MRI of the spine: how the procedure goes and what it shows. What is an MRI of the lumbar spine?
Magnetic resonance imaging is innovative safe method diagnostics of diseases of bone and soft tissues on different stages... Information on how an MRI of the spine is done, the reasons for the appointment and contraindications will be useful for people with injuries, back pain and lower back pain.

Of course, the group of doctors should be mentioned. Through collective evaluation of results and careful introduction to surgery under the guidance of experienced colleagues, our junior physicians quickly gain erudition. Thus, they are exposed a large number cases and during certification, our doctors repeatedly exceed the number of operations lumbar spine that should be allowed for independent work in this area.
All patients are provided with informational guides and receive the exact date control in our clinic, which revised and adjusted the condition of the recommendations for further treatment and potential stress. This check is carried out on all patients regardless of the result, and we have a very good overview the results of our work. We also cooperate with the coordination of spa care.
Previously known CT ( CT scan) and radiography are not able to convey the complete picture inflammatory process or abnormal change... The MRI method is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance, which allows scanning of body tissues using protons, which are contained in all bioorganic compounds. Under the influence of a strong magnetic field and impulses, they change their position. The energy that is released during their movement is captured by the tomograph, transmitted to the computer, processed and the image is displayed on the screen.
For supporting good result even in the long term, further work with the patient is necessary, especially in the field of physiotherapy. The vast majority of patients can benefit from a good diagnosis of the causes of spinal fractures. Correct exercise design that is ready for a specific person is an important prerequisite for the long-term function of the lumbar spine. But still this is only an assumption, since the practice of the patient himself, and only himself can help - the physiotherapist plays the role of a consultant who develops and monitors the implementation of its proper implementation.
There are two types of MRI scanners: closed (camera) and open.
The latter is more functional. Allows to carry out examination of children, patients with large (120-200 kg) body weight or patients with claustrophobia.
Apparatus are also distinguished by the level of the magnetic field in Tesla:
- 0.1 Tesla - ultra-low tomographs
- 0.1-0.5 Tesla - low tomographs
- 0.5-1 Tesla - medium tomographs
- 1-2 Tesla - high tomographs
- More than 2 T - ultra-high tomographs
When there is a suspicion of the presence of an oncological tumor, metastases, multiple sclerosis or a check is needed after removal of the intervertebral hernia, the patient may be prescribed a contrast agent. The image conveys a better visualization of the course of the disease, the area of the lesion, the size of the neoplasms.
The procedure itself is performed in general anesthesia... Do not eat, drink or smoke before surgery, usually this prohibition is in effect from midnight until morning. Before the operation, patients fulfill the needs of the body, wash with special antibacterial soap, and lower limbs get stockings to prevent blood clots in the veins.
The procedure itself is performed with a sigh. For sleep, the anesthesiologist must have information about all the basic parameters in the body of a particular patient, all current diseases, as well as the medications the patient is taking. Before the operation, patients fulfill their physical needs, wash with a special antibacterial soap, stockings are made on their legs, which prevent the formation of blood clots in the veins.
The substance is administered intravenously before examination or during tomography (in certain doses). The drugs are safe, but there are contraindications for use in case of pregnancy, allergies to the constituent components or kidney failure. The products use compounds of the gadolinium metal.
A referral for an MRI scan can be obtained from a neurologist or vertebrologist. You can get tested in a private clinic or public hospital.
If the clot is released into the bloodstream, a serious complication called pulmonary embolism can occur. Patients are sent to the gym, transported on a roller coaster and taken to the operating room after preoperative treatment. The patient's anesthesiologist succeeds, then the patient is put into a surgical position. In our hospital, we most often use the so-called general or “Mecca” position, which is comfortable for the patient and when the operator has better access to the spine. X-ray targeting of the diseased disc is done, the site is marked, and the entire area is completely disinfected.
MRI procedure:
- The procedure is painless and does not require any special preparation. To obtain the correct image, it is necessary to remove all metal items (belt, earrings, hairpins) that can disturb the magnetic field.
- It is also necessary to report the presence of a pacemaker, metal prostheses, pins, plates.
- The patient lies down on a special movable table, it is fixed with belts. The rollers can be adjusted depending on the area of study.
