Impulse currents in physiotherapy, amplitude impulse therapy. Pulse current used during electrical stimulation
The student should know : block diagram of an electrostimulator, a method for obtaining pulse currents rectangular using a multivibrator; main characteristics of impulse currents and methods of their measurement; the principle of converting rectangular pulses into pulse currents of a different shape using differentiating and integrating circuits;
The student must be able to : with the help of a multivibrator layout, to receive pulse currents of various shapes on the oscilloscope screen, measure pulse parameters, work with electrostimulation devices.
Brief theory Impulse currents used in medicine.
In medicine, for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, in addition to direct current of low strength (galvanization), current is used in the form of separate pulses, which are characterized by a certain duration and a pause that follows. 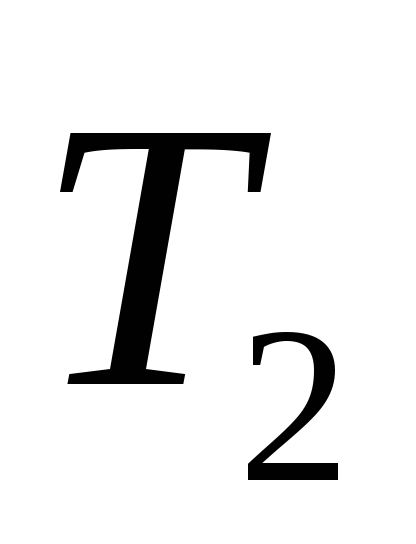 ... Time
... Time  and
and  constitute the period of an ideal impulse
constitute the period of an ideal impulse  (fig. 1).
(fig. 1).


Ideal impulses
During galvanization, a slow increase in the current strength causes a gradual change in the concentration of ions in the cells, which leads to a slight irritation of the nerve endings and no muscle contraction occurs (tissue adaptation).
A significant physiological effect on the tissues of the body is exerted by a sharp change in the strength of the current, for example, at the moment of closing or opening a circuit. In this case, a rapid shift of ions from a steady state occurs, which has a significant irritating effect on easily excitable tissues, especially nervous and muscular tissues, and this effect is proportional to the rate of change in the current strength, i.e.  .
.
The therapeutic method using the excitation of muscles or organs by impulse currents is called electrical stimulation. Currently, the following types of current pulses are used in medicine, different in shape, duration and frequency.
1. Impulse current rectangular shape (Fig. 2a) - the duration of which is 0.1 - 1.0 ms at a frequency of 10 - 100 Hz. Such currents enhance inhibitory processes in the central nervous system, therefore they are used to obtain a state similar to physiological sleep (electrosleep). Impulse current is used for some mental illness, as well as diseases associated with dysfunction of the corticosteroid system (peptic ulcer, hypertension);
Tetanizing current(Fig. 26) - characterized by a triangular shape of pulses with a signal duration of I - 1.5 ms and a frequency of 100 Hz. It causes prolonged contraction of striated muscles. It is used for electro-gymnastics - exercise of muscles with their impaired function;
Exponential current(Fig. 2c) with a pulse duration of 1.6 to 60 ms with a frequency of 8 to 80 Hz is used to stimulate muscles. Depending on the degree of muscle damage, an appropriate exponential current is selected, the advantage of which over tetanizing current is that it can cause a motor reaction of more deeply affected muscles.

Impulse currents used in medicine
Diadynamic currents are two currents with a half-sinusoidal pulse shape - with a frequency of 50 pulses per second (single-cycle continuous) (Fig. 2d) and 100 pulses per second (push-pull continuous) (Fig. 2e). The fundamental difference them from others is that they can be rhythmically modulated in frequency, amplitude and shape to prevent tissue adaptation to electrical stimulation.
Diadynamic currents have gained recognition due to their analgesic effect, the mechanism of which is neuro-reflex, like a nerve blockade. The action of such a current leads to physicochemical changes in cells, changes in capillary permeability, causes reactive hyperemia, improves lymph and blood circulation, enhances the flow of nutrients and removes metabolic products, which leads to a decrease in edematous and inflammatory processes in tissues, decreases vegetatively - vascular disorders.
To obtain a physiological effect, use the current strength between the thresholds of perception and pain (Fig. 3).

