Double screening test above threshold. prenatal screening.
Prenatal screening examination of the first trimester consists of two procedures: ultrasound diagnostics and blood tests for the possibility of genetic abnormalities of the fetus. There is nothing wrong with these events. The data obtained through the ultrasound procedure and blood tests are compared with the norm for this period, which allows you to confirm the good or bad condition of the fetus and determine the quality of the gestation process.
Very rarely, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura has been reported after clopidogrel, sometimes after disastrous treatment. It is characterized by thrombocytopenia and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia associated with neurological findings, renal dysfunction, or fever. TTP is a potentially fatal disease requiring timely treatment including plasmapheresis. Given the lack of data, clopidogrel is not recommended during the first 7 days after an acute ischemic stroke.
Therapeutic experience with clopidogrel in patients with kidney failure limited. Therefore, clopidogrel should be used with caution in these patients. Experience is limited in patients with moderate hepatic disease who may have hemorrhagic diathesis. Therefore, clopidogrel should be used with caution in this population.
For future mother main task is the preservation of a good psycho-emotional and physical condition. It is also important to follow the instructions of the obstetrician-gynecologist leading the pregnancy.
Ultrasound is only one examination of the screening complex. To obtain full information about the health of the baby, the doctor should check the blood of the future woman in labor for hormones, evaluate the result general analysis urine and blood
Patients with rare hereditary problems of galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine due to the lactose content of the product. The product contains Castor oil, hydrogenated, which can cause stomach upset and diarrhea.
Interaction with other drugs and other forms of interaction
Oral anticoagulants: The co-administration of clopidogrel and oral anticoagulants is not recommended, as bleeding may be increased. Possible pharmacodynamic interaction between clopidogrel and acetylsalicylic acid which increases the risk of bleeding. Therefore, their sharing should be given with caution. Heparin: In a clinical study conducted with healthy subjects, clopidogrel did not require a change in the dose of heparin, nor did it change the effect of heparin on coagulation.
Standards for ultrasound diagnostics I screening
During the first prenatal screening in 1st trimester doctor of ultrasound diagnostics Special attention pays to the anatomical structures of the fetus, clarifies the gestational age (gestation) on the basis of, comparing and with the norm. The most carefully evaluated criterion is the thickness of the collar space (TVP), since. this is one of the main diagnostically significant parameters, which makes it possible to identify genetic diseases of the fetus during the test. With chromosomal abnormalities, the collar space is usually expanded. Weekly TVP norms are shown in the table:
Concomitant administration of heparin did not affect the inhibition of clopidogrel-induced platelet aggregation. A pharmacodynamic interaction between clopidogrel and heparin is possible, which increases the risk of bleeding. Thrombolytics: The safety of the specific thrombolytic products clopidogrel, fibrin or nefibrin has been evaluated in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: In a clinical study conducted with healthy volunteers, the simultaneous administration of clopidogrel and naproxen increased occult gastrointestinal blood loss. However, due to the lack of interaction studies with other NSAIDs, it is currently unclear whether there is increased risk gastrointestinal bleeding with all NSAIDs.
When conducting ultrasound screening of the first trimester, the doctor pays special attention to the structure of the facial structures of the fetal skull, the presence and parameters of the nasal bone. At 10 weeks, it is already quite clearly defined. At 12 weeks - its size in 98% of healthy fetuses is from 2 to 3 mm. The baby's maxillary bone size is evaluated and compared with the norm, because a noticeable decrease in jaw parameters in relation to the norm indicates trisomy.
Other concomitant treatment: Several other clinical studies have been conducted to investigate the potential pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions of clopidogrel and other concomitant medications. medicines. No clinically significant pharmacodynamic interactions were observed when clopidogrel was co-administered with atenolol, nifedipine, or atenolol and nifedipine together. Thus, the pharmacodynamic activity of clopidogrel is not significantly affected by co-administration with phenobarbital, cimetidine, or estrogen.
On ultrasound 1 screening, the fetal heart rate (heart rate) is recorded and also compared with the norm. The indicator depends on the gestational age. Weekly heart rate rates are shown in the table:
The main fetometric indicators at this stage during the ultrasound procedure are the coccyx-parietal (KTR) and biparietal (BPR) sizes. Their norms are given in the table:
The pharmacokinetics of digoxin or theophylline does not change with simultaneous application clopidogrel. Antacids do not alter the absorption of clopidogrel. In addition to the specific drug interactions described above, interaction studies of clopidogrel with some other commonly used medicines have not been performed in patients with atherothrombotic disorders.
