Preparation of the patient for computed tomography of the abdominal cavity. How to Prepare for an Abdominal MRI
Conducting magnetic resonance imaging allows you to identify and characterize the focus of pathology, which further simplifies the choice of treatment regimen. The painless procedure, which is safe for health, is very popular, especially since the information content of the method reaches 98%. In this way, doctors determine the real state of health internal organs, systems.
Introduction to Abdominal MRI
Specialists widely use this non-invasive method in practice, since it determines malignant tumors first stage and benign cysts different sizes, improves the prognosis, gives a chance for the survival of the organism. Among the indications for the procedure, doctors stipulate pathologies of internal organs and congenital anomalies individual systems, violation of the structural integrity of blood vessels and bleeding. MRI of any internal organ determines the cause of the disease, its features, and are involved in the appointment of effective treatment.
In order for this non-invasive method to be as reliable as possible, it is required to prepare in advance for the procedure. To do this, 4-5 days before the MRI, you need to slightly adjust your usual diet. For example, food with coarse plant fiber falls under strict ban, it is desirable to reduce the consumption of fats, choose a carbohydrate-free diet for yourself. From drinks, carbonated water, coffee, alcohol are prohibited. These are the foods that provoke increased intestinal gas content with a subsequent decrease in the information content of the MRI method.
Preparation for an MRI of the abdominal organs
It is very important for a few hours before the procedure itself to refrain from eating any food, stop smoking, perform a cleansing enema or use medical preparation Microlax. This is necessary for quality cleaning intestines, elimination of slagging, obtaining a reliable result during an MRI of the retroperitoneal space.
Before the procedure, it is best not to eat or drink anything, wait until the end of the MRI. In order to exclude increased gas formation in the intestines, it is necessary to drink several tablets of activated charcoal or another sorbent, according to body weight.

In terms of time intervals, preparing for an MRI abdominal cavity, provides:
- do not eat 7-8 hours before the procedure;
- Do not drink liquids 3-4 hours before the MRI.
If the indicated time frames are violated, the effectiveness of the diagnostic method drops significantly, and there is a need for a second examination. The procedure is absolutely harmless, but it takes a lot of free time from the clinical patient. Also, to confirm the functionality of the internal organs, it is necessary not to move, to remain on the couch in the tomograph in a fixed position.
If you follow these instructions, you can get reliable information about the functionality of the liver, gallbladder, abdominal aorta, intestines, pancreas and spleen. The results of the study will allow you to quickly determine the focus of the pathology, take therapeutic measures to eliminate it immediately.
Note to the patient
To get a true conclusion of the MRI of the abdominal organs, it is important to correct not only nutrition, but also to calm down morally, to treat the central nervous system. Increased irritability and nervous disorders- these are pathogenic factors that can spoil the session, require additional anesthesia or sedative in a hospital setting.

Before doing an MRI, you need to remove all metal jewelry and accessories, change into a cotton shirt. Otherwise, potential magnets disturb the flow of high frequency magnetic fields. With regard to clothing, if there are metal elements, you can get a thermal burn.
30 minutes before clinical examination abdominal organs, it is required to use an antispasmodic, No-shpu is often chosen. This is another preparatory measure that makes it easier general state, allows the patient long time stay motionless.
If you need to undergo an MRI, first of all, you need to inform your doctor about the diseases that are in the body in chronic form. Some of them are contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging, since they can significantly worsen the health of the patient under study. The same goes for implants, biostimulants and metal fragments in the structure of the body that act as absolute contraindications for an MRI.
With the introduction of an intravenous contrast agent, an anesthesiologist is invited to the procedure, however, it is first important to take a sample for the presence of allergic reaction. If there are no restrictions, only this highly specialized specialist can make an injection to clarify the diagnosis, to obtain a clearer image. Otherwise, you can only aggravate the general condition by such subcutaneous administration of the reagent.
The procedure itself lasts up to 40 minutes, so you have to tune in to such a long immobile position. If the patient has premenstrual syndrome, it is best to postpone the examination until the end of menstruation. Periods of lactation and pregnancy are also relative contraindications that are temporary.
