To health! Health problems are solved here. X-ray computed tomography
Computed tomography of vessels and other organs: the essence of the method, indications, pros and cons, comparison with MRI
A correct diagnosis is a half-cured disease. Doctors of antiquity identified diseases unusual methods: by eyes, nails, skin color and other signs. Even today, an experienced doctor will say a lot about a patient when he sees him for the first time. Many, but not all. Possibilities modern medicine have grown significantly, new diagnostic methods have appeared that allow you to look inside human body and visually assess the degree of damage to a particular organ. Computertomography is one of such methods.
What it is?
As soon as X-rays were discovered, people learned to take images of human organs. This is not to say that these pictures are perfect. Radiography does not allow you to see small foci of disorders, as tissue overlaps one another. The method of linear tomography, with which an image of a certain layer of an organ is obtained, is also far from perfect.
And only with the invention of the method CT breakthrough in diagnostics. For this discovery, scientists Cormack and Hounsfield were awarded the Nobel Prize. In the arsenal medical workers it became possible to see many sections of the organ in different places. The accuracy and speed of the study has increased due to the introduction of spiral technology. A modern multislice technique allows to make up to 64 images of different layers of the organ(There is already information about the appearance of a 320-slice tomograph).
How is it going?
The CT setup is quite massive. It is a ring that can rotate with the emission of x-rays. A person lying on a special table is placed inside the ring. The scanner, rotating around it, examines the organ under study layer by layer. With spiral tomography, the table with the patient also moves. It has something of the world space fiction, is not it?
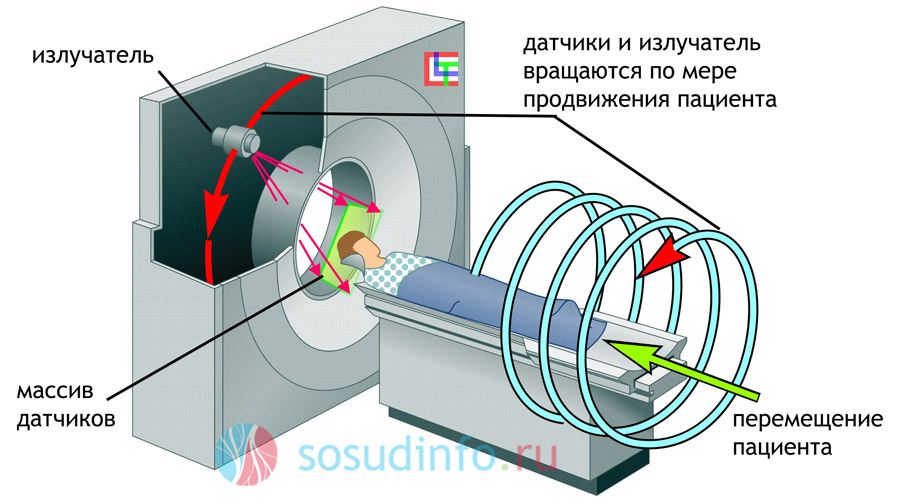
All images can be printed. The CT scan is done with contrast. A contrast agent (iodine containing) is used to better visualize the image. The fact is that x-rays of certain characteristics almost do not see soft tissues. A contrast agent is injected into a vein and individual cases the patient simply drinks it.
Using the method computed tomography almost all organs are examined human body: heart, blood vessels, kidneys, lungs, brain and spinal cord, bladder, abdominal cavity, bones. Did you forget to remember something? And this is also being investigated!
Why CT?
- Computed tomography of vessels, using x-rays, allows you to see the arteries and veins in any part of the human body.
- An image of the pathological part of the vessel is obtained, located in the most inconvenient place for other research methods.
- It is possible to provide a detailed three-dimensional image of the entire vascular pool.
- It is possible to see not only the vessels, but also the adjacent tissues, which is a significant plus in diagnostics.
- CT of the vessels of the heart and other organs is safe for most patients.
- The CT procedure is slightly invasive.
Who is not eligible for CT?
- Allergic patients.
- Patients with severe renal insufficiency.
- People who have thyroid disease. The fact is that the iodine contained in the contrast agent enhances the production of thyroid hormones, and this can lead to complications.
- CT is prohibited for pregnant women. First, the contrast agent can have a toxic effect on the fetus. Secondly, the influence of X-rays is also unsafe for the child.
