When take tumor markers. Cancer embryonic rea antigen in the diagnosis of oncological diseases
CEA tumor marker in the diagnosis of oncological diseases takes important place... Tumor markers are highly specific proteins produced by tumor cells. The indicators of tumor markers in the blood increase in direct proportion to the active growth and metastasis of the malignant neoplasm.
Often, the CEA tumor marker is attributed only to female diseases... However, in relation to gender, CEA analysis is used only in the diagnosis of mucinous and serous ovarian cancer. In all other cases (except for prostate cancer) CEA participates in the main tests without regard to gender.
And even in the diagnosis of bone metastases, the CEA oncomarker takes precedence, regardless of gender. It should be noted that tumor markers can moderately increase in benign tumors and some somatic pathologies.
Rea tumor marker is an indicator of malignant neoplasms and the prevalence of their metastasis. In fact, the cancer embryonic antigen is a glycoprotein containing a large number of carbohydrates. It is produced in minimum quantity tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas and liver of an adult.
Normally, the CEA tumor marker is practically not detected in healthy people. The overwhelming part of the tumor marker is synthesized by the tissues of the embryo and fetus (in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas). In a newborn child, CEA synthesis stops.
CEA tumor marker: what it shows
Most often, rea tumor marker is effectively used to diagnose oncological lesions of the colon and rectum. Rea is also increased in cases of tumor damage to the lungs, mammary, pancreas and prostate glands, ovaries. Cancer antigen increases sharply in the presence of metastatic foci in the liver and bone tissue.
OK, y healthy person the embryonic cancer antigen is practically undetectable. Its content increases with some somatic diseases (severe pancreatitis, pneumonia, ulcerative colitis, tuberculosis), smoking, alcohol abuse (including alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver). In addition, CEA can increase with autoimmune diseases and the development of benign tumors.
However, a sharp increase in the level of CEA tumor marker is characteristic precisely for active growth and the process of metastasis of malignant tumors.
In the tissues of the embryo and fetus, CEA performs important role- it stimulates cell reproduction and growth. In this regard, when carrying out the analysis, it must be borne in mind that it should be detected in the serum of the fetus, and not in the pregnant woman.
For reference. In women carrying a child, the CEA tumor marker does not normally increase.
The process of synthesizing the cancerous embryonic antigen by tissues is suppressed immediately after the birth of the baby. The role of CEA in adults is normal and still uncertain.
The greatest importance of determining the level of the oncomarker rea is in the detection of oncological neoplasms. Considering that in a healthy person, the antigen indicator will be minimal, with an active oncological process, the presence of foci of metastasis, tumor recurrence after chemotherapy and radiation therapy, as well as surgical treatment- the indicator will increase.
In the presence of a malignant neoplasm, the RA tumor marker can accumulate:
- pleural fluid;
- ascitic effusion;
- urine;
- the secret of the gastrointestinal tract.
Due to the fact that this analysis makes it possible to diagnose the occurrence of relapse and metastases as accurately as possible, assess the quality of treatment and help identify the primary tumor, CEA is the most frequently used tumor marker in clinical practice.
It is necessary to understand that there is no ideal oncology marker in terms of specificity and sensitivity, therefore, this analysis should not be assigned to all patients during mass preventive examinations. However, the study of tumor markers allows them to be used with high accuracy and sensitivity for the primary diagnosis of malignant neoplasms in:
- categories of patients with cancer symptoms;
- persons who have undergone treatment (the analysis is used to control the quality of treatment and timely detection of relapse);
- patients with an increased risk of developing oncology.
Also, an increased level of the tumor marker rea allows one to suspect the presence of distant and unvisible metastases, to reveal a tumor on initial stage in patients from groups at increased risk of oncology, as well as to detect a relapse long before the onset of clinical symptoms (four to six months).
Reasons for the increase in CEA
 The rea tumor marker index increases in direct proportion to the stage of the disease, damage to other organs and the presence of metastases. The CEA level constantly increases with tumor growth, and even at the initial stage, the marker deviates significantly from the norm.
The rea tumor marker index increases in direct proportion to the stage of the disease, damage to other organs and the presence of metastases. The CEA level constantly increases with tumor growth, and even at the initial stage, the marker deviates significantly from the norm. CEA can sharply increase in malignant lesions of the pancreas, its sensitivity in this case reaches eighty percent. However, it should be borne in mind that CEA also responds with an increase to pancreatin (acute and chronic relapse).
CEA tumor marker increases in half of patients with breast and lung cancer.
Important. When decoding the analyzes, it is necessary to take into account that CEA indicators above 20 ng / ml will testify in favor of oncology.
Such indicators are noted when the tumor is in:
- colon and rectum;
- lungs;
- mammary glands;
- pancreas and prostate glands;
- ovaries.
Also, such values are typical in the presence of metastases in the liver and bones.
In addition to being used for the primary diagnosis of the conditions described above, CEA is effectively used to assess the quality of treatment.