If you properly prepare for an MRI of the abdominal organs, in conclusion you can get a real clinical picture, define suitable scheme treatment and hope for a speedy recovery.
In diseases of the internal organs, it is difficult to do without additional methods examinations. Ultrasound is usually used first, which allows absolutely safe visualization of the structures of the organs under study at any age and condition of the patient.
To clarify the picture of the disease, endoscopy can be performed, including in the form of laparoscopy, cholangiopancreatography (PCG), and colonoscopy. But these methods have contraindications: acute processes in the organs, serious condition patient, cardiopulmonary insufficiency, impaired blood clotting. X-ray examination of internal organs is widely used.
These include: plain radiography and fluoroscopy, angiography, radioisotope study, CT. They are quite informative, but they have one important drawback: they are based on X-rays, which are dangerous for the body, especially for children. Increasingly, CT and magnetic resonance imaging are used for control.
The main advantage of MRI is, in contrast to CT, its absolute harmlessness, which allows using this method to examine adults and children as many times as required for high-quality treatment.
There is one more advantage - everything is clearly visible in the resulting images. the smallest features internal organs, CT more clearly shows bone structures. The three-dimensional image allows you to see the nuances from a convenient angle without distortion. The doctor has the opportunity to study a specific area of the abdominal cavity and the interaction of adjacent parenchymal and hollow organs, revealing the pathology at the initial stage.
Possibilities of MRI of the retroperitoneal space and abdominal organs
The method can be used along with CT for:
- detection of neoplasms of parenchymal internal organs;
- identifying areas of acute and chronic inflammation in them;
- determination of stones in the bile ducts, their localization, number and size;
- determination of the state of the stomach and intestines;
- studies of the retroperitoneal space, urinary tract, abdominal aorta, lymph nodes and blood vessels with contrast for their better identification.
How to prepare for an MRI?
Preparation for MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal region begins a few days before the scheduled examination. A diet is observed 2 days before the MRI. The patient's diet should exclude:
- dairy products;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- Rye bread;
- Tea coffee;
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks.
If an examination of the pancreas, spleen or liver is to be performed, then the patient should not eat carbohydrate foods. 1 day before the examination, to prevent excessive gas formation, you need to take Activated carbon- for 10 kg of the patient's weight, 1-2 tablets, or "Espumizan". As directed by your doctor, you can take a laxative to cleanse the intestines. The patient should eat for the last time 6-7 hours before the examination. 4 hours before the MRI - the last fluid intake. Half an hour before the examination, you can take an antispasmodic (no-shpa).
If an examination of hollow internal organs (intestines and stomach) is planned, then just before the examination, the doctor will prescribe a intake of 0.8-1 l of liquid - to stretch the objects under study. MRI of the organs located in the small pelvis is performed with an average filling of the bladder.
In an examination with contrast (MRI usually uses gadolinium), the substance is injected intravenously immediately before being placed in the machine's chamber, or even when the procedure is carried out after several contrast-free images - for comparison.
The patient brings with him a passport, an insurance policy, as well as the results of all previous examinations (ultrasound, x-rays, CT scans of internal organs, previously made MRI scans, extracts from the medical history). MRI is not performed for women during menstruation, 5-15 days of the cycle are considered optimal. It is also necessary to take into account some contraindications.
How is MRI of the internal organs performed?
The patient changes into special clothing, leaves a watch, a phone in the box, jewelry, metal hairpins. In an adjacent office, he is placed on a horizontal table in the scanner chamber, where he must remain for 20-60 minutes, while maintaining immobility. This condition is difficult to fulfill for children and people with an unbalanced psyche. The device makes a lot of noise. The cell has lighting and ventilation.
Contraindications
There are absolute contraindications:
- The presence of metal needles and staples in the patient's body after injuries.
- The presence of a pacemaker or endoprosthesis of the middle ear.
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding during examination with contrast - the drug can enter the child's body through the mother's blood and milk.
- Renal failure on examination with contrast.
Relative contraindications that can be corrected:
- Weight over 120-130 kg can make it difficult to place the patient in the chamber of the device.