Video: the process of conducting computed tomography
CT of vessels
The cause of organ disease may be vascular disease. After all, blood moves through them, providing oxygen to the cells of the whole body. Blockage by blood clots, atherosclerotic plaques - all this leads to impaired blood flow and, as a result, damage to the corresponding organ. Using the method of computed tomography, you can examine the vessels of any part of the body. For example, you can study the state of the coronary veins and arteries using CT of the coronary vessels. A CT scan of the vessels of the head and neck examines cerebral circulation.
Tomographyvessels is indicated if the patient has:
- signs of chronic and acute disorders and (including the head): pain, swelling, numbness, and others;
- Embolism, ;
- Angiopathy of different origin;
- Pathologies in the development of blood vessels;
- and others.
Most patients can pass the study without harm to health. But still, some of the procedure is not shown. Mostly people for whom a contrast agent (in particular, iodine) or x-rays can become dangerous.
brain CT
While conventional radiography provides an overview image of the brain, CT "photographs" the brain in layers. The distance between the layers is about 1 mm. As a result, the doctor required amount images that allow you to look at any point of the organ. With the help of CT of the brain, you can examine its structure, see, assess the state of venous and arterial vessels.

To make the image of the layers of the brain clearer, as is the case with peripheral vessels, a contrast agent is injected. As for contraindications, they are the same as for vascular tomography. The only difference is that pregnant women are sometimes still examined, but first the area of \u200b\u200bthe uterus is covered with a lead apron. For children, tomography of the vessels of the brain is carried out for very serious indications. If a woman is breastfeeding, then a break in feeding should be at least 48 hours. During this time, the contrast agent will be completely eliminated from the body.
Studyprescribed if a person has:
- fainting;
- Memory loss;
- slurred speech;
- convulsions;
- visual impairment;
- Signs indicating brain damage;
- Suspicion of tumors or metastases;
- Preoperative determination of the localization and size of formations;
- Traumatic brain injury;
- Stroke (both types - and);
- Suspicion of;
- Meningitis;
Preparation for the study is also minimal. It is recommended not to eat for 6 hours before the procedure. Drinks are allowed only pure water.
Important! When performing a CT scan, the patient's head must be completely still. The slightest movement greatly distorts the readings.
What does a CT scan tell about the brain?
Computed tomography can detect:
- hemorrhages;
- tumors;
- Hematomas of any localization;
- Edema and its severity;
- Displacement of brain structures;
- cysts;
- Inflammatory diseases;
- Presence purulent discharge between shells.

CT scan of the pelvis and abdomen
The procedure helps to diagnose the cause pain V abdominal cavity, pelvis, identify pathologies internal organs.
Main indications:
- kidney stones and bladder;
- pancreatitis;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Ulcerative colitis;
- Thrombosis of the vessels of the abdominal cavity (,).
- Cirrhosis of the liver;
- Appendicitis;
- Abscesses;
- Tumors of internal organs,;
- , stenosis.
Abdominal CT is needed for:
- Assessment of the state of internal organs after injury;
- Proper management of radiotherapy for tumors and monitoring of the condition after chemotherapy;
- Evaluation of postoperative consequences in organ transplantation and gastric bypass;
- Guidelines for minimally invasive methods of treatment of tumor-like diseases.
Preparation for the procedure
- Clothing should be comfortable. Some clinics offer a bathrobe during the examination.
- Since metal objects can distort the research data, it is recommended to eliminate them. It can be Jewelry, hair clips, dentures, hearing aid, glasses, piercings, bra with metal bones. It is necessary to inform the specialist about the existing pacemaker. Under certain conditions, this may not prevent the examination.
- It is recommended not to eat for several hours before the study.
- It is necessary to warn the doctor about allergic reactions and medications taken.
- Kidney disease, diabetes, health problems thyroid gland also increase the possibility of side effects.
- It is also very important to warn the doctor about pregnancy or suspected pregnancy. For almost all types of CT, pregnancy is absolute contraindication.
Cardiac tomography
The heart is compared to a motor. Because of the tireless performance or in connection with its importance to the body. Violations in the work of the heart lead to interruptions in the blood supply to all organs and tissues. Therefore, the diagnosis of diseases of the "motor" is especially important.
What can be determined?
- reason;
- The condition of the vascular walls;
- Valve problems;
- Tumors of the heart (etc.);
- Calcification of the coronary arteries;
- Causes of pain;
- The beginning of changes in the myocardium and coronary vessels.
What is special about performing a CT scan of the heart?
