The concept of natural loss of drugs
Chapter 2. Limit rates of natural wastage of medicines in pharmacy warehouses
According to the order of the Ministry of Health and social development RF dated January 9, 2007 No. 2 "On the approval of the norms of natural loss during storage of medicines in pharmacies (organizations), drug wholesalers and healthcare institutions", in connection with the use of new technologies for organizing storage in pharmacies (organizations) of medicines, as well as in the order of control over ensuring their safety, the norms of natural loss of medicines in pharmacies (organizations) were approved. Natural loss rates of medicines and products medical purpose in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership and the Instructions for their use were approved by order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated July 20, 2001 No. 284 "On approval of the norms of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmaceutical organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and forms of ownership ”.
The maximum rates of natural loss of medicines are established to cover the loss that occurs in pharmacy warehouses during the process of industrial packaging (spraying, volatilization, bottling, adhesion to container walls, losses when moving from a large package to a smaller one, etc.)
The rates are established to reimburse the cost of losses within the limits of natural loss in the manufacture of medicines according to the prescriptions of doctors and the requirements of health care institutions, intra-pharmacy procurement and packaging in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership and are applied only in the event of a shortage of inventory items when taking inventory.
The specified rates of natural loss do not apply to finished medicinal products industrial production and medicines by weight (including ethyl alcohol) sold in original (factory, factory, warehouse) packaging.
Application of these norms, i.e. calculating the amount of losses from natural loss within established norms, is made on the basis of the data of primary accounting documents for the dispensing (sale) of medicines, individually manufactured according to the prescriptions and requirements of health care institutions, intra-pharmacy preparation and packaging, as well as when dispensed in bulk, in violation original packaging... Natural loss rates apply only to medicines and medical products sold during the inter-inventory period. Fight, marriage, damage, losses due to the expiration of the shelf life of medicines are not written off at the rate of natural loss.
In accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, losses from shortages and (or) damage during storage and transportation of inventories within the limits of natural loss, approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, are equated to material costs for tax purposes.
By order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of January 9, 2007 No. 2, the norms of natural loss during storage of medicines in pharmacies (organizations), drug wholesalers and healthcare institutions were approved (see Table 3).
Table 3
Appendix to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of January 9, 2007 No. 2
Norms of natural loss during storage of medicines in pharmacies (organizations), drug wholesalers and healthcare institutions
According to the Instruction on the Application of Limiting Norms of Natural Waste (Production Waste) of Medicines in Pharmacy Warehouses (Appendix 2 to the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 375 dated November 13, 1996 "On Approval of the Limit Norms of Natural Waste (Production Waste) of Medicines in Pharmacy Warehouses ) ", The limit rates of natural loss of medicines are established to cover the loss that occurs in pharmacy warehouses during the process of industrial packaging (spraying, volatilization, spillage, adhesion to container walls and auxiliary items, during packing, losses when moving from a large package to a smaller one) etc.).
The shortage of medicines that occurred due to damage and breakage of containers, damage to the drug should be recorded by a special commission in an act in the form of 20-AP (not included in the norms).
The application of limiting norms of natural loss to the consumption of medicines in industrial packaging or in dosage form without carrying out any production operations in the warehouse is not allowed.
Natural decline- these are losses that occur during transportation, storage, as well as due to:
1) spraying a number of powder preparations, drying them, breaking in glass containers;
2) natural loss of medicines and cotton wool in pharmacies;
3) loss of glass pharmaceutical utensils at pharmaceutical factories (production) and pharmacy warehouses (bases);
4) natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership.
Natural attrition rates do not apply to:
1) finished pharmaceuticals of industrial production and weight medicines (including ethyl alcohol), sold in the original (factory, factory, warehouse) packaging (Instructions for the application of the norms of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership (Appendix 2 to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of July 20, 2001, No. 284));
2) technological losses and losses from marriage;
3) battle, marriage, damage;
4) expired medicines;
5) losses of inventory items during storage and transportation caused by violation of the requirements of standards, technical and technological conditions, rules of technical operation, damage to containers, imperfection of means of protecting goods from losses and the state of the applied technological equipment (Guidelines on the development of norms of natural loss (annex to the order of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation of March 31, 2003 No. 95)).
The amount of losses can be determined from the results of the inventory.
Accounting for losses within the norms of natural loss in accounting depends on the place of their formation.
Losses identified during procurement:
Debit account 10 "Materials", 41 "Goods",
Losses identified during storage or sale:
The debit of account 20 "Main production", 44 "Selling expenses",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- written off losses within the limits of natural loss norms.
In tax accounting, it is impossible to reduce income for losses within the limits of natural loss rates. The legislative framework by this issue not finalized.
In case of losses in excess of the norms of natural loss without identifying the perpetrators:
Debit of subaccount 91-2 "Other expenses", Credit of account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to values"- written off losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
The grounds for writing off in accounting of losses from damage and shortages in excess of the norms of natural loss, when the perpetrators are not identified, are a well-founded conclusion and decisions of the investigating authorities, which confirm the absence of perpetrators, a conclusion on the fact of damage to valuables received from the relevant specialized organizations (for example, inspections by quality).
In tax accounting, the amount of losses of material assets for which the guilty persons have not been identified can be included in the non-operating expenses, but with the attachment of a copy of the order to suspend the criminal proceedings, confirming the fact that there are no persons guilty of the theft.
According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 13, 1996, No. 375 "On Approval of the Limit Norms of Natural Waste (Production Waste) of Medicines in Pharmacy Warehouses (Bases)", writing off natural loss in the absence of a shortage or preliminary write-off is prohibited.
Natural loss (production waste) is determined by the size of the group rate or individually (if any) in accordance with the attached table.
Natural loss (production waste) is established according to the filling journal (Form 101-AP), which reflects the deviations in the weight of the medicinal product after filling from its original actual weight before filling. This form is presented in Appendix 1.
The natural loss (production waste) of medicines is written off within the limits of the norms only based on the results of the inventory.
The basis for determining the actual losses is the data of the packing journal, in which a separate sheet is opened for each drug.
Packing magazinemust be numbered, laced, sealed and signed by the head of the pharmacy warehouse.
The packing journal for poisonous and narcotic drugs must be numbered, laced, sealed with a wax seal and signed by the head of the parent organization.
When writing off the packing journal data on actual losses for each item are summed up and the actual amount of losses is determined, to which the rate of loss is applied.