- Children require special psychological preparation.
- Fear of closed spaces.
- Presence of seizures.
The cost of MRI studies
The cost of the examination depends on the status of the clinic, the qualifications of the specialist, the number of organs examined, the desire to record the results on disk, as well as the availability of promotions or discounts. The price of the procedure can vary from 2.5 thousand to 16 thousand rubles:
- organs of the abdominal cavity - about 3.5 thousand rubles;
- retroperitoneal space and its organs - 4-5 thousand rubles;
- abdominal cavity and cholangiography - 4-5 thousand rubles.
It is important that as a result of the study, objective data will be obtained that facilitate the diagnosis of the disease.
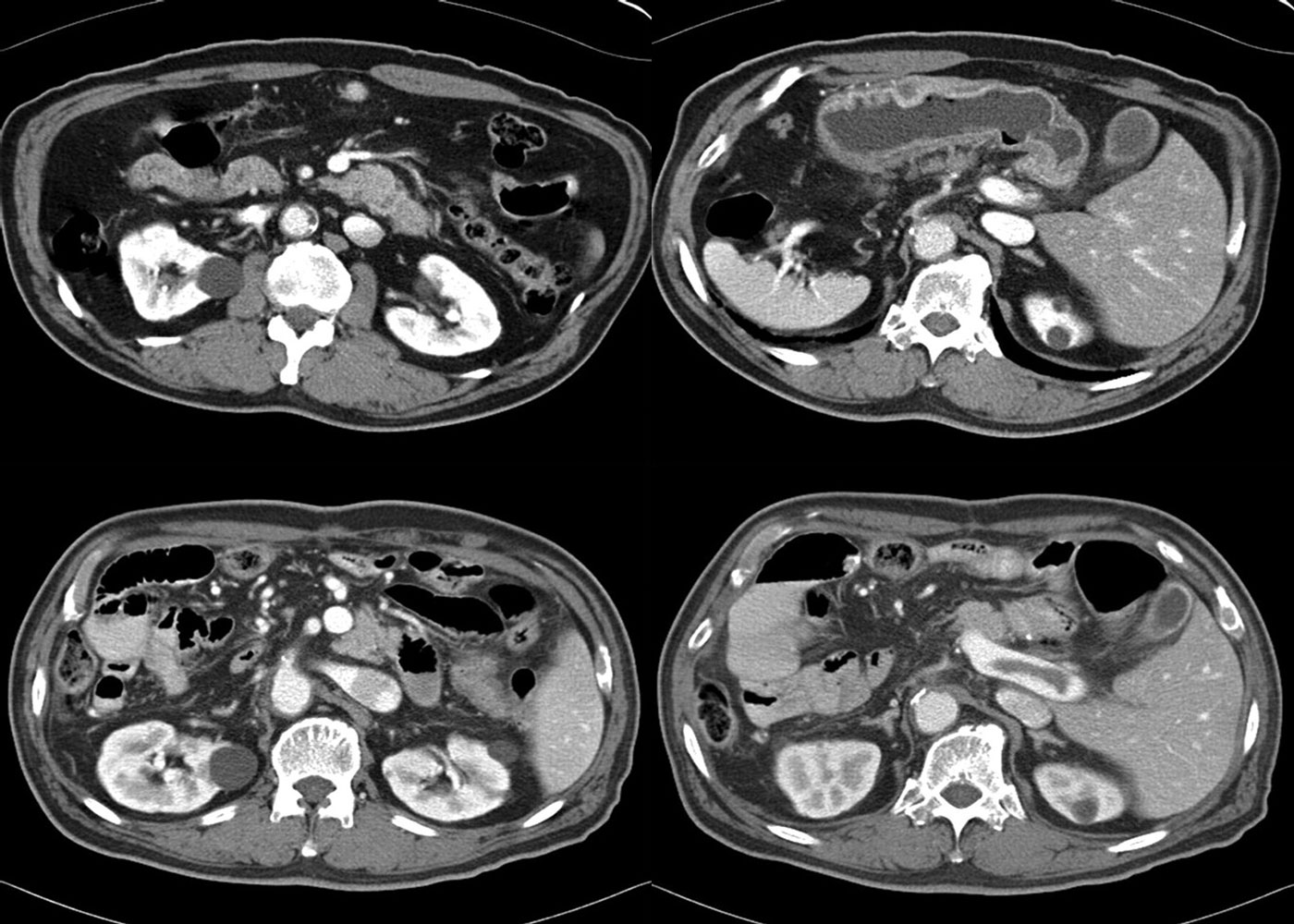
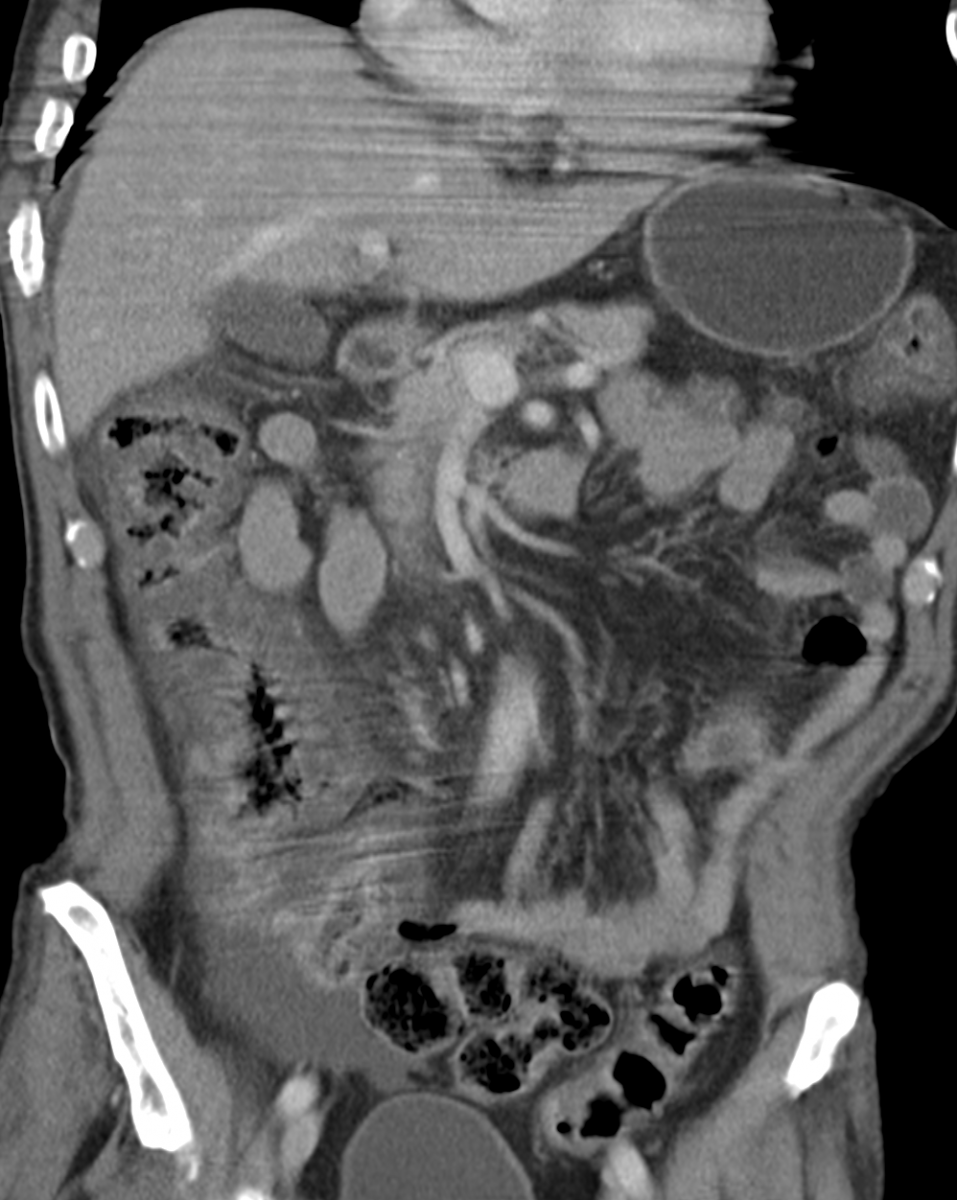
Magnetic resonance imaging is recognized as one of the most exact ways diagnosis of various pathologies. It is absolutely safe, as it is based on the use magnetic field and radio frequency impulses. MRI of the abdominal organs allows you to see not only parenchymal (liver, spleen, kidneys with adrenal glands, pancreas), but also hollow organs (stomach, intestines, gallbladder, its ducts, urinary tract), as well as all types of vessels, lymph nodes and soft tissues.