- The medical staff is obliged to leave the premises during the procedure. The duration of the study depends on the presumptive diagnosis and takes from 5 to 30 minutes. The operating tomograph makes noise and clicks. There is a microphone for communication with the staff in case of deterioration of health.
- The results are issued on the same or the next day.
When is an MRI of the spine prescribed?
 With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, diseases are determined on initial stages... The attending physician, based on the finished image and description, will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, diseases are determined on initial stages... The attending physician, based on the finished image and description, will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
This is followed by covering the entire patient with sterile wrinkles. The surgical procedure begins with lateral or longitudinal incisions about 5 cm long, and the muscles are removed from the vertebrae. The operator then penetrates between the two vertebral arches into the spinal canal to the nerve roots. At the bottom of the channel, discarded mass of the disc detects and removes them using special ticks. Then it penetrates the disc itself and removes the existing free and degenerate parts to avoid overturning.
The inner "springy" part of the disc is removed and remains a solid connecting ring, which additionally holds and connects the vertebrae. Instead of the material to be removed, no implants or implants are replaced. Following is the control and careful release of nerve roots. Thus, their own action ends and the wound gradually closes after the anatomical layers. In some cases, a drain must be left in the wound to remove blood.
Reasons for doing an MRI of the spine:
- Examination of congenital pathologies.
- Diagnostics of the state of the structure of the vertebrae and discs.
- Detection of inflammatory processes.
- Violations motor function limbs.
- Before and after surgical intervention.
- Identifying the cause of back pain ( intervertebral hernia, compression fractures of the vertebrae).
- Fracture, injury to any part of the spine.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Pinched nerves.
- Dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Depending on symptoms and location pain syndrome, the doctor will order an MRI scan of a specific part or the entire spine. Examination of the cervical, thoracic and complex lumbosacral regions is carried out. This diagnostic method detects the slightest abnormalities in bone tissue, blood vessels, and the spinal cord. The picture clearly shows the structure (cut) of each vertebra, discs, nerve endings. The doctor has the opportunity to study the area of interest from all sides and from different angles.
After the operation, the anesthesiologist cancels sleep, and after sufficient release of the effect of the drug, the patient returns to the neonatal unit. At least 6 hours after surgery, patients should not eat or drink, and then as little liquid as possible per teaspoon. The next day they dry out in the morning and with the help of a rehabilitation worker, patients get up and exercise. There will be instructions for correct exercise, and the patient leaves the room within 3 days after the procedure - the carriage lies in the sanatorium, but the patient can walk at home and gradually settle in.

The condition of the cervical vertebrae, nerve endings and blood vessels is an important definition of the normal functionality of the whole organism. The first symptoms for an MRI are unreasonable pain. cervical, hearing impairment (tinnitus) and vision, frequent dizziness, a sharp change blood pressure, loss of sensitivity in the hands. If the pathology causes compression of the spinal canal, nerve endings, roots, then gait disturbance is possible.
After lumbar intervertebral disc surgery, all patients are invited to register with specialized clinic 6 weeks after surgery. The final report sets the exact day and control frame. It is classically recommended to remain incapacitated for 1 to 2 months after surgery until complete healing and normal physical mode... Postoperative recovery is very individual and depends, among other things, on the severity of the preoperative problems and the duration of their duration.
These include, but are not limited to, residual pain, tingling, injury electric shock, impaired residual sensitivity or weakness of the limbs. Changing nerve function is a long-term process that can take many months. When material is removed on the disc, the pattern of movement of the vertebrates changes; posterior back pain may be temporarily present during movement and when changing position - the so-called "mechanical back pain". Here is the optimal solution for gradual, focused, spraying and loading of the spine.
An MRI of the cervical spine can reveal the following problems:
- Protrusion and hernia of the intervertebral substance
- Violation of the function of blood circulation in tissues and blood vessels
- Tumors
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae
- Bone infection and spinal cord
Vascular pathology of the cervical region of the spine impairs the blood supply to the brain. It is imperative to define this on early stages to avoid serious consequences such as stroke, cerebral or spinal cord infarction.