If a surplus of medicines is found in the process of manufacturing operations, the reasons for their formation are established. Surplus is subject to posting. If there is a surplus of poisonous and narcotic drugs, the head of the department is obliged to notify the warehouse manager and the higher organization about this within three days.
The results of the inventory of medicines and medicines are indicated in the inventory list of inventories (form No. INV-3) and in the comparative statement of the results of inventory of inventories (form No. INV-19). Next, the calculation of losses is performed within the limits of the norms of loss and the amount of excess losses is established.
According to sub. 2 p. 7 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an accountant can reduce the income tax base for losses from shortage or damage during the storage and transportation of medicines within the limits of natural loss.
Example
In January 2007, pharmacy No. 15 purchased 50 kg of hygroscopic cotton wool for sale at a price of 20 rubles. (excluding VAT) per 1 kg.
In April 2007, cotton wool was packaged in 200 g each and sold. At the same time, the shortage of cotton wool during packaging was established - 0.1 kg.
The established norms of natural loss as a percentage of the cost for packaging are 0.45%.
Writing off the shortage of cotton wool, the accountant of pharmacy No. 15 made the following entries:
Credit account 41 "Goods"- 2 rubles. - the lack of cotton wool is reflected;
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- 2 rubles. - written off the shortage within the norms of natural loss.
The pharmacy accountant can reduce taxable profit by the amount of losses from shortages (2 rubles).
When asked whether it is necessary to restore the "input" VAT, which falls on losses within the limits of natural loss rates, the tax authorities answer what is needed. They substantiate their point of view as follows: important condition deduction of "input" VAT is the use of property in activities that are taxed. Consequently, if VAT is not charged on the property for which a shortage has been identified within the limits of natural loss, then the corresponding tax must be restored.
At the same time, medical organizations do not need to recover the "input" VAT. True, in this case, most often they have to defend their point of view in court. The defense in court can be built on the following argument. In ch. 21 "Value Added Tax" of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation lists all cases in which it is required to recover VAT:
1) for goods purchased before the organization received VAT exemption (clause 8 of article 145);
2) for VAT, presented for deduction, and not included in the value of the property (clause 2 of article 170).
Among these cases, there is no situation with the write-off of missing property. Accounting for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss in accounting is based on whether there are culprits who will compensate for the losses.
The procedure for compensation for the inflicted medical organization damage due to damage to medicines depends on the relationship between the organization and the employee who caused the damage. If the employee is not a full-time employee and performs work on the basis of a civil law contract (work contract), then he will have to compensate the losses in full. This is established by paragraph 1 of Art. 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
If the employee is concluded employment contract, compensation for damage caused is made in accordance with Ch. 39 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the employee is obliged to compensate for the direct actual damage caused. Unearned income (loss of profits) is not subject to collection from the employee.
If the culprit is identified who will compensate for the loss, then the accountant must make the following entry:
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- attributed to the culprit of the loss.
In tax accounting, recoverable losses must be included in non-operating income. This follows from paragraph 3 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The situation with the restoration of the "input" VAT, which is included in losses in excess of the norms of natural loss, is the same as in the case of writing off losses within the norms of natural loss.
Example
Let's use the data of the previous example, only now the shortage of cotton wool was 2 kg. And at the same time, the packer was recognized as the culprit of the shortage in excess of the norms of natural loss. She agreed to compensate for losses in excess of the rate of natural attrition.
To write off the shortage of cotton wool, the following document was drawn up:
In the accounting, the accountant of the pharmacy number 15 made the following entries:
Debit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables",
Credit account 41 "Goods"- 40 rubles. - the lack of cotton wool is reflected;
The debit of account 44 "Costs of sale",
4.5 RUB - written off the shortage within the norms of natural loss;
Debit of subaccount 73-2 "Calculations for compensation for material damage",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" -RUB 35.5 - written off the shortage in excess of the norms of natural loss;
Debit account 50 "Cashier",
Credit of sub-account 73-2 "Calculations for compensation of material damage" -RUB 35.5 – received money from the packer.
In tax accounting, losses of cotton wool (35.5 rubles) were not included in expenses. At the same time, the accountant included the received compensation for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss (35.5 rubles) in the structure of non-operating income.
In the event that there are no perpetrators of losses in excess of the norms of natural loss, then the amount of losses is written off by the following wiring:
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" -written off losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
It should be noted that the write-off in accounting of losses from damage and (or) shortage in excess of the norms of natural loss, provided that the culprit is not identified, is carried out on the basis of a well-grounded conclusion. In addition, there should be decisions of the investigating authorities, which confirm the absence of perpetrators, or a conclusion on the fact of damage to valuables received from the relevant specialized organizations (for example, quality inspection). Such documents are required to collect clause 5.2 of the Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of June 13, 1995 No. 49).
In tax accounting, the amount of losses of material assets, for which the guilty persons have not been identified, can be included in non-operating expenses. IN in this case the fact that there are no guilty persons must be documented by the authorized government body. This is established by sub. 5 p. 2 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Example
The packer refused to compensate for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss. Pharmacy No. 15 did not apply to the investigating authorities in order to obtain from them a document confirming the absence of the guilty persons.
The accountant of pharmacy No. 15 reflected the shortage of cotton wool in excess of the natural loss rate as follows:
Debit of subaccount 91-2 "Other expenses",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- 35.5 rubles. - written off losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
The accountant of pharmacy No. 15 cannot reduce taxable income for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss (35.5 rubles).
Write-off of expired drugs
According to the Federal Law of June 22, 1998 No. 86-FZ "On medicines», It is prohibited to sell drugs that have become unusable, expired, as well as counterfeit drugs.
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2002 No. 382 “On Approval of the Instruction on the Procedure for the Destruction of Medicines”, medicines that have become unusable and medicines with an expired shelf life are subject to withdrawal from circulation and subsequent destruction in full. Funds are confiscated and withdrawn from circulation by the customs authorities of the Russian Federation, legal entities and individual entrepreneurswho own or are the owners of these medicinal products. The destruction of medicines must be carried out in compliance with the mandatory requirements of regulatory and technical documents for the protection environment and carried out by the commission for the destruction of medicines, created by the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, in the presence of the owner or owner of the medicines to be destroyed.