This method is the most informative, with its help the final diagnosis is established. It can replace other complicated and sometimes painful, long examinations.
What does an abdominal MRI show?
With the help of MRI during the study of the abdominal organs, the doctor can recognize various neoplasms (tumors, cysts) and determine their nature, see foreign objects and stones, identify congenital developmental disorders and pathological changes resulting from diseases. Also, damage to blood vessels (ruptures, thrombosis, aneurysms, deformities) and nerves are visible.
Preparing for an MRI of the Abdomen
A few days before the examination, the patient should not eat foods and dishes that lead to increased gas production. These are fresh fruits, carbonated drinks, beans, raw vegetables, brown bread and sour-milk products. It is recommended to give up coffee and tea. If, nevertheless, there is flatulence, then enterosorbents (activated carbon, enterosgel and others) must be taken the day before.
Abdominal MRI is performed on an empty stomach. Immediately before the procedure, an antispasmodic (no-shpu, papaverine) is prescribed. If the patient is very worried, then they give him sedatives(valerian, motherwort, relium).
You have to take everything off foreign objects: jewelry, watches, dentures, wig, clothes with metal accessories. Before you are called, it is better to go to the toilet. You need to take with you the results of all previous studies (ultrasound, X-ray, tomography, and others), if they were carried out.
How is the examination
An MRI usually requires an appointment. Going to the appointment, you need to take your passport, medical card and doctor's referral.
The examination takes place in a special room where the equipment is installed: it is a large cylinder with a built-in couch. Having removed everything unnecessary from himself, the patient lies down on a sliding table. The head and limbs are fixed with straps to avoid unconscious movements. Then the doctor, after a warning, pushes the couch into the cylinder using the control panel.
During operation, the device emits various, quite loud sounds. This may cause a little discomfort, but you have to be patient. A communication system with medical workers is installed inside.
The examination lasts about half an hour, however, its duration is to a large extent depends on which organ is being examined, and on the proposed diagnosis. The result is usually issued the next day.
Indications
Since magnetic resonance imaging of the abdominal organs is an expensive procedure, it is used, as a rule, for diagnostics. difficult cases. Therefore, it is almost always carried out after x-rays, ultrasound and other examinations, if they did not allow for an accurate diagnosis. This procedure is indicated in the following situations:
- suspicion of malignant neoplasms in the abdomen;
- detection of developmental disorders of internal organs;
- clarification of the nature and source of tumors;
- detection of abscesses inside the abdominal cavity, as well as in the retroperitoneal space with unclear causes of intoxication or hyperthermia;
- diagnosis of postoperative complications;
- suspicion of severe illness abdominal organs;
- clarification of the severity of injuries after injuries;
- the impossibility of carrying out other research methods (for example, radiography with the use of contrast, when the patient does not tolerate it).
Contraindications
Despite its accuracy and safety, an abdominal MRI should not be done if:
- the patient has a pacemaker;
- there is inappropriate behavior;
- the patient's weight is above 110 kg;
- on average or inner ear have implants;
- the patient suffers from claustrophobia;
- there is a pregnancy up to 14 or after 28 weeks;
- installed magnetic stents in the patient;
- Has an insulin pump
- there are magnetic foreign objects in the tissues near the eye.
Interpretation of the result
Before filling out the conclusion form, the doctor examines the layered images. Then he indicates the numbers of the transverse and longitudinal dimensions of the organ under study, its volume, describes the structure and structure by lobes or segments, notes the state of the vessels (blood and lymphatic) passing through it and next to it.