As with any surgery, disc surgery is an intervention on the body and can be perceived by the patient, especially when the weather changes. During recovery, the patient adjusts their daily schedule to manage normal daily running and return to work. If the patient is working on proper rehabilitation, then this is a normal return to more difficult activities, sports, etc. in addition to the nature of the disability and the operation, the overall result depends on the patient's motivation and honest treatment.
Surgery of the intervertebral disc of the cervix is one of the most common neurosurgical procedures. Despite the fact that neurosurgery is a minor procedure, we do not underestimate these operations and try to improve them. Our workplace became the first in the Czech Republic to regularly use mobile cervical replacement and to participate in the research and development of these implants.
The cervical spine is prone to osteochondrosis, the main symptoms of which are muscle spasms, pain in the shoulders and neck.
A sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, lack of vitamins and congenital pathologies this is the most common reasons diseases. MRI allows you to diagnose the disease and determine the type of treatment (physiotherapy, manual treatment, acupuncture, laser, surgery).
The area of the cervical spine is quite delicate, the discomfort of the discs is often multiple, and the correct indication can be a more difficult decision-making process. As with big performances, we also do a collective assessment of each case prior to surgery. We are of the opinion that the planned backbone performance requires maximum safety, technical support and meticulous execution. Therefore, we carry out all operations using a working microscope using a high speed cutter to remove the protrusions.
Protrusions of the cervical intervertebral discs often occur against the background of osteochondrosis. The disc loses the ability of a shock absorber, i.e., preventing friction of adjacent vertebrae. An MRI of the cervical spine will help to detect the problem in time. Thus, it is possible to prevent serious consequences - hernia and rupture of intervertebral discs, stenosis of the spinal canal.
The current lifestyle and aging population are the main reasons for the increase in the number of degenerative cervical spine. The most common problem is the so-called osteochondrosis, i.e. increased wear of the cervix, often also without a disc. Decreased disc height, new growth, and loss of ligaments are typical factors that depress nerve structures and cause problems. The operation of the cervical intervertebral discs is performed annually. As with lumbar discs, in its simplest form, it is more of a small procedure, as opposed to accidental injuries planned to correct painful problems.
 The thoracic region includes 12 vertebrae. Pain in the chest and between the shoulder blades, limitation of movement, numbness in the legs and arms are the first reasons for seeking medical attention and prescribing magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic vertebrae.
The thoracic region includes 12 vertebrae. Pain in the chest and between the shoulder blades, limitation of movement, numbness in the legs and arms are the first reasons for seeking medical attention and prescribing magnetic resonance imaging of the thoracic vertebrae.
Do not eat, drink or smoke before surgery, usually this prohibition is in effect from midnight until morning. Before the operation, patients fulfill the needs of the body, wash with special antibacterial soap, and receive stockings on the lower extremities to prevent the formation of blood clots in the veins. The patient's anesthesiologist succeeds, then the patient is brought into a working position with the head and shoulders fixed in the desired position using adhesive strips.
An x-ray of the target disc is taken, the site is marked, and the entire area is completely disinfected. The surgical procedure begins with approximately 5 cm of cross-section at the front of the neck slightly from the side, while trying to exploit existing wrinkles. By gradual preparation, we penetrate the muscles and vessels to the front of the cervical spine, which we open and create a trap for a minimally invasive approach. After another X-ray inspection of the disc, we cut and completely remove the pliers and then the high speed cutter.
Thanks to the examination, infectious, fungal infections, degenerative-dystrophic diseases, osteomelitis, tuberculous processes of bone tissue, intervertebral hernias and protrusions, oncological tumors and metastases in the chest, abnormal development of the vertebrae. Front surgical intervention v mandatory do an MRI of the spine.
At the back of the intervertebral space, we remove any disc or projections that suppress nerve roots or the spinal cord. Since the cervical disc has been completely removed, we place the implant between the vertebra. Depending on the nature of the operation and the disease, it can be a separate implant, in some cases we choose a bone graft, in the case of strictly specified cases, a mobile disc replacement can be used.
If bone grafts are used, secure the vertebrae with a splint and screws, all this takes place behind an X-ray machine. Once we have finished working on the disc and vertebrae, we remove the trap and we introduce an exhaustive drain to remove the blood. We cut the breasts using the so-called intradermal suture, which gives good cosmetic results and can be easily removed.