Exist procedure for the destruction of medicines:
1) liquid dosage forms (solutions for injections in ampoules, packages, vials, aerosol cans, medicines, drops, etc.) are destroyed by crushing, followed by dilution of their contents with water in a ratio of 1: 100 and draining the resulting solution into the industrial sewer (in aerosol holes are pre-made in cylinders). Remains of ampoules, aerosol cans, bags and bottles are disposed of as industrial or household waste;
2) solid dosage forms (powders, tablets, capsules, etc.) containing water-soluble substances of medicinal products, after crushing to a powdery state, are diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 100 and the resulting suspension is discharged into the industrial sewer;
3) solid dosage forms (powders, tablets, capsules, etc.) containing drug substances that are not soluble in water, soft dosage forms (ointments, suppositories, etc.), transdermal forms of drugs, as well as pharmaceutical substances are destroyed by burning ;
4) narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances included in lists II and III of the List drugs, psychotropic substances and their precursors, further use which in medical practice is recognized as inappropriate, are destroyed in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
5) flammable, explosive medicines, radiopharmaceuticals and medicinal plant raw materials with increased content radionuclides are destroyed in special conditions for special technologyheld by the destruction organization in accordance with the license.
The Commission for the Destruction of Medicines is act specifying:
1) date and place of destruction;
2) place of work, position, full name of persons participating in the destruction;
3) the basis for the destruction;
4) information about the name (indicating dosage form, dosage, units of measurement, series) and the amount of the destroyed medicinal product, as well as containers or packaging;
5) the name of the manufacturer of the medicinal product;
6) the name of the owner or owner of the medicinal product;
7) method of destruction.
The act on the destruction of medicinal products is signed by all members of the commission and sealed by the seal of the enterprise that carried out the destruction of the medicinal product.
For reasons of battle, damage, scrap of inventories subject to markdown or write-off, loss of quality of goods that are not subject to further sale, a pharmacy can use forms No. TORG-15 and TORG-16, approved by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 No. No. 132 "On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for the accounting of trade operations."
Example
In March 2008, the pharmacy "Calendula" revealed unsold drugs with an expired shelf life.
For medicinal products expired on 03/31/2008, acts were drawn up according to forms No. TORG-15 and TORG-16.
The act of writing off the goods (form No. TORG-16)
Reverse side of form TORG-16
The act of damage, battle, scrap of inventory (form No. TORG-15)
Ending
Reverse side of form No. TORG-15
Record scrap (scrap):
The act of damage to inventory items in form No. A-2.18 is drawn up by a specially appointed inventory commission at the time of discovery of the fact of damage or during an inventory. The act is written out in triplicate separately for each group of values \u200b\u200b(medicines, containers, etc.) with the determination of the causes of damage and the perpetrators.
Write-off of medicines and containers is carried out at current prices. Attached to the act are explanatory explanations for the perpetrators of damage to values. Two copies of the act must be sent for approval, the last one is with the materially responsible person and is attached to the report when the values \u200b\u200bare written off.
Example
Let's supplement the conditions of the above example. Let's assume that the medicines arrived at the pharmacy from Doctor LLC. At the same time, the retail price for medicines is:
1) cardanum p / o 50 mg No. 50 - 150.55 rubles;
2) multi-tabs V-comp. No. 100 - 198.76 rubles.
The pharmacy, instead of acts according to forms No. TORG-15, TORG-16, drew up an act of damage to goods and materials according to form No. A-2.18.
Ending
The pharmacy must enter into an agreement with an organization dealing with the destruction of expired drugs. The transfer of such medicinal products is formalized by an appropriate act.
The cost of the work of a specialized organization depends on the weight of the drugs, their volume and packaging. The most costly is the destruction of aerosolized drugs.
Also, the costs incurred will be confirmed by the contract for the performance of work, the bill for the work performed and the act of acceptance of the work performed. The costs of the destruction of medicines are taken into account when calculating income tax and are determined as economically justified.
It should be noted that in the absence of production and small batches of medicines to be destroyed, medicines with an expired shelf life can be destroyed by the pharmacy organization itself.
For accounting purposes, the pharmacy's costs associated with the write-off of expired drugs are related to other costs and are reflected in the reporting period in which they occurred.
In the accounting of the pharmacy organization, the amount of losses from the write-off of expired drugs is established by the following entry:
Debit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables",
Credit of subaccount 41-2 "Goods in retail trade"- the amount of losses from drug write-off is reflected. Moreover, if the pharmacy keeps records medical supplies at sales prices (using account 42 "Trade margin"), you should write off the amount of the mark-up that relates to spoiled medicines:
Debit of account 42 "Trade margin",
Credit of subaccount 41-2 "Goods in retail trade" -the amount of the mark-up related to spoiled medicines has been written off.
Only the purchase price of medicines (excluding the margin, but taking into account the costs of their delivery to the pharmacy, if this is provided for by the accounting policy of the pharmacy organization) will be written off to the debit of account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables".
Based on the decision of the commission, the amount of losses from the write-off of expired medicinal products is attributed either to the perpetrators or to the financial result:
Debit of subaccount 73-2 "Calculations for compensation for material damage",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- attributed to the guilty persons the amount of losses from the write-off of medicines;
Debit of subaccount 91-2 "Other expenses",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" -the loss from drug write-off is reflected.
Example
Pharmacy LLC "Calendula", which is the payer of UTII, in the course of the inventory in the warehouse, revealed unsold drugs with an expired shelf life. In accordance with the accounting policy of the pharmacy, goods are recorded at sales prices. The book price of expired medicines was 15,200 rubles, including a trade margin of 1100 rubles. Destruction of these drugs produced by a specialized organization. The cost of work on their destruction is RUB 3,620, plus VAT - RUB 651.
To reflect the operations to write off expired drugs, the pharmacy accountant will make the following entries:
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not stipulate that the cost of destroyed medicines can be reflected in expenses that reduce taxable profit. Tax legislation gives the right to include in expenses losses from shortages of material assets in production and warehouses (subparagraph 5 of paragraph 2 of article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and (or) damage during storage and transportation of goods and materials within the limits of natural loss (sub. 2 clause 7 of article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
However, the costs associated with the production of drugs that are destroyed due to the expiration date can be accounted for as a deductible expense in other expenses, similar to the cost of canceled production orders, in the amount of direct costs.
For the purpose of taxing the profits of organizations, expenses are recognized as justified, economically justified and documented costs incurred by the taxpayer to carry out activities aimed at generating income (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The economic feasibility of the expenses incurred by the taxpayer is established by the direction of such expenses to generate income, that is, the conditionality of the economic activity of the taxpayer, taking into account the content of the entrepreneurial goals and objectives of the organization, and not the actual receipt of income in a specific reporting (tax) period. Thus, the acceptance of expenses for tax purposes is not excluded in the event of a loss by the taxpayer (letter of the Department of Tax and Customs and Tariff Policy of the RF Ministry of Finance dated October 27, 2005, No. 03-03-04 / 4/69).
