 weeks of gestation). In addition, it is necessary to correct the pathological process that caused the premature birth.
To stop tonic and regular contractions of the uterus, complex treatment and individual selection of therapy are used, taking into account the obstetric situation.
Drug-free treatment
An advantageous position on the left side, which helps to restore blood flow, reduce the contractile activity of the uterus and normalize the tone of the uterus in 50% of pregnant women with threatening preterm birth. Other studies have shown that prolonged bed rest, used as the only treatment, does not work.
There is no convincing data on the benefits of hydration (increased drinking regimen, infusion therapy), used to normalize placental blood flow to prevent premature birth.
Drug treatment
In the presence of conditions for conducting tocolytic therapy, it is given preference. The drugs of choice currently remain P-adrenergic agonists, the drug of the second stage is magnesium sulfate, which can quickly and effectively reduce the contractile activity of the myometrium.
r-Adrenomimetics can be used to delay delivery during the prevention of respiratory distress syndrome with glucocorticoids or, if necessary, to transfer the woman in labor to the perinatal center, where it is possible to provide highly qualified care for premature infants.
Of the p-adrenergic agonists, hexoprenaline, salbutamol, fenoterol, terbutaline are used.
Mechanism of action: stimulation of p2-receptors of smooth muscle fibers of the uterus, which causes an increase in the content of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and, as a consequence, a decrease in the concentration of calcium ions in the cytoplasm of myometrial cells. The contractility of the gadromuscular muscles of the uterus decreases.
Indications and prerequisites for prescribing p-mimetics:
- therapy of threatening and incipient preterm labor;
- a whole fetal bladder (an exception is the situation with leakage of amniotic fluid in the absence of chorioamnionitis, when it is necessary to postpone labor for 48 hours to prevent respiratory distress syndrome of the fetus with glucocorticoids);
- opening of the uterine pharynx by no more than 4 cm (otherwise, therapy is ineffective);
- live fetus without developmental abnormalities;
- no contraindications for the use of p-adrenergic agonists.
Contraindications:
Extragenital pathology of the mother:
- cardiovascular diseases (aortic stenosis, myocarditis, tachyarrhythmias, congenital and acquired heart defects, cardiac arrhythmias);
- hyperthyroidism;
- angle-closure glaucoma;
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Obstetric contraindications:
- chorioamnionitis (risk of generalization of the infection);
- detachment of a normal or low-lying placenta (danger of developing Couveler's uterus);
- suspicion of inconsistency of the uterine scar (risk of painless rupture of the uterus along the scar);
- conditions when prolongation of pregnancy is inappropriate (eclampsia, preeclampsia).
Fetal contraindications:
- fetal malformations incompatible with life;
- antenatal fetal death;
- fetal distress not associated with uterine hypertonicity;
- severe fetal tachycardia associated with the characteristics of the cardiac conduction system.
Side effects.
From the side of the mother's body: hypotension, palpitations, sweating, tremors, anxiety, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, hyperglycemia, arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, pulmonary edema.
From the side of the fetus / newborn: hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia after birth as a result of ineffective tocolysis and, as a consequence, hypoglycemia; hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, intestinal atony, acidosis. When using tablets in medium doses, side effects are not pronounced.
Hexoprenaline. With threatening and incipient preterm labor, it is advisable to start with an intravenous drip of the drug at a rate of 0.3 μg per minute, i.e. 1 ampoule (5 ml) - 25 μg of hexoprenaline is dissolved in 400 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution and injected intravenously, starting at 8 drops per minute, gradually increasing the dose until the contractile activity of the uterus decreases. The average rate of administration is 15-20 drops per minute, the duration of administration is 6-12 hours. 15-20 minutes before the end of the intravenous administration, oral administration of the drug is started at a dose of 0.5 mg (1 tablet) 4-6 r / day for 14 days ...
Salbutamol. Intravenous tocolysis: the rate of intravenous administration of the drug is 10 μg / min, then gradually, under the control of tolerance, it is increased with a 10-minute interval. The maximum allowable speed is 45 μg / min. The drug is taken orally at 2-4 mg 4-6 r / day for 14 days.
