How MRI of the spine is done in the clinic, how to prepare, is it possible to do an MRI of a healthy spine.
The medical industry is developing rapidly, new methods of treatment, diagnostic technologies, new effective medications. AND ordinary person hard to keep up with the news. Thanks to the Internet, we have this opportunity. Today we will try to tell you as fully as possible what MRI of the spine and its departments is.
Its resistance, in fact, would be represented by the formula: 42 1 =. It is enough to look at the spinal column to see that this long bone stock is morphologically formed by two pyramids, which will be united by their base at the level of the sacro-lumbar joint. One of these pyramids or the upper pyramid starts from the last lumbar and ends at the atlas. It is very long and includes the first three regions, the cervical, dorsal and lumbar spine. The other pyramid or inferior pyramid extends mainly transversely and extends from the base of the sacrum to the top of the coccyx.
More recently, only X-ray examination was possible for the diagnosis of the ridge, which cannot be called safe. Then came computed tomography (CT), but it is also far from perfect. With the advent of a new method - magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), medicine switched to new level diagnosing diseases and other pathologies.
This, as we can see, is much shorter than the previous one. The column of vertebrae, essentially consisting of a superposition of a number of similar bony elements, the vertebrae, presents as the latter a configuration which is no doubt very irregular, but the details of which are easily deduced from the previous descriptions.
We consider his four faces and the central channel. Anterior aspect The vertebral column, seen from its anterior surface, represents us as a cylindrical stalk that makes up all the vertebral bodies. In the first three areas - cervical, dorsal, lumbar, alternating rows of fibrous intervertebral discs. In the area of sacrococciosis, where the vertebrae are welded together, these discs are replaced by simple transversely directed bony ridges.
This non-invasive test allows you to get an image of the pathology in different planes, with its help you can study the progression of processes in the body in dynamics. The method is based on the use of powerful magnetic field, high RF pulses and a computer that processes the received data and displays the image on the monitor.
back aspect. The column of the brain, seen from its posterior aspect, presents in the midline, first, a regular series of spinous processes forming them all, which is called the dorsal crest. On each side of the dorsal crest and parallel to it are two deep gutters, vertebral canals, which are limited externally by the superimposed ends of the transverse apophyses. These gutters are formed internally.
(1) lateral faces of spinous processes; (2) externally, articular processes and the posterior aspect of the transverse processes; (3) in their middle part, with vertebral lobes plastered from top to bottom in the form of roof tiles. Lateral sides. From the sides, the spine shows us consistently.
The MRI examination procedure allows:
- detect congenital problems of the spine;
- identify a problem with intervertebral discs, such as a ruptured disc;
- understand whether the damaged disc is pressing on the nerve roots;
- detect stenosis of the spinal canal (narrowing of the canal);
- find a tumor that has affected bone tissue or nerve fibers. It may be a metastasis of prostate, breast, or lung cancer;
- determine in which part of the spine blood circulation is not enough;
- find damage to nerve fibers during injuries or caused by diseases (for example, multiple sclerosis);
- find the infected area;
- see joint inflammation or osteoporosis.
Contraindications for MRI
Such a survey cannot be carried out if:
1. tops of the transverse apophyses, bearing their anterior part, but only in the dorsal region, articular granules intended for tuberosity of the ribs; (2) the lateral surface of the vertebral bodies located at their most distant part, in the dorsal region, a number of facets and half-fraxes corresponding to the head of the ribs; (3) pedicle series; (4) finally, between the latter, a series of interface holes that establish relationships between the spinal canal and the regions located outside this canal. Their dimensions are less related to the volume of the nerves than to the calibers of the large veins passing through them. These conjugation openings increase as they approach the sacrum. . The spinal canal The spinal canal, made up of all three vertebrae, extends throughout the spine and regularly follows all kinks.
- there are mental disorders;
- the patient has epilepsy or frequent convulsions;
- the presence of pacemakers, prostheses, fragments;
- Allergy to a contrast agent (if there is a need for its introduction);
- pregnancy must be reported to the doctor;
- claustrophobia.
Preparation and conduct of the study of the spine
The procedure does not require special preparation. But before starting, the patient must take off everything that a magnet can attract: watches, glasses, jewelry, hairpins, dentures, hearing aids, and leave it in another room. mobile phone, disks, floppy disks, bank cards, as all this can be damaged or injure you.