The pharmacy has the right to take into account the cost of destroyed medicines as expenses that reduce taxable profit.
Taxpayers have the right to reduce the amount of VAT accrued to be paid to the budget by the amount tax deductions (Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, according to general rule the amount of "input" VAT on purchased goods can be claimed for deductionunder the following conditions:
1) the purchased goods are intended for carrying out transactions subject to VAT (clause 2 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
2) the goods are accepted for accounting (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
3) there is a properly executed invoice (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, a pharmacy has purchased a batch of medicines for subsequent resale. Medicines were posted to the warehouse. The invoice has been properly issued. Therefore, the amount of VAT related to purchased medicines is deducted.
Some of the medicines were not sold before the expiration date, and they were destroyed. The amounts of VAT accepted by the taxpayer for deduction on goods purchased for the performance of transactions recognized as objects of taxation, but not used for these transactions, must be restored and paid to the budget.
The sale of expired drugs is qualified in accordance with the Regulation on Licensing Activities for the Production of Medicines, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 415 of July 6, 2006 “On Approval of the Regulation on the Licensing of Production of Medicines”, as a gross violation of licensing conditions.
For such a violation of paragraph 4 of Art. 14.1 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation a fine is foreseen:
1) for organizations - in the amount of 4 thousand to 5 thousand rubles or suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
2) for officials - in the amount of 4 thousand to 5 thousand rubles;
3) on legal entities - from 40 thousand to 50 thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
Violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation on medicines can be detected during an on-site tax audit. For example, checking the primary documentation, the controllers discovered the facts of the sale of expired drugs.
Upon discovery of facts indicating violations of the legislation on medicines, the tax authorities have the right to contact Federal Service on supervision in the field of health care and social development with a petition to revoke or suspend the license pharmacy to implement pharmaceutical activities... Further, in accordance with Art. 13 Federal law dated August 8, 2001 No. 128-FZ "On licensing of certain types of activities", the suspension or cancellation of the license is carried out in judicial procedure based on the application of the licensing authority.
- Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of July 20, 2001 N 284 "On Approval of the Norms of Natural Waste of Medicines and Medical Products in Pharmacy Organizations Regardless of the Form of Incorporation and Ownership"
- Appendix No. 1. Norms of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership
- Appendix No. 2. Instructions for the application of the norms of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership
- Application. Calculation of the natural loss of medicines and medical products
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of July 20, 2001 N 284
"On Approval of Norms of Natural Waste of Medicines and Medical Products in Pharmacy Organizations Regardless of the Form of Incorporation and Ownership"
In order to reduce unproductive losses and increase responsibility for the safety of inventory items in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership, I order:
1. To approve:
1.1. The rates of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership (Appendix N 1).
1.2. Instructions on the application of the norms of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership (Appendix No. 2).
2. Heads of healthcare authorities and pharmaceutical organizations of the subjects Russian Federation accept this order for guidance and execution.
3. Control over the implementation of this order shall be entrusted to the Deputy Minister AVKatlinsky.
Yu.L. Shevchenko |
Registration N 2997
Ethanol:
Individual production of medicines, including according to homeopathic prescriptions
Weighing alcohol into a pharmacy container without additional technological operations (mixing with other medicines, dividing into doses)
"Approved" The head of the legal entity ______________________________ signature, surname, etc., about. "__" ___________ 200_
Organization name _________________________________________________ Department ___________________________________________________________________
Payment natural loss of medicines
and medical products
for the period from _______ 200 to _______ 200
Financially responsible person __________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ position, surname, and., O. (amount)
Name | unit of measurement | Turnover for the inter-inventory period | Natural loss rate,% | Charged at the rate of natural loss | Written off according to the rate of natural loss | Lack in excess of the norms of natural loss |
At the rate of loss ________________________ above the rate of loss _______________________
The calculation was made by the accountant _______________________________________________ signature surname, and., O. Financially responsible person __________________________________________ signature surname, and., O. "__" ___________200
Chapter 2. Limit rates of natural wastage of medicines in pharmacy warehouses
According to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of January 9, 2007 No. 2 "On the approval of the norms of natural loss during the storage of medicines in pharmacies (organizations), drug wholesalers and health care institutions", in connection with the use in pharmacies (organizations) of new technologies for organizing the storage of medicines, as well as in the order of control over ensuring their safety, the norms of natural loss of medicines in pharmacies (organizations) were approved. The rates of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership and the Instructions for their use, were approved by order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated July 20, 2001 No. 284 "On approval of the rates of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership ”.
The maximum rates of natural loss of medicines are established to cover the loss that occurs in pharmacy warehouses during the process of industrial packaging (spraying, volatilization, bottling, adhesion to container walls, losses when moving from a large package to a smaller one, etc.)
The rates are established to reimburse the cost of losses within the limits of natural loss in the manufacture of medicines according to the prescriptions of doctors and the requirements of health care institutions, intra-pharmacy procurement and packaging in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership and are applied only in the event of a shortage of inventory items when taking inventory.
The indicated rates of natural loss do not apply to finished medicinal products of industrial production and medicinal products by weight (including ethyl alcohol), sold in their original (factory, factory, warehouse) packaging.
The application of these norms, that is, the calculation of the amount of losses from natural loss within the established norms, is made on the basis of the data of the primary accounting documents for the dispensing (sale) of medicines, individually manufactured according to the prescriptions and requirements of healthcare institutions, intra-pharmaceutical preparation and packaging, as well as when released in bulk, in violation of the original packaging. Natural loss rates apply only to medicines and medical products sold during the inter-inventory period. Fight, marriage, damage, losses due to the expiration of the shelf life of medicines are not written off at the rate of natural loss.
In accordance with paragraph 7 of Art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, losses from shortages and (or) damage during storage and transportation of inventories within the limits of natural loss, approved in the manner established by the Government of the Russian Federation, are equated to material costs for tax purposes.
By order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of January 9, 2007 No. 2, the norms of natural loss during storage of medicines in pharmacies (organizations), drug wholesalers and healthcare institutions were approved (see Table 3).
