Quality assurance system in pharmacy organizations. Creation of a quality management system for medicines in a pharmacy
Full text search:
Home> Abstract> Medicine, health
medicines in the pharmacy
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 80 of 03/04/2003 "On approval of the Industry standard" Rules for the dispensing (sale) of medicinal products in pharmacy organizations... Basic Provisions ". Contains Section IX Quality Assurance drugs(medicines) in pharmacy organizations.
Pharmacy organizations or individual entrepreneurs should have a quality assurance system that includes:
premises and equipment corresponding to the scope of activities of the pharmacy facility and allowing to ensure compliance with the conditions for storage and manufacture of drugs;
documentation that allows you to identify the origin, quantity and quality of incoming and keep records of stored and sold drugs;
incoming control of drugs arriving at a pharmacy organization or an individual entrepreneur;
personnel of the required qualifications;
system of continuous training of personnel;
a fund of regulatory and reference materials that must be provided for all pharmacy facilities of a given pharmacy organization.
The pharmacy organization should have a quality management system for the pharmacy organization.
Each pharmacy organization must have internal labor regulations approved by the head of the organization, with a mark on familiarization of employees. The revision of the rules and re-familiarization with them of the employees of the pharmacy organization is carried out annually.
The pharmacy organization must regularly conduct internal checks for compliance with the requirements of GOST. When carrying out inspections, attention should be paid to the presence in the pharmacy organization of the relevant documents for the premises occupied, job descriptions of employees, standards, and other necessary documents.
Inspections can be carried out both by employees of the pharmacy organization, independent of the persons directly carrying out the activity being inspected, and by independent experts. The frequency of checks is determined by the pharmacy organization itself. The results of the inspections are recorded and brought to the attention of the personnel responsible for the inspected area of work and the management of the pharmacy organization. During subsequent checks, the implementation of the recommendations and their effectiveness are monitored. Each employee of a pharmacy organization must be familiar with GOST, the procedure for fulfilling the duties assigned to him, regulatory legal acts and standards related to the activities of the organization. Pharmacy organizations must have job descriptions for each employee, approved in the appropriate order.
Pharmacy organizations should provide for a system of continuous professional development of employees on current legislation, the use of medicines, etc. The plan and topics of the classes are approved by the head of the pharmacy organization. The head of the pharmacy organization appoints a quality representative from the management staff.
In this regard, there is no doubt about the need for continuous improvement of the professional skills of pharmaceutical personnel. One of the ways to solve this problem is to increase the efficiency of the system of postgraduate training of pharmacists.
The pharmacy organization ensures the maintenance of documentation in accordance with legislative and regulatory legal acts Russian Federation.
First of all, the task of the pharmacy is to provide the preserved characteristics of the goods received by the pharmacy organization. These are two groups: functional qualities - efficiency and safety, physical and physicochemical, requiring compliance with the rules for handling them. Within the framework of the quality management system of a pharmacy organization, each pharmacy should organize:
1. Acceptance control... It is carried out in order to prevent the receipt and sale of counterfeit, rejected and substandard products through the pharmacy network. It is regulated by the Industry Standard OST 91500.05.0007.-2003 “Rules for the Dispensing (Sale) of Medicines in Pharmacy Organizations”. The areas (premises) for receiving medicinal products and dispensing should be separated from the storage area and should provide adequate (reliable) protection of the received medicinal products from bad weather during loading (unloading) operations. The resulting products are subject to incoming quality control. The results of the incoming control must be registered in accordance with the established in the pharmacy internal order... During unloading products check for its compliance with the order and the absence of damage to the packages or containers. Medicines and other goods approved for sale from pharmacy organizations with expired shelf life, not meeting quality requirements, standards and without documents certifying their quality are not subject to acceptance. For medicinal products (medicinal products) in damaged packaging that do not have certificates and / or the necessary accompanying documentation, rejected when receiving or dispensing to the patient, not corresponding to the order or with an expired shelf life, an act is drawn up; they must be appropriately labeled and placed in a designated area separate from other medicinal products until they are identified, returned to the supplier, or destroyed in accordance with the established procedure. Poisonous and potent substances narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances, thermolabile medicinal products must be immediately placed in storage areas in accordance with the requirements of this OCTa.
The number of medications taken that require special storage conditions must correspond to the available capacity of special equipment. Accepted medicines and other goods allowed for dispensing from pharmacy organizations are credited within the time allotted for the acceptance of the goods by the number of commodity units and completeness in the prescribed manner. 6. All deliveries of the goods must be accompanied by documents allowing to establish the date of shipment, the name of the medicinal product (including the dosage form and dosage), the batch and batch number, the quantity of the supplied goods, the price of the dispensed medicinal product, the name and address of the supplier and recipient, as well as documents, confirming the quality of drugs. The documents confirming the quality of medicines are a declaration of conformity or a certificate of conformity An important indicator is that the pharmacy or pharmacy chain work with a reliable wholesale link, well-known multinational companies, which have their own "drug safety service" set very seriously.
Acceptance control, along with checking the correctness of paperwork, includes checking medicines according to the indicators "Description", "Packaging", "Marking", which is determined by the requirements of the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated 07.16.97. No. 214 "On quality control of medicines manufactured in pharmacy organizations (pharmacies)". Control according to the "Description" indicator includes checking the appearance, color, odor. Inconsistency in color, presence of foreign smell, sediment, flakes, mechanical impurities, freezing, stratification are grounds for rejection. In case of doubt about the quality of medicines, samples are sent to the territorial center for quality control of medicines. Such medicines with the designation: “Rejected during acceptance control” are stored in the pharmacy separately from other medicines. Control according to the “Packaging” indicator includes checking the integrity of the packaging, the presence of secondary packaging, and the compliance of the packaging with the physicochemical properties of medicines.
2. Premises and equipment. Basic requirements for the organization of storage of medicines and products medical purpose in pharmacies established by the Instruction from the organization of storage in pharmacies different groups medicines and medical supplies. Medicines that require special storage conditions must be immediately identified and placed in appropriate storage rooms (zones) according to the requirements of the current legislation. The storage room in the pharmacy should be large enough to accommodate the orderly storage of the various categories of materials and products. Clean and secure. Medicines in production warehouses should be stored on racks, pallets, podtovariye, in cabinets, refrigerator and other special equipment to ensure storage conditions for medicinal products in accordance with current requirements . If there are immunobiological preparations in the pharmacy base (warehouse), the total volume of refrigeration equipment must ensure, in accordance with the current requirements, the storage of the entire amount of these drugs, which is contained in the base (warehouse). When storing medicinal products, the licensee is obliged to exclude their damage (spilling, spilling, breaking), contamination with microorganisms and cross-contamination. The storage of medicines requires special temperature conditions, controlled by constant temperature monitoring devices or thermal containers.
3... Staff... A third management principle applies to resources - employee involvement. It is the employees of all levels that form the backbone of the organization. Their full involvement enables the organization to benefit from their capabilities. On the one hand, the management decision that the management system should function, and on the other hand, only when the entire staff realizes that the management system is not a simple collection of additional pieces of paper that will be on the shelf. It must be an effective structure, and it will only work when everyone understands what it is based on and why it is being done. In each pharmacy, in one form or another, a quality management system has been created and is successfully functioning - for some it is 10%, for some it is 90%.
4. Documentation Operations affecting the quality of the goods should be described in written procedures. The quality management system is aimed at systematizing the processes, to see if all of them are provided with the necessary resources and documents. It is important to know if all processes have documented procedures and rules for their implementation. The process of review and improvement is needed to make factual management decisions - this is the seventh management principle of ISO standards. Effective solutions are based on analysis of data and information.
7. Refunds... The presence of substandard or falsified medicines in circulation, excluding those whose shelf life has passed, is not allowed. Having identified the fact of the presence of substandard, counterfeit and the like medicines, the business entity must draw up an appropriate act and take measures to exclude them from circulation. The exclusion of such medicinal products from circulation occurs through disposal and destruction in accordance with the Rules for the disposal of medicinal products. A procedure for working with letters from Roszdravnador about rejected and falsified products for the Center's specialists has been developed in accordance with the requirements and in the forms specified in the letter Federal Service on supervision in the field of health care and social development from 28.09.2004. No. 4082/04.
5. Optimization of the quality management system pharmaceutical activities in the pharmacy
As a result of studying the literature on PL quality management, it is possible to propose to optimize the activities of pharmacy organizations by introducing the following principles:
The quality of management is a multifaceted concept, it includes many components, such as: transparency and controllability of processes, quality of information, the possibility of operational control of current activities, and much more. At the same time, various documents are practically the only tool for implementing management. Thus, the obvious way to change the quality of enterprise management is to improve the efficiency of work with documents.