Visualization allows you to accurately determine the location of the pathology, the need and risk of surgery.
Control examination shows the result of treatment and its effectiveness. X-rays are not always able to detect injuries spinal column... Magnetic resonance imaging thoracic with the use of a contrast agent, it reveals the slightest traumatic destruction and displacement of the vertebrae, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, osteoporosis, scoliosis.
After the operation, the anesthesiologist cancels sleep and after sufficient removal of the effect of the drug, the patient is transported either to the department intensive care, or back to a standard bed - it all depends on the degree of surgery and possible other diseases of the patient. Patients should not eat or drink at least 6 hours after surgery, and then less fluid can be taken in a teaspoon. The next day they dry out in the morning, X-rays are taken, and a special rehabilitation worker sets the patient up and begins to walk.
Problems in the thoracic spine entail disruption of the work of some internal organs(stomach, intestines).
Contraindications for MRI of the thoracic spine:
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- The presence of metal implants (exceptions - braces, dentures, titanium elements).
- Lactation period (if a contrast agent is injected).
- Intolerance to drugs for contrast scanning.
- Mental deviations and disorders.
The MRI procedure is also limited for children under 7 years of age. It is important to maintain a stationary state on the tomograph table while reading information. This is the most important requirement for an accurate diagnosis. For children younger age It is difficult to lie motionless during the examination, so doctors may prescribe anesthesia or sedatives.
MRI of the lumbar and sacral spine
According to statistics, among diseases of the spine, pathological processes in the lumbosacral region. This is due to constant stress, sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle, weight lifting, injuries. Sacral and lower back pain can also occur with other health problems not related to the spine.
Diseases in the gynecological sphere (endometriosis, fibroids, parametritis, oncology of the uterus and ovaries) provoke tension in the sacro-uterine ligaments. Problems of the prostate gland (prostate) and pelvic organs make themselves felt in the form of pain syndrome of the sacrum, lower back, coccyx.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, an MRI of the lumbar, sacral spine is done.
Symptoms for which this procedure is prescribed:
- Pulling, aching pains in the lower back or sacrum (sacrodynia, lumbodynia). Increased pain occurs when sitting, standing, bending the body. Will extend to inner surface hips, feet partially numb, toes. Perhaps light feeling tingling.
- Osteochondrosis, arthrosis, spondyloarthrosis. Such diseases more affect the elderly, but the younger generation (over 30) is increasingly receiving similar diagnoses after examination.
- Spasms of the muscles of the back and buttocks. This is how the body responds to pain in the lumbar region, which may not go away in a state of complete rest.
- Inflammatory, infectious and non-infectious processes in the lumbar spine. Reiter's syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis affect the structure of the bone tissue of the vertebrae and joints. Men are more exposed to this pathology.
- Contusions, injuries, fractures of the lumbosacral spine.
An MRI scan and a conclusion (transcript) of the doctors who performed the examination help to identify: tumors, hernias (protrusions) of discs, dysfunction of blood vessels, the state of the vertebrae after injuries, defects of nerve endings.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method

The main positive point in carrying out MRI of the spine is the non-invasiveness of the method, the absence of harmful X-ray irradiation. it safe option examinations for people with contraindications to CT and children of any age. The resulting picture is a visualization of the state of bone and soft tissues.
In a three-dimensional image, you can get the exact location and size of neoplasms, lesions, the state of the spinal cord and blood vessels.
Magnetic resonance imaging with contrast can detect cancer tumors and their Exact size, changes (malformations) of blood vessels. The contrast agent can be used in children. No special preparation is required prior to the study.
Despite the advantages, magnetic resonance imaging over CT and X-rays, like any diagnostic method, has its drawbacks:
- The high cost of the procedure. You can be examined in a public hospital, which will reduce costs.
- The duration of the lying position. Patients with acute pain, it is rather difficult for children to lie motionless during the entire time of the examination. In some cases, staying on the tomograph table can last up to 45 minutes.
- Contraindications for MRI in patients with iron implants, braces, plates, implanted prostheses, pins, pacemakers. Metal elements can move and heat up under the influence of the magnetic field of the tomograph. Exceptions are ferromagnetic materials.
- Mental disorders (epilepsy), claustrophobia. If you are afraid of a confined space, you can undergo an MRI examination on an open machine.
