What does computed tomography look like? Difference between CT and MRI Which tomography is better
CT SCAN
CT SCAN, a method of X-ray transmission, in which images of "slices" are created internal organs body. The scanning tomograph has an X-ray source that produces a narrow beam. It passes through the patient's body and is recorded by the sensor. The X-ray source and probe are rotated around the patient's body to produce a set of images taken from different angles. The computer analyzes all this data coming from the sensor and creates on its basis the big picture, showing whether there is a disease in this area.
Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary.
See what "COMPUTER TOMOGRAPHY" is in other dictionaries:
CT scan- CT A procedure in which the image of a part in a selected plane perpendicular to the sample axis is calculated based on a large number X-ray absorption measurements made according to different directions perpendicular to the axis ... Technical translator's guide
- (CT) is a method of obtaining images of tissues and organs. Based on the X-ray picture that gives big number X-rays, the computer builds a detailed image. These images are a kind of transverse sections ... ... Medical terms
CT scan- a method of obtaining a layer-by-layer X-ray image of an organ or part of a patient's body using computer technology ... METHODOLOGICAL RECOMMENDATIONS (approved by ... ... Official terminology
Request "CT" is redirected here; see also other meanings. Computer tomograph CT scan method of non-destructive layer-by-layer investigation of the inner p ... Wikipedia
CT scan- kompiuterinė tomografija statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Įvairiomis kryptimis peršviesto tiriamo erdvinio objekto vaizdų apdorojimas kompiuteriu siekiant gauti objekto sluiza atitikmenys: angl. computed ... ... Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
CT scan- one of modern methods studies of the brain, allowing to obtain layer-by-layer images of its structures ... Dictionary of Psychogenetics
CT is a method of radiation diagnostics that radically changed honey. diagnostics. In particular, CT scanning of the head eliminated the need for widespread use of more invasive neurodiagnostic techniques (for example, angiography or ... ... Psychological encyclopedia
HRCT showing signs of pulmonary fibrosis High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) of the lungs medical research used for the diagnosis and assessment of interstitial ... Wikipedia
Computed tomography method was proposed in 1972 by Godfrey Hounsfield and Allan Cormack, who were awarded the Nobel Prize for this development. The method is based on the measurement and complex computer processing of the X-ray attenuation difference ... ... Wikipedia
This article is missing links to sources of information. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it can be questioned and removed. You can ... Wikipedia
Books
- Computed tomography, Hofer Mathias. The book is the third edition in Russian basic course training and retraining of specialists in computed tomography in international standards... Submitted by ...
Computed tomography is a non-invasive diagnostic method that determines the state of internal organs and systems. The examination is carried out using X-ray radiation, gives a layer-by-layer image of the pathological focus on the tomograph screen. it safe procedure which guarantees reliable result, excludes irradiation of the organism, mutations. Opinion about the dangers of radiation in in this case erroneous, since such chemical elements do not affect the body at all. This fact is confirmed by the information that after an inaccurate CT scan, a second examination is possible without a time interval.
Decoding computed tomography
After completing the diagnosis, the patient receives an opinion on the state of internal organs, systems, and the presumptive focus of pathology. With the results, he goes to the attending physician, who will determine the prevailing clinical picture... Deciphering a CT scan speeds up the recovery process, the main thing is to accurately conduct an examination and use the services of a competent specialist.
After the CT scan, you can get the following information about the real state of health:
- proliferation of cancer cells in the intestines, kidneys, liver, bladder, lungs, adrenal glands, pancreas;
- determination of the location and patency of blood vessels;
- determination of the shape and size of internal organs and systems, visualization of the focus of pathology;
- the presence of metastases, an increase in lymph nodes;
- diagnostics of pulmonary embolism;
- signs of lung infection;
- symptoms of inflammatory bowel processes;
- obstruction of the bile ducts and intestines;
- diagnosis of aortic aneurysm;
- determination of kidney stones and biliary tract;
- visualization of cysts, foreign bodies.
It is not at all necessary to do the procedure for the whole body, since it is a very expensive pleasure. Most often, the doctor prescribes a CT scan of individual internal systems and organs where the presumptive focus of pathology is concentrated. To clarify the final diagnosis, it is required to use a contrast agent that illuminates separate zones, dispels all the doubts of specialists regarding progressive diseases.