Important! If, after the diagnosis is made: cancer, against the background of chemotherapy or radiation therapy, the tumor marker index begins to decrease, this indicates a positive trend and a decrease in the tumor.
After complete removal of the tumor, CEA should completely decrease to normal in a maximum of two months. The persistence of high rates will indicate a relapse or the presence of distant metastatic foci.
CEA can also increase with some somatic pathologies and benign tumors... In this case, its values, as a rule, do not exceed 10 ng / ml.
The level of cancer embryonic antigen can increase with:
- autoimmune pathologies (the normalization of its indicators will indicate the achievement of remission);
- tumors of the ovaries, intestines, liver, mammary glands of a benign nature;
- cirrhosis of the liver, severe hepatitis (acute and chronic);
- intestinal polyposis and neurinoma;
- Crohn's disease;
- ulcerative colitis;
- liver hyperplasia;
- cystic fibrosis;
- acute and chronic (in the stage of relapse) pancreatitis;
- kidney failure;
- severe pneumonia;
- bronchiectasis;
- emphysema of the lungs;
- tuberculosis;
- chronic bronchitis (including chronic bronchitis of smokers).
In addition, CEA will be increased in alcohol abusers (even before the onset of cirrhosis) and smokers.
Indications for research
Rea analysis is carried out with standard screening of high-risk groups (burdened heredity, work on chemical  production, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, etc.), to control the quality of treatment and early detection of relapses and metastases.
production, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, etc.), to control the quality of treatment and early detection of relapses and metastases.
Also, CEA analysis is indicated for patients with symptoms of colorectal cancer, namely:
- detection of streaks of blood in the stool;
- positive occult blood test;
- intestinal bleeding;
- frequent alternations of constipation and diarrhea;
- drastic weight loss;
- increased in the analysis (without other signs of the inflammatory process);
- anemia;
- the presence of a palpable or visualized (ultrasound, MRI) dense formation;
- pain and cramps in the abdomen;
- discomfort during bowel movements;
- constant urge to defecate and a feeling of "full" bowel.
Attention. It is important to remember that most often, the first signs of a malignant neoplasm are: unexplained, severe weight loss, weakness, lethargy, increased ESR and anemia in the analyzes. Specific symptoms due to the localization of the tumor appear much later.
How to take a blood test
There is no specific preparation for the analysis for a tumor marker. Blood is taken in the standard way - from a vein. Half an hour before taking the material, nervous and physical stress is excluded. Considering that smoking and alcohol have a significant effect on the indicator, smoking is excluded at least one day, and alcohol intake - seven days before the analysis.CEA tumor marker: decoding
Attention. When interpreting the analysis, it is important to remember that the rate for non-smokers and smokers will differ.
 CEA norm for non-smokers is up to 5.0 ng / ml (in some laboratories up to 3.8). For smokers - up to 5.5 ng / ml (in some laboratories up to 5.0).
CEA norm for non-smokers is up to 5.0 ng / ml (in some laboratories up to 3.8). For smokers - up to 5.5 ng / ml (in some laboratories up to 5.0).
It is important to remember that the limit limits of the norm in different laboratories may differ, therefore, when interpreting the analysis, it is necessary to focus on the norm values indicated in the form.
Normal indicators of a tumor marker indicate low risks of developing a malignant neoplasm, but do not completely exclude the presence of the disease. It is necessary to understand that it is unacceptable to evaluate CEA in isolation from other studies.
Important! The diagnosis of cancer cannot be established only by the results of a study for a tumor marker.
Also, patients at risk who work for hazardous production living in areas with poor ecology, the analysis for the CEA must be submitted once a year. The interpretation of the analysis and the issuance of a referral for research should be dealt with exclusively by the oncologist.
Indicators above 20 ng / ml will speak in favor of oncology. Values below 10 ng / ml, but above 5.5, are more typical for somatic diseases and benign tumors.
Tumor markers are organic substances (proteins), the amount of which increases with the development of cancer cells in the human body. What do tumor markers show? The amount of these substances helps to identify the presence of malignant tumors and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment. Tumor markers make it possible to diagnose cancer in the early stages and approximately determine the location of the tumor formation.
What tumor markers show and how to get tested correctly
Analysis for tumor markers allows:
Find out if the patient is at risk;
... roughly identify the affected organ;
... suspect a relapse of oncology;
Upon receipt of the results of the analysis for tumor markers Special attention worth turning:
On the increased performance;
... a seemingly elevated tumor marker.
Changes in indicators indicate that there are deviations from the norm in the human body, including progressive cancer cells... The main advantage of the analysis is that tumor markers show the presence of cancer in the early stages, which is very important for the effectiveness of treatment.
Analysis rules:
Blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach, excluding food intake 8 hours before the procedure;
- the analysis is carried out before 11 o'clock in the morning;
- three days before the test, stop drinking alcohol and junk food, reduce physical activity;
- on the day of the analysis, smoking and taking medications are prohibited;
- passing the analysis for PSA, abstain from sexual intercourse for seven days.