Photographers know that getting a good shot of a moving subject is almost impossible. Therefore, they are always asked to “freeze”. But you can't stop your heart. In this regard, they came up with a brilliant technique: the camera, which takes slices of the heart, moves synchronously with the movement of the organ. It is important that the patient's pulse is not accelerated. But no matter how the patient reassures himself, the excitement is still present during any procedure, even such a painless one. Therefore, tomography of the heart and blood vessels involves taking beta-blockers for removal. Sometimes drugs are injected directly into the vessel before the procedure. To get the most true results The patient is asked to hold their breath.
Chest tomography
With the help of CT chest determine in the early stages a number of pulmonary pathologies. Usually, a CT scan of the lungs is performed after an X-ray examination.
Possibilities of CT in the study of the lungs
- Early pneumonia, cancer, tuberculosis, emphysema, are detected;
- Tidal volume is measured;
- A lung density test can be done;
- It is possible to diagnose occupational diseases associated with the entry into the lungs of silicon, quartz, asbestos;
- Diseases of the intrathoracic lymph nodes, trachea, bronchi are detected.
Lung tomography also uses contrast agents. The study does not require special preparation.

Video: computed tomography in the plot of "Channel 1"
So what is CT or MRI?
Many patients are at a loss: which research method should be preferred? Let's compare the two most popular techniques: CT and.
MRI and CT are technologically different. Computed tomography is based on the use of x-rays. Therefore, it is characterized by the same drawback as for other x-ray techniques - radiation exposure. Although it was possible to minimize it in new generation tomographs, CT is still contraindicated in a certain category of patients. And a large area (for example, the entire spine) cannot be examined due to an overdose of radiation.
MRI is based on magnetic waves. This method is more secure. It is recommended even for children and pregnant women.
They "see" the methods also in different ways. MRI is excellent for diagnosing pathologies of the brain and spinal cord, but weakly distinguishes hollow organs: bladder, lungs, gallbladder. Using this method, you can examine the kidneys, joints, spleen, liver. MRI "takes" ligaments, muscles, and the eyeball well.
Computed tomography is used to diagnose diseases of internal organs. It can 100% detect a violation cerebral circulation, early stage stroke. High information content in the study of the pancreas. Tumors are well recognized internal bleeding. Any x-ray perfectly sees the bones. Therefore, the method is indispensable for bone injuries.

an MRI machine looks very similar to an X-ray CT machine, but has a longer “tunnel” and a completely different principle of operation
The MRI procedure is more comfortable for patients, it does not even need to undress during it. New generation devices ( open type) do not cause bouts of claustrophobia for certain categories of patients.
The results of an MRI study are affected by metal located anywhere in the body: dentures, braces, a pacemaker, pins, braces, electronic devices during inner ear, implants. All these "things" can become an absolute contraindication for the study.
The average cost of a CT scan of one site in Moscow is 2,500 - 3,500 rubles, and an MRI is from 4,500 to 5,000 in the same currency. The price depends on the equipment of the clinic. A more expensive procedure is most likely performed on a higher power machine. Patients who have compulsory medical insurance policy, you can go through these studies for free, but the queue is such that with some diseases you can simply not wait for it.
Important! Whatever the differences between CT and MRI and the prices for procedures, the doctor individually for each patient selects the most suitable method research.
Video: Comparison of CT and MRI
CT scan- a diagnostic method that combines X-ray scanning and subsequent image processing using special software. During a CT scan, the area of interest is illuminated with an X-ray beam. Ultra-sensitive detectors mounted on the rotation ring of the tomograph capture attenuated radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. The result of CT is layered images (sections) of the cross section of the area under study. Through computed tomography, it is possible to obtain high-resolution images of any anatomical area: head and neck, chest and abdominal cavity, small pelvis, bones and joints, blood vessels, soft tissues.

Computed tomography is a non-invasive method of radiation diagnostics that allows you to explore the layered structure of a specific organ or anatomical region. It provides for computer processing of information about the attenuation of X-ray radiation during the passage of tissues with different densities. Due to the high information content, low radiation exposure, the absence or minimum quantity discomfort, ease of preparation and affordable price computed tomography in Moscow is one of the most popular methods used in the process of diagnosing many diseases various bodies and systems.
Research History
This technique became known and began to spread rapidly around the world in the 70s of the last century. However, the history of the creation of computed tomography began much earlier. In the early 1930s, principles for obtaining a layered X-ray image were developed, but not enough high development technology has not allowed to bring developments to a level that allows for affordable mass research. In 1963, the American physicist Cormack created tomographic reconstruction programs similar to Radon's algorithms, but performed in a different way. In 1969, the British physicist Hounsfield designed the first CT scanner. The equipment was tested in 1972, and in 1979 Cormack and Hounsfield received the Nobel Prize for the development of computed tomography.