Table 3
Appendix to the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation of January 9, 2007 No. 2
Norms of natural loss during storage of medicines in pharmacies (organizations), drug wholesalers and healthcare institutions
According to the Instruction on the Application of Limiting Norms of Natural Waste (Production Waste) of Medicines in Pharmacy Warehouses (Appendix 2 to the Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 375 dated November 13, 1996 "On Approval of the Limit Norms of Natural Waste (Production Waste) of Medicines in Pharmacy Warehouses ) ", The limit rates of natural loss of medicines are established to cover the loss that occurs in pharmacy warehouses during the process of industrial packaging (spraying, volatilization, spillage, adhesion to container walls and auxiliary items, during packing, losses when moving from a large package to a smaller one) etc.).
The shortage of medicines that occurred due to damage and breakage of containers, damage to the drug should be recorded by a special commission in an act in the form of 20-AP (not included in the norms).
The application of limiting norms of natural loss to the consumption of medicines in industrial packaging or in dosage form without carrying out any production operations in the warehouse is not allowed.
Natural decline- these are losses that occur during transportation, storage, as well as due to:
1) spraying a number of powder preparations, drying them, breaking in glass containers;
2) natural loss of medicines and cotton wool in pharmacies;
3) loss of glass pharmaceutical utensils at pharmaceutical factories (production) and pharmacy warehouses (bases);
4) natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal form and form of ownership.
Natural attrition rates do not apply to:
1) finished pharmaceuticals of industrial production and weight medicines (including ethyl alcohol), sold in the original (factory, factory, warehouse) packaging (Instructions for the application of the norms of natural loss of medicines and medical products in pharmacy organizations, regardless of the organizational and legal forms and forms of ownership (Appendix 2 to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of July 20, 2001, No. 284));
2) technological losses and losses from marriage;
3) battle, marriage, damage;
4) expired medicines;
5) losses of inventory items during storage and transportation caused by violation of the requirements of standards, technical and technological conditions, rules of technical operation, damage to containers, imperfection of means of protecting goods from losses and the state of the technological equipment used (Guidelines for the development of norms of natural loss ( annex to the order of the RF Ministry of Economic Development of March 31, 2003 No. 95)).
The amount of losses can be determined from the results of the inventory.
Accounting for losses within the norms of natural loss in accounting depends on the place of their formation.
Losses identified during procurement:
Debit account 10 "Materials", 41 "Goods",
Losses identified during storage or sale:
The debit of account 20 "Main production", 44 "Selling expenses",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- written off losses within the limits of natural loss norms.
In tax accounting, it is impossible to reduce income for losses within the limits of natural loss rates. The legal framework on this issue has not been finalized.
In case of losses in excess of the norms of natural loss without identifying the perpetrators:
Debit of subaccount 91-2 "Other expenses", Credit of account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to values"- written off losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
The grounds for writing off in accounting of losses from damage and shortages in excess of the norms of natural loss, when the perpetrators are not identified, are a well-founded conclusion and decisions of the investigating authorities, which confirm the absence of perpetrators, a conclusion on the fact of damage to valuables received from the relevant specialized organizations (for example, inspections by quality).
In tax accounting, the amount of losses of material assets for which the guilty persons have not been identified can be included in the non-operating expenses, but with the attachment of a copy of the order to suspend the criminal proceedings, confirming the fact that there are no persons guilty of the theft.
According to the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of November 13, 1996, No. 375 "On Approval of the Limit Norms of Natural Waste (Production Waste) of Medicines in Pharmacy Warehouses (Bases)", writing off natural loss in the absence of a shortage or preliminary write-off is prohibited.
Natural loss (production waste) is determined by the size of the group rate or individually (if any) in accordance with the attached table.
Natural loss (production waste) is established according to the filling journal (Form 101-AP), which reflects the deviations in the weight of the medicinal product after filling from its original actual weight before filling. This form is presented in Appendix 1.
The natural loss (production waste) of medicines is written off within the limits of the norms only based on the results of the inventory.
The basis for determining the actual losses is the data of the packing journal, in which a separate sheet is opened for each drug.
Packing magazinemust be numbered, laced, sealed and signed by the head of the pharmacy warehouse.
The packing journal for poisonous and narcotic drugs must be numbered, laced, sealed with a wax seal and signed by the head of the parent organization.
When writing off the packing journal data on actual losses for each item are summed up and the actual amount of losses is determined, to which the rate of loss is applied.
If a surplus of medicines is found in the process of manufacturing operations, the reasons for their formation are established. Surplus is subject to posting. If there is a surplus of poisonous and narcotic drugs, the head of the department is obliged to notify the warehouse manager and the higher organization about this within three days.
The results of the inventory of medicines and medicines are indicated in the inventory list of inventories (form No. INV-3) and in the comparative statement of the results of inventory of inventories (form No. INV-19). Next, the calculation of losses is performed within the limits of the norms of loss and the amount of excess losses is established.
According to sub. 2 p. 7 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an accountant can reduce the income tax base for losses from shortage or damage during the storage and transportation of medicines within the limits of natural loss.
Example
In January 2007, pharmacy No. 15 purchased 50 kg of hygroscopic cotton wool for sale at a price of 20 rubles. (excluding VAT) per 1 kg.
In April 2007, cotton wool was packaged in 200 g each and sold. At the same time, the shortage of cotton wool during packaging was established - 0.1 kg.
The established norms of natural loss as a percentage of the cost for packaging are 0.45%.
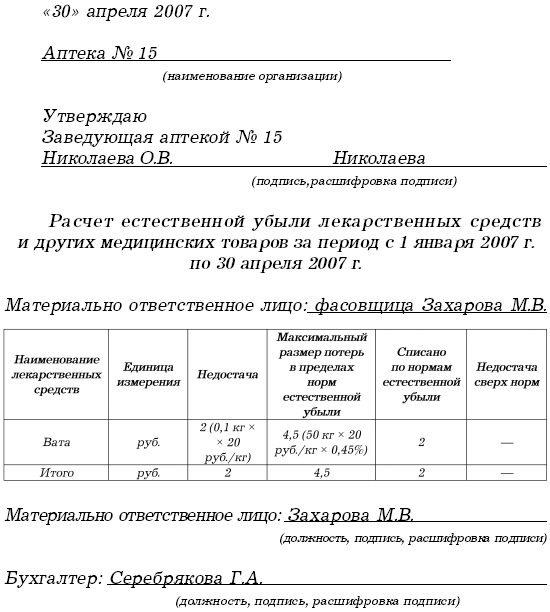
Writing off the shortage of cotton wool, the accountant of pharmacy No. 15 made the following entries:
Credit account 41 "Goods"- 2 rubles. - the lack of cotton wool is reflected;
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- 2 rubles. - written off the shortage within the norms of natural loss.