Tumor markers are found in the blood, urine of children, young, adult and elderly patients. In most cases, such an analysis shows the presence of cancer cells six months earlier than other diagnostic methods.
It is important that tumor markers show even the slightest changes and help to solve the following tasks:
1. Tracking the effectiveness of therapy, which allows in some cases to change the treatment regimen or change drugs.
2. Tracking recurrences of neoplasms, tracking the emergence of new metastases. This will help you start on time. re-treatment and watch out for the disease.
3. Analysis will help you decide which therapy is worth using.
4. Tumor marker helps to assess how much the organ is affected by cancer cells, the degree of progression, which contributes to the selection of a more adequate treatment regimen.
5. The analysis helps to assess how the remission is going and to make a prognosis of the patient's life expectancy.
Who needs analysis and when
 Screening tests should be performed 1 - 2 times a year for those patients who have a genetic predisposition, benign neoplasms, suspicious papillomas and moles. The rest of the people can be tested no more than once every two years, and also:
Screening tests should be performed 1 - 2 times a year for those patients who have a genetic predisposition, benign neoplasms, suspicious papillomas and moles. The rest of the people can be tested no more than once every two years, and also:
After severe nervous strain;
... when living in unfavorable environmental conditions;
... under other circumstances that can cause cancer.
Diagnosed;
... with treated malignant tumor;
... with the initial detection of a neoplasm;
... before and after surgery;
... during the course of therapy.
1. First year - every month.
2. Second year - once every two months.
3. Third year - once every three months.
Subsequent years are tested every six months. Before screening actions, the patient should visit an oncologist, who will find out which markers need to be tested.
AFP
Norm: up to 10 ng / ml. What do AFP tumor markers show? Pathological results analyzes may indicate oncological diseases:
The liver;
- gastrointestinal tract;
- ovaries;
- testicles;
- kidneys.
The accuracy of the test can be influenced by diseases:
Diabetes;
. multiple pregnancy;
... hepatitis;
... renal failure.
Low rates in a pregnant woman may indicate the risk of fetal pathology.
CEA
 CEA marker is secreted mainly by the digestive tract of the fetus. In adults, the substance is found in the blood in minimal amounts.
CEA marker is secreted mainly by the digestive tract of the fetus. In adults, the substance is found in the blood in minimal amounts.
Norm: up to 6.3 ng / ml. A slight increase in CEA norms is determined in smokers. At high rates marker there is a risk of neoplasms in the following organs:
Digestive tract;
- the mammary gland;
- prostate;
- liver;
- lungs.
Shortness of breath, causeless cough;
... the appearance of a visible tumor;
. chronic fatigue;
... unreasonable loss of strength;
... sweating;
... prolonged increase in body temperature;
... weight loss;
... the appearance of new moles;
... decreased appetite or complete reluctance to eat with bouts of nausea and vomiting;
... malfunctions digestive tract.
CA 125
This tumor marker is an indicator of ovarian cancer.
Rate: 0 to 30 IU / ml. Indications outside the norm speak of oncology:
Female genital organs;
- respiratory organs;
- Gastrointestinal tract.
CA 15-3
Breast neoplasm marker.
Norm: from 9.2 to 38 U / l. What do tumor markers show if the indicator is too high? As a rule, this is a suspicion of cancer:
The mammary gland;
... digestive tract;
... liver;
... respiratory organs.
It may also indicate inflammatory pathology in the area of biliary organs and the development of autoimmune disorders.
CA 19-9
The marker is characteristic of the gastrointestinal tract pathology.
The norm is: from 0 to 37 U / ml. Exceeding the norm in most cases indicates neoplasms in:
Gallbladder;
... pancreas;
... liver;
... organs, digestive tract.
CA 72-4
Provides comprehensive information on sarcoma of the stomach, ovaries, lungs.
Norm: up to 6.7 U / ml. High values indicate that cancer cells develop in:
Uterus;
... stomach;
... mammary glands;
... ovaries;
... pancreas;
... liver.
CYFRA 21-1
Indicates cancer Bladder, lungs. Analysis for CYFRA 21-1 in most cases is assigned in conjunction with CEA.
Norm: up to 3.5 ng / l. If the indicators are above the norm, an in-depth check for malignant formations is necessary in:
Genitourinary system;
... respiratory organs.
Elevated tumor marker (PSA)
PSA is a protein secreted by the prostate gland. Tumor marker will help determine a prostate tumor, adenoma. The analysis is used to monitor ongoing therapy.
Norm: up to 4.1 ng / l. If the norm is exceeded, then tumor markers show the presence of a malignant pathology in the prostate. Experts recommend that males after 50 years of age be tested for prostate-specific antigen annually. This will help to identify diseases of the prostate gland in the early stages, which will simplify therapy and make it as effective as possible.