Pharmacy quality management is based on following principles:
Sufficient assortment and volume of affordable prices LS
The task of the pharmacy is nothing more than providing the population with drugs and pharmacy products v the right place and at a convenient time for visitors, for which needs, a supplier are determined, an application is drawn up, a purchase is made, and the dosage is studied.
Social accessibility
Research on assortment within synonyms and analogues. The pharmacy contains more than one trade name of one active substance. Trade names sometimes vary by 100-700%, depending on the manufacturer. The pharmacy purchases different brand names at different levels to ensure social inclusion for different social groups visitors. In one pharmacotherapeutic group, you can take both expensive and medium- and low-cost drugs.
Information and consulting support
Pharmacy workers must anticipate consumer expectations and ensure that the product meets those expectations. This is not always possible. For example, a consumer wants to consult a pharmacist before purchasing a drug. But a pharmacist is not a doctor and does not bear any statutory responsibility for the patient's health in our country. However, not getting what was expected, the consumer remains dissatisfied.
Implementation of computer systems in pharmacies and the use of barcodes in drug quality control in a pharmacy
The pharmacy automation system differs from the retail automation systems. Pharmacies have a lot of their own specifics, mainly related to pricing, which in Russia has always been a complex and confusing process. Pricing in a pharmacy is carried out according to certain legislative documents and is strictly regulated; there is a list of drugs that are not taxed. The retail price is formed differently for such medicines. Previously, the process of receiving goods and registering prices for pharmacy workers was laborious and time-consuming. Therefore, automation is simply indispensable here.
Automation systems enable pharmacy workers to view data on what is in stock, what medicines have run out, and what needs to be purchased. The process of quickly viewing real balances is one of the most important when choosing an automation system.
In any ordinary pharmacy, where there is a simple cash register, when making a purchase, the money that we pay to the cashier is in no way directly related to the goods we receive.
And here several problems arise at once:
Firstly, the pharmacy lacks a full and detailed accounting of the movement of goods and funds. It is impossible, for example, at any given time to say how much of a given product was sold, left in trading floor or in a warehouse, it is impossible to automatically prohibit the punching of goods that have already ended, etc.;
Secondly, it is difficult to avoid mistakes that the cashier can make;
Thirdly, the lack of detailed accounting does not make it possible to conduct statistics and detailed analysis of the dynamics of sales, which makes it difficult to respond more flexibly to changes in demand.
6. Analysis and ways of improving the quality management system of medicines in the pharmacy of LLC "MAIR"
MAIR LLC has been operating in the pharmaceutical market for over 15 years in the Primorsky Territory. Its pharmacy network unites 5 outlets and is very popular - several thousand residents of Vladivostok have cards regular customers... Occupies the second floor of a 2-storey building. The premise of the pharmacy is new, has been operating since May 2010, meets all the requirements of the NTD and sanitary standards, works from 9:00 to 20:00 seven days a week. There are signs about the name of the pharmacy and about the opening hours. Located in a convenient place for visitors, near the bus stop.
Mair considers its main mission not so much the sale of drugs, the sale of pharmaceuticals and medicines, medical products, but the provision of pharmaceutical services for high level, therefore, the company strives to be customer-oriented, to guarantee the quality of the drugs, and to serve the buyer as best as possible. All this, along with an understandable desire to make their work more efficient, made the management think about introducing a quality management system.
Having worked on a quality management system for less than a year, a pharmacy can draw some conclusions. Objective indicators confirm that the introduction of a quality management system contributed to the optimization of working capital: the volume of sales in the chain's pharmacies increased, the number of low-income and illiquid goods, as well as expired products, decreased. The number of regular customers has increased. Analysis of their demand, wishes and offers made it possible to practically get rid of the defects. In addition, due to the orientation of the staff to work with customers, not only the number of online purchases has significantly increased, but they have also been optimized. average cost... Quality management specialists currently point out that the main and most problematic link in any management structure is people. In our case, these are specialist pharmacists. Those who are in direct contact with customers, visitors, consumers. For the implementation of the quality management system in the pharmacy, some changes were made in the organizational structure and in the relationships in the team. An effective personnel training system, constant monitoring of training have increased the quality of personnel work.
As a result of the analysis of data from foreign and domestic literature, it was found that the issues of the quality management system of medicines in pharmacological institutions both in Russia and abroad are given great attention... When studying the basic concepts in the construction of models and the functioning of quality management systems, clear leadership is demonstrated by approaches based on the concept of total quality management (TQM) and the ISO 9000 series standards, which provide for a number of general principles: customer orientation, management leadership, processor approach, systems approach, continual improvement, mutually beneficial supplier relationships, etc.
The quality management system in the field of drug circulation in Russia is determined by the Federal Law No. 86 "On Medicines". The quality management of pharmaceutical organizations is based on the principles of TQM and the ISO 9000 series and standards. industry standards: OST91500.05.0005-2002 "Rules for Wholesale Trade in Medicines. Basic Provisions", approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 03/15/2002 No. 80; OST 91500.05.0007-2003.
In accordance with international practice, the pharmacy is fully responsible for the quality of products purchased from suppliers, only the mandatory requirements for products are determined by law, and all other conditions are stipulated in an agreement between market participants.
The quality management system in the field of drug circulation should be reliable, be preventive, preventing the provision of substandard pharmaceutical services to the consumer, as well as personalized, i.e. have specific persons responsible for this.
Some principles are considered that make it possible to optimize the quality management system in the field of drug circulation in a pharmacy. The study of the literature on drug quality management can be proposed to optimize the activities of pharmacy organizations by introducing the following principles.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 03/04/2003. No. 80 “On Approval of the Industry Standard“ Rules for Dispensing (Selling) of Medicines in Pharmacy Organizations. Basic Provisions ".
Skulkova R.S., Yagudina R.I., Parkhomenko D.V. Formation of a quality management system for pharmaceutical organizations. New pharmacy. Regulations. 2005.-N 4.-С.32-37 .
I. G. Komissinskaya Modern concept quality management of a pharmacy organization // Moscow pharmacies. - 2007. - No. 11.
Alferova, T.V. Production management at pharmaceutical enterprises / T.V. Alferova, E.A. Tretyakov, A.V. Builin. - Yekaterinburg: Publishing house of the Institute of Economics of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 2008. - 214p.
Moskvin V.A. Evolution in the field of quality management / V.A. Moskvin // Investments in Russia. 2004. No. 5.- S. 27-28.
Lagutkina T.P. NS principles of quality management in the activities of a pharmacy organization // Bulletin of the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. 2008.-N 4.-С.36-39.
Polesskiy V.A. Evolution of quality system models: international practice / V.A. Polesskiy, S.A. Martynchik, V.G. Zaporozhchenko, V.Z. Kucherenko // Health Economics. - 2005. - No. 8. - S. 25-36.
the federal law"On Medicines" No. 86-FZ dated 22.06.98
Drugova Z.K., Biteryakova A.M. Internal control system and quality of management // Russian pharmacies. - No. 2. - 2007.
Kononova S.V. The system of quality assurance of pharmaceutical services in the regional pharmaceutical complex: Monograph. -Nizhny Novgorod: VGIPA Publishing House, 2003.
Storage conditions for medicinal products. - M .: Medicine, 2006 .-- 184p.
Kulaev V.A., Egorov V.A., Gladunova E.P., Ezhkov V.N. Integrated quality management system for pharmaceutical care // Pharmacy, 2011, No. 3, pp. 30-33
GOU VPO "PERM STATE PHARMACEUTICAL ACADEMY"
Department of Management and Economics of Pharmacy FDPO and FZO
Refresher courses for correspondence courses
using remote technologies in the specialty "Management and Economics of Pharmacy"
Duration of training (from 15.10.2010 to 14.09.2011)
Course work on this topic:
“Creation of a quality management system for medicines in a pharmacy ”
EXECUTOR:
Fadeeva Maria Valerievna, pharmacist-intern
Research base:
Pharmacy "MAIR"
Vladivostok city
Perm 2011
Introduction
1. State of the art quality management systems for medicines in pharmacy activities in foreign countries…………....……5
2. The legislative framework quality management of medicines in pharmacy organizations according to literature and regulatory documents …………………………………………………………… ..… ..10
3. Pharmaceutical management in a pharmacy ..................... 12
4. Creation of a quality management system for medicines in a pharmacy ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ..... 17
5. Optimization of the quality management system for pharmaceutical activities in a pharmacy ...................... 22
6. Analysis and ways of improving the quality management system of medicines in the pharmacy of LLC "MAIR" ………………… ... …… 23
Conclusions …………………………………………………………………… ..… 25
List of used literature ………………………………………… ..26
INTRODUCTION
The social orientation of the pharmaceutical market, which provides the need for vital drugs, and, consequently, the need to maintain and improve health, necessitates the development of a quality management system for pharmaceutical products and services introduced to the market. The basis of this system is the system of drug quality management at all stages of their life cycle and the quality of pharmaceutical care as an activity of providing pharmaceutical services to the population. The quality of medicines at the federal level is legally defined as compliance with the state standard.