The doctor also pays attention to the environment adipose tissue, muscles, bags and fascia, peritoneum, indicates the presence of fluid in the anatomical pockets and its nature (blood, pus, and so on). Looks at nearby lymph nodes. Describes the shapes and sizes of the detected volumetric structures and foreign bodies. The patient is given a paper with a conclusion, layered photos, as well as a recording on a disk.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdominal cavity is an effective and safe view diagnostics, allowing to assess the anatomical and functional state organs and tissues gastrointestinal tract in real time. During the MRI procedure, the components are examined digestive system and hepatobiliary complex, retroperitoneal space, lymph nodes, veins and arteries, muscular and adipose tissue belly.
The implementation of the procedure is based on the combined effect of a powerful magnetic field and radio frequencies. Atomic hydrogen, concentrating in the organs, reacts to stimuli and moves perpendicular to the tomograph ring. This process allows you to take pictures from different projections and convert them into a three-dimensional image using a computer program.
What organs are examined during the procedure?
The procedure visualizes the following internal organs:
- stomach and pancreas;
- duodenum;
- gallbladder (and ducts);
- spleen;
- kidneys, adrenal glands, pararenal tissue (with MRI of the retroperitoneal space);
- liver;
- intestines (all departments).
Destabilization of the work of these organs can become a direct clinical indication for MRI.
What will the MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space show?
Diagnosis is carried out with the following symptoms:
- acute or chronic pain in the abdomen (pulling, cutting, stabbing);
- flatulence and belching;
- abnormal increase in intestinal motility;
- changes in the color and consistency of feces;
- bloating;
- feeling of heaviness after eating;
- lack or increase in appetite without objective reasons.
Magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed on the basis of anamnesis data, subjective complaints of the patient, and test results.
Abdominal MRI reveals the following: pathological processes:
- defects in the development / structure of internal organs;
- calculi in the gallbladder (cholelithiasis);
- enlargement of the liver and spleen;
- pancreatitis;
- ulcerative lesions of the stomach;
- jaundice (mechanical);
- inflammation (including purulent) and infections;
- hepatic lesions (hepatitis, hepatosis, cirrhosis, fibrosis, necrosis);
- vascular pathologies (thromboses and aneurysms);
- intestinal ischemia;
- post-traumatic complications (cicatricial changes, internal hemorrhages);
- benign neoplasms (cysts, lipomas, adenomas, etc.);
- malignant (cancerous) tumors;
- metastatic (secondary) lesions of internal organs in oncopathologies.
Proper preparation before the procedure guarantees reliable result diagnosis, so all patients are advised to treat it conscientiously and responsibly.
Preparing for an MRI of the Abdomen
The main stage of preparation for MRI of the abdominal organs is the preliminary diet.
2-3 days before the study, it is important to refuse food that increases gas formation:
- bakery products and pastries;
- milk / dairy products;
- fresh herbal products;
- peas, beans, chickpeas;
- sweet and unsweetened carbonated drinks.
If the study of the hepatobiliary system is a priority, the patient may be prescribed a sparing low-carbohydrate diet.
Preparation for the study of the intestine includes taking mild laxatives or sorbents. Doctors usually recommend activated charcoal. It is also possible to prescribe a cleansing enema or microclyster before the procedure. With flatulence, you should take "Espumizan" or an equivalent.
Meals should take place no later than 6-7 hours before. It is necessary to stop drinking water 4 hours before the examination. On the day of the MRI, it is important to avoid caffeinated drinks.
The diagnostic method requires the mandatory adoption of an antispasmodic in 30 minutes (preferably "No-Shpa").
Preparing for an MRI with Contrast
Studies that require prior administration of a contrast agent are especially common in the oncology industry. The substance used in contrast-enhanced MRI consists of gadolinium salts and some auxiliary components. It can be given orally or drip (intravenously). The patient must in without fail Tell your doctor if you have a history of allergic reactions to medications.
Before the introduction of a contrast agent, fasting should be maintained for 6-12 hours, depending on the time of day at which the study is performed. This will help prevent the effects of nausea or vomiting.