Rice. 3.
Schematic representation of a sinusoidal (a),
tetanizing (b), exponential (c) currents
(coverage area shaded)
Pulse currents are generated using vacuum tube or transistor generators. The purpose of this work is to study a multivibrator-generator of rectangular pulses (Fig. 4) with a wide range of adjustment of their duration and frequency.
PULSE CURRENTS- electric currents of different polarity, used for the purpose of treatment and diagnostics, coming to the patient intermittently in the form of separate "shocks", "portions" (impulses). I.'s treatment of t. Is applied independently or (more often) as part of complex therapy. The pulses have a different shape, recorded by the oscilloscope, the edges are determined by the different rate of voltage rise after a pause and fall before the next pause. They follow each other either evenly or in the form of periodically repeating series with intervals between them. Pulse frequency is expressed in hertz, duration in milliseconds, amplitude and average values of their strength and voltage - in milliamperes and volts.
To group I. t. Include: 1) I. t. Constant polarity and low frequency - currents Ledyuk, Lapik, tetanizing and diadynamic; 2) I. t. Variable polarity and middle frequency- interference, sinusoidal modulated, fluctuating; 3) And. T. Variable polarity and high frequency - see Darsonvalization.
Ledyuk's current - I. t. With pulses, steeply increasing and after a while rapidly falling, rectangular. In practice, a current with a frequency of 5-150 Hz is used. First proposed with lay down. the purpose of the French. physicist and biologist S. Leduc. Lapik's current - I. t. With impulses gradually increasing and decreasing, that is, of an exponential form. First proposed by French. neurophysiologist L. Lapik. The tetanizing current is characterized by pulses close to a triangular shape, with a frequency of 100 Hz and a duration of 1 -1.5 ms; is an improved version of the proposed by Faraday (M. Faraday) alternating current unstable frequency.
Diadynamic currents - I. t. With pulses of a half-sinusoidal form (Fig. 1) with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz. For the first time offered by A.N. Obrosov and I.A.Abrikosov for lay down. use in 1937 In the 50s. 20th century these currents are introduced to lay down. practice by P. Bernard. The method of treatment is called diadynamic therapy.
Interference currents (syn. Nemek currents) arise as a result of interference (superposition) in the tissues of the patient's body of two alternating currents with pulses of unequal average frequency (4000 and 3900 Hz); offered for lay down. application of Austr. physicist H. Nemec in 1951.

Sinusoidal modulated alternating currents with a frequency of 5000 Hz and coming after modulation (low-frequency conversion) to the electrodes in the form of pulses from 10 to 150 Hz are proposed and introduced into the lay down. practice by V.G. Yasnogorodsky in 1966 (Fig. 2). The method of treatment with currents is called amplipulse therapy after the name of the domestic apparatus that generates these currents, Amplipulse. Fluctuating (aperiodic) currents with randomly combining pulses with a frequency of 100 to 2000 Hz were proposed in 1964 by LR Rubin for therapeutic purposes in dentistry. The method of treatment with these currents is called fluctuation.
Mechanism of action
The main thing in action And. T. Is the analgesic effect. Currents with sinusoidal and half-sinusoidal impulses (diadynamic, interference, sinusoidal modulated and fluctuating) have the greatest analgesic effect. In the mechanism of the analgesic action of these currents, two points can be distinguished. The first is a direct inhibitory effect of the type of nerve blockade in the zone of influence on the conductors. pain sensitivity... This leads to an increase in the pain threshold, a decrease or cessation of the flow of afferent pain impulses in the c. n. page, that is, to the emergence of anesthesia of one degree or another. The second stage is the creation in c. n. with. dominants of irritation (according to A. A. Ukhtomsky) in response to a powerful stream of rhythmically incoming impulses from intero- and proprioceptors from the zone of influence of I. t. The dominant of rhythmic irritation "overlaps" the dominant of pain.
As a result, the response impulses from c is also normalized. n. page, which contributes to breaking the vicious circle "focus of pain - c. n. s.- a focus of pain. " The irritation of the autonomic nerve fibers arising under the influence of the current and the rhythmic contractions of the muscle fibers in the affected area contribute to the stimulation of collateral circulation, normalization of tone peripheral vessels, which improves blood supply and trophism in patol, focus.