For almost half a century that has passed since the introduction of the technique into clinical practice, 4 generations of CT devices have been created. The first tomographs had one X-ray tube and one detector, which rotated together and scanned each layer separately with each rotation. Scanning of one layer lasted several minutes. Modern devices for performing computed tomography have more than a thousand detectors installed along the equipment ring. Only the X-ray tube rotates, the rotation period is less than 1 second. Along with the classical technique, multislice tomography (SCT) and multilayer computed tomography (MSCT) are used to minimize the radiation dose, reduce the duration of the study and increase its information content.
In order to accurately diagnose the disease, the doctor usually refers the patient to special analyzes. Standard set medical research This: general analysis urine, coprogram, etc. However, in order to examine the internal organs of the patient for the occurrence dangerous pathologies, the doctor may send it for x-rays.
The invention of X-ray opened a new page in the diagnosis of diseases, as it made it possible for the doctor to “look inside” the patient and see true reason his complaints of malaise. But soon the doctors were faced with new problem: a two-dimensional image of the insides of the human body on x-rays. This type of image made it difficult for specialists to see one organ after another, since layering occurred, which significantly distorted big picture and made it difficult to diagnose diseases.
And in 1972, the British engineer G. Hounsfield and the American physicist A. Cormack designed a CT (computed tomography) apparatus, for the invention of which both scientists were awarded the Nobel Prize. Initially, the CT machine was intended for x-raying the head, but was soon improved, and with its help it became possible to examine the entire human body.
What is the main difference between conventional X-ray and CT? X-ray differs from computed tomography in a feature of the image of the organs of the human body in the picture. Using a conventional X-ray machine, you can get a picture of the internal organs in only one plane, which significantly interferes with the diagnosis of the disease, since such a picture is not able to show a specific organ from all sides. The CT image shows the organs in a three-dimensional image, which allows the doctor to examine them from all sides, quickly identify pathologies dangerous to health and prescribe the appropriate treatment sooner.
A CT scan is done using a special machine called a tomograph. What he really is? This is a long couch that slowly moves towards the rounded frame - it takes x-rays the right organs. The opening in the frame is wide enough, which means that during the examination, the patient will not have the feeling of a “closed space” and there will be no stress associated with this feeling (claustrophobia).
The CT procedure itself does not cause any discomfort to the patient. The only thing that is required from the subject is to lie still. The tomogram is done in a special room, and the patient can hear the voice of the doctor via audio. Sometimes the doctor may ask the patient not to breathe to avoid blurring the images produced by the CT machine.
IN special occasions For example, if a doctor wants to see a particular organ on a CT scan, a contrast agent may be injected into the patient intravenously. What it is? The contrast is special solution with an iodine content (of the order of 60-80%), which is administered intravenously for X-ray studies in order to visually improve the brightness of the image of a particular organ. Since almost any contrast agent contains iodine, the doctor must ask the patient before performing a CT scan if he has any allergic reactions to iodine-containing drugs.
After the tomograph takes a series of images (usually the procedure takes no more than half an hour), a 3D image of the organs will be modeled using a computer. This type of image is the main advantage of CT, because with its help the doctor can personally see the cause of the patient's complaints in great detail, which in turn will help to maximize short time make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Types of computed tomography
Depending on the object of study, the following types of computed tomography are distinguished:
- CT scan of the abdominal cavity (including radiography of the liver);
- small pelvis;
- CT scan of the lungs;
- CT scan of the brain.
Abdominal CT is an X-ray examination of the gastrointestinal tract ( gastrointestinal tract). Sometimes abdominal CT is performed without contrast injection, and sometimes CT with iodine is prescribed. What does it depend on? A contrast agent is usually used if the doctor needs to see a particular organ of the gastrointestinal tract in the picture, for example, the liver.
Indications for computed tomography may be different. Eg, bad results blood test, pain in the liver area, doctor's suspicions of certain pathologies. Radiation exposure during CT can be dangerous for women in position (as, in fact, any x-ray studies). Pregnant women and children should have serious reasons for performing computed tomography.
Computed tomography of the small pelvis is a study of the pelvic organs for the occurrence of pathologies and diagnosis inflammatory processes, which can begin in the pelvic organs. CT scan of the pelvis helps to diagnose:
- rectal cancer.
- bone metastases.
- cancer of the cervix, bladder, vagina.
- the nature of damage in trauma to the pelvic organs.
This type of computed tomography is characterized by the use of contrast iodine-containing preparations that are administered to the patient intravenously.