Fenoterol. For intravenous tocolysis, 2 ampoules of 0.5 mg of fenoterol are diluted in 400 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution (1 ml - 2.5 μg of fenoterol), which is administered intravenously at a rate of 0.5 μg / min. Every 10-15 minutes the administered dose is increased until the effect is achieved. The average rate of administration is 16-20 drops per minute, the duration of administration is 6-8 hours. 20-30 minutes before the end of intravenous administration, oral administration of the drug at a dose of 5 mg (1 tablet) 4-6 r / day for 14 days is started.
Terbutaline is diluted in 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Dose for 1 intravenous infusion of 5 mg. The rate of administration is a minimum of 5 mcg per minute, after 20 minutes it is increased by 2.5 mcg until the contractions stop, not exceeding the dose of 20 mcg per minute. Then the dose is reduced to the minimum, maintaining the achieved effect. The duration of the infusion is 8 hours. The drug is taken orally at 2.5-5 mg 4-6 r / day for 14 days.
There is evidence of the inexpediency of long-term oral use of β-adrenergic agonists due to desensitization of receptors. Some foreign authors recommend using tocolytics for 2-3 days, i.e. during the period when the prevention of fetal distress syndrome is carried out.
Intravenous tocolysis is performed with the woman on the left side under cardiac control.
During the infusion of any r-adrenergic agonists, it is necessary to control:
- mother's heart rate every 15 minutes;
- maternal blood pressure every 15 minutes;
- blood glucose level every 4 hours;
- the volume of injected fluid and urine output;
- the amount of blood electrolytes once a day; I auscultate the lungs every 4 hours;
The frequency of side effects as a manifestation of the selectivity of action on receptors depends on the dose of β-adrenergic agonists. When tachycardia, hypotension occurs, the rate of administration of the drug should be reduced, with the appearance of chest pain, the administration of the drug should be discontinued.
The use of calcium antagonists (verapamil) for the prevention of side effects of b-adrenomimetics in a daily dose of 160-240 mg in 4-6 doses 20-30 minutes before taking the tablet preparation of b-adrenomimetic has been substantiated.
Tocolytic therapy with magnesium sulfate is used if there are contraindications to the use of b-adrenergic agonists or if they are intolerant. Magnesium sulfate is an antagonist of calcium ions involved in the contraction of smooth muscle fibers of the uterus.
Contraindications:
- intracardiac conduction disorders;
- myasthenia gravis;
- severe heart failure;
- chronic renal failure.
Intravenous tocolysis with magnesium preparations: when preterm labor begins, intravenous tocolysis of magnesium sulfate is carried out according to the following scheme: 4-6 g of magnesium sulfate is dissolved in 100 ml of 5% glucose solution and administered intravenously for 20-30 minutes. Then they switch to a maintenance dose of 2 g / h, if necessary, increasing it every hour by 1 g to a maximum dose of 4-5 g / h. The efficiency of tocolysis is 70-90%.
With threatening premature birth, a solution of magnesium sulfate is injected intravenously at the rate of 20 ml of 25% solution per 200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution at a rate of 20 drops per minute or intramuscularly 25% solution 2 r / day, 10 ml ...
The tocolytic concentration of the drug in serum is 5.5-7.5 mg% (4-8 meq / l). In most cases, this is achieved at an injection rate of 3-4 g / h.
When carrying out tocolysis with magnesium sulfate, it is necessary to control:
- blood pressure;
- the amount of urine (at least 30 ml / h);
- knee reflex;
- respiratory rate (at least 12-14 per minute);
- the condition of the fetus and the contractile activity of the uterus.
If there are signs of an overdose (suppression of reflexes, a decrease in the frequency of respiratory movements), it is necessary:
- stop intravenous administration of magnesium sulfate;
- within 5 minutes intravenously inject 10 ml of a 10% solution of calcium gluconate.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have antiprostaglandin properties. Preferred in cases where it is necessary to provide a quick effect for transporting the patient to the perinatal center.
