What is the difference between MRI and MSKT and which is better? All-seeing eye: mrt or msct
V recent times doctors around the world have made a huge breakthrough in diagnostics internal organs... The doctors came to the aid of magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) and multi-spiral CT scan(or MSCT). Let's consider what are the differences between these types of diagnostics and which one is better.
MSCT is a scan of the human body using a directed X-ray beam th. In the course of such a tomography, the X-ray radiation used is converted into an electrical signal, which is transmitted to a computer. With the help of a special program, these signals are processed, which makes it possible to obtain a high-quality image. Today, such diagnostics are among the most effective and reliable.
With the help of MRI, it is also possible to obtain a high-quality image of structures. human body... In this case, radiation exposure does not occur, and the image is obtained using a high-frequency magnetic field... Specialized preparation of the patient is not required for such an examination.
MRI and MSCT are most effective in diagnosing the spine, blood vessels, brain, abdominal cavity, etc.... Computed tomography makes it possible to have a thin section, to display the structures of thin walls of organs, the structure of the spine, the spread of tumors in organs, etc. The differences between these types of diagnostics are as follows.
- With MSCT, high-quality spiral sections of organs of the human body, including the spine, are obtained. In MRI, the image is formed by the action of a high frequency magnetic field. The image quality is the same.
- Computed tomography is used to scan the bones (also the spine). But MRI is most suitable for studying soft structures.
- MSCT allows the use of X-rays, that is, it gives radiation exposure. But MRI does not use such rays.
- To obtain an image during magnetic resonance imaging, you must big time... This is why the patient must lie still for about half an hour or more. With MSCT, the doctor acts on the examined organ with X-rays for about ten seconds.
When examining an organ of the human body, the doctor chooses what is best for the person - magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
Which is better - MRI or CT?
This question was asked by many people who are recommended to diagnose the spine, brain, joints, bones, blood vessels and other organs using the latest high-tech techniques. The answer is not easy. It all depends on the goal of the research.
If we talk about radiation exposure, then magnetic resonance imaging is undoubtedly better: the patient is in a strong magnetic field that does not harm the person. Computed tomography, on the other hand, takes much less time and can be safely done to claustrophobic patients. However, X-rays are used, and this is what a significant number of patients are afraid of.
In any case, it is best for a doctor to consult a specialist in radiation research techniques before performing a tomography. It is possible that in some cases it is advisable to carry out the same no less high-quality computer tomography instead of expensive magnetic resonance imaging.
MRI or CT of the spine: which is better?

CT scan lumbar spine

MRI of the lumbar spine
Magnetic resonance imaging excellently imaging soft tissue... In this case, the bone tissue of the spine may be poorly distinguishable. In general, bones on magnetic resonance imaging are very poorly visible. This is due to the lack of resonance from calcium atoms.
That is why MSCT is used to diagnose the condition of the bone tissue of the spine, not MRI. A short-term exposure to bone tissue using strong X-rays will give the doctor a clear and reliable picture of the functioning of the body.
But if we are talking about the diagnosis of the spinal cord, in particular, its focal lesion, the presence of tumor processes in the soft tissues of the spine, then in this case, MRI is much preferable.
In this case, computed tomography is uninformative and even uninformative.
Sometimes the doctor performs both magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of the spine. Such a multi-study makes it possible to find out many of the nuances of the state of this section of the musculoskeletal system and the spinal cord and more accurately make a diagnosis.
So when examining the spine, the doctor chooses desired method, which differs based on the goals set, as well as the patient's condition. Right choice the diagnostic method allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe an effective treatment.
Comparative characteristics of MRI, MSCT
At the heart of CT is the peculiarity of X-rays absorbed by the tissues of the body. Depending on the density of the tissue, this absorption occurs in different ways. In fact, computed tomography is no different from a simple x-ray examination of the body. The work of a computer differs from radiography or fluoroscopy in the way of obtaining information: images are obtained using a specially created program. The load on the body remains high.