CT of the lungs helps the specialist to determine the cause as accurately as possible. lung diseases, such as:
- inflammatory processes of the respiratory system (pneumonia);
- tuberculosis, sarcoidosis;
- tumors of the respiratory organs (pleura, bronchi, lungs);
- emphysema;
- pneumofibrosis;
- bronchiectasis.
The patient does not need any special preparation for the examination of the lungs. Before the procedure, you should remove metal objects (chains, other jewelry) from yourself. Be sure to tell your doctor about allergies to iodine-containing drugs (contrast), if you have one.
Actually, initially the CT machine was created to examine the human head. Today, the possibilities of computed tomography have expanded significantly. The CT scan shows:
- malignant neoplasms of the brain.
- nature of the skull injury.
- cerebral circulatory disorders.
- various traumatic brain injuries.
- cysts.
- hydrocephalus.
- cortical atrophy.
The difference between X-ray and MRI
The discovery of such an advanced diagnostic method as CT has given way to new methods of studying the human body. One of them is the method of magnetic resonance imaging, abbreviated as MRI. Experts from various fields of medicine have long been puzzling over what is better than CT, MRI, or the good old X-ray? Let's figure it out. We have already found out what CT and X-ray are, now it remains to understand the basic principle of conducting research on the human body using MRI.
The medical term MRI means a method medical diagnostics, the main principle of which (as in CT) is 3D modeling of certain human organs based on pre-taken pictures. However, another type of radiation is used for MRI - electromagnetic.
So, we figured out that the essence of the CT and MRI methods is almost the same - it is the creation of 3D models of the patient's organs based on ready-made images taken by the devices for these studies. As a result, X-ray significantly loses to CT and MRI in terms of the accuracy of diagnosing diseases, the quality and nature of the image obtained. However, MRI is used for other purposes than CT. MRI is commonly used for:
- diagnosis of soft tissue tumors;
- examination of the nerves of the brain, spinal cord;
- ligament examinations;
- muscle examinations;
- study of the state of the articular surfaces.
Which is better: ultrasound or X-ray?
Sometimes patients ask themselves: what is more harmful - ultrasound or X-ray? Of course, it is important for each of us that the ongoing research does not harm our body with its radiation.
The basic principle of ultrasound is the reflection of ultrasonic waves from the tissues and organs of the body. Due to this, a certain image appears on the monitor of the device. For the body, ultrasound is safer than any x-ray studies, since during the ultrasound procedure the body does not receive the slightest dose of radiation. The ultrasound procedure is best suited for pregnant women, because X-ray diagnostics during the period of bearing a child is strictly prohibited.
Cons of CT
The main disadvantage of CT is the fact that during the procedure, the radiation of the tomograph can adversely affect the internal organs. The harm of computed tomography is determined by the quantitative component of the radiation dose - the more often the procedure is performed, the more radiation a person will receive. Therefore, the patient's stay on the table of the CT apparatus is strictly fixed (from 15 minutes to half an hour).
Exposure for CT scans of the lungs (as with examinations of other organs) should not exceed 20 mSv (millisieverts) per year.
Study preparation
Plain computed tomography does not require special preparation. But if for the study you will be injected intravenously with contrast (the doctor must inform you about this), that is, it is prohibited before the tomography, because then the contrast agent can cause sudden nausea or vomiting.
Computed tomography (CT, MSCT) is a method of radiation diagnostics, which consists in a layer-by-layer examination of the human body using X-rays with the possibility of subsequent construction of multiplanar, including 3D, images.
To date this method has become one of the main ones in the diagnosis of most diseases and is widely used both in the case of primary and clarifying diagnostics. One of the main advantages of computed tomography is the speed of the study and the ability to simultaneously scan large anatomical areas.
CT diagnostics at EMC: equipment
The clinic has the most modern equipment, allowing you to get pictures as much as possible High Quality with minimal radiation exposure- computer tomographs 64-256 slices from Toshiba, Philips, with latest systems radiation dose reduction (iDose7).
Fields of application of CT diagnostics
A CT scan of the brain is a very quick and completely painless procedure that allows you to see changes in the brain as a result of injury or infection. With the help of CT of the brain, it is possible to monitor the recovery of an organ after an injury, and at the same time monitor whether complications develop.
CT scan of the joints is carried out according to the same principle as computed tomography of the brain, only the joint is not visible, but the head. CT of the joints is used to diagnose inflammatory processes, as well as the consequences of injuries.
In modern medical practice, in many areas, CT techniques have almost completely replaced the classic radiological ones.