Indomethacin is used in the form of rectal suppositories of 100 mg, and then 50 mg every 8 hours for 48 hours. The drug is used orally (25 mg every 4-6 hours) with caution due to the ulcerogenic effect on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. The drug has a cumulative effect. If necessary, you can resume taking the drug after a 5-day break. There is a risk of fetal narrowing of the ductus arteriosus and oligohydramnios. It is necessary to determine the volume of amniotic fluid before starting treatment, and then after 48-72 hours. If oligohydramnios is detected, the use of indomethacin should be discontinued. The use is limited to a gestational period of less than 32 weeks in pregnant women with threatening or incipient preterm labor, with a normal volume of amniotic fluid, lasting 2-3 days.
Fetal contraindications are fetal growth retardation, kidney anomalies, oligohydramnios, heart defects with involvement of the pulmonary trunk in the process, transfusion syndrome in twins.
In our country, a scheme for the use of indomethacin orally or rectally has been developed and is being applied, while the course dose should not exceed 1000 mg. To relieve tonic contractions of the uterus, indomethacin is used according to the scheme: 1st day 200 mg (50 mg 4 times in tablets or 1 suppository 2 r / day), 2nd and 3rd days 50 mg 3 r / day, 4-6 days, 50 mg 2 r / day, 7 and 8 days, 50 mg at night. The total course dose should not exceed 1000 mg. If it is necessary to reuse, the interval between the administration of the drug should be at least 14 days. Calcium channel blockers - nifedipine.
Used to stop labor. Side effects are comparable to magnesium sulfate and are less pronounced than those of p-adrenergic agonists.
Dosing regimen:
Maintenance dose of 10 mg every 8 hours (can be used for a long time up to 35 weeks of gestation).
Possible complications: hypotension (nausea, headache, sweating, feeling hot), decreased uteroplacental and fetal blood flow. Prescribing together with magnesium preparations is contraindicated due to the synergistic effect on the suppression of muscle contractions, in particular on the respiratory muscles (respiratory paralysis is possible).
Ed. IN AND. Kulakova
"Treatment of premature birth" and other articles from the section
For citation: Serov V.N., Sukhorukova O.I. Prevention of premature birth // BC. Mother and child. 2014. No. 1. P. 3
Until 2012, in Russia, the concept of "the birth of a live child (newborn)" was understood as "complete isolation or extraction from the mother's body of the fetus at a gestational age of 28 weeks or more" (Order of the USSR Ministry of Health 12.06.86, No. 848, Appendix 1, p. . 3).
In 2012, the Russian Ministry of Health, “in accordance with the International Convention on the Rights of the Child, the Declaration on Ensuring the Survival, Protection and Development of Children,” canceled this instruction on the territory of the Russian Federation. Since January 2012, the Russian Federation has introduced the criteria recommended by the World Health Organization (order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 318 of 04.12.2011). Criteria for fetal viability: term - 22 weeks. and more, body weight - 500 g or more. Among those born at 22-23 weeks. survive 20% (every 5th newborn), at 26 weeks. - 60%, at 27-28 weeks. - about 80% of premature newborns. Almost 100% survival was noted among newborns at 32 weeks. pregnancy and more. Premature babies account for 60-70% of early neonatal mortality and 65-75% of infant mortality. Stillbirth in premature birth is 8-13 times higher than in timely birth. Children born with a weight of less than 1500 g are 200 times more likely to die as newborns and, if they survive, 10 times more likely to have neurological and somatic complications than children born with a weight of more than 2500 g.
The leading causes of premature birth before 28 weeks are: infection, premature rupture of amniotic fluid and isthmic-cervical insufficiency, followed by prolapse and infection of the membranes of the fetal bladder. According to the literature, from 30 to 40% of premature births are due to the presence of an infectious process [Vlasova TA, Valdman SF, Ivanova NV, 2008]. Urogenital infection plays a key role in the genesis of various pathological processes during pregnancy and the health of the newborn. The most common cause of premature birth is the opportunistic flora of the urogenital tract. At the same time, a change in the biocenosis of the vagina with a corresponding change in pH can be used as a marker for assessing the risk of preterm birth [Radzinsky V.E., Khamoshina MB, Kalendzhyan A.S., 2010]. Premature rupture of membranes complicates the course of premature birth in 19.95% of cases. Studies have shown that the main way of changing the membranes with their subsequent rupture is their infection with various microorganisms ascending. Early diagnosis of premature rupture of amniotic fluid largely determines the further management tactics. The detection of protein-1, which binds insulin-like growth factor in the vaginal discharge, is one of the reliable methods for diagnosing premature rupture of the membranes. In the existing system of prophylactic medical examination, unified methodological guidelines for the prevention of preterm labor are not sufficiently developed and the possibilities of using modern methods of predicting them are limited, allowing early detection of risk factors and the choice of optimal tactics for managing pregnancy [Radzinsky V.E., Orazmuradova A.A., 2009] ...