Since there are no clinical data on the effects of clopidogrel during pregnancy, it is preferable not to use clopidogrel during pregnancy as a precautionary measure. It is not known if clopidogrel has been seized in mother's milk. It is possible that inhibition of platelet function in infants. Therefore, as a precaution breast-feeding should not continue during treatment with Trombek.
| Fetal age (week) | Average CTE (mm) | Average BPR (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 31-41 | 14 |
| 11 | 42-49 | 13-21 |
| 12 | 51-62 | 18-24 |
| 13 | 63-74 | 20-28 |
| 14 | 63-89 | 23-31 |
The first screening involves an ultrasound assessment of blood flow in the venous (Arancius) duct, since in 80% of cases of its violation, a child is diagnosed with Down syndrome. And only 5% of genetically normal fetuses show such changes.
Starting from the 11th week, it becomes possible to visually recognize Bladder during an ultrasound. At the 12th week, during the first ultrasound screening, its volume is assessed, since an increase in the size of the bladder is another evidence of the threat of developing trisomy (Down) syndrome.
Effects on the ability to drive and use machines
In addition to clinical trial experience, spontaneously reported adverse reactions. Bleeding is the most common reaction reported in both clinical trials and also in post-marketing experience, where it was mostly reported within the first month of treatment.
The incidence of severe cases was 1.4% for clopidogrel and 1.6% for ASA. The risk of bleeding decreases during the study: 0-1 months, 1-3 months, 3-6 months, 6-9 months, 9-12 months. Frequency heavy bleeding the two groups are similar. This observation persists in patient subgroups determined by baseline characteristics and type of fibrinolytic or heparin therapy.
It is best to donate blood for biochemistry on the same day that ultrasound screening is performed. Although this is not a requirement. Blood sampling is carried out on an empty stomach. The analysis of biochemical parameters, which is carried out in the first trimester, is aimed at identifying the degree of threat of occurrence genetic diseases at the fetus. For this, the following hormones and proteins are determined:
The following are adverse reactions that have either occurred during clinical trials or have been reported spontaneously. An overdose of clopidogrel may lead to an increase in bleeding time with subsequent bleeding complications. If bleeding occurs, appropriate treatment should be considered. No antidote to the pharmacological activity of clopidogrel was found. If immediate correction of prolonged bleeding time is required, platelet transfusion may inhibit the effects of clopidogrel.
- pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A (PAPP-A);
- free hCG(beta component).
These figures depend on the week of pregnancy. The range of possible values is quite wide and correlates with the ethnic content of the region. In relation to the average-normal value for this region, the level of indicators fluctuates within the following limits: 0.5-2.2 MoM. When calculating the threat and deciphering the data, not just the average value is taken for analysis, all possible amendments to the anamnestic data of the expectant mother are taken into account. Such an adjusted MoM allows you to more fully determine the threat of developing a genetic pathology of the fetus.
Pharmacotherapeutic group: inhibitors of platelet aggregation with Heparin. To achieve inhibition of platelet aggregation, biotransformation of clopidogrel is required. As a result, platelets in contact with clopidogrel were altered for the remainder of their lives, and restoration of normal platelet function was performed at a rate consistent with platelet circulation. Multiple doses of 75 mg per day cause significant suppression of ADP-induced platelet aggregation from the first day; it gradually increases and reaches a steady state from 3 to 7 days.
 A blood test for hormones is necessarily performed on an empty stomach and is often scheduled on the same day as the ultrasound. Due to the presence of standards for the hormonal characteristics of the blood, the doctor can compare the results of a pregnant woman's tests with the norms, identify a deficiency or excess of certain hormones
A blood test for hormones is necessarily performed on an empty stomach and is often scheduled on the same day as the ultrasound. Due to the presence of standards for the hormonal characteristics of the blood, the doctor can compare the results of a pregnant woman's tests with the norms, identify a deficiency or excess of certain hormones HCG: assessment of risk values
In terms of information content, free hCG (beta component) is superior total hCG as a risk marker for a genetic abnormality in the fetus. The norms of beta-hCG with a favorable course of gestation are shown in the table:
At steady state, the average retention rate achieved at a dose of 75 mg per day is 40% to 60%. Platelet aggregation and bleeding time gradually return to baseline, usually 5 days after stopping treatment. Recent myocardial infarction, stroke, or established peripheral arterial disease.
Clopidogrel significantly reduced the number of new ischemic events compared with ASA. In a subgroup analysis based on qualifying condition, the gain is the same as in patients with PAD and less in patients with stroke. In addition, a subgroup analysis by age group showed that the benefit of clopidogrel in patients over 75 years of age was less than in patients. Patients were treated for up to one year. Heparins were administered in more than 90% of patients, but the relative bleeding rate between clopidogrel and placebo did not significantly affect concomitant heparin therapy.
The biochemical indicator one of the most informative. This applies to both the detection of genetic pathology and the marking of the course of the gestation process and the changes taking place in the body of a pregnant woman.