According to general biol. According to the law of adaptation, the ratio "irritation - reaction" under the influence of treatment I. t. changes significantly over time: the threshold for the perception of currents increases, and the analgesic effect decreases (the reaction of addiction). To reduce this phenomenon, I. t. Is usually used not only at one frequency, but also in the form of various and consistently applied modulations, alternating I. t. Of unequal frequencies in different time ratios (currents "short and long period", etc.).
I. t. Of constant polarity and low frequency have significant sensory and motor irritation due to the rapid increase and decrease in voltage in the impulse; this irritation manifests itself even with a small current strength by a burning or tingling sensation under the electrodes and intensifies with an increase in the current, accompanied by a tetanic contraction of the exposed muscles. In connection with the given features of the action, the currents of Ledyuk, Lapik, tetanizing are used mainly for electrodiagnostics (see) and for electrical stimulation (see).
I. t. Of variable and constant polarity, in particular sinusoidal and half-sinusoidal forms and medium frequencies, cause less sensory irritation while maintaining motor excitation. This allows them to be used for both pain relief and electrical stimulation.
Diadynamic currents have not only an analgesic effect; their use in case of trophic disorders and skin damage accelerates regeneration, helps to replace rough scar tissue with looser connective tissue. The impact of diadynamic currents on the area of sympathetic nodes contributes to the normalization of blood circulation in the extremities, with atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels with the syndrome of regional cerebral hypertension, a decrease in the tone of intracerebral vessels and an improvement in blood flow in them, and with migraine it stops an attack. Sinusoidal modulated currents have the broadest spectrum of action, causing positive responses from both the sensory and motor spheres and trophic function nervous system... In this regard, they have found application for a number of functional disorders; so, the use of sinusoidal modulated currents in patients with initial stage lymphostasis of the extremities helps to improve the drainage function of the limf, the system. In sick arterial hypertension renal genesis stage I-IIA, the application of these currents to the area of the projection of the kidneys helps to reduce blood pressure due to changes in glomerular filtration and increased renal blood flow, etc.
Fluctuating currents have not only analgesic, but also anti-inflammatory effects. Their use in purulent inflammation promotes increased phagocytosis in the focus, delimiting it from "healthy" tissue and improving the course of the wound process.
Indications, contraindications
The main indications for the therapeutic use of diadynamic, interference, sinusoidal modulated currents: diseases and injuries of the soft tissues of the trunk and extremities (contusion, sprains of ligaments and muscles, myositis, ligamentitis, etc.), diseases and consequences of injuries of the spine and joints (osteochondrosis, deforming spondylosis, osteoarthritis, Spondyloarthrosis, etc.); peripheral nerves (sciatica, plexitis, neuritis, neuralgia, shingles), spinal cord and its membranes (arachnoiditis, myelitis), occurring with pain or paresis and paralysis of the limbs; lesions of the vessels of the brain and peripheral vessels of the extremities or disturbances in their tone (atherosclerosis of the vessels of the brain in the initial period, Raynaud's disease, obliterating endarteritis of the I-III stage, atherosclerotic occlusion of the vessels of the extremities of the I-II stage, various forms migraine); hron, organ diseases abdominal cavity and conditions after operations on them, proceeding with atony of smooth muscles; a number of diseases of female and male genital organs (hron, inflammation of the appendages of the uterus and prostate gland), accompanied by severe pain. Diadynamic currents, in addition, are used when vasomotor rhinitis, hron, average adhesive otitis media, sinusitis. Diadynamic and sinusoidal modulated currents are used to expel stones from the ureter (with appropriate urine, indications and special technique). Interference currents are used, in addition to the indications listed above, for electron anesthesia (see). Sinusoidal modulated currents are also used to treat patients with hron. limf, edema of the lower extremities.
Fluctuating currents are predominantly used in dentistry: with neuralgia of the trigeminal, glossopharyngeal and other nerves, with arthritis temporomandibular joint, alveolitis (alveolar pain), periodontal disease, with inflammatory diseases(acute, chronic, exacerbated) and acute purulent processes of the maxillofacial and submandibular regions (phlegmon, abscess in postoperative period).