The current functioning of the Russian pharmaceutical market is characterized by a constantly expanding range of medicines (MP) and an unreasonably large number of suppliers. In these conditions, the problem of ensuring the quality of medical care provided to the population is of particular relevance. In accordance with the requirements of the current industry standard “Rules for the Dispensing (Sale) of Medicines in Pharmacy Organizations. Basic Provisions "a quality management system should be created in each pharmacy organization that carries out retail sale of drugs. This is due to the special professional responsibility for the quality of drug care assigned to pharmacies. Today there is whole line publications in leading pharmaceutical publications, various sectors of the economy, but, unfortunately, in pharmacy, quality management and the activities of a quality commissioner are confused with the performance of the functional duties of a pharmacist-analyst.
If the quality management system has been introduced in industry for a long time, then in the activities of a pharmacy organization it is just beginning to live and work. Until now, there are no (documented) recommendations for the implementation of the system in pharmacy organizations, which should be built on the basis of international standards quality.
The concept of quality is formed from the relationship between the manufacturer and the consumer of the product. The products are so high-quality, so they satisfy the requests and needs of the consumer. The main properties of quality are as follows: inalienability from the object (if we are talking about a retail network, then quality should be present at every point); inconsistency in time, it is impossible to measure the quality once, since the influencing factors change and the quality changes accordingly (for example, new personnel came, the load on him increased and, as a result, the quality changed). The quality formula can be expressed as follows: the ratio of the perceived characteristics of services to the characteristics of services expected by the customer. Quality is maximum if its indicator is equal to one.
The introduction of a quality management system for pharmacy activities in accordance with international requirements makes it possible to move away from licensing pharmaceutical activities. It is more important to license a specialist. If there are violations in the activities that the specialist carries out, he is deprived of his license, and the enterprise continues to work.
Besides, modern stage The development of the Russian pharmaceutical market is characterized by an avalanche-like growth in the range of drugs introduced to the market for the first time. This, on the one hand, allows the doctor, provided there is sufficient professional awareness of the availability of proposals and the properties of drugs, to choose the optimal pharmacotherapy regimen for the disease, on the other hand, it complicates the selection procedure itself due to the many criteria for choosing the optimal drug. The pharmacist involved in the sale of medicines, when providing advice to consumers, also often encounters certain difficulties caused by insufficient information about the pharmacoeconomic characteristics of new drugs. For a specialist to answer modern standards and requirements, it is necessary to clearly define the degree of his responsibility for the assigned case. Exactly professional level specialist should become one of the main elements of the quality management system at a pharmacy.
Therefore, the purpose of this work is to study theoretical and practical approaches to creating a quality management system for medicines in a pharmacy, as well as to analyze the problems that arise in this case and develop ways to solve them.
The implementation of this goal requires the solution of the following tasks:
1. Study of the current state of the drug quality management system in pharmacy activities in foreign countries and the Russian Federation
2. Consideration theoretical foundations quality management systems for medicines in pharmacy organizations according to the literature and regulatory documents.
3. Optimization of the quality management system for pharmaceutical activities in the pharmacy.
4. Analysis of quality management of medicines in the “MAIR” pharmacy in Vladivostok.
The research methodology is based on the constitutional principles of state guarantees of citizens' health protection, legislative and regulatory acts of the Russian Federation in the field of health care and drug supply, the WHO concept of national policy in the field of drug provision, scientific works of domestic and foreign authors in the field of management and economics of pharmacy and health care and pharmaceutical management. To write the work, educational literature on the discipline, articles from specialized journals, as well as Internet sources were also used.
1. The current state of the drug quality management system in pharmacy activities in foreign countries
While developing its own national policy in the field of drug supply, Russia should take into account the accepted international requirements as much as possible. The special instruction of the President of Russia V.V. Putin, given in September 2003, emphasizes the need to harmonize the regulatory acts of the Russian Federation in the field of drug circulation with internationally accepted standards. In the main law in 1998 and later in 2003 in the 80th industry standard, concepts such as a pharmacy (including a hospital), a pharmacy of a health care institution, a pharmacy, a pharmacy shop, a pharmacy kiosk were called “pharmacy institutions”. In fact, there are two types of pharmaceutical organizations on the pharmaceutical market today - pharmacies associated with retail, and others - drug wholesalers.
I.G. Komissinskaya (2007) examined in detail the modern concept of quality management of a pharmacy organization in the world. An international organization that assists in the development of universally recognized standards, rules and other similar documents in order to facilitate the international exchange of goods and services is ISO (ISO) - International Organization for Standardization. ISO is an abbreviation for the Greek word isos, meaning "universal." It is important to understand what ISO standards are, why exactly they regulate requirements all over the world, give basic provisions and concepts in the field of quality management systems.
The history of the emergence of ISO 9000 standards is associated with the adopted in the EU the Global Concept of Legal Assurance of the Quality of Goods and Services, which includes: a manufacturer's quality management system; checking products in testing laboratories; product certification; application of the quality management system in organizations as a guarantee of the stable quality of products and services.
World experience in organizing work in the field of quality management is summarized and systematized in the ISO 9000 series - this is a package of documents on quality assurance prepared by the 176th committee of the International Organization for Standardization.
In accordance with international practice, only mandatory requirements for products are determined by law, and all other conditions are stipulated in an agreement between market participants, i.e. the pharmacy is fully responsible for the quality of products purchased from suppliers. The ISO 9000 series is the international benchmark for quality requirements for business. Their main purpose is to assist pharmacies in identifying potential suppliers with an effective quality management system; reduction in quality costs due to confidence in the quality of the supplier; assistance and methodological assistance to organizations in the creation of quality systems. The main ones are: ISO 9000-2001, which is called “Quality Management System. Fundamentals and vocabulary "is a fundamental standard from which all terminology and concepts are based. Its logical continuation is GOST R ISO 9001-2001, which is called “Quality Management System. Requirements". Today in the world practice there are more than 20 ISO standards.
The quality of medicines is understood as their compliance with all registration conditions, production conditions (technology, production site, personnel) and specified characteristics. Pharmaceutical products, like any other product, go through various stages of the life cycle (quality loops) (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. The system of quality assurance of medicines
The current global trend in the field of rationing and regulation of drug production is the global harmonization of requirements for drug production throughout the entire life cycle of a drug and an emphasis on consumer satisfaction in accordance with the intended use of the drug (Fig. 2).
When a medicinal product enters the market from an enterprise, it receives a quality certificate signed by authorized person manufacturer if it meets the quality indicators of the registration dossier for safety, efficacy and is produced in accordance with GMP rules.
At the same time, there are two clearly expressed areas - the increasing social responsibility of the drug manufacturer, imposed by the state and society as a whole, and the emphasis on ensuring product output. proper quality through organizational and managerial measures at all stages - from the development of a new drug to implementation finished product- with an active regulatory role of state bodies.

Rice. 2. WHO basic requirements for the quality of medicines
The result of the work of the executive committee on this moment the development and adoption of documents related to the process of creating medicines (Q8 "Pharmaceutical Development"), quality risk management (Q9 "Quality Risk Management") and the quality system (Q10 "Pharmaceutical Quality Systems") (Fig. 3).
Further, from the standpoint of ISO standards, we will consider what a pharmacy organization does, who is interested in what, and how to make this activity more effective and efficient. The concept of quality assurance for medicines provides an opportunity for a deeper understanding, awareness and fulfillment of the obligations incumbent on all practicing pharmacists. Good pharmaceutical practice (GPP) is an activity related to the supply, storage and use of medicines and medical devices carried out in pharmacies.
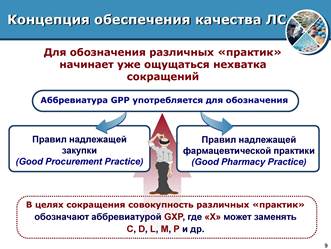
Fig. 3. Good Pharmacy Practice Rules for Quality Assurance of Medicines
Rule-making is initiated by national regulatory authorities in close cooperation with manufacturers represented by pharmaceutical associations.