Pregnancy-Associated Plasma Protein-A Guidelines
This is a specific protein that the placenta produces throughout the entire gestational period. Its growth corresponds to the period of development of pregnancy, has its own standards for each period. If there is a decrease in the level of PAPP-A in relation to the norm, this is a reason to suspect the threat of developing a chromosomal abnormality in the fetus (Down and Edwards disease). The norms of PAPP-A indicators for normal gestation are indicated in the table:
There was no effect on readmission rates for unstable angina. Results obtained in populations with different characteristics, correspond to the results of the primary analysis. In addition, the safety profile of clopidogrel in this subset of patients is not of particular concern. Thus, the results of this subgroup are consistent with the results of the test as a whole.
The benefits seen with clopidogrel are independent of other acute and prolonged cardiovascular procedures. Patients were observed for 30 days. The primary endpoint is the occurrence of a combination with a clogged, infarcted arteriographic angiogram prior to onset or death, or a recurrence of myocardial infarction prior to coronary angiography.
However, the level of pregnancy-associated protein loses its information content after the 14th week (as a marker of the development of Down's disease), since after this period its level in the blood of a pregnant woman carrying a fetus with a chromosomal abnormality corresponds to normal- as in the blood of a woman having a healthy pregnancy.
For patients who did not have angiography, the main endpoint was death or recurrent myocardial infarction by day 8 or the day of discharge from the hospital. This advantage appears across all subgroups, including age and gender distribution, infarct location, and type of fibrinolytic or heparin.
Concomitant primary endpoints are death from any cause and the first occurrence of recurrent heart attack, stroke, or death. Clopidogrel significantly reduced the relative risk of death from any cause by 7% and the relative risk of recurrent heart attack, stroke, or death by 9%, representing an absolute reduction of 0.5% and 0.9%, respectively. The benefit is the same for different age groups, sex and use of fibrinolytics, and monitored for up to 24 hours.
Description of 1st trimester screening results
To evaluate the results of I screening, each laboratory uses a specialized computer product - certified programs that are configured for each laboratory separately. They produce a basic and individual calculation of threat indicators for the birth of a baby with a chromosomal abnormality. Based on this information, it becomes clear that it is better to take all tests in one laboratory.
Following repeated oral doses of 75 mg daily, clopidogrel is rapidly absorbed. However, the plasma concentration of the parent compound is very low and below the limit quantification within 2 hours. Absorption is only 50% based on urinary excretion of metabolites of clopidogrel. Clopidogrel is extensively metabolized in the liver, the main metabolite, which is not active, is a carboxylic acid derivative, which accounts for about 85% of the compound circulating in plasma. Peak plasma levels of this metabolite are approximately 1 hour after dosing.
The most reliable prognostic data are obtained during the first prenatal screening in the first trimester in full (biochemistry and ultrasound). When deciphering the data, both indicators biochemical analysis considered in combination:
low values of protein-A (PAPP-A) and increased beta-hCG - the threat of developing Down's disease in a child;
low levels of protein-A and low beta-hCG - the threat of Edwards disease in a baby.
There is a fairly accurate procedure to confirm a genetic abnormality. However, this is an invasive test that can be dangerous for both the mother and the baby. To clarify the need to use this technique, the data of ultrasound diagnostics are analyzed. If there are echo signs of a genetic anomaly on the ultrasound scan, the woman is advised to invasive diagnostics. In the absence of ultrasound data indicating the presence of chromosomal pathology, expectant mother it is recommended to repeat biochemistry (if the period has not reached 14 weeks), or wait for the readings in the next trimester.
The active metabolite, the thiol product, is formed by oxidation of clopidogrel to 2-oxo-clopidogrel and subsequent hydrolysis. The metabolite was not found in plasma. The major circulating kinetics of the metabolites is linear at doses of 50 to 150 mg clopidogrel.
The half-life of the main circulating metabolite is 8 hours after single and multiple dosing. Following repeated doses of 75 mg of clopidogrel per day, blood levels of the major metabolite were lower in patients with severe renal impairment compared with patients with moderate renal impairment and levels observed in other studies in healthy people. Although inhibition of ADP-induced platelet aggregation was lower than in healthy individuals, prolonged bleeding was similar to that observed in healthy individuals receiving clopidogrel 75 mg daily.
 Chromosomal disorders of fetal development are most easily detected using a biochemical blood test. However, if the ultrasound did not confirm the fears, it is better for the woman to repeat the study after a while, or wait for the results of the second screening.
Chromosomal disorders of fetal development are most easily detected using a biochemical blood test. However, if the ultrasound did not confirm the fears, it is better for the woman to repeat the study after a while, or wait for the results of the second screening. Risk assessment
The information received is processed by a program specially created to solve this problem, which calculates the risks and gives a fairly accurate forecast regarding the development threat. chromosomal abnormalities fetus (low, threshold, high). It is important to remember that the resulting transcript of the results is only a forecast, and not the final verdict.