The main contraindications to the use of diadynamic, interference, sinusoidal modulated, fluctuating currents: individual intolerance to currents, bone fractures and dislocations (until consolidation or reduction), extensive hemorrhages or a tendency to them, thrombophlebitis, acute purulent infection (use of fluctuating currents in the postoperative period is possible ), neoplasms, essential hypertension II B and III stages, hron, stage II-III circulatory insufficiency; hron, ischemic disease hearts with symptoms of angina pectoris and severe sinus bradycardia, pregnancy of all periods.
Indications, contraindications and to lay down. methods for impulse current Lapik, Ledyuk and tetanizing (rectangular, triangular and exponential) - see Electrodiagnostics, Electrosleep, Electrostimulation.
Apparatus for the treatment of impulse currents. For the treatment of diadynamic currents, there are domestic devices SNIM-1, Model-717, Tonus-1 and Tonus-2. Current pulses with a frequency of 50 and 100 Hz in devices are obtained by one- and two-half-wave rectification of the mains alternating current.

In the circuit of devices, in addition to rectifiers, there is a rectangular pulse generator with a multivibrator (an electronic device with the help of which one obtains I. t. With a wide frequency range and with a shape close to rectangular). This current is then used in the apparatus to obtain I. t. Of a half-sinusoidal form with a gradual decay of the pulse. The SNIM-1 apparatus (Fig. 3) generates seven types of currents: single-cycle and push-pull continuous and wave currents, currents in the syncope rhythm (alternation of a single-cycle continuous with a pause), "short and long period" currents (alternation of one- and two-cycle continuous currents in different time ratios).
All currents, except for continuous ones, can be used in two forms of messages - "constant" and "variable". With a "constant" form, the currents are constant set parameters... With "variable" - some parameters of the currents (duration of the sending period, increasing and decreasing the amplitude of the pulses) can be changed within certain limits. This allows you to significantly expand to lay down. the use of diadynamic currents, in particular, to use them for pain relief in patients with intolerance to continuous currents and for electrical stimulation of muscles in diseases internal organs and peripheral nerve damage. Power consumed by the device from the network, 60 W, weight 12 kg. Model-717 - portable apparatus generating the same types of currents as SNIM-1, in the "constant" form of parcels. Power consumption of the device is 35 W, weight is 4 kg. The Tonus-1 device is used in stationary conditions and at home; generates all types of currents as the devices described above, as well as single-cycle and push-pull currents in various new combinations. The form of the parcels is "permanent". The power consumption of the device is 25 W, weight is 7 kg. Foreign devices for the treatment of diadynamic currents - D padinam and k (PNR), Bipulsator (NRB), etc. - generate diadynamic and galvanic current and, which can be used separately and in combination with each other. The form of the parcels is "permanent".
For amplipulse therapy, the domestic devices Amplipulse-3T and Amplipulse-4 are used (Fig. 4). The circuit of the apparatus includes a generator of carrier sinusoidal oscillations of medium frequency (5000 Hz), a generator of modulating oscillations of low frequency (10-150 Hz), a generator of parcels and a power supply unit. Amplipulse-3T generates continuous sinusoidal modulated oscillations ("constant modulation") and alternating with a pause ("send - pause") with pulses of other frequencies ("intermittent frequencies") or with modulated oscillations ("send - carrier frequency"). The duration of the messages can be adjusted from 1 to 5 seconds. The currents are used in alternating and direct current modes. The modulation depth (the degree of its expression) can be changed. With an increase in the modulation depth, the exciting effect of currents increases. This is taken into account in the technique to lay down. use of the device. The power consumption of the device is not more than 170 W, weight is 17 kg. Amplipulse-4 - portable model of the device (weight 7.5 kg); generates the same types of currents as Amplipulse-3, but with fewer modifications.
In the domestic apparatus for fluctuating ASB-2, a germanium diode is the source of ac voltage of audio frequency (from 100 to 2000 Hz). The voltage in the apparatus is supplied in three versions: in variable, partially "rectified" and constant polarity (respectively, current No. 1, 2, 3). For use in dentistry, a set of intraoral electrodes is attached to the device. The weight of the device is 6.5 kg, the power consumption is 50 W.