Computed tomography: examination of the lungs
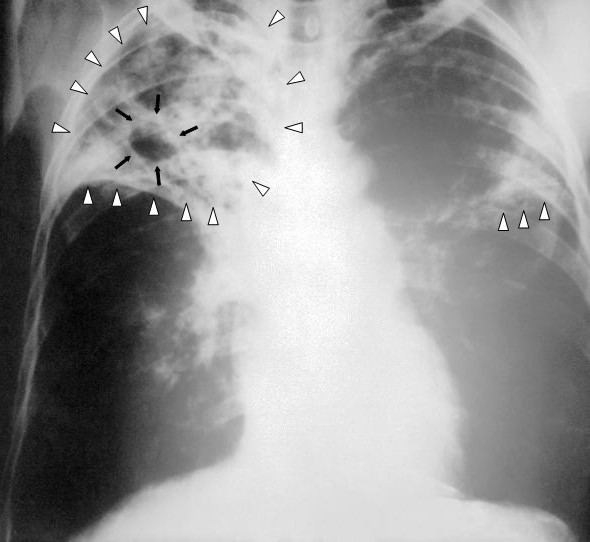
If you suspect tuberculosis, doctors do a CT scan of the lungs. If the diagnosis coincided, then the following phrase is indicated in the conclusion: "small focal dissemination of the lungs", which confirms the fact of the appearance of Gona foci. The disease is progressing cancer cells spread, bringing death the patient.
By decoding CT of the lungs, it is possible to determine exactly where the tumor is located, what size has reached and the total number of pathogenic neoplasms. Also, the image shows metastases, if any, the degree of malignant neoplasm... If diagnosis is difficult, it is additionally necessary to undergo MRI, X-ray, ultrasound, although these non-invasive diagnostic methods are less informative. CT of the lungs is appropriate for tuberculosis if not enough accurate results radiography. Diffuse changes in lung tissue are strictly outlined in size, but computed tomography also determines whether adjacent organs are affected.
If tuberculosis is accompanied by the proliferation of foci of lung necrosis, then malignant tumor the picture shows an asymmetric neoplasm, which has a contoured shape and size. CT is not able to determine the origin of such a neoplasm, therefore, to clarify the diagnosis, a biopsy is required, as invasive method diagnostics.
You can get the results of CT immediately after the examination, then immediately consult a doctor for decoding. The conclusion is given on the basis of the photographs, therefore, in this issue it is advisable to contact qualified specialist also visit an oncologist.
What does computed tomography show?
Among the common diseases diagnosed with the help of such a diagnosis, the following should be highlighted:
- In case of liver damage, cysts and tumors of the gland, fatty degeneration of the liver, echinococcosis, abscess, cirrhosis of the "human filter" are not excluded.
- With damage to the spleen, it is possible to determine the degree of injury, to predict the clinical outcome for the patient.
- In case of damage to the pancreas, it is also realistic to determine inflammatory and infectious processes, cysts and tumors.
- If the gallbladder is affected, the patency of the bile ducts can be assessed and the presence of stones determined.
- When vascular structures are damaged, it also determines obstruction, the presence of neoplasms and the presence of foreign bodies.
it once again proves that the diagnostic method is really informative, it is mandatory when making a number of diagnoses. In addition to all the above-described pathologies, foreign bodies in the body, enlarged lymph nodes, the presence of free fluid or gas, diverticulitis, internal bleeding, inflammatory processes intestines, aneurysm of the abdominal aorta.
Useful notes for the patient
If the doctor insists on performing a CT scan, it is necessary to find a specialized medical Center with a good reputation. Before starting the procedure, it is important to additionally consult how this examination takes place. Preparatory activities depend on the area that will be studied using specialized equipment. For example, preparation for a CT scan of the lungs is not required, while studying abdominal cavity requires preliminary cleaning of the intestines, getting rid of slagging and gas contamination.

CT scan must be coordinated with the attending physician in advance, to completely eliminate the risk of contraindications and side effects, to prevent health complications. In most cases, the effectiveness of the method is 97%, so it is better not to ignore such a diagnosis, even at financial costs.
If the patient is interested in looking at the finished images, then he can independently determine the focus of the pathology. Most often, the neoplasm resembles a spot that differs in the color of the picture, has outlined borders, and is asymmetric. You don't even need to go to the doctor to determine where it is located problem area, to see its real size, closeness to healthy tissues and systems.