It ends at the bottom with a simple open groove on the back, which laterally limits the horns of the sacrum and coccyx. It continues above the atlas with a large cranial cavity. Passing through different areas spinal column, this canal, designed to accommodate the spinal cord and its membranes, changes in shape and size. Its shape is derived naturally from the shape of the vertebral foramina. It is a prismatic triangular region of the cervix, a cylindrical dorsal region, and again a prismatic triangular region in the other two regions.

If there is a tattoo on the body or a recent tattoo with metal additives, irritation may occur. If you wear a medical patch, then in its place you may get a burn.
The patient is placed on the table, arms, head and chest are fixed with straps. The table slides into the apparatus. You must lie still. The procedure can take from half an hour to two hours, depending on the clinical case.
As for its dimensions, they are not related to the volume of the segment of the cord that it is designed to protect, but to the degree of mobility of the region in which it is considered. Vertebral canal, very prominent in the neck and lumbar region, in which the vertebral column is very mobile, shrinks to the dorsal region, where the vertebrae are almost immobile and descend to smaller sizes still in the pelvis, Where the sacral vertebrae are stricken with absolute immobility.
Spine, articulated frame. Rahi is the true articulated structure of the body, divided into stages, the functions of which are different. This bony stalk is not straight; It has several curvatures in the anterior-posterior plane that correspond to many different areas.
If you are very nervous, you may be offered sedatives. New generation devices are wide and spacious and usually do not cause fear of confined spaces. Noise from the working equipment appears inside the device, therefore headphones are provided there.
To communicate with the operator there is a special intercom. The device is fed Fresh air which helps you feel more comfortable. None pain does not occur during the session. The only thing that can bother you is the need to lie motionless on a hard table for a long time.
Its mobility allows you to move your head in three dimensions, allowing you to navigate in all directions. The cervical spine plays a predominant role in the mobility of the head in all directions. The spine forms a posterior curvature called kyphosis. This lumbar region has a convex curvature in front. The lumbar part is the mechanical support of the entire spine, since it is located at the very bottom and is articulated by the pelvis. The vertebrae are cubic, massive, adapted for support. Coccial rachis: More commonly known as the coccyx, this part consists of four or five vertebrae welded together that, unlike the others, are not denominated by a letter. The coccyx is a bone remnant corresponding to the tail of mammals. It does not have much interest in anatomy or medicine, except that it is often the site of pain during severe shock on the buttocks or even fractures. The cervical spine is the connection between the head and the body. . It is a sacral part with a curve, more prominent than all the others, concave in front: this area is called the sacrococcygeal or pelvic.
But if you suddenly get a headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting reflex breathing problems, notify the operator immediately. You may feel warmth at the scan site and a slight tingling sensation - these are quite normal phenomena.
If needed, you may be given an intravenous contrast agent.
MRI of the spine
The MRI method of the lumbosacral spine is the most informative in the diagnosis of pathologies with the development of degenerative-dystrophic processes. A timely diagnosis allows you to start treatment in a timely manner, and the information obtained from tomograms often allows you to put on your feet even those patients who would have previously been refused by official medicine.
MRI of the lumbosacral region is done with suspicion of such diseases:
Very often, a herniated lumbar disc or a herniated disc affects the lower back, that is, the caudal part of the spine. Lumbar disc herniation especially affects the lumbar vertebrae. It represents over 80% of disc herniations. This pathology is very painful, but in most cases it is quickly absorbed.
Origin of lumbar disc herniation
The vertebral column consists of successive vertebrae: cervical, dorsal, lumbar, and sacral. All these vertebrae, with the exception of the sacrum, formed from sutures, are separated by cartilaginous discs, a kind of cushion filled with a gelatinous substance. These intervertebral discs serve to protect the spine from shock and injury. A change in one of these discs by wear or protrusion towards the outer surface of the spine is called a herniated disc. We speak of a lumbar hernia when the attachment touches the lumbar vertebrae.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Protrusions and hernias.
- Various spinal injuries (fracture, instability, canal stenosis).
- Anomalies in the development of the spine.
- Metastases of tumor cells in the lumbar region.
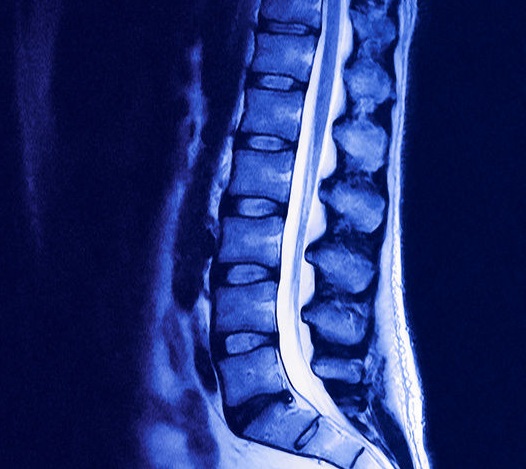
To identify diseases of the spine and examine the spinal cord, a neurologist prescribes an MRI scan of the lumbosacral spine. It is done necessarily in two projections at the level of the lesion: transverse and sagittal. The best image slice thickness is 3-4 mm with no gaps between them.