All described devices, with the exception of Tonus-1 and Amplipulse-4, need to be grounded when used.
Apparatus generating I. t. With rectangular, triangular and exponential impulses - see Electrosleep, Electrodiagnostics, Electrostimulation. There is no serial production of domestic devices for the treatment of interference currents, since devices of the Amplipulse type are more effective. Apparatus for electrolysis by interference currents - see Electronarcosis.
Healing techniques
Therapeutic techniques (outlined in relation to treatment pain syndrome- the most frequent cases use I. t.). Influence of I. t. Is carried out through electrodes (with wetted hydrophilic gaskets), which are connected to the output terminals of the device and fixed on the patient's body. The value of the current "in the patient's circuit" is set according to his feelings (up to a clear but painless vibration of tissues under the electrodes) and according to the indications measuring instrument- milliammeter. The procedures are carried out daily, and when acute pain 2 times a day at intervals of 3-4 hours. With sequential exposure to several zones, the duration of the entire procedure should not exceed 20 minutes. For the course of treatment, depending on the analgesic effect, from 1 to 5 to 12-15 procedures are prescribed. When treating with currents of constant polarity, the cathode on the limb is placed on the pain zone, the anode - more often transversely with respect to the cathode; when exposed to the spine - paravertebral.
In diadynamic therapy, first, a push-pull continuous or push-pull wave current (in a "constant" or "variable" form of messages) is applied sequentially for 10 seconds - 2 minutes. (depending on the area of exposure), then currents "short and long" periods (each for 1 - 3 minutes), depending on the severity of pain.
During the procedure, it is possible to switch the polarity (in the presence of several pain points) in compliance with the safety rules (all switching of the device handles are carried out with the "patient current" turned off).
In amplipulse therapy, the action is sequentially applied for 3-5 minutes. modulations "burst-carrier frequency" and "intermittent frequencies". The mode of action, frequency and depth of modulations are prescribed depending on the severity of pain. For acute pains - AC mode, frequency 90-150 Hz, modulation depth 25-50-75%, with mild pain - AC or DC mode, frequency 50-20 Hz, modulation depth 75-100%. In cases where a sharp stimulating effect of currents is undesirable, they are used at a modulation depth of 25 to 75% (depending on the zone of exposure and the severity of pain).
The influence of interference currents is carried out with two pairs of electrodes from two separate current circuits, positioning them so that the intersection of the lines of force is in the projection zone of the patol, focus. The rhythm and frequency of modulations are prescribed depending on the severity of pain in the range from 50 to 100 Hz.
Effects of fluctuating currents on the mucous membrane oral cavity are carried out with intraoral electrodes, on the skin - with plate. With acute and aggravated inflammatory processes in the maxillofacial area, a current of alternating polarity is used, with hron, inflammatory processes and periodontal disease - a current of partially rectified or constant polarity.
Repeated courses of treatment And. T. At a wedge, indications can be prescribed in 2-3 weeks. Variables And. T. Medium frequencies (sinusoidal modulated) are prescribed to children at the age from 1 year; other types of I. t. - more often to children over 5 years old for the same indications and using the same methodological techniques as in adults.
V complex treatment I. t. Is widely combined not only with drug treatment, but also with other physiotherapy and balneotherapy - medicinal electrophoresis (see), galvanization (see), general warm fresh and mineral baths and warm showers, local thermal procedures, massage and lay down. gymnastics. At correct conduct procedures And. t. complications are not observed. It is not recommended to influence the same zone I. t. And ultraviolet rays in an erythemal dosage.
Bibliography: Bernard P. D. Diadynamic therapy, trans. from French, M., 1961; Liventsev N.M. and Livenson A.R. Electromedical equipment, M., 1974; A practical guide on carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures, ed. A. N. Obrosov, p. 40, M., 1970; Physiotherapy Handbook, ed. A. N. Obrosov, p. 37, M., 1976; Physical factors in the complex treatment and prevention of internal and nervous diseases, ed. A.N. Obrosova, M., 1971.
M.I. Antropova.
V recent times for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, an intermittent direct current is used in the form of separate shocks (impulses) with pauses between them, the so-called impulse current.