To properly prepare for the analysis, you must:
For 10 hours to refuse to eat food, they recommend clean, non-carbonated water, other drinks are excluded;
... two days you need to adhere to a diet;
... do not go in for sports and load yourself as much as possible for several days.
... seven days not to be sexually active.
PSA diagnostics are required:
When diagnosing prostate adenoma;
... while monitoring the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy;
... when cancer is detected at the first stage.
An elevated PSA tumor marker can be not only in cancer, but also in other cases:
Presence of prostate adenoma;
- problems with potency;
- if there are irregularities in the process of urination;
- during a long bike ride on a bad road.
It is very important to know that small deviations in the indicators of tumor markers can indicate benign processes in the human body, for example, inflammation. An elevated tumor marker cannot speak of 100% presence of oncology, but gives an informative reason to continue an in-depth examination of the patient. It is not worth conducting a screening test for all types of markers, you just need to contact a specialist and he will already decide what tests are needed.
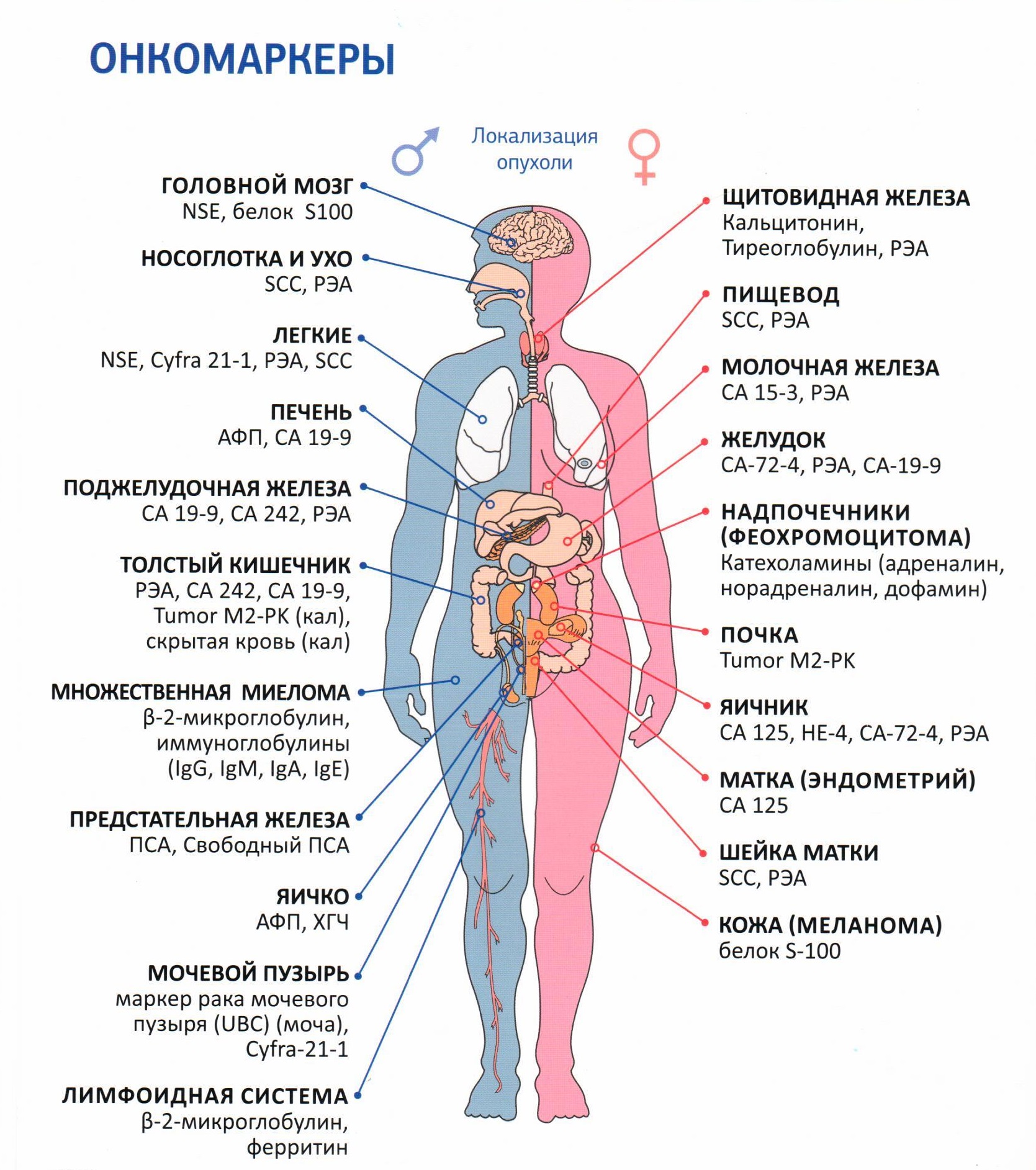
Tumor marker CA 125 is a highly specific protein located on the membrane of ovarian epithelial cells affected by oncology. Normally, it can be detected at low levels in the tissues of the endometrium and serous membranes, but there should be practically no protein in the blood.