Symptomatic pain of a herniated lumbar disc. A herniated lumbar disc leads to intense and more or less common painful manifestations in the lower back. The path of sensations of pain depends on the nerve compressed by the damaged disc. It is called nervous neuralgia when the affected nerve is the nerve responsible for sensation and motor function front of the leg. When a lumbar hernia affects sciatic nerve, one speaks of the ischial region from a herniated disc.
If a herniated disc does not compress the nerve roots, it may remain asymptomatic, meaning the patient will not feel any pain. Solutions to relieve a herniated lumbar disc. In the case of a hernia, the most important thing would be to treat the sick symptom that causes the patient great discomfort on a daily basis. Doctors usually prescribe analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants to relieve pain, reduce inflammation of a compressed nerve, and relax muscles. When the back pain is too intense, the patient may be infected with corticosteroids.
In transverse view, a weighted T2 image is taken with the minimum slice thickness as possible. The cut is made at an angle corresponding to the position of the intervertebral disc.
To differentiate the disease from a tumor or malformation, MRI is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent. At the same time, it is clearly visible intervertebral discs and if there is - hernia.
The rest, in the case of one, should not exceed 2 days, since the long bed rest can lead to weakening and atrophy of the back muscles. In order for the patient to quickly return to their daily activities, even when the pain persists, doctors recommend vertical lumbar stretching systems. IN last years there is an ambulatory lumbar stretching system with an inflatable lumbar belt. This accessory allows you to aim at the corresponding lumbar region and restore the space between the intervertebral discs.
The rules of conduct for MRI of the lumbar remain the same. To do this, you can be given special disposable clothes and allow the presence loved one. To obtain the clearest images, you need to lie in the apparatus without moving.
If you have a feeling of fear when the table enters the scanner, it is better to inform the operator about this. But this usually does not happen because modern devices are designed in such a way that most of the body is outside the tunnel.
Before the procedure, you can eat, drink and take medication if necessary. An exception is MRI with contrast.
The patient will adjust the intensity of the inflation and the duration of the daily wearing of this, depending on his activity. These systems are guaranteed without risk of loss muscle mass. It also helps to protect the spine from shock and vibration, minimizing the risk of relapse, especially in connection with difficult professional activities for the lumbar region.
We analyzed data on the effectiveness of non-surgical treatments in people suffering from leg pain caused by pressure on spinal nerves. If the ependyma canal becomes narrow and presses on the nerves, it can cause pain in the legs or buttocks. Spinal stenosis is treated with various non-surgical methods, including analgesics, other drugs, spinal injections, physical exercise, physiotherapy and similar therapies. We wanted to know if there was any use non-surgical methods more or less effective than other options.
MRI cervical spine - modern method diagnostics, quite promising and rapidly developing.
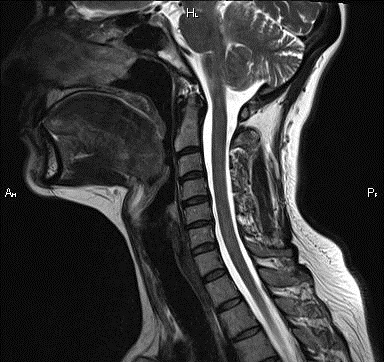
Hernias in this part of the spine are much less common than in the lumbar. Their peculiarity is that they are often accompanied by bone growths along the edges of the vertebrae - osteophytes. Sometimes, cervical MRI reveals hernias and osteophytes that do not cause any symptoms in the patient. At the same time, they can even slightly shift spinal cord posteriorly, and almost always with a hernia, stenosis of the spinal canal is observed.
We included 21 randomized controlled trials comparing non-surgical treatment with placebo, with no treatment or surgery. All participants had leg pain and had a confirmed diagnosis of lumbar spinal stenosis. The follow-up period ranged from one week to six years. This search has been updated to June.
Overall, the review shows that surgery is more effective in relieving pain than non-surgical treatments. Some digestive problems were reported with both drugs in the prostaglandin test, and some people in the gabapentin study reported dizziness and drowsiness.
In order to detect a hernia in the cervical region, T2-weighted MRI scans performed in the sagittal and axial projections at a standard slice thickness of 3 mm are sufficient.