The contrast agent does not harm the human body and does not provoke side effects. However, if a patient is diagnosed with chronic renal failure, it is better to refrain from MRI with contrast.
How to prepare for an MRI of the abdominal organs of a child?
The rules for preparing for an MRI in children are the same as in adults. However, parents should take into account that the procedure in newborns and babies under 7 years of age is carried out under intravenous sedation (medicated sleep). Light anesthesia is necessary to ensure immobility during the study (otherwise, the results are distorted).
For these reasons, the child must maintain a long (8-12 hours) fast, even if the introduction of a contrast agent is not provided.
On the day of the magnetic resonance imaging, the child should be woken up an hour earlier than usual. The mother or father must ensure that he does not fall asleep on the way to the clinic.
MRI and metal objects
MRI of the abdominal organs is contraindicated in the presence of the following foreign objects in the body:
- pacemakers/defibrillators;
- cochlear implants;
- vascular clips;
- insulin pumps;
- joint endoprostheses;
- fragments or bullets in soft tissues;
- elements for osteosynthesis (plates, pins, screws, spokes, staples);
- braces;
- fixed dentures and implants.
This contraindication is relative. Diagnostics is allowed if certain metal alloys (para- and diamagnets) predominate in the listed structures, and if an anatomical region remote from their location is examined.
When you go for an MRI, bring loose-fitting clothing with no metal fittings, or purchase a disposable gown.
Women should refrain from using make-up and skin care products on the day of the procedure, as they may contain metallic particles.
Why is proper preparation so important?
MRI is not a cheap diagnostic procedure, so proper preparation for the study is beneficial to the patient. Neglect of the listed norms and restrictions will not harm the body, but will distort the result of the examination, as a result of which you will have to go through it again.
- an informative diagnostic method that helps to identify and differentiate various pathologies of the digestive and hepatobiliary systems in early stages. Magnetic resonance imaging can fully replace other, painful and uncomfortable invasive examinations. The only thing that is required from the patient to obtain reliable data is the observance of simple rules for preparing for an MRI of the abdominal cavity.
Preparation for MRI of the abdominal cavity is required to improve contrast and visualization of organs.
It is not long, but the patient needs to make some efforts, otherwise the results of the study will be unreliable.
During the preparation, on the one hand, the age and state of health of the patient is taken into account, and on the other hand, the organ of the study.
About the features of the procedure
Magnetic resonance imaging is the most promising and modern method diagnostics. In fact, this is a multifunctional scan.
During the study, three-dimensional images of organs or thin layered sections are obtained.
The method is based on measuring the electromagnetic response of some atoms, therefore it is absolutely safe procedure for the patient.
The body is not exposed to any harmful radiation, unlike radiography.
Main advantage this study is highly informative, which helps to establish the correct diagnosis and conduct differential diagnosis with other diseases of the digestive system in complex clinical cases.
Since the method is absolutely safe, the study can be recommended for the diagnosis of diseases of the digestive system in pregnant women and young children due to the exclusion of radiation exposure to the body.
MRI of the abdominal organs allows to identify functional and anatomical changes in the abdominal organs.
The study is used to diagnose both parenchymal organs (liver, pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands, spleen) and hollow organs (stomach, gallbladder with bile ducts).
Magnetic resonance imaging is always prescribed after preliminary research methods, such as ultrasound or radiography, because it has a high resolution.
Also at ultrasound examination only the soft tissues of the organs can be seen, and with MRI, bone structures are also well visualized.
If we compare this procedure with routine endoscopic research methods (gastroscopy, colonoscopy), the latter will significantly lose in terms of the comfort of the procedure.
MRI is often used for malignant neoplasms organs of the abdominal cavity in order to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and the intensity of the tumor growth rate.
Diet and medication intake
Before the study for 2 days, you should abandon all products that cause gas formation and constipation.
These include strong tea, coffee, sweets, chocolate, legumes, fresh and sauerkraut, bread and flour products containing yeast, alcohol.