Each pulse is characterized by a certain duration t followed by a pause t 0, which together make up a period T.
Impulse currents are distinguished by:
- a) the shape of the impulses;
- b) the repetition rate of impulses per second (expressed in hertz - Hz);
- c) the duration of each pulse (expressed in milliseconds - msec).
During galvanization, a slow increase in the current strength, causing a gradual change in the concentration of ions in the cells, under conditions of tissue adaptation, leads to a mild irritation of the nerve endings. Muscle contraction does not occur in this case; if the current is turned on and off quickly, muscle contraction is observed. This can be explained by some displacement of ions and a lag of diffusion processes during short-term current pulses. The degree of change in the concentration of ions is determined by the strength of the current and the duration of its exposure.
Some forms of current pulses were used earlier under different names... For example, an intermittent galvanic current was widespread, which was obtained by connecting various types of interrupters to the DC circuit (manual electrode-interrupter, metronome-interrupter, etc.). The Ledyuk current was known with the number of interruptions of 100 per second (with the ratio of the duration of the closure and the duration of the opening of 1: 9), which caused the phenomena of electrically anesthesia.
A faradic current obtained from an induction coil with a pulse frequency of 60-80 per second and a duration of an opening pulse of 1-2 msec was widely used. (The use of faradic current for therapeutic purposes is called faradization.) Since the faradic current is capable of causing a prolonged ("tetanic") contraction in skeletal muscles, leading to muscle fatigue and ultimately to its atrophy, it was proposed to use periodic interruptions of the current for electrical stimulation of the muscles, the so-called rhythmic faradization, which alternately causes contraction and relaxation of muscles.
Currently mainly used the following types current impulses of different shape, duration and frequency.

1. Current with rectangular pulses. The duration of each pulse is 0.1-1 ms at a frequency of 10-100 Hz. This type of current enhances inhibitory processes in the central nervous system and is used to obtain a state similar to physiological sleep(electrosleep).
The apparatus for electric sleep is a pulse generator based on an electronic lamp circuit. Electrodes are placed on the eye sockets and mastoid processes. This type of treatment with protective inhibition is used for certain mental illnesses, as well as for diseases associated with dysfunction of the cortical-visceral system (gastric ulcer, hypertension).
2. The tetanizing current is characterized by a triangular pulse shape. The duration of each pulse is 1-1 1/2 ms, the frequency is 100 Hz.
The source of this form of current are devices with electronic lamp circuits.
The tetanizing current causes a prolonged contraction of striated muscles, and it is used for electro-gymnastics - muscle exercise in case of impaired function.
3. Exponential current (Lapik current) has a gently increasing curve shape), reminiscent of the shape of the currents of the action of the nerve when it is stimulated. Pulse duration from 1.6 to 60 msec. The pulse frequency can be changed. Depending on the degree of muscle damage, the corresponding exponential current is also selected. To obtain a rhythm of contraction - muscle relaxation, a so-called modulator is used. The advantage of an exponential current waveform is that it can cause motor reaction and more deeply affected muscles, when the tetanizing current does not. This form of current is used to stimulate muscles.
The source of impulse currents is the AFM apparatus. It consists of a short-time pulse generator, a pulse modulator and a conversion modulation stage. In addition to tetanizing and exponential current forms, the device can be used for treatment with continuous direct current (galvanization) and rhythmic galvanization.

The ACM device is used for electrical stimulation (electro-gymnastics) of muscles in case of violation of their contractility. Rhythmic electrical stimulation improves the blood supply and trophism of the neuromuscular apparatus, helps to increase the volume and performance of muscles, restore the conduction of nerve elements, and has a beneficial effect on the regeneration of nerve fibers, thereby accelerating the restoration of the function of the affected muscle.

Electrical stimulation is used for lesions of the peripheral motor neuron (residual effects after postponed poliomyelitis, neuritis of the facial nerve, traumatic neuritis, secondary atrophy and paresis that developed due to prolonged muscle inactivity, functional paralysis). In order to enhance the function of smooth muscles, electrical stimulation is indicated, for example, in atony of the stomach, intestines, and bladder.