The risk of developing idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants with a gestational age of less than 28 weeks. is 60%, from 32 to 36 weeks. - 20%, more than 37 weeks - 5% . Steroid therapy with glucocorticoids reduces early neonatal mortality by 40%.
Preterm labor is divided into spontaneous and induced, associated with the health of the pregnant woman and / or the fetus. Spontaneous premature labor, in turn, can begin with regular labor with a whole fetal bladder - idiopathic (about 40-50% of cases) or with discharge of amniotic fluid in the absence of labor (about 50%). According to the clinical picture, preterm labor is divided into threatening, characterized by irregular contractions of the uterus and opening of the cervix up to 3-4 cm, and begun - in this case, regular labor occurs and the cervix opens by 3-4 cm or more. Every third case of preterm birth occurs in pre-pregnant women, whose risk factors include previous abortions or spontaneous miscarriages, urinary tract infection, and inflammatory diseases of the genitals.
The diagnosis of the onset of preterm labor is associated with certain difficulties due to the absence of specific symptoms. Predicting the onset of preterm labor is an extremely important problem in practical terms, since in about 50% of cases, the contractile activity of the uterus spontaneously stops. As a predictor of preterm birth, a rapid test for the determination of the phosphorylated form of protein-1 is currently quite successfully used, the diagnostic sensitivity of which is 88.9%, and the diagnostic specificity is 100%.
Phosphorylated protein-1, which binds insulin-like growth factor, is synthesized by decidual cells. The amniotic fluid, fetal and pregnant serum, on the other hand, contain a large amount of non-phosphorylated PSIFR-1. When the term of labor approaches, the amniotic membranes begin to separate from the decidua, as a result of which a small amount of fPSIFR-1 is released. A negative result indicates a low risk of premature birth within 7 days of the test. The predictive value of a negative result is 94%.
At the first stage of the study, we carried out a retrospective clinical and statistical analysis of 137 stories of preterm birth. These studies were carried out according to a specially developed examination technique, which took into account passport, anamnestic, clinical data, information about education, about the presence of occupational hazards, parity, features of the course of previous and current pregnancy and childbirth, as well as about the state and outcome of childbirth for the fetus and newborn ... The identification of risk factors and the formation of high-risk groups for preterm birth were made.
At the second stage, which constituted the main part of the study, a dynamic prospective observation of 143 pregnant women was carried out from the moment of their registration to discharge from the hospital after delivery. This group was formed on the basis of questionnaire data, in the process of which the risk factors for preterm birth were ascertained.
Inclusion criteria: the presence of urogenital infection, diagnosed isthmic-cervical insufficiency, placental insufficiency and anamnestic factors (history of premature birth, multiple intrauterine interventions, history of premature placental abruption).
Exclusion criteria: severe extragenital pathology, multiple pregnancy.
All monitored pregnant women underwent an in-depth clinical examination.
Fetal outcomes during the early neonatal period were analyzed in 280 newborns. In the course of the work, general clinical (clinical and anamnestic, laboratory), special (ultrasound, Doppler, CTG), genetic, pathological, anatomical, immunological and statistical research methods were used.
To perform the research tasks, including the use of highly sensitive test systems based on the determination of protein-1, which binds insulin-like growth factor in the vaginal discharge, 85 patients with the threat of termination of pregnancy and 29 patients with diagnosed mutations in thrombophilia genes were selected from among the examined pregnant women, with the subsequent use of low molecular weight heparin, who are familiar with the purpose and methods of research, who have given written consent to their inclusion in scientific research.