MRI of the cervical spine is done:
- with osteochondrosis of this department;
- with anomalies in the development of the cervical spine;
- with protrusions and hernias in the department;
- when injuries of the cervical spine are received;
- with suspicion of metastases of tumors in the cervical region.
By conducting an MRI of this part of the spine, you can check the performance of the brain and neck. The procedure follows the same principle as MRI of other parts of the spine.
epidural injections. Two small studies have shown short term improvement pain and quality of life, and the other two showed no difference compared to placebo injections. The studies did not report on adverse reactions or problems.
Calcitonin injections. Six small studies showed that calcitonin was no more effective than paracetamol or placebo. A number of people have indicated that they feel sick or develop a rash. Mixed approaches compared to surgery. Five studies compared the results of surgery with those of a range of non-surgical treatments. One study found that after two years there was no difference between pain management between 5% and 18% experienced unwanted side effects as a result of surgery, and some were serious.
To date exact method Diagnosis of pathologies of the spinal column is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It refers to a highly informative method medical purpose. Competitor of MRI is CT - multislice computed tomography. How to do an MRI of the spine: indications for diagnostics and warnings, we will consider later in the article.
Research features
Magnetic resonance imaging has an abbreviated abbreviation - MRI. The research method is considered non-radiological, safe for people. It is used for testing internal organs and fabrics. The study of the ridge provides a complete picture of the state of the cartilage, the matter of the spine. MRI has an advantage over other methods because it is not capable of showing a complete picture of the skeletal structure.
The method is based on the movement of atoms under the influence of an electromagnetic field. Thanks to strong impact electromagnetic field particles move, creating a resonance, which is transformed into an image of a three-dimensional plane. The diagnostic method of MRI provides an opportunity to see adjacent tissues that occur degenerative changes vertebra. With it, it is possible to examine all parts of the spine, or a separate area. medical method simplifies diagnosis, promotes rapid detection pathological process at an early stage.
What does it show?
The capabilities of diagnostic equipment make it possible to detect a disease that has not been detected in other ways. The procedure can reveal:
- Displacement of the vertebrae;
- Tumors at the initial stage;
- Bechterew's disease;
- Spondylolisthesis;
- Spinal cord compression;
- congenital pathology;
- insufficient blood supply;
- Inflammatory process of the joint;
- infected area;
- Damage to nerve fibers;
- Spinal stenosis;
- spine injuries;
- Scoliosis, osteochondrosis, kyphosis.
- Arthrosis of the joint;
- Disturbed state of the intervertebral disc;
- Place of localization after injury;
- Affected centers of the brain;
- congenital anomaly;
- Oncological neoplasms;
- Deviation in the anatomy of the spine.

Indications for carrying out
MRI is one of the most effective methods research through High Quality, reliability of the received data. The procedure provides Full description patient's health. This method used for people with a violation of the musculoskeletal system, suspected oncology.
Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to detect tissue deformation after a bruise, injury, surgery. The device is able to examine that part of the body that cannot be seen on ultrasound, X-ray, computed tomography. This refers to the activity of the gray matter cortex, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid, which are very important for studying and compiling clinical picture the patient's condition.
Basically, such an examination is carried out by patients of oncological, urological areas. Indications for a spine procedure include:
- Osteomyelitis;
- Inflammatory disease;
- Backache;
- Metastases;
- Herniated disc;
- Anomaly (congenital);
- vascular disorder;
- Demyelinating disease.

Contraindications
This procedure has some contraindications, which the specialist is obliged to inform the patient about. Since the event is associated with an impact on the human body, it is necessary to take them into account. They are relative and absolute:
- Implant in the body;
- pacemaker;
- Vascular clips;
- Dentures;
- Fear of closed space;
- Metal fragment in the skin;
- Body weight more than 130 kg;
- Chronic pathology of the heart.
Care must be taken with the procedure when a woman is in position. Information about the negative impact of the device on the fetus and future mother so far not enough. But over the years, no case has been established when the procedure ended with a serious consequence, harmed the health of the mother. You can undergo an MRI in the 2nd or 3rd trimester.

How is it different from CT?
Computed tomography (CT) is based on X-ray radiation, which is absorbed by the matter of a biosystem. It is very similar to a regular x-ray. A different feature is the receipt, processing of the received data. It should be remembered that computed tomography cannot be used repeatedly due to the influence of the rays, because they adversely affect the organs, the well-being of the individual. The duration of CT is from 10 seconds to a couple of minutes.