Impulse currents
Are electric currents characterized by a temporary deviation of voltage or current from a constant value.
Depending on the distribution of current and pulse, rectangular, triangular, exponential and other pulse shapes are distinguished.
The amplitude and duration of the pulses are important, and if the pulses are not single, then the frequency of 1 second is also important. They are widely used in practice following methods based on the use of impulse currents.
Electrosleep
- exposure to impulsive currents of low intensity in order to normalize the functional state of the central nervous system through the receptor apparatus of the head. V classic version the method uses impulses with a duration of 0.2-0.3 ms at a frequency of 1 to 150 Hz, passing a current through the bifurcated electrodes located on closed eyes and the area of the mastoid process, at a current intensity that causes threshold sensations.
The impaired functional state central nervous system and its regulatory effect on other systems of the body, which explains the many-sided beneficial effect of electrosleep in many pathological conditions.
Diadynamic therapy - treatment with direct currents with polysinusoidal impulses with a frequency of 50 - 100 Hz, which are applied separately or with continuous alternation as part of short or long periods. These currents encounter great resistance from the epidermis and, above all, cause excitation of exteroreceptors, which is manifested by a burning sensation and tingling sensation under the electrodes, as well as the appearance of hyperemia due to the expansion of superficial vessels and accelerated blood flow through them. With an increase in current strength, rhythmic excitation of nerves and muscle fibers is caused. This leads to activation of peripheral blood circulation, metabolism, and a decrease in pain in the area of exposure, which is used mainly for diseases of the peripheral nervous system, organs of support and movement. With an even greater increase in current strength, tetanic muscle contraction is caused.
Interference — medicinal use low-frequency (1-150 Hz) "beats", the frequency of which can be constant during the procedure or periodically change in the selected limit. "Beats" are formed inside the tissues of the body as a result of hysterference (addition) of two initial medium-frequency currents supplied to the surface of the body through two separate circuits and differing in frequency. They have an exciting effect on motor nerves and muscle fibers, which increases blood circulation, activates metabolism and reduces pain in the affected area and is used for diseases of the peripheral nervous system (in the subacute stage).
Amplipulse therapy - treatment with sinusoidal modulated currents (CMT), which are amplitude pulsations of low frequency (from 10-150 Hz) of medium-frequency currents (2000 -5000 Hz). When such currents are supplied to the body, the medium frequencies ensure a good passage of the current through skin without causing them irritation and unpleasant sensations under the electrodes, and low-frequency amplitude pulsations - an exciting effect on the neuromuscular structures. SMTs have a rhythmic stimulating effect on nerve and muscle fibers, activate blood circulation and metabolic processes not only in superficial, but also in deeply located organs and tissues, have an analgesic effect, and at high current density they cause tetanic muscle contraction, which is used for electrostimulation of nerves and muscles. The ability to change many parameters of the current and the use of various combinations of them makes it possible to change the nature and intensity of the exciting action within a wide range and to successfully use them for the treatment of patients not only with diseases and injuries of the support and movement organs, the nervous system, but also with many other pathological conditions.
Indications:
1) pain relievers ( urolithiasis disease, calculous cholecystitis, obliterating endarteritis, impaired peristalsis, ureteral atony);
2) antispasmodic action.
You can add a medicine to the pads - CMT phoresis (with hypertension, Ischemic heart disease, biliary dyskinesia, bronchial asthma, exacerbation peptic ulcer, dumping syndrome, etc.).
Contraindications:
- tumor (relative p / p);
- bleeding;
- II half of pregnancy (carefully);
- individual intolerance;
- fresh hemarthrosis.
Electrostimulation - application electric current in order to excite or enhance the activity of certain organs and systems. Despite the fact that many organs and systems can be stimulated by currents using adequate techniques and parameters for this, in practical work most wide application received electrical stimulation of the heart and electrical stimulation of motor nerves and muscles.
When a pulsed current passes through the tissues at the moments of its rapid switching on and interruption, a sudden accumulation of a large number like charged particles. This leads to a reversible change in the state of cellular colloids and brings the cell into a state of excitation, in particular a motor state, if the action is carried out on the motor nerve or muscle. Electrical stimulation is used to maintain the vital activity and nutrition of the muscle, prevent its atrophy during the recovery of the damaged nerve, to prevent muscle atrophy during the period of its forced inactivity during immobilization or joint diseases, to strengthen weakened muscles and other purposes.