In addition, clinical tolerance is good for all patients. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of clopidogrel were evaluated in single and multiple doses in healthy individuals and those with cirrhosis. However, plasma levels of the major circulating metabolite, together with the effect of clopidogrel on ADP-induced platelet aggregation and bleeding time, are similar in these groups. In non-clinical studies with rats and baboons, the most commonly observed effects were liver changes. There was no effect on liver metabolizing enzymes in people who received clopidogrel at therapeutic doses.
In each country, the quantitative expressions of the levels vary. We have high level a value less than 1:100 is considered. This ratio means that for every 100 births (with similar test results), 1 child is born with a genetic pathology. This degree of threat is considered an absolute indication for invasive diagnostics. In our country, the threshold level is the threat of the birth of a baby with malformations in the range from 1:350 to 1:100.
Threat threshold means that a child can be born sick with a risk of 1:350 to 1:100. At a threshold level of threat, a woman is sent to an appointment with a geneticist, who gives comprehensive assessment received data. The doctor, having studied the parameters and anamnesis of the pregnant woman, defines her as a risk group (with a high degree or a low one). Most often, the doctor recommends waiting until the screening study of the second trimester, and then, having received a new calculation of threats, come back to the appointment to clarify the need for invasive procedures.
The information described above should not scare expectant mothers, nor should you refuse to undergo first trimester screening. Since most pregnant women do not have high risk to carry a sick baby, they do not need additional invasive diagnostics. Even if the survey showed bad condition fetus, it is better to learn about it in a timely manner and take appropriate measures.
 If studies have revealed a high risk of having a sick child, the doctor must honestly convey this information to parents. In some cases, an invasive study helps to clarify the situation with the health of the fetus. With unfavorable results, it is better for a woman to terminate the pregnancy for early term in order to be able to take healthy child
If studies have revealed a high risk of having a sick child, the doctor must honestly convey this information to parents. In some cases, an invasive study helps to clarify the situation with the health of the fetus. With unfavorable results, it is better for a woman to terminate the pregnancy for early term in order to be able to take healthy child If adverse results are obtained, what should be done?
If it so happened that the analysis of the indicators of the screening examination of the first trimester revealed a high degree threats of having a baby genetic anomaly, first of all, you need to pull yourself together, as emotions negatively affect the bearing of the fetus. Then start planning your next steps.
First of all, it is hardly worth spending the time and money to get re-screened in another lab. If the risk analysis shows a ratio of 1:100, you can not hesitate. You should immediately contact a geneticist for advice. The less time wasted, the better. With such indicators, most likely, a traumatic method of confirming the data will be prescribed. At 13 weeks, this will be an analysis of the chorionic villus biopsy. After 13 weeks, it may be recommended to perform cordo- or amniocentesis. Analysis of the chorionic villus biopsy gives the most accurate results. The waiting time for results is about 3 weeks.
The expectant mother always undergoes many examinations, of which the double and triple tests. "Double test" helps to suspect serious abnormalities in the development of the fetus, as well as congenital diseases. Any future mommy she always worries about the health of her unborn child, she worries that her child does not have any pathologies in development, neither in height, nor in weight, so that the baby does not have deviations and genetic defects. For this, doctors prescribe to undergo a special examination - this is. Such a study will help to detect Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome in a child, as well as anencephaly, which means a defect neural tube, etc. But all these tests never make a definitive diagnosis, only a risk.
Prenatal screening always carried out twice during pregnancy: the first time at the eleventh - thirteenth week, and the second time at the eighteenth - twenty-first week. Such an examination is a combination of and, which determines specific placental proteins, which has its own name - “double test”. This procedure includes - and biochemical screening. Such tests are safe and absolutely do not affect the health of mom and baby. Doctors recommend doing a "double test" during pregnancy for all pregnant women. These studies can help detect chromosomal abnormalities, but do not make an accurate diagnosis. For example, if the twenty-first chromosome is changed, then this is Down syndrome. For example, if the eighteenth chromosome is changed, then this is Edwards syndrome.
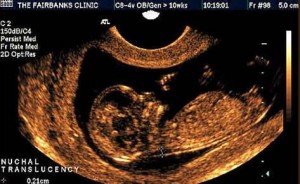
How is a “double pregnancy test” done? Mommy in the morning on an empty stomach goes to donate blood from a vein, which determines two indicators:; PAPP-A, a plasma protein A that is associated with pregnancy. And if there are changes in these proteins, then this means that there is a risk for the fetus chromosomal disorders. You also need to do an ultrasound of the collar zone of the fetus, which shows whether or not there is fluid on the surface of the fetal neck. When the doctor found that the baby unbends the head, then this value can increase by six tenths of a millimeter, and if it bends, then decrease by four tenths of a millimeter. That is, the total value is three millimeters. Usually, when the numbers are high, then there is a risk of pathology.