The appearance of protein in the blood in normal conditions can be associated only with the menstrual cycle, as well as with pregnancy, and then only in the first trimester.
Increased levels of Ca125 in the blood indicate a malignant degeneration of ovarian tissue. Less often, the values of the CA 125 tumor marker increase with the development of oncological neoplasms in other organs (endometrium, liver, stomach, etc.). In fact, CA 125 is a glycoprotein that is actively secreted by tumor cells.
Please note that if the doctor prescribed you a referral to donate blood for CA 125, this does not always mean suspicion of oncology. This protein is involved as a complementary marker for several other pathologies. Therefore, it does not make sense to immediately panic.
Although, of course, the study of the level of CA 125 is carried out most often for the purpose of early detection of ovarian oncology, as well as for monitoring the dynamics of the activity of the established disease, the spread of the metastatic process, the quality and effectiveness of the therapy, as well as for the diagnosis of relapses.
What do tumor markers of blood show?
V general case the analysis of the levels of tumor markers is carried out in order to:
- early detection of malignant neoplasms and their recurrence after chemotherapy, radiation therapy or surgical removal;
- control of tumor growth and metastasis;
- monitoring the quality of treatment;
- screening of oncological pathologies among high-risk groups, according to their development (smokers, persons working in hazardous work, patients with a burdened family history, etc.).
However, it is important to understand that there are no absolutely specific tumor markers that increase only with certain form cancer. They can also slightly increase in severe inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, smoking, alcohol abuse, etc.
Attention. Only an oncologist can answer the question: what the tumor marker shows. It is unacceptable to assign yourself this analysis in private laboratories and interpret it with the help of reference books, colleagues and the Internet. Especially when diagnosing a disease such as cancer, where any mistake can lead to a psychological catastrophe.
It is also important to remember that the study of indicators of tumor markers is not included in mandatory list analyzes during a preventive examination in patients who are not at risk for the development of malignant neoplasms and do not have cancer symptoms.
All studies of tumor markers should be carried out strictly according to indications and interpreted in conjunction with other analyzes. Only on the basis of an elevated tumor marker, the diagnosis is not made.
Tumor marker CA 125. What shows
A blood test for CA 125 is effectively used in the primary monitoring of oncological processes in the ovaries, diagnosis  recurrent oncological process after treatment, as well as to control the spread of metastases.
recurrent oncological process after treatment, as well as to control the spread of metastases.
Cancer antigen 125 may also increase if the oncological process (or metastases) affects:
- the lining of the uterus,
- serous membranes,
- lung tissue,
- mammary gland,
- pancreas.
CA 125 will also significantly increase with the spread of metastatic foci from the above organs to the liver.
Attention. The accuracy (otherwise specificity) of the CA-125 assay is not very high. Only cases of at least a twofold increase in the level of the marker CA125 in the blood (especially for women aged 55 and older) should be taken into account to assert the possibility of ovarian cancer.
Also, together with the level of ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide), the CA 125 tumor marker can be used in addition to basic studies to assess the severity of HF (heart failure).
Additionally, ca125 is examined for the diagnosis of serous cavity effusions (pleurisy, peritonitis).
In addition to diagnosing oncological processes, blood for ca 125 is examined for endometriosis, cysts in the ovaries and tumors of benign etiology that affect the female reproductive system.
The tumor marker CA 125 is of greatest importance in detecting serous type ovarian epithelial carcinomas, as well as adenocarcinomas of the endometrium and fallopian tubes.
When to take CA test for 125 women
Oncomarker 125 is investigated for suspected oncological processes in the ovaries (for the purpose of primary diagnosis), as well as for monitoring the quality of treatment and control of relapses.
monitoring the quality of treatment and control of relapses. Analysis of CA 125 for the purpose of primary diagnosis must be taken when symptoms of ovarian cancer appear:
- regular irregularities in the menstrual cycle ( this symptom is not the main one, since some patients may have regular menstruation even with bilateral ovarian cancer);
- frequent urination with false urge and sensation incomplete emptying Bladder;
- persistent mucous discharge streaked with blood ( bad smell discharge is rare);
- constant pain in the lower abdomen and lower back;
- constipation, flatulence, heaviness in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, indigestion;
- pain during intercourse;
- weakness, weight loss, emotional lability, depression;
- increased ESR in a general blood test;
- an increase in the abdomen due to the accumulation of fluid in abdominal cavity(ascites).
The main symptoms are quite nonspecific and are often regarded by women as a manifestation of ovarian inflammation. Many patients go to the doctor for the first time when ascites appears. That is, when the tumor reaches large sizes and metastasizes.
Important! According to statistics, up to 70% of women first visit a doctor for later stages illness. It should be noted that 95% of ovarian cancer cases are hereditary.