During the session, the effect of ray beams occurs, which pass through tissues of different densities. As a result, a layered image of a body part appears. The equipment processes the received images and reflects them in a three-dimensional plane.
With the help of a magnetic field, an MRI is diagnosed, as a result of which an active movement of hydrogen atoms in the body is observed. The tomograph processes the received electromagnetic impulse into a three-dimensional image.
Conducting an MRI study can last 10-20 minutes, but in a motionless position. If you need to carry out the procedure little child, then the doctor applies anesthesia. It allows you to accurately distinguish healthy tissue from damaged, to identify pathological change. The MRI procedure consists of several images, which are formed and processed no more than 5 minutes. Total time the event is 45 minutes.
Research procedure
Diagnosis does not require much effort, lengthy preparation. MRI is performed on an outpatient basis or in a hospital. Around the anatomical part, the nurse places a device with wires that will receive and transmit radio waves to the computer.
If necessary, the doctor may prescribe the introduction of a contrast agent into the arm of the patient. In addition, the doctor's assistant can put a dropper to clear the vessels and prevent blockage. Depending on the location, it is possible to study not only the spine itself, but also its branches (spinal, thoracic, cervical).
Patient preparation
How to prepare for the procedure? If you are taking medication, inform the specialist about it, also inform the doctor about the presence of a pin, prosthesis, pacemaker. Before the start of the session, you must remove all jewelry, watches, metal objects.
The preparation of this method is based on cleansing the intestines from excess food and liquid. How should a patient prepare for an MRI? It is advisable not to eat foods such as: milk drinks, bread, cabbage. After eating, it is recommended to use drugs that promote rapid digestion (Festal, Mezim). Before starting the session, the patient must have an empty stomach.
The patient is placed in a flask elongated shape, in a horizontal position. To pass the examination without defects, it is necessary to maintain the immobility of the anatomical region. The person will be under the equipment for about 30 minutes. During the study, communication with the patient occurs through the intercom (microphone), because they are in different rooms. Results may be available within a couple of hours, or the next day.

X-ray progress
The procedure does not cause any discomfort or pain for the patient. The only thing that is required from the patient is complete calmness, immobility, patience. People who are afraid of confined spaces are advised to take a sedative (valerian, hawthorn tincture).
MRI - scanning takes place in a special chamber (pipe shape), it contains a sliding table for positioning a person. The contour of the so-called "tunnel" has a magnet sheathed with a specific sheathing. The patient is placed on this table, head, arms, chest are fixed with straps. After that, the bed smoothly goes into the apparatus.
When the person is completely under the apparatus, the study begins. The equipment emits noise that is unpleasant to the human ear. Therefore, the patient is put on headphones to lower it. The device enters fresh air to make people feel more comfortable and relaxed. Thus, a tomogram is made.

But, if the patient felt dizzy, vomiting, shortness of breath, then you should immediately tell the specialist about this through a microphone. The only drawback of the procedure is the high noise figure and long lying on a hard plane. In private clinics, such equipment is equipped with a video system, and a person can watch a movie, listen to music while the machine is scanning. It is not difficult to make an MRI of the spine, but not everyone can afford the cost of the procedure.
Before the passage of magnetic resonance imaging, you can take an x-ray of the back in a lateral, direct projection. Based on it, the damaged area of the spine is analyzed, which needs to be further examined by MRI scanning.
Image interpretation
We figured out how to take pictures, but what does the image show? Only a radiologist can understand and decipher it. The picture is black and white with different areas of coloring. Light x-rays are bones, soft tissues are almost invisible, and all because they pass rays through themselves. A fracture, a crack, a displacement of the bone joints are clearly visible.
Pillar to the side - characterizes scoliosis. Deciphering areas of dark color indicate the presence of tumors. The wrong distance, the height of the spinal fissures indicates the development of osteochondrosis.
Danger and Consequences
Everyone knows about such a procedure as an MRI. But every person wonders if it is harmful to health, are there any consequences? According to scientific research it has been proven that this method is safe, does not have serious contraindications, and eliminates the risk of radiation exposure. The risk of radiation is 5 times lower compared to talking on a mobile device. Negative influence missing, you can repeat the procedure after unsatisfactory results.
The main advantage is the absence of radiation. Behind long years there was no case in medical practice where, after the event, the patient felt unwell, no harm or consequences on the body were revealed. The inconvenience of MRI for many patients is the duration of the session. After all, the person is forced to lie motionless on the table from 15 to 45 minutes. But at the same time, no discomfort None of the patients experienced any complications.
You can get acquainted with the diagnostics in the next video.