ISO standard and certificate are two inseparable concepts. Of course, you can implement an ISO system without certifying it, but who can check how well it is built? V in this case there is a document called "ISO 9000 Certificate", which confirms the compliance of the organization's quality management system with the established requirements. A drug certificate is a document that confirms the compliance of a drug with quality. An ISO certificate is a document that confirms the conformity of the quality management system to the requirements imposed by the corresponding GOSTs. Speaking about the quality management system, one cannot but talk about ISO standards.
The main provisions of the quality management system are described in the ISO 9000 standard. It formulates 8 quality management principles:
1. Customer orientation: understanding his current and future needs, fulfilling his requirements and striving to exceed his expectations.
2. Leadership of the leader, ensuring the unity of purpose and direction of the organization.
3. Involvement of workers, making it possible to profitably use their abilities.
4. A process approach to managing activities and related resources.
5. Systems approach to management: identifying, understanding and managing interrelated processes as a system contributes to the effectiveness and efficiency of the organization in achieving its goals.
6. Continuous improvement of the organization's activities.
7. Making decisions based on the analysis of data and information.
8. Mutually beneficial supplier relationships.
Achieving quality objectives can have a positive impact on product quality, operational efficiency and financial performance, and therefore on the satisfaction and confidence of interested parties.
The main provisions of the quality management system include documentation, which makes it possible to convey the meaning and sequence of actions.
Currently, it is no longer envisaged to provide only product quality, but delivered goal customer satisfaction by fulfilling and overfulfilling their requirements through the implementation of effective quality management systems, continuous improvement of its efficiency, as well as prevention of discrepancies between customer expectations and the quality of products and services offered to them.
The most methodologically strong, effective and popular is currently recognized as the Total Quality Management (TQM) model, which is based on the implementation of such principles as: customer orientation, leader leadership, involvement of all personnel in solving quality problems, systemic and process approach to management, continuous improvement of production, mutually beneficial cooperation, decision-making based on facts.
2. Legislative framework management of the quality of medicines in pharmacy organizations according to literature and regulatory documents
It is important to consider what fundamental standards exist in Russia, which of them provide a decoding of the basic concepts and definitions, which standard makes requirements in the certification process of an organization and to the quality management system. From Russia participates in the activities of ISO government agency- Gosstandart of Russia.
In connection with the integration into the world community, a set of ISO standards is taken into account and implemented in Russia, where, on the basis of these standards, the following were developed:
GOST R ISO 9000-2001, describes the main provisions and contains terminology related to the quality management system.
GOST R ISO 9001-2001, defines the requirements for the quality management system
The standard (GOST R ISO 9004-2001) is called “Quality Management System. Recommendations for improving performance ". The 9001 and 9004 standards are completely identical in structure, but the 9001 standard is clearer and more concise. The 9004 standard is, as it were, based on the 9001 standard, contains the same sections, but in expanded form, with explanations and additions. It reflects not only how to create a quality management system, obtain an ISO certificate for it, but also use it to improve the organization's activities. All three designated standards are closely related.
The current quality management system has been developed and implemented strictly in accordance with the requirements of the national standards of the Russian Federation GOST R 52249-2009 (GMP) "Rules for the production and quality control of medicines" and GOST R ISO 9001-2008 (ISO 9001: 2008) "Quality management systems. Requirements".
The Russian GMP standard was prepared by the Association of Micro Pollution Control Engineers (ASINCOM). In 2004, it was approved by the Decree of the Gosstandart of Russia on March 10, 2004 No. 160-st GOST R 52249-2004 “Rules for the production and quality control of medicines”, which is harmonized with the rules of GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice for medicinal products) of the European Union. The order of the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Economy was put into effect on January 1, 2005, and compliance with GMP rules in pharmaceutical production in the Russian Federation is mandatory.
Quality assurance of medicines (MP) is one of the most important tasks of modern pharmacy. To standardize and unify the process of ensuring the quality of drugs at the stage of their direct delivery to patients (retail link of drug distribution), it is recognized necessary use principles and methods of Good Pharmacy Practice (GPP) standards. A pharmacy organization, in terms of ISO standards, is a group of employees and necessary funds with the distribution of responsibilities, powers and relationships that carry out pharmaceutical activities at pharmacy facilities such as a pharmacy, point, kiosk, store, etc. ...
A prerequisite for the implementation of pharmaceutical activities is quality assurance at wholesale enterprises and in pharmacy organizations, which is reflected in the OSTs. The first step in creating a modern legal framework regulation of the pharmaceutical market, taking into account international standards, is the adoption of the following industry standards:
OST91500.05.0005-2002 "Rules for the Wholesale Trade in Medicines. Basic Provisions", approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 03/15/2002 No. 80;
OST 91500.05.0007-2003 "Rules for the Dispensing (Sale) of Medicines in Pharmacy Organizations. Basic Provisions", approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated 04.03.2003 No. 80.
3. Quality management systems for pharmaceutical activities in a pharmacy
The problems of creating an effective quality management system for medicines (drugs) in a pharmacy are reflected in the publications of a number of domestic scientists: D.V. Parkhomenko, I. G. Komissinskaya, Z.K. Drugovoy, A.M. Biteryakova, S.V. Kononov and others.
A system is a collection of interrelated and interacting principles. Each system has a so-called entrance - that is, processes and material values that initiate actions, their own processes take place within the system. The quality management system in the field of drug circulation in Russia is determined by Federal Law No. 86 "On Medicines", and its main stages are registration of a medicinal product, licensing of production of a medicinal product and licensing of pharmaceutical activities .
In accordance with article 45 of this law, a special professional responsibility is assigned to the pharmacy employees for providing the consumer with high-quality medicinal care. Damage associated with harm to health caused as a result of the use of drugs that have become unusable as a result of violations of the rules of pharmaceutical activity, shall be compensated by the organization through whose fault the violation was committed.
The complexity, multistage and duration of the "drug life cycle" - from their creation to their receipt by the end user - predetermine the need to introduce an effective preventive drug quality management system that does not allow substandard drugs to enter the pharmaceutical market. On the way of a drug from the manufacturer to the consumer, the last link where the quality of a drug is assessed by qualified specialists is a pharmacy. Pharmacy quality management is based on TQM principles and ISO 9000 series standards.
V pharmacies a quality management system should be formed, one of the functions of which is to control compliance with the requirements of regulatory documents of the standardization system in health care, in particular the aforementioned OSTs. The main goal of creating an effective system for managing the quality of medicines (drugs) and pharmaceutical activities in a pharmacy is to ensure that the consumer can purchase good-quality drugs and receive high-quality drug services. .
OST 91500.05.0007-2003 "Rules for the release (sale) of drugs in pharmacy organizations, basic provisions" (approved by the Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia) regulates the rules for retail sale in pharmacy organizations, in section 9, paragraph 9.1 it says: " quality management ". In clause 9.9 it is indicated: "The head of the pharmacy organization appoints a quality representative from the management personnel."
Pharmaceutical services have a high consumer value, as they are one of the types of intelligent services that contribute to the maintenance and preservation of human health. High consumer value predetermines the legitimacy of high prices for these services.
The results of services are usually delayed and differentiated, which determines special approach to the formation of prices for services and a special regime for financing pharmaceutical organizations. The consumer of pharmaceutical services is both an individual and society as a whole.
These features define a dual approach to the problem of the quality of pharmaceutical services. First, improving quality is one of the main factors in a pharmaceutical organization's competitive advantage and maximizing profits. That is why the problem of the quality of pharmaceutical services starts at the center of the economic interests of the organization and makes it possible to strengthen its economic stability. On the other hand, the quality of pharmaceutical services is essential condition they fulfill their social function - providing high-quality pharmaceutical care, and ultimately - maintaining human health. A pharmaceutical organization can consider that it has achieved its goals and objectives only if it has ensured a high level of quality of the services provided. That is why it is necessary to develop a quality system in an organization, or rather a quality management system.
The quality of pharmaceutical services consists of two main components: quality of medicines (drugs) and the quality of pharmaceutical activities.
Quality of medicines is determined by the following components :
Determination of market needs (quality of consumer choice);
Drug design quality;
The quality of the production process;
Compliance with the quality of the final product to the project;
After-sales service quality.
The main properties that determine the quality of pharmaceutical and medical products include:
security- the condition of the goods in normal conditions its use, storage, transportation and disposal, in which the risk of harm to life, health and property of the consumer is limited to an acceptable level.
functional properties ... They determine the suitability of products to perform their functions as intended under specified conditions of use or consumption.