Two types of malignant neoplasms of the ovaries give specific symptoms. These are hormone-producing tumors:
- granulosa cell - causes feminization (can manifest itself by early puberty in girls, as well as the resumption of uterine bleeding in women during menopause);
- adenoblastoma - leads to masculinization (provokes the growth of a beard, mustache, a decrease in the size of the mammary glands, coarsening of the voice, etc.).
How to donate blood for analysis
In order to determine the level of CA 125, venous blood is examined using immunochemiluminescence.The material is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. At least 3 days before the analysis, fatty, fried and spicy foods must be excluded from the diet. It is forbidden to drink strong tea (especially with sugar), coffee, juices and soda. It is also necessary to exclude the use of alcoholic beverages. Smoking is prohibited on the day of the test. The day before blood sampling, physical and emotional stress is excluded.
The physician and laboratory staff should be advised of the medications they are taking. If possible, the medication should be discontinued a week before the study.
Important. When donating blood to CA 125, the day must be marked menstrual cycle, for which the analysis is submitted.
Norm CA 125
CA 125 the norm in women is less than thirty-five U / ml. Optimal values are below fifteen U / ml.
CA 125 is the norm for age - the analysis for a tumor marker does not have age fluctuations, however, in women during menopause, an increase in CA 125 to borderline values or with a slight excess of normal values may be detected.
Reasons for increasing CA 125
The main reasons for the increase in this tumor marker are malignant neoplasms. CA 125 is elevated when swelling  strikes:
strikes:
- organs reproductive system women (ca125 is the main diagnostic marker of ovarian cancer);
- breast and pancreas;
- Gastrointestinal tract (stomach and intestines (especially the rectum));
- lung tissue;
- liver (including metastatic lesions).
Of the non-oncological reasons for the increase in the level of tumor marker, it should be noted:
- ovarian tumors and cysts of benign origin,
- borderline tumors (low-grade tumors: serous, mucinous, endometrioid, clear cell (mesonephroid) type),
- mixed tumors,
- Brenner's tumor.
Also, an increase in CA 125 can be caused by:
- endometriosis,
- severe infectious and inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs,
- diseases accompanied by a serous effusion (pericarditis, pleurisy, etc.),
- chronic hepatitis,
- pancreatitis,
- autoimmune diseases.
Analysis results
With ovarian cancer, in eighty percent of patients, the ca125 indicator can increase from 124 to 164 U / ml.CA 125 is the norm in women with ovarian cysts - borderline values can be observed, closer to 35 U / ml or with a slight increase.
Considering that in patients with malignant neoplasms affecting the cervix, endometrium, stomach, as well as with ovarian tumors of benign etiology, CA 125 tumor marker also increases. Decoding of diagnostic results, in this regard, should be based on data from other studies. Only a comprehensive interpretation of the analyzes will help to carry out the correct differential diagnosis and make the correct diagnosis.
Attention! It is important to note that the absence of an elevated CA 125 in a blood test does not allow the diagnosis of cancer to be excluded with 100% probability. In some patients, in the early stages, the CA 125 tumor marker does not increase. At the third - fourth stage, the indicator is increased in all patients.
The CA125 test can be used to monitor the quality of treatment. A decrease in its indicators against the background of chemotherapy or radiation therapy indicates the effectiveness of the treatment.
 In women carrying a child, an increase in CA 125 values can be diagnosed. As a rule, the deviations in the analyzes are insignificant. The maximum increase in CA125 is observed in the 1st trimester, which can reach a value of 1250 U / ml. However, during an uncomplicated pregnancy, the level of the marker often remains normal.
In women carrying a child, an increase in CA 125 values can be diagnosed. As a rule, the deviations in the analyzes are insignificant. The maximum increase in CA125 is observed in the 1st trimester, which can reach a value of 1250 U / ml. However, during an uncomplicated pregnancy, the level of the marker often remains normal.
Borderline values (closer to 35 U / ml) are detected in women who are breastfeeding. This is not a pathology and does not require treatment.
An increase in the level of the CA 125 tumor marker during pregnancy requires constant monitoring, especially for those women who have previously been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or who have been diagnosed with uterine appendages pathology during the examination.
For reference. In some cases, during pregnancy, the levels of markers CA 125, CA 15-3, and CA 19-9 and are monitored. Studies are performed both in the mother's blood and in the umbilical cord blood. In one study with elevated levels of these markers, pregnancies of all subjects (53 pregnant women) ended in caesarean section.
Even people, in whose family there were no cancer patients, sooner or later may begin to be interested in the reliability of tumor markers as a way to control possible tumors in the body. This analysis is one of the popular methods. early diagnosis cancer. After it was opened in the second half of the twentieth century, in Western Europe and there was a real boom in the USA. A huge number of people almost stood in line, regularly donating blood and urine for tumor markers. But gradually the excitement began to decline: doubts arose about the reliability of this analysis.