Many European clinics have almost completely abandoned X-rays. temporal bones in favor of CT;
With recurrent diseases of ENT organs (chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc.);
In children suspected of having foreign bodies in the lumen of the tracheobronchial tree;
The "gold standard" for examining cancer patients - assessing the location, shape, size, prevalence of tumor processes and assessing the dynamics of ongoing therapy;
The primary method of examination of patients with severe traumatic brain injuries and any traumatic injuries of other localization;
It is indispensable for complex intra-articular fractures, confirmation or exclusion of epiphyseolysis (fractures characteristic only of patients childhood, with the presence of growth zones in the bone structure);
Increasingly used to examine children with pathology urinary system in studies with intravenous contrast.
The clinic employs experienced anesthesiologists who will make the examination easy and comfortable. Low-dose protocols, according to which the study is carried out, will provide maximum informative result with minimal radiation exposure.
Computed tomography (CT) with contrast is performed at EMC. The contrast agent makes it possible to accurately determine the size, contours and location of the pathological formation. CT with contrast is used to study almost all organs and systems of the body.
Ways of maintaining a contrast agent:
intravenous,
intravenous bolus,
Oral.
For CT with contrast, iodine-containing substances are used, so the indications for the study are always determined individually. It is important to exclude an allergic reaction to the contrast components. Also, before conducting the study, it is necessary to perform biochemical analysis blood, as renal and hepatic insufficiency are contraindications for CT with contrast.
Prices for computed tomography with contrast can be clarified at EMC (Moscow). Tomography can be done around the clock by appointment.
The standard CT procedure (without contrast, without anesthesia) does not require the patient to special training and lasts no more than 40 minutes. Before the procedure, it is necessary to remove objects with metal elements that fall into the scanning area in order to avoid a decrease in image quality.
Important! It is recommended to stop antidiabetic drugs containing metformin 24 hours before the study and within 48 hours after it.
CT scan of the abdominal cavity, small pelvis and retroperitoneal space
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach or not earlier than 3-4 hours after the last meal. It is allowed to take medications (drink a small amount water). Immediately before the study, about 500-600 ml of water is drunk in the department.
CT scan of the urinary system
CT of the heart and coronary arteries, CT angiography of any segment of the vascular bed
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach or not earlier than 3 hours after the last meal. On the day of the study, it is recommended to refrain from smoking, drinking coffee, tea and energy drinks.
CT enterography of the small intestine
The procedure is performed on an empty stomach, not earlier than 6 hours after the last meal. You should arrive at the department one hour before the scheduled examination time. Within an hour, you will need to drink 2 liters of Fortrans solution (1 sachet per 1 liter of water) or mannitol solution (200 ml per 1.5 liters of water), 150-200 ml every 5 minutes. All medications are dispensed at the department.
Colon CT (CT colonography)
Within 3 days before the study, you must follow a slag-free diet. Legumes, black bread, milk, carbonated drinks, vegetables, fruits, convenience foods, sweets are not recommended. Allowed buckwheat, oatmeal, lentils, rice, tea, dairy products(if there is no intolerance), lean meat, fish, vegetable soups. The day before the study, it is necessary to take a solution of urografin (60 ml per 1 liter of water) fractionally during the day with meals (the drug is purchased by the patient independently). On the day of the study, a light breakfast is allowed in the morning. You must arrive at the office 30 minutes before the start of the study.
Important! Do not forget to bring any extracts, protocols or records (discs) of previous studies. The more information the radiologist has before the study, the clearer the task assigned to him. In addition, previous results will allow us to assess the dynamics of the disease.
CT scan(CT) is an examination method in which X-rays are used to obtain a detailed image of the internal organs and structures.
During the procedure, the patient lies on a special table connected to a CT scanner, which is a large apparatus in the shape of a ring. Rotating, the scanner passes X-rays through the studied area of the body. Each revolution takes less than a second, and a section of the organ under study appears on the computer screen. All layered images are saved as a group and can also be printed. In order to make the image more distinct, iodine-containing contrast agents are often used in computed tomography. They are used in the study of blood flow, to detect tumors and other diseases. The contrast agent is injected into a vein or directly into the area of interest (such as the intestines or joint), in some cases the patient must drink it. Pictures are taken before and after the contrast is applied. CT is used to examine almost all parts of the body and organs: chest, abdomen, pelvis, limbs, liver, pancreas, intestines, kidneys and adrenal glands, bladder, lungs, heart, as well as blood blood vessels, bones and spine.
Fluoroscopy- a narrower method of x-ray examination, which uses a stable beam of x-rays. The procedure allows you to track the movement of organs or correctly position a biopsy needle or other instrument inside the body.