N reliability... In many cases, the safety of a product is determined by its reliability, i.e. the property to maintain its original characteristics for a long time within certain limits during operation.
environmental friendliness... It characterizes the degree harmful effects medical supplies for environment arising at the stage of the entire life of the product. Environmental indicators: the level of hazardous chemical emissions, radiation, concentration harmful substances as well as the ability to be recyclable.
aesthetics- an indicator of the qualitative and quantitative assessment of the aesthetic value of products, depending on the group of consumers, specific conditions of consumption and the purpose of the product.
resource consumption... It is characterized by the costs of the consumer for the purchase, operation and maintenance of the product during the period of the average technical resource, i.e. before taking the product out of service.
Assessment of the quality of medicines
The quality of drugs is assessed in accordance with the Instructions for assessing the quality of drugs manufactured in pharmacies (order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated 10.16.97 No. 305) "On the norms of deviations permissible in the manufacture of drugs and packaging of industrial products in pharmacies"). This order applies to all pharmacies, pharmacies (with the right to manufacture drugs) and territorial control and analytical laboratories that control the quality of drugs manufactured in pharmacies.
The quality of drugs (including homeopathic drugs) manufactured in pharmacies is established by a set of indicators. The quality level of drugs is assessed in accordance with the requirements regulated by the current State Fund, orders and instructions of the Ministry of Health of Russia.
To assess the quality, the terms "Satisfied" ("Good product") and "Not satisfied" ("Marriage") are used. The quality level of manufactured drugs is determined by organoleptic and measuring methods.
The unsatisfactoryness of the manufactured drugs is established according to the following indicators:
Inconsistency in the description ( appearance, color, smell);
· Inconsistency in transparency or color;
· Inconsistency in disintegration;
· Heterogeneity of grinding or mixing of powders, ointments, suppositories, homeopathic triturations;
· Presence of visible mechanical inclusions;
· Inconsistency of the recipe for authenticity;
· Erroneous replacement of one L V with another, lack of a prescribed or the presence of an unregistered substance;
Replacement of drugs with similar ones pharmacological action without indicating this replacement on the demand, prescription (copy of the prescription, label);
· Deviations from the prescription by weight or volume;
· Deviations in total mass (volume);
· Deviations in the mass of individual doses and their number;
· Deviations in the weight of the sample (or in concentration) of individual LV;
· Mismatch in pH value;
· Discrepancy in density value;
· Discrepancy in sterility;
· Inconsistency in microbiological purity;
· Violation of fixation of the closure (for sterile dosage forms);
· Violation of the rules for registration of drugs intended for vacation.
Changes in the composition of the dosage form (if necessary) should be made only with the consent of the doctor and should be noted on the requirement, prescription (copy of the prescription, label). In the absence of a specified mark on the requirement, recipe (copy of the recipe, label), the manufacturing quality of the dosage form is assessed as “Unsatisfactory”.
Changes in the amount of dispensed drugs or the dispensing of tablets instead of powders should also be noted on the demand, prescription, etc.
When determining deviations in the tested dosage forms, measuring instruments of the same type (with the same metrological characteristics) should be used as in their manufacture in pharmacies.
The norms of deviations allowed in the manufacture of medicinal products (including homeopathic drugs) in pharmacies have been established (order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated 10.16.97 No. 305).
When determining the permissible deviations in the tested drugs, manufactured in the form of a series of intra-pharmacy blanks, the above deviation rates should be used, as well as the current regulatory documentation governing the production and quality control of various dosage forms in pharmacies.
The quality of pharmaceutical activities
The pharmaceutical services market has clearly defined territorial boundaries. In the course of the functioning of the pharmaceutical market, control by the state is necessary, since pharmaceutical services are a public good and it is necessary to avoid their monopolization. The state performs functions related mainly to legal regulation, information support and other aspects of the formation of the market. Thus, we can talk about a certain dual nature of pharmaceutical services. On the one hand, they are a product that has its own consumer value and is able to act as a subject of market relations. The implementation, in this case, must be of a commercial nature and pursue the goal of obtaining maximum profit.
On the other hand, pharmaceutical services are public good, the distinctive characteristics of which are indivisibility, the joint nature of consumption, high social significance, the predominance of public and state property in their production and consumption. From the point of view of the consumer, pharmaceutical organizations provide a comprehensive service, meeting the most important social needs, both of an individual and of society as a whole. An important feature it is also the fact that the provision of pharmaceutical services requires compliance with certain moral and ethical standards. It all makes it difficult quantification activity, which limits the use of commercial principles of activity in pharmaceutical activities.
It follows from this that a drug quality management system is usually understood as a complex of organizational measures that ensure the provision of quality drug care to the consumer, which is a combination of the quality of the drugs themselves and the quality of the pharmaceutical activities of the pharmacy organization. The current situation in the field of quality management requires the development of practical approaches and management principles to solving the problem of ensuring the availability of high-quality drugs to the population in each pharmacy organization.
4. Establishment of a quality management system
medicines in the pharmacy
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 80 of 03/04/2003 “On approval of the Industry standard“ Rules for the dispensing (sale) of medicinal products in pharmacy organizations. Basic Provisions ". Contains Section IX Quality Assurance of Medicines (Medicines) in Pharmacy Organizations.
Pharmacy organizations or individual entrepreneurs should have a quality assurance system that includes:
Premises and equipment corresponding to the scope of activities of the pharmacy facility and allowing to ensure compliance with the conditions for storage and manufacture of drugs;
Documentation that allows you to identify the origin, quantity and quality of incoming and keep records of stored and sold drugs;
Incoming control of those entering the pharmacy organization or individual entrepreneur Drugs;
Personnel with the required qualifications;
System of continuous training of personnel;
Job descriptions;
The fund of normative and reference materials with which all pharmacy facilities of a given pharmacy organization should be provided.
The pharmacy organization should have a quality management system for the pharmacy organization.
Each pharmacy organization must have internal labor regulations approved by the head of the organization, with a mark on familiarization of employees. The revision of the rules and re-familiarization with them of the employees of the pharmacy organization is carried out annually.
The pharmacy organization must regularly conduct internal checks for compliance with the requirements of GOST. When carrying out inspections, attention should be paid to the presence in the pharmacy organization of the relevant documents for the premises occupied, job descriptions of employees, standards, and other necessary documents.
Inspections can be carried out both by employees of the pharmacy organization, independent of the persons directly carrying out the activity being inspected, and by independent experts. The frequency of checks is determined by the pharmacy organization itself. The results of the inspections are recorded and brought to the attention of the personnel responsible for the inspected area of work and the management of the pharmacy organization. During subsequent checks, the implementation of the recommendations and their effectiveness are monitored. Each employee of a pharmacy organization must be familiar with GOST, the procedure for fulfilling the duties assigned to him, regulatory legal acts and standards related to the activities of the organization. Pharmacy organizations must have job descriptions for each employee, approved in the appropriate order.
Pharmacy organizations should provide for a system of continuous professional development of employees on current legislation, the use of medicines, etc. The plan and topics of the classes are approved by the head of the pharmacy organization. The head of the pharmacy organization appoints a quality representative from the management staff.
In this regard, there is no doubt about the need for continuous improvement of the professional skills of pharmaceutical personnel. One of the ways to solve this problem is to increase the efficiency of the system of postgraduate training of pharmacists.
The pharmacy organization ensures the maintenance of documentation in accordance with the legislative and regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation.
First of all, the task of the pharmacy is to provide the preserved characteristics of the goods received by the pharmacy organization. These are two groups: functional qualities - efficiency and safety, physical and physicochemical, requiring compliance with the rules for handling them. Within the framework of the quality management system of a pharmacy organization, each pharmacy should organize:
1. Acceptance control... It is carried out in order to prevent the receipt and sale of counterfeit, rejected and substandard products through the pharmacy network. It is regulated by the Industry Standard OST 91500.05.0007.-2003 “Rules for the Dispensing (Sale) of Medicines in Pharmacy Organizations”. The areas (premises) for receiving medicinal products and dispensing should be separated from the storage area and should provide adequate (reliable) protection of the received medicinal products from bad weather during loading (unloading) operations. The resulting products are subject to incoming quality control. The results of the incoming control must be registered in accordance with the internal procedure established at the pharmacy. During unloading, the products are checked for compliance with the order and the absence of damage to the packages or containers. Medicines and other goods approved for sale from pharmacy organizations with expired shelf life, not meeting quality requirements, standards and without documents certifying their quality are not subject to acceptance. For medicinal products (medicinal products) in damaged packaging that do not have certificates and / or the necessary accompanying documentation, rejected when receiving or dispensing to the patient, not corresponding to the order or with an expired shelf life, an act is drawn up; they must be appropriately labeled and placed in a designated area separate from other medicinal products until they are identified, returned to the supplier, or destroyed in accordance with the established procedure. Poisonous and potent substances, narcotic drugs, psychotropic substances, thermolabile medicinal products must be immediately placed in storage areas in accordance with the requirements of this OCTa.