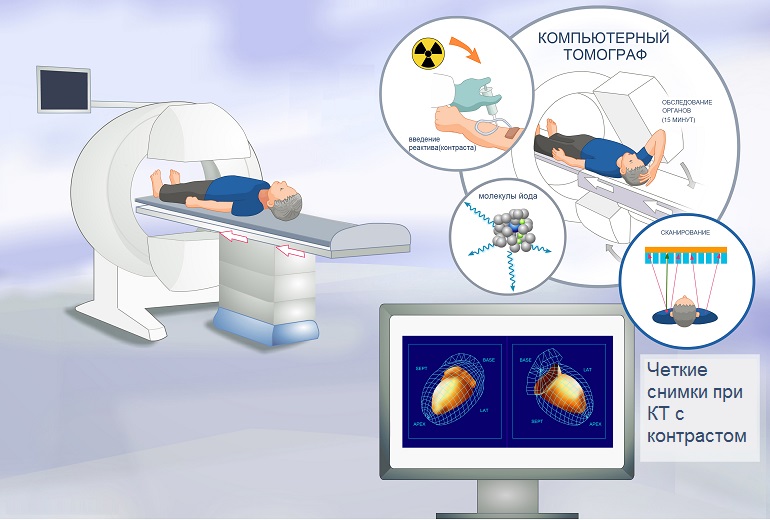
During MSCT, a narrow X-ray beam is directed to the area of the body being examined. It runs through the tissues human body and is absorbed by them in different ways. When processing such radiation, layer-by-layer sections are obtained. Computers process such sections in order to obtain an image of an organ or part of the body. Then such sections are analyzed, studied, and only after that a diagnosis is made.
Magnetic resonance imaging uses a very powerful magnetic field. It serves to create nuclear magnetic resonance. At the same time, hydrogen atoms (and there are most of them in the body) change their position. Electromagnetic pulses are generated. They are captured by sensitive equipment, and with the help of a high-precision computer, they are processed into high-quality images, as a rule, three-dimensional ones.
Thus, the difference between such studies is clear. It should be noted that CT cannot be used repeatedly, as it increases the radiation exposure to the body. MRI can be done many times.
When is MRI used and when is MSCT?
Magnetic resonance imaging is good for visualizing soft tissues. On the contrary, CT is suitable for diagnosing diseases of the bones, small pelvis, skull, spine, etc. MRI is preferable in such cases:
- with individual intolerance to a substance that is used during computed tomography for contrast;
- to determine the malignant processes of the brain, inflammation of the tissue of this organ;
- with apoplectic stroke;
- with multiple sclerosis;
- for the diagnosis of all pathologies of the spinal cord;
- to study the state of the intracranial nerves;
- when diagnosing the surfaces of joints;
- while studying muscle tissue;
- to determine the stages of cancer (in this case, a gadolinium-based drug is injected as a contrast agent to facilitate diagnosis).
In turn, CT is best done in such cases:
- with suspicion of acute intracranial hematomas;
- with lesions of the spine, skull (including fractures);
- in the case of bone diseases, including the base of the skull;
- with fractures of the paranasal sinus, temporal bone;
- for scanning the skeleton of the face;
- if there is a suspicion of otitis media of any etiology;
- osteoporosis, herniated intervertebral discs - also an indication for CT;
- with lung carcinoma or tuberculosis, as well as pneumonia;
- to search for the localization of lung carcinoma;
- when studying changes in the vertebrae, as well as discs (CT in this case is more informative than MRI);
- joint and bone diseases are also an indication for computed tomography.
Conclusion
Magnetic resonance imaging and MSCT are modern high-tech types of diagnostics of many diseases. The answer to the question, which of them is better, can be answered by studying each specific situation. Both the one and the other type of diagnostics are highly informative and suitable for the detection of many pathologies. The choice of the most preferred type of diagnosis remains with the attending physician.
During such studies, patients do not feel pain at all. Such diagnostics compares favorably with traditional ways definitions of diseases.
The second half of the twentieth century was marked by the rapid development of science, including medical physics. One of her most significant achievements is new diagnostic methods, primarily magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography, an improved version of which is the multispiral technique. What to choose for a health assessment - or an MRI? What is the difference between MRI and MSCT, what is common and different between these research methods and which one is preferable?