Why do you need a CT scan?
CT is prescribed to examine various areas of the body and limbs.
- Rib cage ( thorax) . A CT scan of the chest helps to detect diseases of the lungs, heart, esophagus, the main blood vessel of the aorta, and chest tissues. Computed tomography can detect infectious diseases, lung cancer, metastases from cancer of other organs, pulmonary embolism and aortic aneurysm.
- Abdomen. Abdominal CT can detect cysts, abscesses, infections, tumors, abdominal aortic aneurysms, swollen lymph nodes, presence of foreign bodies, bleeding, diverticulitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and appendicitis.
- urinary tract. Computed tomography of the kidneys, ureters and bladder is called a computed urogram. This type of tomography helps detect kidney stones, bladder stones, or obstructions. urinary tract. A special type of computed tomography using an intravenous contrast agent is called an intravenous pyelogram and is used to detect kidney stones, obstructions, infectious tumors and other diseases of the urinary tract.
- Liver. CT can detect tumors and bleeding of the liver, as well as other diseases of this organ. The procedure will also help determine the cause of the bile spill (jaundice).
- Pancreas. A CT scan may reveal the presence of a pancreatic tumor or inflammation (pancreatitis).
- gallbladder And bile ducts. CT is used to diagnose the patency of the bile ducts. Along the way, using this procedure, you can detect the presence of stones in gallbladder, but, as a rule, other methods are used to diagnose diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. diagnostic methods such as ultrasound.
- adrenal glands. CT can detect tumors or enlargement of the adrenal glands.
- Spleen. CT is used to determine damage to the spleen or its size.
- Taz. In women, CT detects diseases of the pelvic organs and fallopian tubes, in men - the prostate gland and seminal vesicles.
- limbs. CT can diagnose joint diseases and various parts limbs, including the shoulder, elbow, wrist, hand, thigh, knee, ankle and foot.
Other cases of CT appointment
Computed tomography allows you to control the correct execution medical procedures. For example, a doctor may use CT to accurately insert a needle during a tissue biopsy procedure, or to check needle placement when draining an abscess.
In cancer patients, CT can help determine the stage of the cancer, as it shows how far metastases have spread.
How to Prepare for a CT Scan
Before the procedure, be sure to tell your doctor if you:
- Are pregnant.
- Are allergic to medications, including iodine in the contrast agent.
- Have a cardiovascular disease (such as heart failure).
- If you have diabetes mellitus or if you are taking metformin (Glucophage) for its treatment. You may need to stop taking this drug the day before and for the day after your procedure.
- Have kidney disease.
- You suffer from asthma.
- Use a pacemaker or insulin pump.
- Have multiple myeloma.
- Passed within the previous 4 days an X-ray examination using a barium contrast agent (irrigoscopy) or used medications containing bismuth. Barium and bismuth, appearing on x-ray film, interfere with image clarity.
- You suffer from the fear of closed spaces. Since you will have to lie still inside the scanner during the procedure, you may need to take sedatives. In this case, it is worth asking someone to take you home after the procedure.
If you are scheduled for a CT scan of the abdominal organs, refrain from eating solid food from the evening before the examination. Before the procedure, you may be asked to drink a contrast agent and, in some cases, to take a mild laxative or a barium enema.
Discuss with your doctor all questions regarding the upcoming procedure, its need, associated risks and the process itself, and ask him to explain the results.
How is a CT scan performed?
The examination is usually carried out by a radiologist. The resulting images are read by a radiologist, who also gives a medical report. In addition, the therapist or surgeon can comment on the results.
All jewelry and clothing must be removed prior to the procedure. In some cases, you can leave the linen. You may be offered a disposable gown.
The tomograph is a large annular apparatus. During the study, the patient lies on a table that slowly slides through the annular part of the tomograph, which rotates around the examined area of the patient's body, making layered images of the corresponding organ. In this case, a slight hum or clicks may be heard. During the procedure, you can not move.
During the examination, the patient may be alone in the treatment room; through a special window, the technician observes the process from the adjacent room and can talk to the patient through the intercom.
If the study is performed using a contrast agent, it can be introduced into the patient's body different ways depending on the purpose of the study:
- Intravenously - with CT scan of the chest, abdomen and pelvis.
- Some abdominal exams require you to drink a contrast agent.
- A contrast agent is injected through a special catheter into the bladder or intestines, or through a thin needle into a joint.
The CT scan procedure usually takes 15-30 minutes.
During the day after the study, you need to drink more fluid; this will speed up the excretion of the contrast agent from the body.