The number of medications taken that require special storage conditions must correspond to the available capacity of special equipment. Accepted medicines and other goods allowed for dispensing from pharmacy organizations are credited within the time allotted for the acceptance of the goods by the number of commodity units and completeness in the prescribed manner. 6. All deliveries of the goods must be accompanied by documents allowing to establish the date of shipment, the name of the medicinal product (including the dosage form and dosage), the batch and batch number, the quantity of the supplied goods, the price of the dispensed medicinal product, the name and address of the supplier and recipient, as well as documents, confirming the quality of drugs. The documents confirming the quality of medicines are a declaration of conformity or a certificate of conformity. An important indicator is that a pharmacy or a pharmacy chain works with a reliable wholesale link, well-known transnational companies, which have their own "drug safety service" set very seriously.
Acceptance control, along with checking the correctness of paperwork, includes checking medicines according to the indicators "Description", "Packaging", "Marking", which is determined by the requirements of the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated 07.16.97. No. 214 "On quality control of medicines manufactured in pharmacy organizations (pharmacies)". Control according to the "Description" indicator includes checking the appearance, color, odor. Inconsistency in color, presence of foreign smell, sediment, flakes, mechanical impurities, freezing, stratification are grounds for rejection. In case of doubt about the quality of medicines, samples are sent to the territorial center for quality control of medicines. Such medicines with the designation: “Rejected during acceptance control” are stored in the pharmacy separately from other medicines. Control according to the “Packaging” indicator includes checking the integrity of the packaging, the presence of secondary packaging, and the compliance of the packaging with the physicochemical properties of medicines.
2. Premises and equipment. The basic requirements regarding the organization of storage of medicines and medical products in pharmacies are established by the Instruction on the organization of storage in pharmacies of different groups of medicines and medical supplies. Medicines that require special storage conditions must be immediately identified and placed in appropriate storage rooms (zones) according to the requirements of the current legislation. The storage room in the pharmacy should be large enough to accommodate the orderly storage of the various categories of materials and products. Clean and secure. Medicines in production warehouses must be stored on racks, pallets, pods, in cabinets, refrigeration and other special equipment to ensure storage conditions for medicines in accordance with current requirements . If there are immunobiological preparations in the pharmacy base (warehouse), the total volume of refrigeration equipment must ensure, in accordance with the current requirements, the storage of the entire amount of these drugs, which is contained in the base (warehouse). When storing medicinal products, the licensee is obliged to exclude their damage (spilling, spilling, breaking), contamination with microorganisms and cross-contamination. The storage of medicines requires special temperature conditions, controlled by constant temperature monitoring devices or thermal containers.
3... Staff... A third management principle applies to resources - employee involvement. It is the employees of all levels that form the backbone of the organization. Their full involvement enables the organization to benefit from their capabilities. On the one hand, the management decision that the management system should function, and on the other hand, only when the entire staff realizes that the management system is not a simple collection of additional pieces of paper that will be on the shelf. It must be an effective structure, and it will only work when everyone understands what it is based on and why it is being done. In each pharmacy, in one form or another, a quality management system has been created and is successfully functioning - for some it is 10%, for some it is 90%.
4. Documentation Operations affecting the quality of the goods should be described in written procedures. The quality management system is aimed at systematizing the processes, to see if all of them are provided with the necessary resources and documents. It is important to know if all processes have documented procedures and rules for their implementation. The process of review and improvement is needed to make factual management decisions - this is the seventh management principle of ISO standards. Effective decisions are based on the analysis of data and information.
7. Refunds... The presence of substandard or falsified medicines in circulation, excluding those whose shelf life has passed, is not allowed. Having identified the fact of the presence of substandard, counterfeit and the like medicines, the business entity must draw up an appropriate act and take measures to exclude them from circulation. The exclusion of such medicinal products from circulation occurs through disposal and destruction in accordance with the Rules for the disposal of medicinal products. A procedure has been developed for working with letters from Roszdravnador about rejected and falsified products for the Center's specialists in accordance with the requirements and in the forms specified in the letter of the Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare and Social Development dated 09/28/2004. No. 4082/04.
5. Optimization of the quality management system for pharmaceutical activities in a pharmacy
As a result of studying the literature on PL quality management, it is possible to propose to optimize the activities of pharmacy organizations by introducing the following principles:
The quality of management is a multifaceted concept, it includes many components, such as: transparency and controllability of processes, quality of information, the possibility of operational control of current activities, and much more. At the same time, various documents are practically the only tool for implementing management. Thus, the obvious way to change the quality of enterprise management is to improve the efficiency of work with documents.
Pharmacy quality management is based on the following principles:
Sufficient assortment and volume of medicines at affordable prices
The task of the pharmacy is nothing more than providing the population with drugs and pharmaceutical goods in the right place and at a convenient time for visitors, for which needs are determined, a supplier, an application is drawn up, a purchase is made, and the dosage is studied.
Social accessibility
Research on assortment within synonyms and analogues. The pharmacy contains more than one trade name of one active substance. Trade names sometimes vary by 100-700%, depending on the manufacturer. The pharmacy purchases different brand names at different levels to ensure social inclusion for different social groups of visitors. In one pharmacotherapeutic group, you can take both expensive and medium- and low-cost drugs.
- Information and consulting support
Pharmacy workers must anticipate consumer expectations and ensure that the product meets those expectations. This is not always possible. For example, a consumer wants to consult a pharmacist before purchasing a drug. But a pharmacist is not a doctor and does not bear any statutory responsibility for the patient's health in our country. However, not getting what was expected, the consumer remains dissatisfied.
- Implementation of computer systems in pharmacies and the use of barcodes in drug quality control in a pharmacy
The pharmacy automation system differs from the retail automation systems. Pharmacies have a lot of their own specifics, mainly related to pricing, which in Russia has always been a complex and confusing process. Pricing in a pharmacy is carried out according to certain legislative documents and is strictly regulated; there is a list of drugs that are not taxed. The retail price is formed differently for such medicines. Previously, the process of receiving goods and registering prices for pharmacy workers was laborious and time-consuming. Therefore, automation is simply indispensable here.
Automation systems enable pharmacy workers to view data on what is in stock, what medicines have run out, and what needs to be purchased. The process of quickly viewing real balances is one of the most important when choosing an automation system.
In any ordinary pharmacy, where there is a simple cash register, when making a purchase, the money that we pay to the cashier is in no way directly related to the goods we receive.
And here several problems arise at once:
Firstly, the pharmacy lacks a full and detailed accounting of the movement of goods and funds. It is impossible, for example, at any given time to say how much of a given product was sold, remained in the trading floor or in a warehouse, it is impossible to automatically prohibit punching a product that has already ended, etc .;
Secondly, it is difficult to avoid mistakes that the cashier can make;
Thirdly, the lack of detailed accounting does not make it possible to conduct statistics and detailed analysis of the dynamics of sales, which makes it difficult to respond more flexibly to changes in demand.
6. Analysis and ways of improving the quality management system of medicines in the pharmacy of LLC "MAIR"
MAIR LLC has been operating in the pharmaceutical market for over 15 years in the Primorsky Territory. Its pharmacy network unites 5 outlets and is very popular - several thousand residents of Vladivostok have loyalty cards. Occupies the second floor of a 2-storey building. The premise of the pharmacy is new, has been operating since May 2010, meets all the requirements of the NTD and sanitary standards, works from 9:00 to 20:00 seven days a week. There are signs about the name of the pharmacy and about the opening hours. Located in a convenient place for visitors, near the bus stop.
Mair considers its main mission not so much the sale of medicines, the sale of pharmaceuticals and medicines, medical products, but the provision of pharmaceutical services at a high level, therefore the company strives to focus on the client, guarantee the quality of medicines, and serve the buyer as best as possible. All this, along with an understandable desire to make their work more efficient, made the management think about introducing a quality management system.
Having worked on a quality management system for less than a year, a pharmacy can draw some conclusions. Objective indicators confirm that the introduction of a quality management system contributed to the optimization of working capital: the volume of sales in the chain's pharmacies increased, the number of low-income and illiquid goods, as well as products with an expired shelf life, decreased. The number of regular customers has increased. Analysis of their demand, wishes and offers made it possible to practically get rid of the defects. In addition, due to the orientation of the staff to work with customers, not only the number of online purchases has significantly increased, but their average cost has been optimized. Quality management specialists currently point out that the main and most problematic link in any management structure is people. In our case, these are specialist pharmacists. Those who are in direct contact with customers, visitors, consumers. For the implementation of the quality management system in the pharmacy, some changes were made in the organizational structure and in the relationships in the team. An effective personnel training system, constant monitoring of training have increased the quality of personnel work.