Features of MRI
MRI allows you to obtain volumetric images with high accuracy.
Magnetic resonance imaging is an apparatus that allows you to study the state of tissues and organs due to the magnetic field and radio waves. Under their influence, the hydrogen protons contained in the tissues emit signals that are read by the device and transmitted to the computer, which forms them into a three-dimensional image.
MRI is used to determine pathologies of internal organs, soft tissues, heart and vascular structures. In this case, there is no radiation exposure, as well as invasiveness, so several procedures can be carried out, including after a short period of time. The resulting volumetric images are highly accurate and allow you to examine the thinnest sections of the organ.
Features of MCST
Multispiral computed tomography is an improved type of CT scan that was originally used as a way to diagnose diseases only of the brain, but over time it has found more wide application... The multispiral method differs from the standard computed tomography by the device of the equipment:
- During scanning, the device moves in a special way: the ring rotates, and the table moves along a horizontal path. Thus, the emitter moves in the form of a spiral.
- The tomograph is equipped with several detectors. This allows you to obtain images with the finest cuts up to 0.5 mm.
- In one turn of the ring, the device takes up to 300 pictures.
- Pictures can be played back in multiple planes.
This technology is truly breakthrough because it allows you to:
- Reveal the minimum pathological changes thanks to its high resolution.
- Get the most informative pictures.
- Track changes in the functioning of organs.
In this case, the basic principle of diagnostics is similar to that used in conventional computed tomography. Scanning occurs due to exposure to X-rays, which pass through the tissue and change the properties at the exit. It is this change that is recorded by a computer tomograph and, after processing, forms it into an image. Thus, the received radiation dose is one of the main disadvantages of CT, which is also typical for MSCT.
MSCT and MRI, what's the difference?
MSCT and MRI, what's the difference? In the first case, it is based on a magnetic field, in the second - X-ray radiation.
These methods have many characteristics in common:
- Non-invasiveness.
- Minimal preparation.
- The ability to introduce contrast to improve visualization.
- Obtaining thin slices.
- The ability to identify pathologies at the initial stage.
What is the difference between MRI and MSCT?
- Diagnostic principle. In the first case, it is based on a magnetic field, in the second - X-ray radiation.
- Opportunities. MRI better visualizes soft tissues, whereas MSCT - hard ones.
- An important difference is the list of contraindications.
- Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed on people who carry metal electronic devices that cannot be removed during the study (for example, implants and pacemakers).
- Contraindications for MSCT are, first of all, pregnancy, as well as childhood, since we are talking about radiation.
- Allowable number of procedures. Due to the fact that MRI does not involve X-rays, the study can be carried out as needed. When prescribing MSCT, the doctor takes into account the radiation dose (the maximum possible - up to 5 mSv per year).
- Studies carried out with the introduction of contrast will differ in the substances used. With MSCT, iodine-containing preparations are injected, with MRI - substances based on the viscous metal gadolinium.
- Duration of the study. With magnetic resonance imaging, the patient must lie still for about an hour, while being inside the tunnel. The time for multislice tomography is much shorter (from a few minutes to half an hour). The immobility is also important, but not as significant as during an MRI.
What's better?
The difference also lies in the cost: MSCT is cheaper.
Which diagnostic method is the best? There can be no answer to this question, since they are not mutually exclusive, but complementary, and one does not contradict the other. The doctor makes the choice depending on what is appropriate for a particular patient, and on the tasks facing the study:
- The choice will largely depend on the available contraindications.
- For the study of joints, muscles, nervous system it is advisable to use MRI. It is also indicated for the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases, assessment of the brain, trachea and esophagus.
- With the diagnosis of the state of bones and organs with cavities (stomach or lungs), MSCT will cope well.
Finally, the difference between the two methods is also in the cost. MSCT is cheaper than MRI. In addition, both techniques, as a rule, are used to clarify the diagnosis, after primary basic examinations such as ultrasound and X-ray. Therefore, self-passing tomography is a fundamentally wrong and impractical decision.