How does a patient feel during a CT scan?
The procedure itself is absolutely painless. Some inconvenience can be caused by the hard surface of the table, the inability to move, it can be cool in the office. Some patients experience nervousness while inside the CT scanner.
If there is a need to administer a sedative or intravenous contrast agent, the injection is usually given in the arm. you will feel light prick at the site of the needle insertion, and if the contrast agent enters the vein, you may experience a feeling of warmth, heat, or a metallic taste in your mouth. Sometimes patients experience nausea or headache. Let the doctor or technician know how you feel.
Is computed tomography dangerous?
The risk of complications after the procedure is negligible.
- There is a possibility allergic reaction to the contrast agent.
- If you are suffering from diabetes and are taking metformin (Glucophage), contrast may cause problems. Discuss this issue with your doctor.
- There is a small possibility of developing cancer associated with the passage of certain types of CT scans. This likelihood is higher in children or adults who are undergoing a large number of examinations using x-rays. If this is a concern for you, talk to your doctor about how much radiation you (or your child) will receive from this test and make sure it is really needed.
- There is a small risk that the operation of the scanner will interfere with the operation of implanted or external medical devices such as a pacemaker, insulin pump, defibrillator, or neurostimulator.
Computed tomography results
CT scans use X-rays to obtain detailed images of the body's internal structures.
The radiologist can discuss the immediate results of the CT scan with you immediately after the examination. A complete conclusion is usually transmitted to the attending physician in 1-2 days
| The size of the organ is larger or smaller than normal, the organs are damaged, there are signs of infection. There are cysts or abscesses. |
| The presence of foreign bodies (fragments of metal or glass). |
| Presence of kidney or gallstone stones |
| There is an overgrowth of tissue (tumor) in the intestines, lungs, ovaries, liver, bladder, kidneys, adrenal glands, or pancreas. |
| A chest CT scan shows a pulmonary embolism, fluid, or signs of infection in the lungs. |
| The presence of an aortic aneurysm. |
| Obstruction of the intestines or bile ducts. |
| Abdominal CT scan shows signs inflammatory diseases bowel or diverticulitis. |
| Lymph nodes are enlarged. |
| Obstruction of one or more blood vessels. |
| Presence of a tumor, fracture, infection, or other limb problems. |
What can affect CT results
Interfering with the examination or distorting its results can:
- Pregnancy. Usually the procedure is not performed during pregnancy.
- Use of barium and bismuth in previous studies. These substances show up on the CT image. If an abdominal examination is required, this should be done prior to barium procedures (eg, barium enema).
- Movement during the procedure.
- The presence of metal in the patient's body; surgical clamps or metal fragments of the artificial joint can distort the clarity of the image in the study area.
What you need to know
- Sometimes the results of a CT scan may differ from those of other x-ray studies, such as ultrasound or MRI, because the CT scan shows a different perspective.
- A child who is scheduled for a CT scan should be given special instructions. Most likely, during the procedure, he will have to hold his breath. If the child is too small or scared to lie still, the doctor may give him a sedative.
- Before the procedure, it is worth discussing with the pediatrician its necessity and the degree of radiation risk for the child.
- Sometimes in computed tomography, helical or multidetector tomographs are used, which provide efficient acquisition of multilayer images. These devices are used to detect kidney stones, pulmonary embolism, prostate adenoma or atherosclerosis. You can also use them to:
- Get clearer pictures of blood vessels and organs. There is no need to conduct other visual studies.
- Reduce procedure time.
- CT scan results are often compared to positron emission tomography (PET) scans for cancer detection. Some newer scanner models perform both types of examinations at the same time.
- Electron beam tomography is another type of computed tomography that helps to detect atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. EPT is much faster than standard CT and gives a clearer picture of the coronary arteries during the heart's work. Currently, electron beam tomography is not widely used. Much more often, multidetector computed tomography is used, which is almost the same speed.
- A CT angiogram provides clearer 2D and 3D images of blood vessels.
- Assessment of the level of calcification of the coronary arteries helps to identify the potential risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. This analysis is not ordered very often, because the examination and other tests in this case quite informative. It is also not recommended to do it with a conventional tomograph.
- For some diseases, magnetic resonance imaging is a more informative method than computed tomography.
- There is no consensus among experts on the advisability of using the CT method, which involves scanning the whole body, to detect coronary disease heart and cancer.
Whole-body tomography is a rather expensive procedure that can lead to unnecessary examinations or surgical interventions while increasing the risk of developing cancer due to exposure. Most doctors do not recommend this survey people who are not at particular risk of developing a particular disease.