Patients of both groups included in the study were comparable in age and somatic health. In the retrospective group (RG), all analyzed patients had a complicated course of pregnancy (Table 1).
Analysis of risk factors for preterm birth in the prospective group (PG) showed a similar distribution of the frequency of risks as in the RG. In both groups, in one third of cases there was a combination of risk factors (R = 0.22; p = 0.01). Analyzing the state of the somatic status, it is worth noting that in chronic kidney disease, as well as in states of asymptomatic bacteriuria, childbirth up to 28 weeks. occurred 3 times more often (58%) than at 33-37 weeks. - 17% (p<0,01). Влагалищная инфекция в нашем исследовании занимает ключевую позицию, т. к. в 18 случаях роды наступили до 28 нед., что почти в 6 раз превышает таковые показатели при родах на сроке 33-37 нед. (p<0,01). Половина родов на сроке 28-33 нед. происходили на фоне влагалищной инфекции — 51% (p<0,01). При родах в 28-37 нед. предлежание плаценты отмечено в 17,86% случаев.
Placenta previa anomalies were observed 5 times more often with preterm birth before 28 weeks than with delivery at 33-37 weeks. (p<0,01). Преждевременная отслойка плаценты произошла в 23 (16,8%) случаях, на сроке до 28 нед. — 31,6%, на сроке 28-32 нед. 6 дн. — 13,1% и при сроке 33-37 нед. — 17,7% (p<0,01) (рис. 1).
We noted that all RG women had a burdened obstetric and gynecological history. Thus, 56.93% of women had a history of premature birth, 33.58% had an artificial termination of pregnancy or diagnostic curettage, and a history of surgical interventions on the cervix - 24.82% (Table 2).
In 54% of RH patients, pregnancy was threatened with termination at various times, of which 89% received inpatient care. Tocolytic therapy in the hospital was carried out mainly with magnesium sulfate preparations - 54%, β-adrenomimetics - 27%, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - 11%, their combination took place in 7.5% of cases. Therapy with β-adrenergic agonists and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for up to 28 weeks. was not assigned.
In the close relatives of the analyzed pregnant women in the study of heredity, strokes, deep vein thrombosis and heart attacks were noted in 24 cases. When studying the history of women in the retrospective group, premature placental abruption was noted in 17% of cases, placental insufficiency with intrauterine fetal growth retardation - in 53% of cases. In such patients, in 63.33% of cases, very early preterm birth occurred, which is 3 times more often than childbirth at 33-37 weeks. (R = 0.21; p = 0.01).
In 63% of cases, premature birth before 28 weeks. began with premature rupture of amniotic fluid, at a period of 28-32 weeks. 6 days - in 74%, during childbirth at 33-37 weeks. - in 30% of cases (p<0,02).
The frequency of preterm birth in the period 2010-2012. , according to statistical reports, ranged from 7.8 to 10.6% (Fig. 2).
All pregnant PGs were registered before the 6-week gestation period, after ultrasound, specifying the gestational age and the place of implantation of the ovum.
Self-screening for vaginal infection revealed a deviation in the pH of the vaginal contents in the PG in 43% of pregnant women. Bacterioscopic examination found that bacterial vaginosis occurs in 37 (59.68%) cases, vaginal candidiasis - in 11 (17.74%) cases, nonspecific vaginitis - in 14 (22.58%) cases (p<0,05) (табл. 3).
In PG, examination for mutations in the hemostasis system was carried out for all pregnant women with a history of preterm birth - in 59% of cases, premature placental abruption - in 19%, placenta previa - in 17% of cases. Mutations in the genes of the hemostasis system were found in one third of the 102 pregnant women examined (Table 4). All pregnant women with confirmed genetic mutations of thrombophilia were hospitalized for further examination and selection of therapy with low molecular weight heparins.
Patients with a mutation in the MTFHR gene (C667TT) additionally received folic acid preparations during pregnancy. Homocysteine levels were assessed. Dynamic control over the treatment was carried out according to the hemostasiogram indices once every 2 weeks.