Sources:
- Modern medical encyclopedia... St. Petersburg, 2013.
- Morozov S.P., Nasnikova I.Yu., Ternovoi S.K. Multispiral computed tomography in a multidisciplinary hospital. Moscow, 2009.
- Marusina M.Ya., Kaznacheeva A.O. Modern views tomography. St. Petersburg, 2006.
Multispiral tomography - best method radiation diagnostics. With its help, you can carefully examine all parts of the body, including the brain and skull. Compared to conventional computed tomography, it gives more clear results and differs in lower radiation doses.
In the medical literature, MSCT is also called multilayer or multislice spiral tomography.
Features of spiral tomography compared to conventional CT
During diagnostics with a conventional CT scanner, an X-ray unit (called a gantry) with one row of detectors rotates around the patient's body and takes pictures under different angles... In this case, the X-ray tube makes one revolution per second.
When examining with a multispiral apparatus, a gantry with two or more rows of detectors moves around the patient in a spiral, while the X-ray tube makes two revolutions per second.
In just a few seconds, MSCT allows you to obtain clear data on the layer-by-layer structure of the investigated area of the body. A full scan can be done in 20 seconds. The radiation dose is reduced by 50%.

Indications
- As a screening for alarming symptoms: headaches, fainting;
- for examination for emergency indications: in case of injuries, cerebral hemorrhages;
- at planned research- to confirm the diagnosis;
- to monitor the results of treatment;
- for manipulation in hybrid operating rooms. They are equipped with tomographs for better visualization of surgeons' actions and reduce the trauma of operations.
What MSCT shows
Allows you to detect all anomalies even on initial stages their development. In the pictures, both bones and soft tissues (brain, liver, kidneys, etc.) are perfectly visible, foci of bleeding, hematomas are visible. Thanks to such a clear and detailed study, it is possible to find tumors while they are still operable, as well as to accurately detect various injuries and fractures.
How is it done
MSCT is carried out in a separate room.
Stages
- Placement of the catheter. Only in cases where angiography is needed, that is, a study of the vessels.
- The introduction of a contrast agent. Also applies only to angiography.
- Placement of the patient on the table. For diagnosis, you need to take a recumbent position.
- Performing multislice tomography directly. All images are immediately transferred to the computer screen, behind which the doctor is.
Taking into account the time for all preparatory procedures average duration multislice tomography is 15 minutes. With the introduction of a contrast agent - a preparation based on iodine, which is used to improve visualization during examination, discomfort is possible. In other cases, the diagnosis is painless.
Price
The cost of MSCT is on average 4,000 rubles for a study of one of the body parts.
FAQ
Which is better - MRI or MSCT of the brain?
Typically, doctors recommend both studies to get a complete picture. However, the leading method for diagnosing brain diseases is still MSCT.
What does angiography show?
The state of the vessels and veins, namely: the presence of calcium on the walls of the arteries.
Angiography using an MSCT device allows you to make quantification calcium content and detect atherosclerosis in the early stages.
Are there any contraindications?
There are no absolute contraindications. But the procedure is not recommended for pregnant women, nursing mothers and young children. It is carried out only if absolutely necessary.
Is multispiral tomography used in dentistry?
Rarely, as orthopantomographs and cephalostats are preferred, which are designed to accurately position the patient's head during X-ray imaging. Nevertheless, with the help of MSCT, it is possible to obtain a detailed picture of the state of the skull and, in particular, of the jaw bones. This diagnostic method is used in maxillofacial surgery and orthodontics.
On our site is presented full list clinics that perform high-quality diagnostics of the condition of the dentoalveolar apparatus with minimal radiation doses and accurate results.