1. As a result of the analysis of data from foreign and domestic literature, it has been established that great attention is paid to the issues of the quality management system of medicines in pharmacological institutions both in Russia and abroad. When studying the basic concepts in building models and functioning of quality management systems, clear leadership is demonstrated by approaches based on the concept of total quality management (TQM) and the ISO 9000 series standards, which provide a number of general principles: customer focus, leadership leadership, processor approach, systems approach, continuous improvement, mutually beneficial relationships with suppliers, etc.
2. The quality management system in the sphere of medicines circulation in Russia is determined by the Federal Law No. 86 "On Medicines". The quality management of the work of pharmacy organizations is based on the principles of TQM and the ISO 9000 series and standards. industry standards: OST91500.05.0005-2002 "Rules for Wholesale Trade in Medicines. Basic Provisions", approved by order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 03/15/2002 No. 80; OST 91500.05.0007-2003.
3. In accordance with international practice, the pharmacy is fully responsible for the quality of products purchased from suppliers, only mandatory requirements for products are determined by law, and all other conditions are stipulated in an agreement between market participants.
4. The quality management system in the field of drug circulation should be reliable, be preventive, preventing the provision of substandard pharmaceutical services to the consumer, as well as personalized, i.e. have specific persons responsible for this.
5. Some principles are considered that allow to optimize the quality management system in the field of drug circulation in a pharmacy. Studying the literature on drug quality management, it is possible to propose to optimize the activities of pharmacy organizations by introducing the following principles.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1. Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of 03/04/2003. No. 80 “On Approval of the Industry Standard“ Rules for Dispensing (Selling) of Medicines in Pharmacy Organizations. Basic Provisions ".
2. Skulkova R.S., Yagudina R.I., Parkhomenko D.V. Formation of a quality management system for pharmaceutical organizations. New pharmacy. Regulations. 2005.-N 4.-С.32-37.
3. Komissinskaya I. G. Modern concept of quality management of a pharmacy organization // Moscow pharmacies. - 2007. - No. 11.
4. Alferova, T.V. Production management at pharmaceutical enterprises / T.V. Alferova, E.A. Tretyakov, A.V. Builin. - Yekaterinburg: Publishing house of the Institute of Economics of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 2008. - 214p.
5. Moskvin V.A. Evolution in the field of quality management / V.A. Moskvin // Investments in Russia. 2004. No. 5.- S. 27-28.
6. Lagutkina T.P. Principles of quality management in the activities of a pharmacy organization // Bulletin of the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia. 2008.-N 4.-С.36-39.
7. Polesskiy V.A. Evolution of quality system models: international practice / V.A. Polesskiy, S.A. Martynchik, V.G. Zaporozhchenko, V.Z. Kucherenko // Health Economics. - 2005. - No. 8. - S. 25-36.
8. Federal Law "On Medicines" No. 86-FZ dated 22.06.98
9. Drugova Z.K., Biteryakova A.M. Internal control system and quality of management // Russian pharmacies. – №2. – 2007.
10. Kononova S.V. The system of quality assurance of pharmaceutical services in the regional pharmaceutical complex: Monograph. -Nizhny Novgorod: VGIPA Publishing House, 2003.
11. Storage conditions for medicinal products. - M .: Medicine, 2006 .-- 184s.
12. Kulaev V.A., Egorov V.A., Gladunova E.P., Ezhkov V.N. Integrated quality management system for pharmaceutical care // Pharmacy, 2011, No. 3, pp. 30-33
I. Acceptance control
a. Acceptance control is carried out in order to prevent substandard medicines from entering the pharmacy.
b. Acceptance control consists in checking incoming medicines for compliance with the requirements for the following indicators: "Description"; "Package"; "Marking"; in checking the correctness of settlement documents (invoices), as well as the availability of manufacturer's certificates of conformity and other documents confirming the quality of medicines in accordance with the current regulatory documents.
i. Control according to the "Description" indicator includes checking the appearance, color, odor. In case of doubt about the quality of medicines, samples are sent to the territorial control and analytical laboratory. Such medicinal products with the designation: “Rejected during acceptance control” are stored in the pharmacy separately from other medicinal products.
ii. When checking the "Packaging" indicator, special attention is paid to its integrity and compliance with the physicochemical properties of medicinal products.
iii. When monitoring the "Marking" indicator, attention is drawn to the compliance of medicinal products with the current requirements.
iv. Special attention should be paid for the conformity of the labeling of the primary, secondary and group packaging, the presence of an insert leaflet in Russian in the package (or separately in a pack for the entire quantity of finished medicines).
v. On the labels of the packaging with medicinal substances intended for the manufacture of solutions for injection and infusion, there must be an indication "Suitable for injection." Packages with poisonous and narcotic drugs must be designed in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation and regulatory documents.
vi. Medicinal plant raw materials received from the population are checked according to the indicator " External signs»In accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia or the current regulatory document, after which it is sent for analysis to the territorial control and analytical laboratory.
II. Preventive measures
1. Preventive measures are to fulfill the following requirements:
a. Compliance with sanitary norms and rules; anti-epidemic regime, as well as the conditions for aseptic production of medicines in accordance with the current regulatory documents.
b. Compliance with the rules for the receipt, collection and storage of purified water, water for injection; timely sanitization of the pipeline; control over the timely withdrawal of sterile solutions, purified water, water for injection for testing for sterility in accordance with current requirements.
2. Collections for purified water, water for injection must have a clear inscription: "Purified water", "Water for injection". A tag is attached to the water collector indicating the date of receipt, the analysis number and the signature of the person who checked it. When using several collections at the same time, they should be numbered.
a. Ensuring the serviceability and accuracy of instruments, apparatus and weighing facilities, their regularity checks.
b. Careful review of prescriptions and requirements of medical organizations arriving at the pharmacy in order to check the correctness of their prescription; the compatibility of the substances that make up the medicinal products; the compliance of the prescribed doses with the patient's age and the availability of instructions on how to use the drugs.
c. Compliance with the technology of medicines (including homeopathic medicines) in accordance with the requirements of the current State Pharmacopoeia, regulatory documents, guidelines.
d. Provision of storage conditions for medicines in the pharmacy in accordance with their physicochemical properties and the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia, current regulatory documents.
i. In the storage rooms, on all bars with medicinal products, the following must be indicated: the batch number of the manufacturer, the analysis number of the control and analytical laboratory (center for quality control of medicinal products), the expiration date, the date of filling and the signature of the filling in the bar. On bars with drugs containing cardiac glycosides, the number of units of action in one gram of medicinal plant material or in one milliliter of the drug should be indicated.
ii. In the assistant rooms, on all bars with medicinal substances, the following must be indicated: the date of filling, the signature of the person who filled in the bar and who checked the authenticity of the medicinal substance. On the bars with poisonous and potent medicinal substances, the highest single and daily doses should be indicated, and on the barbells with medicinal substances intended for the manufacture of sterile dosage forms, there must be a warning inscription "For sterile dosage forms."
iii. Stands with solutions, tinctures and liquid semi-finished products should be provided with normal droplets or pipettes. The number of drops in a certain volume must be established by weighing and indicated on the rod.
iv. The filling of the rod, burette in a burette unit, rod with a normal droplet meter or pipette should only be carried out after full use medicinal product and appropriate treatment of the rod.
e. The nomenclature of concentrates, semi-finished products and intra-pharmaceutical preparation of medicines manufactured in pharmacies must be approved by the territorial control and analytical laboratory and communicated to all pharmacies of the corresponding territory. This list can only include recipes containing compatible medicinal substances for which there are analytical methods for chemical control *.
f. Pharmacy managers need to monitor compliance with the rules for storing medicines in the departments of medical organizations attached to the pharmacy once a quarter.
3. In the departments of medical organizations, it is not allowed to manufacture medicines, pack them, move from one container (package) to another and replace labels. Medicines should be stored in departments only in their original (factory, factory or pharmacy) packaging.
4. To control the expiration date, the series of the manufacturer must be indicated on the packaging of the packaging dispensed by the pharmacy to the department of the medical organization.