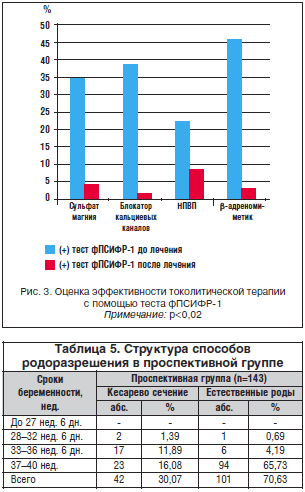
When dealing with complaints of discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen, starting from 22 weeks. gestation, in 85 pregnant women, a highly sensitive strip test was used to diagnose and predict the onset of preterm labor, which determines the phosphorylated form of protein-1 that binds insulin-like growth factor. In 53% of cases of threatened abortion at the first visit, a positive result was obtained, confirmed by ultrasound and manual examination, these pregnant women were hospitalized, 47% of patients continued outpatient observation. The quality of therapy and the threat of termination of pregnancy in the hospital were assessed using a repeated test to determine fPSIFR-1 (Fig. 3).
We noted that with the use of β-adrenergic agonists, the frequency of repeated positive results during testing is 2 times lower than with the use of calcium channel blockers and NSAIDs (R<0,02). По результатам нашего исследования, наиболее предпочтительным для снятия угрозы прерывания беременности на сроке до 28 нед. является блокатор кальциевых каналов — нифедипин, а на сроке 28-33 нед. — сульфат магния и гексапреналина сульфат (р<0,02).
In RG, very early preterm labor up to 28 weeks. gestations occurred in 13.9% of cases, early gestations at 28-32 weeks. 6 days - 61.3% and childbirth at a period of 33-37 weeks. - in 25.8% of cases. In PG, thanks to the comprehensive prevention carried out, preterm birth for up to 28 weeks. did not happen. Childbirth at 28-32 weeks 6 days pregnancies occurred in 2 cases.
Analysis of the data by groups showed that preterm labor at 33-37 weeks. in RG (4.4%) they ended up with caesarean section 2 times less often than in PG (11.9%) (R = 0.17; p = 0.01) (Table 5).
In patients with hereditary thrombophilia, vaginal delivery at 33-37 weeks. occurred in 6.9% of cases (p<0,01), на сроке 37-40 нед. гестации путем кесарева сечения — в 10,3%, через естественные родовые пути — в 79,3% случаев (p<0,01).
143 children were born in PG. Of these, for a period of 28-32 weeks. 6 days - 2.1%, 33-37 weeks - 16.1% and at full term - 81.8% of children. 42 babies were born in an operative way, 101 babies were born naturally (Fig. 4). In the retrospective group for a period of 28-32 weeks. 6 days the leading diseases were pneumonia - 66.1%, conjugational jaundice - 37.3%, respiratory membrane distress syndrome - 59.3% (p<0,02). Сравнивая результаты в группах, стоит отметить, что заболеваемость пневмонией и респираторным дистресс-синдромом у недоношенных детей в ПГ снизилась в 4 раза по сравнению с РГ (R=0,17; р=0,02).
In PH in the first place in the morbidity structure was edematous syndrome - 21.7%, conjugational jaundice - 17.4%, hemolytic disease - 17.4%, pneumonia and respiratory distress syndrome - 13.1% each (Fig. 5) ...
Comparing the results in the groups, it should be noted that the incidence of pneumonia and respiratory distress syndrome in premature infants in the PH decreased by 4 times compared with the RG (R = 0.17; p = 0.02). The number of children in the PG (21.7%) requiring artificial lung ventilation has decreased by 3 times, compared with the RG (R = 0.21; p = 0.02).
The formation of high-risk groups for preterm birth allows you to optimize diagnostic and treatment tactics. Detection of urogenital infection using a simple self-diagnosis test for determining the pH of the vaginal environment, followed by bacterioscopic examination and sanitation, can reduce the incidence of premature birth. It is necessary to determine thrombophilia, and in particular hereditary mutations of thrombophilia genes, with the prophylactic use of low molecular weight heparins. The correct selection of tocolytic therapy using a modern highly sensitive test system that determines the phosphorylated form of protean-1, which binds insulin-like growth factor in the vaginal discharge, to assess its effectiveness, helps to reduce the incidence of preterm birth.