Radiologist Olga Valentinovna Loseva, one might say, was lucky - she never worked on old equipment. With high radiation exposure, low velocity and low information content. She is the head of the Department of Radiation Diagnostics of the Russian-American medical center"Medyunion", in which the American equipment of the expert class is installed. In her department, patients undergo examinations and magnetic resonance imaging open type- MRI, and on a 16-slice multislice computed tomography - MSCT. Very often depends on what the doctor sees future life person. Doctor the highest category Loseva says: “I have the best specialty! If the pathologist issues his conclusion at death, then the radiologist - during life. This means that there is an opportunity to extend and improve this life! "
- Olga Valentinovna, MRI and MSCT - two excellent modern methods surveys that are very popular today. It seems that those who have not checked themselves on a magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography are simply behind the times! Let's see how they are similar and how they differ?
-
They look like only the thinnest scan slices. And that's all. At the heart of MRI examination of the phenomenon of magnetic resonance, at the heart of MSCT is X-ray radiation. The examination time is completely different. Examination on MSCT takes 2-3 minutes, with contrast - 15, for - from 15 to 40 minutes, if contrast is used - up to an hour. As for absolute contraindications, then for MRI - these are pacemakers, the presence of endoprostheses and stabilizing systems made of ferromagnetic alloys, middle ear implants (hearing non-removable prostheses), the state after clipping of the cerebral vessels. There are no absolute contraindications for MSCT, however, it is better not to send pregnant women and children to it without a doctor's referral.
- Indications for the use of this or that examination method are also different.
- Of course! On MRI, we look at the brain, formations in the pituitary gland, arteries of the head and neck, orbits, paranasal sinuses, all parts of the spine, spinal cord, thyroid and parathyroid glands. Abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space, small pelvis, female and male, damage to ligaments in the joints, soft tissues.
On MSCT, we also look at the brain, paranasal sinuses, orbits; and also the larynx, jaws, organs chest(mediastinum, lungs, ribs, diaphragm). We look at all bones for injuries, tumors, metastatic lesions. It must be remembered that MRI and MSCT are two different, but complementary examinations, they have different characteristics fabrics. On MRI, soft tissues are better visualized, on MSCT bones.
- Olga Valentinovna, that we only look at MRI?
- Spinal cord, thyroid and parathyroid glands, pelvis. We have an open MRI at our center, and this is very important for patients with claustrophobia. For some people, panic even starts from putting the coil on their head. You can imagine the reaction of this patient if you put him in a closed-type MRI capsule!
- And, accordingly, only on MSCT ...
-… we look at the lungs. Kidney stones are well visualized. Temporal bones, namely, the structure of the mean and inner ear... Larynx.
- In what cases is contrast prescribed?
- First of all, it is oncological alertness; to exclude or evaluate focal formations of various anatomical areas, to differentiate neoplasms - benign or malignant. The contrast is prescribed for the continued growth of tumors, for recurrent tumors, for metastatic lesions. With vascular pathology. This applies to MRI and MSCT. On MSCT with contrast, we assess in more detail the state of the vessels, tumor invasion, thromboembolism, anomaly of vascular development, aneurysm, aneurysmal dilatation.
The contrast increases the information content of the survey. But it must be borne in mind that the contrast during the examination for MSCT contains iodine, and it can cause allergies, such reactions do not occur on MRI with the most modern contrast agents. Abdomen, the retroperitoneal space and vessels on MSCT look only with intravenous administration of a contrast agent. But to assess the state of blood vessels on MRI, contrast is not required. The blood itself acts in its role.
There are patients who prescribe diagnostic examinations for themselves. What advice would you give to such people?
- Yes, there are quite a few such patients. It happens that a person has a hip joint pain. He comes for an MRI hip joint, and here it turns out that the problem is not in the joint, but in the lumbosacral spine! Or, it hurts in the groin area. We examine the small pelvis and capture the area of the lumbosacral region, and there is a hernia, which gives pain. Or another example. Often, with severe headaches, people immediately suspect they have a brain tumor, although it may be sinusitis. Agree a big difference! And there are plenty of such examples. So, it is still better to come for a consultation with a specialist. But if you have already decided to be examined on your own, and that type of examination is suitable, and the other, then it is better to choose an MRI - due to the lack of radiation exposure.
- Is it always possible to make an accurate diagnosis?
- In our profession, the patient's life depends on the diagnosis, so we have no right to make a mistake. Our diagnosis is final.