The question of possible errors
It turned out that certain proteins produced actively by malignant cells can be found even in the body of a completely healthy person. For example, substances indicative of ovarian cancer are also produced periodically during polycystic disease, the appearance of especially large cysts, and benign tumors. And sometimes an increase in the threshold value can be found even in completely healthy woman, for example, with some hormonal fluctuations, stress or taking an analysis during menstruation.
The most accurate tumor marker is RSA, which can detect prostate cancer on early stages.
Exceeding the norm is such an accurate signal that some clinics even refused a number of additional tests. Although the patient in any case may insist on performing these tests. In total, of the popular tumor markers today in medicine, 20 variants are used everywhere, the rest are already more specific. True, the number of corresponding proteins (and analyzes) is constantly increasing.
The benefits of tumor markers
For example, modern medicine makes it possible to diagnose cancer in the early stages or even the likelihood of cancer by DNA. Certain genes make it possible to trace the tendency in some people to specific types of cancer (tumor diseases internal organs), monitor the tendency of cancer growth after the onset of the age threshold and take appropriate measures in a timely manner.
What measures are we talking about? Women with a high degree of threat can remove the mammary glands and replace them with implants. Sometimes the uterus is removed, for example, after leaving reproductive age... Of course, an appropriate decision is made not only on the basis of data obtained thanks to tumor markers. And doctors do not exclude the possibility of certain errors. However, statistics confidently show that the large-scale introduction of tumor markers into medical practice has saved millions of lives. Today, most types of cancer in the first and second stages are curable.
Tumor markers for cancer patients
The analyzes discussed are also extremely important for those who develop cancer and have been successfully treated. Periodic blood donation for tumor markers allows you to control a possible relapse. If an increase in specific proteins in the blood in a healthy person may not be associated with cancer, then in a patient with a high degree of probability, an increase in certain indicators indicates a repeated progression of the tumor. There is such a tendency: sometimes the level of proteins increases in a healthy person, but the tumor will always give an increase in tumor markers.
The question of credibility
But if we return to the question of reliability, it is worth noting that most tumor markers are only one of the analyzes. They are considered by specialists in a complex, besides different methods research provides a complete picture. Often, specialists in this way discover hidden pathologies, clarify the stage of the disease. Therefore, you should not be surprised if the doctor gives a referral immediately to whole line surveys.
The tested enzymes are normally present in the blood of even a completely healthy person, just in small quantities. There are international standards regarding the threshold value of tumor markers.
Note that they are different for each type of cancer. Some tumor diseases can be checked by several types of such tests at once. Information on international indicators and exceeding the threshold, respectively, is publicly available, so when you receive test results on your hands, you can check for yourself how good your tests are.
However, the optimal medical consultation, since a person without special training simply does not have the appropriate knowledge to make a conclusion about the diagnosis. Therefore, if there is no trust in the attending physician, it is prudent to seek medical help with the issued analyzes to another institution. It is worth noting that several types of cancer can be checked by several tumor markers at once. With higher values in all types of analyzes, the probability of an error decreases.
What can cause an error in the analyzes?
There are certain rules for the delivery of tumor markers, violations of which can cause some errors. Blood is donated early in the morning, on an empty stomach, from a vein. Before that, it is advisable not to eat for 8 hours. Also excluded are juices, any nutritious drinks, milkshakes. With a slow metabolism given time should be increased to 13 hours.
Often the reliability of the analyzes was questioned due to the violation of the above rule. Many patients perceive food intake as an intake. solid food, full meals, using liquid yoghurts, fermented baked milk, kefir, and other products. Subsequently, they are genuinely surprised when they get wrong results.
Women also need to monitor the regularity of their cycle, report any deviations. Tumor markers give increased indicators right before menstruation, in which case it is wiser to redo the tests. Hormonal abrupt changes, taking certain medications, also affect the results. But diagnosticians usually take these factors into account.
As practice shows, many people today turn to methods laboratory diagnostics on their own initiative, without a doctor's prescription. Tumor marker tests are especially popular among patients. The editorial staff of the Sibmeda portal talked about the methods of laboratory diagnostics aimed at identifying oncological risks with Andrei Pozdnyakov, chief physician of the INVITRO-Novosibirsk clinical diagnostic laboratory.
- Andrey Sergeevich, what are the methods of laboratory diagnostics of oncological diseases?
- If we understand laboratory diagnostics as a study of blood, urine, etc. for the subsequent diagnosis and prescription of therapy, the methods of laboratory diagnostics of oncological diseases do not exist. Any oncology is a serious diagnosis due to the risk of disability and death.
Therefore, confirmation of oncological diagnoses should be carried out only by a combination of instrumental and morphological studies.
Instrumental research- this is an X-ray, MRI and so on, and morphology is a study of a "piece" of a tumor, a biopsy. Otherwise, it is impossible to diagnose or exclude the tumor. If there is a suspicion of any oncological process, it does not matter, benign or malignant, morphology is required.
- Why laboratory tests alone are not enough to diagnose cancer?