Literature
- Obstetrics. University of California Handbook / Ed. K. Niswander, A.E. Evans / Transl. from English M .: Praktika, 1999.703 p.
- Vlasova T.A., Valdman S.F., Ivanova N.V. and others. Risk factors and features of management of preterm labor // Reproductive health of women. 2000. No. 2. S. 153-160.
- Kulakov V.I., Serov V.N., Sidelnikova V.M. Premature birth - management tactics taking into account the gestational age // Journal of Obstetrics and Women's Diseases. 2002. No. 2. S. 13-17.
- Makatsaria A.D., Bitsadze V.O., Genievskaya M.G. et al. // Antiphospholipid syndrome in obstetric practice. M .: Russo, 2003.S. 344.
- Mikhailov M.K. Biomechanism of birth injuries of the spine, spinal cord and vertebral arteries: methodological materials. Kazan, 1994.S. 6-8.
- Sidelnikova V.M. Obstetric tactics of preterm labor management // Obstetrics and gynecology. 2000. No. 5. S. 8-12.
- Sidelnikova V.M., Tetruashvili N.K. Premature birth and immunological aspects // Obstetrics and gynecology. 2002. No. 7. S. 44-49.
- Fedorova M.V. Placental insufficiency // Obstetrics and gynecology. 1997. No. 6. S. 40-43.
- 9. Shalina R.I., Kurtser M.A., Plekhanova E.R. and others. Untimely discharge of amniotic fluid: active and expectant tactics of preterm labor management // Questions of gynecology, perinatology usherstva. 2006. T. 5, No. 1. S. 27-32.
- Shalina R.I., Plekhanova E.R. Complex therapy of pregnant women with the threat of premature birth // Questions of gynecology, obstetrics and perinatology. 2007. T. 6, No. 1. S. 33-40.
- 11. Shapovalenko S.A. Complex diagnosis and treatment of placental insufficiency in pregnant women at different stages of gestation // Vestnik Ross. associations of obstetricians and gynecologists. 2001. No. 2.P. 47.
- Gyetvai K., Hannah M., Hodnett E. et al. Tocolytics for preterm labor: a systematic review // Obstet. Gynecol. 1999. Vol. 94. P. 869-877.
- 13. How H.Y., Cook C.R., Cook V.D. et al. Preterm premature rupture of membranes: aggressive tocolysis versus expectant management // J. Matern. Fetal. Med. 1998. Vol. 7.P. 8-12.
- Mattison D., Damus K., Fiore E. et al. Preterm delivery: a public health perspective // Paediatr. Perinatal. Epidemiol. 2001. Vol. 15.P. 7-16.
- Monaghan S., Little R., Hulchiy O. et al. Preterm birth in two urban areas of Ukraine // Obstet. Gynecol. 2000. Vol. 95. P. 752-755.
- 16. Naef R.W. 3rd, Allbert J. R., Ross E. L., et al. Premature rupture of membranes at 34 to 37 weeks’gestation: aggressive versus conservative management // Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 8. Vol. 178. P. 126-130.
- Paternoster D. M., Bertoldini M., Pignataro R. et al. Analisi comparativa dei inarcatori di parto pretermine // Acta biomed. Ateneo parm. 2000. Vol. 71. P.331-356.
- 18. Ramsey P.S., Lieman J.M., Brumfield C.G. et al. Chorioamnionitis increases neonatal morbidity in pregnancies complicated by preterm premature rupture of membranes // Am. J. Obstet. ecol. 2005. Vol. 192 (4). P. 1162-1166.
- Rabe H., Reynolds G. J., Diaz-Rosello J. L. Early versus delayed umbilical cord clamping in preterm infants // Cochrane Library. 2009. Vol. 1.
- Scholl T.O. Iron status during pregnancy: setting the stage for mother and infant // Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005. Vol. 81. P. 1218S-1222S.
- Wolf H., Schaap A.H.P., Bruinse H.W. et al. Vaginal delivery compared with caesarean section in early preterm breech delivery: a comparison of long term outcome // Br. J. Obstet. aecol. 1999. Vol. 106. P. 486-491.