The CT scan also shows metastases, which look like chaotic points concentrated in the vicinity of the main focus of pathology. Such pictures make it clear that the disease is progressing, and treatment may ultimately be ineffective for the patient. It is necessary to look not at the size of metastases, but at their spread, since these are the same cancer cells that can soon lead to the death of the body.
If there are no suspicious points and circles on the black-and-white image, it is possible that the tumor is absent, and the patient still has a real chance of complete healing after long-term treatment and compliance with all the prescriptions of a specialist.
Modern diagnostic techniques identify the earliest pathological changes in the work of human organs and systems. It is difficult to imagine the development of medicine without the use of magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography - non-invasive methods for diagnosing diseases. But, faced with the need to choose between one and the other type of research, many patients begin to wonder how CT differs from MRI, and which method is best to prefer depending on their health condition.
A person who is far from medicine may mistakenly think that these techniques are identical. But this is far from the case. They are united by the word "tomography", which means obtaining layer-by-layer sections of organs and tissues, the image of which, after scanning, is sent to a personal computer and is interpreted. But the difference between CT and MRI still exists, and it is quite significant.
What is the difference between CT and MRI?
In order to understand what is the difference between CT and MRI, it is necessary to understand what each of these research methods is based on.
Computed tomography is based on the specific property of X-ray radiation absorbed depending on the density of specific body tissues. By and large, computed tomography is identical to traditional radiography, but the principle of operation of a computed tomograph with CT differs in a completely different way of receiving and processing information, as well as a higher radiation exposure.
During a tomographic X-ray examination, a beam of X-rays acts on the area under study, which, passing through the patient's tissues with different densities, is absorbed by them. In this case, layer-by-layer images of body slices appear. High-quality computer equipment processes the received data and processes them, giving informative three-dimensional images reflecting the characteristics of the organ or body part being examined.
V MRI diagnostics data is obtained using a powerful magnetic field ( nuclear magnetic resonance), thanks to which the hydrogen atoms in the human body begin to change their position. The tomograph sends electromagnetic pulses, and the effect arising in the body is captured by the equipment and processed into three-dimensional images.
Thus, the difference between MRI and computed tomography becomes obvious. In addition, CT has a significant radiation effect, therefore it cannot be applied repeatedly. X-rays during computed tomography affect organs and tissues for up to 10 seconds, which is preferable for people suffering from claustrophobia, but for a full-fledged magnetic resonance imaging study, it may take 10-20 minutes (while maintaining a stationary state). Therefore, when conducting an MRI study in childhood, anesthesia is often used.
Indications for CT and MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most informative for the study of the soft tissues of the body and is carried out to study:
- neoplasms in muscles, adipose tissue, abdominal cavity and pelvic organs (to clarify the data obtained by ultrasound);
- the state of the structures of the brain and spinal cord;
- circulatory disorders and lesions in the head and spinal cord;
- spine (condition of intervertebral discs), joints (condition of ligaments).
Computed tomography is preferable for diagnosing:
- diseases of the joints and spine (bone component);
- primary and secondary bone lesions of a tumor nature;
- traumatic injuries of the skeleton;
- atherosclerotic vascular changes;
- diseases of the lungs, abdominal organs and pelvic organs (three-phase contrast study);
Contraindications to the use of CT and MRI
The computed tomography method is accompanied by radiation, therefore CT is contraindicated in women from the moment of pregnancy and breastfeeding..
Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed on patients:
- with metal parts on the body and in the body;
- the presence of electronic devices implanted in the tissue (since a powerful magnetic field is created, which can lead to disruption of the operation of pacemakers and other devices);
- patients suffering from claustrophobia (MRI is possible open type);
- sick with nervous pathologies, not allowing to be stationary for a long time.
- patient weight exceeding more than 150-200 kg.
In addition to the listed contraindications, there are a number of absolute and relative contraindications and restrictions for MRI.
Which is better: CT or MRI?
MRI and CT - which is better? Many have asked a similar question. Every person concerned about their health wants to go through the most informative research methods. Despite the differences between CT and MRI, choosing the most effective one is not easy, since for modern medicine both methods are valuable. It all depends on the specific goal.