The pharmacy accountant can reduce taxable profit by the amount of losses from shortages (2 rubles).
When asked whether it is necessary to restore the "input" VAT, which falls on losses within the limits of natural loss norms, the tax authorities answer what is needed. They substantiate their point of view as follows: an important condition for deducting input VAT is the use of property in activities that are taxed. Consequently, if VAT is not charged on the property for which a shortage is detected within the limits of natural loss, then the corresponding tax must be restored.
At the same time, medical organizations do not need to recover the "input" VAT. True, in this case, most often they have to defend their point of view in court. The defense in court can be built on the following argument. In ch. 21 "Value Added Tax" of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation lists all cases in which it is required to recover VAT:
1) for goods purchased before the organization received VAT exemption (clause 8 of article 145);
2) for VAT, presented for deduction, and not included in the value of the property (clause 2 of article 170).
Among these cases, there is no situation with the write-off of missing property. Accounting for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss in accounting is based on whether there are culprits who will compensate for the losses.
The procedure for reimbursing the damage caused to a medical organization in connection with damage to medicines depends on the relationship between the organization and the employee who caused the damage. If the employee is not a full-time employee and performs work on the basis of a civil law contract (work contract), then he will have to compensate the losses in full. This is established by paragraph 1 of Art. 1064 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
If an employment contract is concluded with an employee, compensation for the damage caused is made in accordance with Ch. 39 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, the employee is obliged to compensate for the direct actual damage caused. Unearned income (loss of profits) is not subject to collection from the employee.
If the culprit is identified who will compensate for the loss, then the accountant must make the following entry:
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- attributed to the culprit of the loss.
In tax accounting, recoverable losses must be included in non-operating income. This follows from paragraph 3 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The situation with the restoration of the "input" VAT, which is included in losses in excess of the norms of natural loss, is the same as in the case of writing off losses within the norms of natural loss.
Example
Let's use the data of the previous example, only now the shortage of cotton wool was 2 kg. And at the same time, the packer was recognized as the culprit of the shortage in excess of the norms of natural loss. She agreed to compensate for losses in excess of the rate of natural attrition.
To write off the shortage of cotton wool, the following document was drawn up:


In the accounting, the accountant of the pharmacy number 15 made the following entries:
Debit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables",
Credit account 41 "Goods"- 40 rubles. - the lack of cotton wool is reflected;
The debit of account 44 "Costs of sale",
4.5 RUB - written off the shortage within the norms of natural loss;
Debit of subaccount 73-2 "Calculations for compensation for material damage",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" -RUB 35.5 - written off the shortage in excess of the norms of natural loss;
Debit account 50 "Cashier",
Credit of sub-account 73-2 "Calculations for compensation of material damage" -RUB 35.5 – received money from the packer.
In tax accounting, losses of cotton wool (35.5 rubles) were not included in expenses. At the same time, the accountant included the received compensation for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss (35.5 rubles) in the structure of non-operating income.
In the event that there are no perpetrators of losses in excess of the norms of natural loss, then the amount of losses is written off by the following wiring:
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" -written off losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
It should be noted that the write-off in accounting of losses from damage and (or) shortage in excess of the norms of natural loss, provided that the culprit is not identified, is carried out on the basis of a well-grounded conclusion. In addition, there should be decisions of the investigating authorities, which confirm the absence of perpetrators, or a conclusion on the fact of damage to valuables received from the relevant specialized organizations (for example, quality inspection). Such documents are required to collect clause 5.2 of the Methodological Guidelines for the Inventory of Property and Financial Liabilities (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of June 13, 1995 No. 49).
In tax accounting, the amount of losses of material assets for which the guilty persons have not been identified can be included in the non-operating expenses. In this case, the fact that there are no guilty persons must be documented by an authorized government body. This is established by sub. 5 p. 2 art. 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Example
The packer refused to compensate for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss. Pharmacy No. 15 did not apply to the investigating authorities in order to obtain from them a document confirming the absence of the guilty persons.
The accountant of pharmacy No. 15 reflected the shortage of cotton wool in excess of the natural loss rate as follows:
Debit of subaccount 91-2 "Other expenses",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- 35.5 rubles. - written off losses in excess of the norms of natural loss.
The accountant of pharmacy No. 15 cannot reduce taxable income for losses in excess of the norms of natural loss (35.5 rubles).
Write-off of expired drugs
According to the Federal Law of June 22, 1998, No. 86-FZ "On Medicines", it is prohibited to sell medicines that have become unusable, with an expired shelf life, as well as counterfeit medicines.
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of December 15, 2002 No. 382 “On Approval of the Instruction on the Procedure for the Destruction of Medicines”, medicines that have become unusable and medicines with an expired shelf life are subject to withdrawal from circulation and subsequent destruction in full. The funds are confiscated and withdrawn from circulation by the customs authorities of the Russian Federation, legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who are the owners or owners of these drugs. The destruction of medicines must be carried out in compliance with the mandatory requirements of regulatory and technical documents on environmental protection and carried out by a commission for the destruction of medicines, created by the executive authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, in the presence of the owner or owner of the medicines to be destroyed.
Exist procedure for the destruction of medicines:
1) liquid dosage forms (solutions for injections in ampoules, packages, vials, aerosol cans, medicines, drops, etc.) are destroyed by crushing, followed by dilution of their contents with water in a ratio of 1: 100 and draining the resulting solution into the industrial sewer (in aerosol holes are pre-made in cylinders). Remains of ampoules, aerosol cans, bags and bottles are disposed of as industrial or household waste;
2) solid dosage forms (powders, tablets, capsules, etc.) containing water-soluble substances of medicinal products, after crushing to a powdery state, are diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 100 and the resulting suspension is discharged into the industrial sewer;
3) solid dosage forms (powders, tablets, capsules, etc.) containing drug substances that are not soluble in water, soft dosage forms (ointments, suppositories, etc.), transdermal forms of drugs, as well as pharmaceutical substances are destroyed by burning ;
4) narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances included in lists II and III of the List of narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances and their precursors, the further use of which in medical practice is recognized as inappropriate, are destroyed in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
5) flammable, explosive drugs, radiopharmaceuticals and medicinal plant materials with a high content of radionuclides are destroyed under special conditions using a special technology at the disposal of the destruction organization, in accordance with the license.
The Commission for the Destruction of Medicines is act specifying:
1) date and place of destruction;
2) place of work, position, full name of persons participating in the destruction;
3) the basis for the destruction;
4) information about the name (indicating the dosage form, dosage, unit of measurement, batch) and the amount of the medicinal product to be destroyed, as well as about the container or packaging;
5) the name of the manufacturer of the medicinal product;
6) the name of the owner or owner of the medicinal product;
7) method of destruction.