In the study of the liver and spleen, preparation for MRI of the abdominal cavity includes a two-day carbohydrate-free diet, i.e., the exclusion from the diet of bread and bakery products, raw vegetables and fruits, fermented milk products and cheese whole milk, sweets.
When taking laxative medicines such as Duphalac or probiotics (Normaze), you should tell your doctor.
The doctor during the preparation cancels these drugs, because they increase gas formation.
Regardless of what exactly is to be examined, all hollow organs should be emptied as much as possible.
An MRI is performed on an empty stomach, because a distended stomach and increased intestinal motility can greatly affect the results of the procedure.
You can not only eat, but you need to stop drinking 6 hours before the study.
What should be done before the procedure?
When dressing before the procedure, it is necessary to think over the clothes: there should be no metal parts on it - fasteners, zippers, so that there are no "bones" in the bra.
Contraindications for MRI of the abdominal cavity are metal objects in the human body - dentures, implants, pacemakers, titanium screws in the bones, foreign objects.
This is due to the fact that under the influence of an electromagnetic field, the metal heats up and can injure the patient himself, for which it will be enough minimum quantity ferromagnet.
To prevent gas formation before the study, it is recommended to take drugs that reduce gas formation, for example, simethicone (Espumizan).
For half an hour, patients with motor dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract need to additionally prepare - drink antispasmodics (No-shpu) or medications that depress intestinal motility (Buscopan) in order to relax the smooth muscles of the abdominal organs.
This is usually combined with a small cleansing enema.
Easily excitable patients also need to carefully prepare: take at night sedatives and try to sleep well.
Otherwise excessive physical activity during an MRI will reduce the reliability of the results or make the study impossible.
Women fill before pelvic exam bladder in a volume of 500 ml of water.
The MRI itself does not cause any discomfort or pain.
The patient is placed for half an hour in a special chamber equipped with a fan, lighting fixtures and an intercom to communicate with the doctor.
The patient's task is the same: lie quietly and, if possible, make respiratory excursions as rarely as possible.
When is the contrast agent given?
Abdominal MRI can be done with or without contrast.
A study with the introduction of contrast is more informative and is often used for tumor neoplasms or inflammatory diseases.
In the pictures, these pathological processes in the abdominal cavity will look like illuminated areas with increased metabolism, even if they are only a few millimeters in size.
Before performing an MRI of the internal organs with contrast with contrast, the patient must be informed by the doctor about the presence of diseases of organs and systems that are a contraindication to this method research ( diabetes in decompensated form, hyperthyroidism).
Carrying out the diagnostic method is also contraindicated in patients with premorbid obesity (more than 200 kg) due to the impossibility of placing the tomograph on the couch.
The contrast is excreted through the kidneys, so the procedure is not performed in case of kidney failure.
If the radiologist decides to introduce contrast in order to better visualize the abdominal organs, then a special paramagnetic contrast agent is injected directly during the procedure.
As such a means, gadolinium salts are most often used, which are much less toxic than the substances used in radiography.
They are better tolerated by the patient's body, less likely to give side effects and allergic reactions.
After a series of images of the abdominal organs without contrast, a specialist applies a tourniquet to the patient's arm and approximately 15-20 ml of Gadovist or Omniscan, the most commonly used contrast agents, are injected into the cubital (ulnar) vein.
In terms of pain, the introduction of contrast is comparable to the usual intravenous injection however, some patients may experience side effects, as a feeling of coolness or numbness, spreading along the vein.
The contrast with the blood flow spreads through the vessels and accumulates in the soft tissues.
The very structure of preparations containing gadolinium salts is capable of amplifying the magnetic signal, thereby improving the visualization of organs and the quality of the images obtained.
The second variant of the contrast injection does not provide for the simultaneous administration of the drug, but dosed, through a dropper, the rate of supply of the agent is synchronized with the time of the study.
A similar method of introducing a paramagnetic substance is called magnetic resonance scanning of organs.
This type is used for in-depth study processes occurring in the body in the current time mode.
During the procedure with contrast, the doctor carefully monitors the patient's condition.
The danger signal is the appearance of symptoms such as pruritus, urticaria, nausea, noise and ringing in the ears, pain in the eyeballs, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