5. Medicines from pharmacies to medical organizations should be dispensed only to authorized medical personnel.
III. Written control
1. When manufacturing dosage forms according to prescriptions and requirements of medical organizations, written control passports are filled out. The passport must indicate: the date of manufacture, the number of the prescription (number of the medical organization, the name of the department), the name of the medicinal substances taken and their quantity, the number of doses, the signatures of the manufacturer, who packaged and checked the dosage form. In the case of manufacturing a dosage form, the trainee signs the person responsible for the manufacturing practice.
2. All calculations must be made before the manufacture of the dosage form and recorded on back side passports. The passport is filled out immediately after the preparation of the dosage form, from memory, for Latin, in accordance with the sequence of technological operations. When filling out a passport for homeopathic dosage forms homeopathic names of sequentially taken medicines are indicated.
3. In the case of using semi-finished products and concentrates, the passport indicates their composition, concentration, volume or weight taken. In the manufacture of powders, suppositories and pills, the total weight, number and weight of individual doses are indicated. The total mass of pills or suppositories, the concentration and volume (or mass) of the isotonizing and stabilizing substances added to eye drops, solutions for injections and infusions should be indicated not only in passports, but also on prescriptions.
4. The passport should indicate the calculation formulas and the coefficients of water absorption for medicinal plant materials used in this case, the coefficients of increasing the volume of solutions when dissolving medicinal substances, the coefficients of substitution in the manufacture of suppositories.
5. Keeping passports of written control is also necessary if dosage forms are manufactured and dispensed by the same person. In this case, the passport is filled in during the manufacturing of the dosage form.
6. Passports of written control are kept in the pharmacy within two months from the date of manufacture of the medicinal product.
7. Manufactured medicinal products, prescriptions and completed passports are submitted for verification to a pharmacist who performs control functions in the manufacture and dispensing of medicinal products (hereinafter referred to as the “pharmacist-technologist”). The control consists in checking the compliance of the entries in the passport with the written control of the recipe in the recipe, the correctness of the calculations. If a complete chemical quality control of a medicinal product has been carried out by a pharmacist-analyst, then the analysis number and the signature of the pharmacist-analyst are affixed to the passport.
8. In the manufacture of concentrates, semi-finished products, intra-pharmaceutical preparation and packaging of medicines, all records are made in the books of laboratory and packaging work.
IV. Survey control
1. Survey control is applied selectively. It is carried out after the manufacture of no more than five dosage forms by the pharmacist.
2. When conducting a survey control, the pharmacist-technologist names the first substance included in the dosage form, and in dosage forms of a complex composition also indicates its amount, after which the pharmacist names all the medicinal substances taken and their quantities. When using semi-finished products (concentrates), the pharmacist also names their composition and concentration.
1. As an exception, the production of aromatic waters, intra-pharmaceutical preparation of medicines for external use containing tar, ichthyol, sulfur, Naftalan oil, collodion, lead water, as well as homeopathic medicines, the analysis of which cannot be carried out in a pharmacy, is carried out under supervision of a pharmacist engaged in quality control of medicines.
V. Organoleptic control
1. Organoleptic control consists in checking the dosage form (including homeopathic) according to the indicators: "Description" (appearance, color, odor), uniformity, absence of visible mechanical impurities (in liquid dosage forms). The taste is tested selectively dosage forms intended for children.
2. The homogeneity of powders, homeopathic triturations, ointments, pills, suppositories is checked in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia, current regulatory documents. The check is carried out selectively at each pharmacist during the working day, taking into account different types dosage forms.
3. The results of organoleptic control of dosage forms are registered in the journal according to the attached form (Appendix 2 to of this Instruction).
Vi. Physical control
1. Physical control consists in checking the total mass or volume of the dosage form, the number and mass of individual doses (at least three doses) included in this dosage form.
2. Checked:
3. each batch of packaging and intra-pharmaceutical preparation in the amount of at least three packages (including packaging of industrial products and homeopathic medicines);
4. dosage forms made according to individual prescriptions (requirements), selectively during the working day, taking into account various types of dosage forms, but not less than 3% of the number of dosage forms produced per day;
5. each series of dosage forms requiring sterilization, after filling before sterilization, in an amount of at least five vials (bottles);
6. the number of homeopathic granules in a certain weight of the sample in accordance with the requirements of the current regulatory documents.
7. Results physical control are registered in the journal according to the attached form (Appendix 2 to this Instruction).
8. When checking dosage forms, the quality of the closure is also controlled.
Vii. Chemical control
1. Chemical control consists in assessing the manufacturing quality of a medicinal product according to the following indicators: "Authenticity", "Tests for purity and permissible limits of impurities" (qualitative analysis) and "Quantification" (quantitative analysis) of medicinal substances included in its composition.
2. Qualitative analysis is mandatory:
3. Purified water, water for injection every day (from each cylinder, and when water is supplied through the pipeline at each workplace) to the absence of chlorides, sulfates and calcium salts. Water intended for the manufacture of sterile solutions, in addition to the above tests, must be checked for the absence of reducing substances, ammonium salts and carbon dioxide in accordance with the requirements of the current State Pharmacopoeia. Purified water should be sent to the territorial control and analytical laboratory on a quarterly basis for complete chemical analysis.
4. All medicines, concentrates and semi-finished products (including homeopathic tinctures, triturations, solutions, dilutions) coming from the storage rooms to the assistant room, and in case of doubt - medicines coming to the pharmacy from the warehouse.
5. Concentrates, semi-finished products and liquid medicines in a burette installation and in booms with pipettes in the assistant room during filling.
6. Medicines industrial production prepackaged in a pharmacy, and an intra-pharmacy preparation made and packaged in a pharmacy (each batch). *
7.. Qualitative analysis is carried out selectively:
eight. . Dosage forms made according to individual prescriptions and the requirements of medical organizations, at each pharmacist during the working day, but not less than 10% of the total number of manufactured dosage forms. Various types of dosage forms must be tested. Particular attention is paid to dosage forms: for children; used in eye practice; containing narcotic and poisonous substances.
9. Series - a certain amount of a homogeneous finished product (drug) manufactured in one production cycle under constant conditions.
10. Selectively homeopathic dilutions of the fourth decimal dilution, containing poisonous and potent biologically active substances or poisonous and potent inorganic and organic compounds.
eleven. . The results of the qualitative analysis are recorded in the journals according to the attached forms (Appendices 2,3,4 to this Instruction).
12. Qualitative and quantitative analysis (complete chemical control) is necessarily subject to:
13. . All solutions for injections and infusions before sterilization, including determination of the pH value, isotonic and stabilizing substances. Solutions for injection and infusion after sterilization are checked for pH value, authenticity and quantitative content active ingredients... After sterilization, stabilizers in these solutions are checked in cases stipulated by the current regulatory documents, including methodological guidelines. For control after sterilization, one bottle of solution is taken from each batch.
14. Sterile solutions for external use (ophthalmic solutions for irrigation, solutions for the treatment of burn surfaces and open wounds, for intravaginal administration, etc.).
15. Eye drops and ointments containing narcotic and poisonous substances. When analyzing eye drops, the content of isotonic and stabilizing substances in them is determined before sterilization.
16. All dosage forms for newborns *.
17.. Solutions of atropine sulfate and hydrochloric acid (for internal use), solutions of mercury dichloride and silver nitrate.
eighteen. . All concentrates, semi-finished products, triturations, including liquid homeopathic dilutions of inorganic and organic medicinal substances and their trituration up to the third decimal dilution **.
19. . All intra-pharmacy preparation of medicines (each batch).
20. Stabilizers used in the manufacture of solutions for injection and buffer solutions used in the manufacture of eye drops.
21. The concentration of ethyl alcohol when diluted in a pharmacy, and, if necessary, when taken from a warehouse.
22. As an exception, the manufacture of complex dosage forms for newborns that do not have methods of qualitative and quantitative analysis is carried out under the supervision of a pharmacist-analyst or a pharmacist-technologist.
23. Concentration of ethyl alcohol in aqueous-alcoholic homeopathic solutions, dilutions and drops (each series).
24. Homeopathic granules for disintegration (each batch) in accordance with the requirements of the current regulatory documents.
25. Qualitative and quantitative analysis (complete chemical control) are selectively subjected to:
26. Dosage forms made in a pharmacy according to individual prescriptions or the requirements of medical organizations are checked in the amount of at least three dosage forms when working in one shift, taking into account various types of dosage forms. Particular attention is paid to dosage forms for children: used in ophthalmic practice; containing narcotic and poisonous substances; solutions for medicinal enemas.
27. The results of complete chemical control are recorded in the journal according to the attached form (Appendix 2 to this Instruction). All cases of unsatisfactory manufacture of medicines are necessarily registered in the journal.