– Laboratory research in oncology, this is an auxiliary diagnostics. Unfortunately, today there is not a single test, in the classical oncological sense, on the basis of which we could make a diagnosis.
The only exceptions are hematological problems - that is, the so-called blood tumors, for example, leukemia. There, indeed, the diagnosis is made on the basis of general analysis blood, and is confirmed, most often, by the results of a bone marrow study. But even then, according to one blood test, one can only suspect a disease, the confirmation will only be a bone marrow study. Therefore, laboratory techniques can be auxiliary, but by no means basic.
- Cannot such an analysis as the study of tumor markers be the basis for establishing an oncological diagnosis?
- A very limited number of oncological diseases can be suspected by the study of tumor markers. Although, such diagnostics should be treated very carefully. In fact, there are very few tumor markers used in cancer screening. On the the present stage their diagnostic value is increasingly being questioned.
In the understanding of people, a tumor marker should help to suspect a disease when there are no clinical manifestations yet. But the trouble with all tumor markers is that the tumor can already develop: it may be the first stage, the beginning of the second, and the tumor markers will still be negative. Accordingly, this feature makes them completely unsuitable for an isolated laboratory test for screening.
- What is screening?
- Screening is a search for something, any pathology. When screening, it is very important to be absolutely sure of a negative result, since negative result indicates that the examined patient does not have this pathology. In theory, any normal adequate screening works as follows. We examine a group of people, find any abnormalities in some people, and begin to examine them extensively. If it was false positive, which was not confirmed - good. People, of course, got nervous, they were examined, but, in the end, we ruled out the presence of a problem for which the examination was started. Unfortunately, tumor markers can give false negative result: the tumor is already there, but the tumor marker for it is still normal.
- Then what are tumor markers for? Why are these tests prescribed at all?
- The fact is that most of the tumor markers were created not to confirm or make a diagnosis, but to monitor the effectiveness of treatment of an already confirmed case. In other words, the person has been diagnosed, confirmed by instrumental, morphological research methods. They begin to treat a person - it doesn't matter, by surgery, radiation, chemotherapy. For subsequent stages, tumor markers are needed, and a person with a confirmed diagnosis is prescribed a study.
The initial (before treatment) level of tumor markers is known. They cured, the tumor was removed, it is not clear whether there are metastases or not. Blood is taken from a person. If tumor markers have decreased in comparison with the initial values, then the treatment is recognized as effective.
After some time, another control is assigned: if the level is low, then everything is fine. And this is how a person regularly takes a tumor marker. As soon as the tumor marker begins to rise, this is a sign that the person needs to be examined in depth again. This is the true purpose of tumor markers. Thus, it makes no sense to go through them without a doctor's prescription.

- It turns out that the use of tumor markers for the diagnosis of cancer is generally impossible? And, for example, PSA, which is often recommended for men?
- There are several tumor markers that can be used with reservations when screening a disease, but there are very few of them, no more than four or five. For example, one of the most common cancers in men is prostate cancer. To identify it, there is a tumor marker, PSA. It can be used for screening, but only among patients between 40 and 70 years old. Until the age of 40, it is not very effective, after 70, even if a person is diagnosed with prostate cancer, then there is no point in doing something with him. Sounds harsh, but this is an American study.
We compared the survival rate of patients who were diagnosed after 70 years, among those who were treated and those who were not. It turned out that it makes no sense to radically treat prostate cancer at this age. According to statistics, there is no reliable data on the best survival rate.
Therefore, PSA is not recommended to be used after 70 years as a screening marker for the diagnosis of this type of oncology. Moreover, now more and more data appear that PSA, in principle, not always, not for all types of prostate cancer is reliably manifested in early dates... There are so many subtleties. Although PSA is still being screened. In the United States, PSA has already been canceled as a mandatory screening, including by insurance companies.
- Are there tests to detect specific female cancers?
- In fact, there are no female tumor markers for adequate screening. Take at least CA 15-3 - this is a marker, it says right in the description of the test that it is used mainly to monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
A combination of CA 125 and HE 4 tumor markers (for ovarian cancer) - they are used in search screening in women after a certain age. But they can be effective only if a woman has a suspicion of cancer: the results of an ultrasound scan, clinical picture... In any case, only morphological examination can confirm the diagnosis.
- Are there “reliable” tumor markers used for diagnosis?
- There is another tumor marker, AFP, which is used to diagnose primary liver cancer. This marker is very specific in adults for this type of oncology. But, again, fortunately, primary hepatocellular carcinoma, that is, primary liver cancer, is very rare disease, and most often affects people already with the initial chronic disease liver - chronic hepatitis, most often viral. This is a risk group for the development of this disease.
Patients with an initially healthy liver do not develop cancer. Patients at risk have regular ultrasound scans, and once a year they have an AFP test. This tumor marker is specific: it rises faster than the tumor becomes visible. But this is rather an exception.
In general, we can say that at the present stage of the development of medicine there is not a single tumor marker that could be used in general practice to confirm or exclude oncological diseases.