The act on the destruction of medicinal products is signed by all members of the commission and sealed by the seal of the enterprise that carried out the destruction of the medicinal product.
For reasons of battle, damage, scrap of inventories subject to markdown or write-off, loss of quality of goods that are not subject to further sale, a pharmacy can use forms No. TORG-15 and TORG-16, approved by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998 No. No. 132 "On approval of unified forms of primary accounting documentation for the accounting of trade operations."
Example
In March 2008, the pharmacy "Calendula" revealed unsold drugs with an expired shelf life.
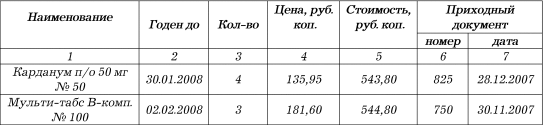
For medicinal products expired on 03/31/2008, acts were drawn up according to forms No. TORG-15 and TORG-16.
The act of writing off the goods (form No. TORG-16)

Reverse side of form TORG-16

The act of damage, battle, scrap of inventory (form No. TORG-15)

Ending
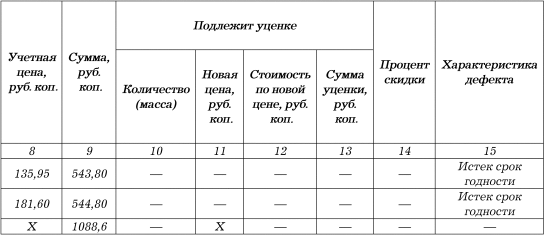
Reverse side of form No. TORG-15
Record scrap (scrap):
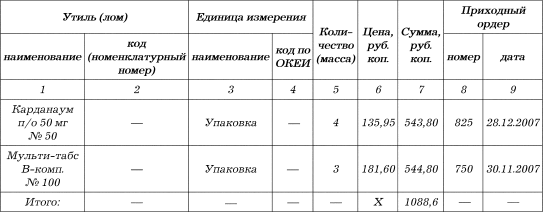
The act of damage to inventory items in form No. A-2.18 is drawn up by a specially appointed inventory commission at the time of discovery of the fact of damage or during an inventory. The act is written out in triplicate separately for each group of values \u200b\u200b(medicines, containers, etc.) with the determination of the causes of damage and the perpetrators.
Write-off of medicines and containers is carried out at current prices. Attached to the act are explanatory explanations for the perpetrators of damage to values. Two copies of the act must be sent for approval, the last one is with the materially responsible person and is attached to the report when the values \u200b\u200bare written off.
Example
Let's supplement the conditions of the above example. Let's assume that the medicines arrived at the pharmacy from Doctor LLC. At the same time, the retail price for medicines is:
1) cardanum p / o 50 mg No. 50 - 150.55 rubles;
2) multi-tabs V-comp. No. 100 - 198.76 rubles.
The pharmacy, instead of acts according to forms No. TORG-15, TORG-16, drew up an act of damage to goods and materials according to form No. A-2.18.

Ending

The pharmacy must enter into an agreement with an organization dealing with the destruction of expired drugs. The transfer of such medicinal products is formalized by an appropriate act.
The cost of the work of a specialized organization depends on the weight of the drugs, their volume and packaging. The most costly is the destruction of aerosolized drugs.
Also, the costs incurred will be confirmed by the contract for the performance of work, the bill for the work performed and the act of acceptance of the work performed. The costs of the destruction of medicines are taken into account when calculating income tax and are determined as economically justified.
It should be noted that in the absence of production and small batches of medicines to be destroyed, medicines with an expired shelf life can be destroyed by the pharmacy organization itself.
For accounting purposes, the pharmacy's costs associated with the write-off of expired drugs are related to other costs and are reflected in the reporting period in which they occurred.
In the accounting of the pharmacy organization, the amount of losses from the write-off of expired drugs is established by the following entry:
Debit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables",
Credit of subaccount 41-2 "Goods in retail trade"- the amount of losses from drug write-off is reflected. At the same time, if the pharmacy keeps records of medicinal products at selling prices (using account 42 "Trade margin"), the amount of the margin that relates to the spoiled medicinal products should be written off:
Debit of account 42 "Trade margin",
Credit of subaccount 41-2 "Goods in retail trade" -the amount of the mark-up related to spoiled medicines has been written off.
Only the purchase price of medicines (excluding the margin, but taking into account the costs of their delivery to the pharmacy, if this is provided for by the accounting policy of the pharmacy organization) will be written off to the debit of account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables".
Based on the decision of the commission, the amount of losses from the write-off of expired medicinal products is attributed either to the perpetrators or to the financial result:
Debit of subaccount 73-2 "Calculations for compensation for material damage",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables"- attributed to the guilty persons the amount of losses from the write-off of medicines;
Debit of subaccount 91-2 "Other expenses",
Credit account 94 "Shortages and losses from damage to valuables" -the loss from drug write-off is reflected.
Example
Pharmacy LLC "Calendula", which is the payer of UTII, in the course of the inventory in the warehouse revealed unsold drugs with an expired shelf life. In accordance with the accounting policy of the pharmacy, goods are recorded at sales prices. The book price of expired drugs was 15,200 rubles, including a trade margin of 1100 rubles. The destruction of these medicinal products was carried out by a specialized organization. The cost of work on their destruction is RUB 3,620, plus VAT - RUB 651.
To reflect the operations to write off expired drugs, the pharmacy accountant will make the following entries:
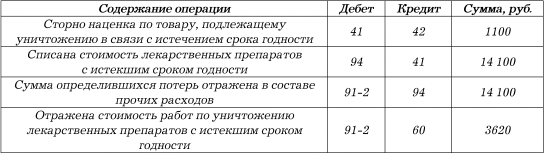
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not stipulate that the cost of destroyed medicines can be reflected in expenses that reduce taxable profit. Tax legislation gives the right to include in expenses losses from shortages of material assets in production and warehouses (subparagraph 5 of paragraph 2 of article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and (or) damage during storage and transportation of goods and materials within the limits of natural loss (sub. 2 clause 7 of article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
However, the costs associated with the production of drugs that are destroyed due to the expiration date can be accounted for as a deductible expense in other expenses, similar to the cost of canceled production orders, in the amount of direct costs.