- Renal failure and allergy to contrast agents.
Among known options diagnostics of problems and diseases of the spine, method of magnetic resonance imaging the best way determines the focus of the lesion. The examination can be carried out more than once without harming health.
More information can be found in the video.
MRI of the lumbosacral spine is a promising and reliable method of radiation diagnostics.
It allows you to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe correct treatment... The examination is carried out in two projections: transverse and sagittal.
An MRI of the lumbosacral spine is performed as directed by a physician or when pain occurs in the lumbar region.
- Time spending: from 30 to 60 minutes (time increases if MRI is performed with contrast).
- The need for a contrast agent injection: depends on the indications, it is prescribed by the doctor.
- Need preliminary preparation: not required
- The presence of contraindications: Yes
- Restrictions: the weight of the subject should not be more than 180 kg, the waist height - less than 32 cm, the waist volume - up to 140 cm.
- Time of preparation of the conclusion: from 30 to 60 minutes
- Children: MRI is performed for patients aged 7 years and older.
Indications for tomography
MRI of the lumbosacral spine is prescribed in the following cases:
- Determining the cause of acute or chronic back pain, making an accurate diagnosis.
- Confirmation of osteochondrosis or other degenerative-dystrophic diseases.
- Confirmation or absence of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which can provoke pain in the lumbosacral spine.
- Examination of the department for the presence or absence of pressure on the spinal bodies, epidural space and blood vessels of the spinal cord.
- Diagnosis of diseases associated with damage to intervertebral discs:,.
- Detection of primary and metastatic tumors, infectious diseases affecting the work of the musculoskeletal system.
- Examination for presence or absence congenital anomalies lumbosacral spine, surrounding tissues and bones of the pelvic column.
- Examination for the presence of transitional vertebrae, spinal column injuries,.
- Diagnostics of the patient's condition with ankylosing spondylitis, sacroiliitis.
- Assessment of spinal cord tissue and blood circulation in this area.
Contraindications
Not in all cases, patients with problems in the lumbosacral spine are prescribed an MRI.
This procedure has contraindications:
- An MRI scan should not be performed if the body contains metal objects: pacemakers, vascular clips, etc. This is hazardous to health, as magnetic fields tomography leads to malfunctions of these devices and heats up the metal. Exception- structures in the human body that are not attracted by a magnet, for example, braces, titanium prostheses, dental implants, etc.
- MRI may be limited by claustraphobia... In this case, the doctor suggests performing the procedure in a state of drug-induced sleep or on a device with an open circuit.
- MRI with contrast cannot be done during pregnancy and lactation... The drug adversely affects the fetus and milk production.
- Allergic reaction on contrast agent.
- Chronic renal failure, due to which the body will not be able to remove the contrast agent for a long time.
Method advantages
The main advantages of MRI of the lumbosacral spine are time savings and no need to use other diagnostic methods.
Previously, during the examination, surgical manipulations (puncture with examination of the cerebrospinal fluid), X-ray techniques (discography, pneumomyelography), X-ray examination (images of the spinal column in different projections under static load and at rest) were used. Now all of them can be replaced by MRI.
The MRI result is known within a few minutes after the examination. The specialist performing the MRI provides the images and descriptions to them; in many medical centers, the examination record can be obtained on a digital medium.
How is an MRI of the lumbosacral spine done?
MRI is the most accurate examination of the body at the moment.
It is carried out experienced professionals using modern equipment.
The procedure is absolutely harmless, but still you need to know about some safety measures.
First, the patient must fill out a questionnaire that will help identify contraindications to the procedure.
Before the MRI scan, you need to take off your clothes with metal elements, metal jewelry, remove a USB flash drive and mobile phone from your pockets.
The procedure is performed horizontally. First, the subject lies on the table, his head and hands are fixed, then the table is moved to the annular part of the apparatus. Only the legs are left open for the patient.
During an MRI, you need to lie still to get high-quality images. If the noise from the machine is unpleasant, you can insert earplugs.
The contrast agent is injected a few seconds before the MRI scan into a vein, unpleasant sensations does not arise.
MRI can be performed in several modes:
- Contrast-enhanced tomography... First, a special substance is injected, then images are taken. Contrast helps to improve the quality of images, it is required in determining the development of malformations of tumors and vessels.