For the purpose of taxing the profits of organizations, expenses are recognized as justified, economically justified and documented costs incurred by the taxpayer to carry out activities aimed at generating income (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The economic feasibility of the expenses incurred by the taxpayer is established by the direction of such expenses to generate income, that is, the conditionality of the economic activity of the taxpayer, taking into account the content of the entrepreneurial goals and objectives of the organization, and not the actual receipt of income in a specific reporting (tax) period. Thus, the acceptance of expenses for tax purposes is not excluded in the event of a loss by the taxpayer (letter of the Department of Tax and Customs and Tariff Policy of the RF Ministry of Finance dated October 27, 2005, No. 03-03-04 / 4/69).
The pharmacy has the right to take into account the cost of destroyed medicines as expenses that reduce taxable profit.
Taxpayers are given the right to reduce the amount of VAT accrued to be paid to the budget by the amount of tax deductions (Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, as a general rule the amount of "input" VAT on purchased goods can be claimed for deductionunder the following conditions:
1) the purchased goods are intended for carrying out transactions subject to VAT (clause 2 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
2) the goods are accepted for accounting (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
3) there is a properly executed invoice (clause 1 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
For example, a pharmacy has purchased a batch of medicines for subsequent resale. Medicines were posted to the warehouse. The invoice has been properly issued. Therefore, the amount of VAT related to purchased medicines is deducted.
Some of the medicines were not sold before the expiration date, and they were destroyed. The amounts of VAT accepted by the taxpayer for deduction on goods purchased for the performance of transactions recognized as objects of taxation, but not used for these transactions, must be restored and paid to the budget.
The sale of expired drugs is qualified in accordance with the Regulation on Licensing Activities for the Production of Medicines, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 415 of July 6, 2006 “On Approval of the Regulation on the Licensing of Production of Medicines”, as a gross violation of licensing conditions.
For such a violation of paragraph 4 of Art. 14.1 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation a fine is foreseen:
1) for organizations - in the amount of 4 thousand to 5 thousand rubles or suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
2) for officials - in the amount of 4 thousand to 5 thousand rubles;
3) for legal entities - from 40 thousand to 50 thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.
Violation of the legislation of the Russian Federation on medicines can be detected during an on-site tax audit. For example, checking the primary documentation, the controllers discovered the facts of the sale of expired drugs.
Upon discovery of facts indicating violations of the legislation on medicines, the tax authorities have the right to apply to the Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare and Social Development with a petition to revoke or suspend the pharmacy's license to carry out pharmaceutical activities. Further, in accordance with Art. 13 of the Federal Law of August 8, 2001 No. 128-FZ "On Licensing of Certain Types of Activities", the suspension or cancellation of a license is carried out in court on the basis of an application from the licensing authority.
From the book Tax Law. Lecture notes author Belousov Danila S.6.3. Norms-principles and norms-definitions in tax law In the mechanism of legal regulation of tax relations, norms-principles and norms-definitions act as norms of general content. They establish general definitions for tax law or initial principles
From the book Short story of money author Ostalsky Andrey VsevolodovichFarmer Bob's Extreme Extremes But let's get back to pricing. For example, Farmer Bob sits on his farm and grows five bags of grain every year. In one sack he collects the inviolable feed grain. One more is enough for him to eat and feed
From the book Accounting in Medicine author Firstova Svetlana Yurievna6.6. Accounting in pharmacy and pharmaceutical organizations (2nd level) By the nature of the activity pharmacy organizations are subdivided into: - manufacturing medicinal products according to prescriptions of doctors, requirements of health care institutions, standard prescriptions, with their subsequent
From the book Institutional Economics. New Institutional Economic Theory [Textbook] author Auzan Alexander AlexandrovichChapter 1. Norms, rules and institutions This chapter will consider one of the main concepts of the new institutional economic theory - the concept of an institution. The first, introductory, paragraph of the chapter is devoted to a discussion of the role of information in the process of making economic
author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 1. Concept and general order calculation of natural loss (production waste) When purchasing, storing and selling certain products, losses and shortages most often occur, the cause of which is natural loss.
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 3. Rates of natural loss ethyl alcohol during storage According to the order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation of December 12, 2006 No. 463 "On approval of the norms of natural loss of ethyl alcohol during storage" in pursuance of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 12, 2002
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 4. Norms of natural loss of products and raw materials of the sugar industry during storage and transportation By the Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2006 No. 270 "On approval of the norms of natural loss of products and raw materials of the sugar industry during storage"
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 5. Rates of natural loss of mass of stop root crops, potatoes, fruit and green vegetable crops different terms maturation during storage The norms are set for standard goods sold by weight as a percentage of their retail turnover to compensate for losses,
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 6. Norms of natural loss of petroleum products during reception, storage, dispensing and transportation. The procedure for applying the norms The norms of natural loss are used by all organizations, regardless of their form of ownership, that sell and receive oil products through the main
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 7. Norms of natural loss of meat, poultry and rabbits by-products during storage and transportation In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation of August 28, 2006 No. 269 "On approval of the norms of natural loss of meat, poultry and rabbits by-products during storage"
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 8. Norms of natural loss of cheeses and cottage cheese during storage and transportation By the Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation dated August 28, 2006 No. 267, the norms of natural loss of cheese and cottage cheese during storage were approved. Consider the rate of natural loss of cottage cheese due to loss of mass fraction
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 9. Norms of natural loss during storage butter, packed in monoliths in parchment and in bags made of polymeric materials Norms of natural loss during storage of butter, packed in monoliths in parchment and in bags made of polymeric materials
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 10. Accounting for losses and shortages. Write-off of goods within the limits of natural loss To organizations engaged in the storage and trade of products, the main problem their loss appears, which arises as a result of both natural causesand by
From the book of the Norm of Natural Waste author Krasnoslobodtseva GKChapter 11. The influence of natural loss on tax accounting Shortages and losses from damage to material assets can be taken into account when calculating income tax on the basis of sub. 2 p. 7 art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But such expenses are written off only within the limits of the norms of natural loss. Order, in
From the book Marketing Management author Dixon Peter R.Marginal costs Marginal costs are direct variable costs of producing and selling an additional unit of output in excess of the current volume of products produced and sold. These costs, as a rule, include additional material,
From the book Loading and Unloading. Cargo manager's guide author Volgin Vladislav VasilievichStandard Free Issuance Rates special clothing, special footwear and other personal protective equipment for workers of cross-cutting professions and positions in all sectors of the economy Extraction (as amended on December 17, 2001) Appendix to the resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation from 30