- Native tomography... It allows you to take a series of images without preliminary preparation and administration of a contrast agent.
Preparing for the procedure
No special training is required for an MRI.
Man can drive his familiar image life, do not change the diet and do not give up taking medications. To undergo the examination, you need to take a referral from a doctor who also decides whether to carry out the procedure with or without contrast.
For an MRI, you need to bring pictures from previous studies, an extract from an outpatient card and medical documents that contain information about the disease.
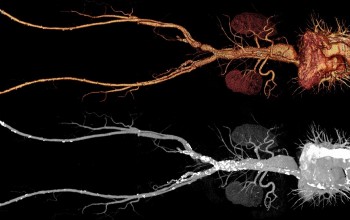
For contrast enhancement MRI uses drugs based on gadolinium.
These drugs increase the information content of the study. The dye is non-toxic, created based on gadolinium chelate complexes, does not have side effects... TO
Ontrust enhancement should not be used for examinations in the first trimester of pregnancy and for individual drug intolerance.
After entering the body, the contrast agent is retained in the tissues and allows them to be better visualized during MRI.
The drug is excreted from the body within 24 hours.
Doctor's conclusion
After the pictures are taken, the examining doctor writes a report.
In most cases it does not take more than an hour, but sometimes it takes longer for the technician. Most clinics in large cities issue examination results on electronic media and send them by e-mail.
With the obtained MRI results, it is necessary to contact the doctor who sent for the examination to establish a diagnosis and treatment. If the MRI was performed on the patient's initiative, then after the examination, if pathologies are detected, you need to contact the following specialists:
- traumatologist if problems in the lumbosacral spine are associated with injuries or their consequences;
- neurosurgeon if necessary, surgical intervention;
- neurologist with diseases of the spinal cord and spine;
- oncologist if a tumor is found during research.
Research opportunity for children
Children can have an MRI of the lumbosacral spine.
Usually, doctors prescribe an examination for patients who have reached the age of 7, but these are only conditional indicators.
The most important thing- the child should lie quietly and not move during the study.
Prices in Moscow and other large cities
MRI is one of the most expensive and effective procedures... The cost of the examination depends on the location, and the difference in price in different medical centers can be significant.
To save on the complex of examination, you need to do an MRI and choose a specialist for consultation in one clinic. But don't skimp on MRI.
Average cost of examination in Moscow - 4500 rubles, time - from 15 to 30 minutes. Some clinics offer discounts and night screenings.
In other large cities in Russia, prices for MRI can vary significantly.
In St. Petersburg average cost examination complex - 3000 - 3500 rubles, in Ufa 2000 - 2300 rubles, in Tula about 3000 rubles, in Yaroslavl - 2500 rubles, in Yekaterinburg - 2800 rubles.
Description of some clinics
In Moscow, MRI can be done in many specialized centers and clinics.
At the Central Committee of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow, an examination of the lumbosacral region will cost 4,700 rubles, with the introduction of a contrast agent 12,200 rubles.
At the MRI center, you will have to pay at least 3,380 rubles, and an MRI with contrast will cost 6,200 rubles.
In the centers of V.I. Dikul, prices for examination are from 3200 to 4700 rubles.
At the Medic-City clinic, an MRI scan costs 4,000 rubles, and to save money, you can come for an examination at night.
V medical center"Capital" the cost of an MRI of the lumbosacral spine is 4,300 rubles, with the introduction of a contrast agent - 9,200 rubles.
In St. Petersburg, you can make an appointment for an MRI at specialized center“Workshop of health”, open equipment is used here. The cost of examining the lumbosacral region is 3300 rubles. There are discounts in the center that allow you to save from 290 to 900 rubles. In the national diagnostic center Petersburg MRI of the lumbosacral spine will cost 3000 rubles.
The cost of MRI in other large cities differs from the prices in Moscow and St. Petersburg. For example, in Ufa, at the Outpatient Center for MRI, the examination will cost no more than 2,100 rubles, and at the MRI center of Tesla LLC, the cost does not exceed 2,300 rubles. In regional centers, the cost of an MRI scan without contrast injection is from 2,000 to 3,000 rubles.