There are many unique techniques treatment various diseases at which goes straight impact on the human body magnetic fields, current pulses, laser, etc.
One of the most popular methods is magnetic therapy, which is effective and shown in many diseases and pathologies.
For the therapy of different pathological diseases, doctors use impulse currents in physiotherapy. Exposure to currents occurs in a certain rhythm, which is set on a special medical device corresponding to the rhythms of work of any internal system or body human body, the frequency of the supplied pulses also changes.
Appointments for use in medicinal purposes low-frequency current pulses can be a number of the following diseases and manifestations:
- electrical stimulation of muscle tissue;
- pain relief;
- antispastic effect;
- action that has a vasodilating effect;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- lesions of the neuromuscular system;
- hyperthyroidism;
- other diseases endocrine system;
- cosmetic problems with the skin;
- intestinal motility disorders;
- diseases of the pelvic organs ( genitourinary system).
 In the course of the procedure, the effect on the muscles of impulse currents is replaced by the so-called rest phases. With each subsequent action, the amplitude of the impulse current and its rhythm gradually increase and, thus reaching highest point, and then, also smoothly decrease their value to zero.
In the course of the procedure, the effect on the muscles of impulse currents is replaced by the so-called rest phases. With each subsequent action, the amplitude of the impulse current and its rhythm gradually increase and, thus reaching highest point, and then, also smoothly decrease their value to zero.
Electrodes through which electrical impulse current, are placed at certain points on the patient's body, through which the action is carried out on a certain muscle group. The strength of the current is calculated by the doctor in such a way as to visually see the muscle contractions, but at the same time do not cause the patient to feel discomfort during the procedure. Typically, the current can be between 10 and 15 mA. As a rule, the course of treatment consists of 15 to 20 procedures, each of which lasts 15 or 30 minutes.
Pulse currents are used in different types of physiotherapy:
- Electrosleep... With this type of physiotherapy, there is an effect of low-intensity portions of current impulses, thus normalizing the functionality of the central nervous system. This effect is carried out through the head receptors. Classical electrosleep uses pulses at a frequency of 1 to 150 Hz, with a duration of 0.2 to 0.3 ms. With this procedure, bifurcated electrodes are applied to both eyes of the patient, as well as to the area of the mastoid process. As a result of such manipulation, there is a normalization of brain activity, improvement of blood circulation, the work of all internal organs and systems.
- Diadynamic therapy... It is carried out using low-frequency pulses of a polysinusoidal form, with a frequency of 50 to 100 Hz. Pulses are applied separately or in a process with continuous alternation of short and long periods... The epidermis resists the action of such a current, causing hyperemia, expansion of the walls of blood vessels and increased blood circulation. In parallel, muscle tissues are excited, the nervous system, it turns out to be a common healing effect... Thus, the work of the circulatory system is activated, in particular, the peripheral, all metabolic processes in the body are improved, pain... This method of impulse therapy is used to treat the peripheral nervous system and the musculoskeletal system.
- Interference... Low frequency impulse currents (from 1 to 150 Hz) are used, with a constant or variable frequency. This technique improves the functioning of motor muscles, increases blood circulation, reduces pain, and activates metabolic processes. More effective treatment for the treatment of subacute stages of diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
- Amplipulse therapy... Electrotherapy is performed using simulated sinusoidal currents with a low frequency (from 10 to 150 Hz), as well as medium-frequency currents (from 2000 to 5000 Hz). Such a sinusoidal current perfectly penetrates the skin without causing irritation, while it has an exciting effect on muscle fibers, nerve fibers, improves blood circulation, metabolic processes. Treatment is prescribed for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, traumatic injuries, problems of the nervous system and many other pathological conditions.
- Electrostimulation used to stimulate or significantly enhance the functionality of certain internal organs and systems. Today, the most common types of electrical stimulation are the stimulation of the heart, nervous system and motor muscles. Also, therapy is indicated for maintaining the vital functions of muscle tissue and its nutrition, preventing such a phenomenon as muscle atrophy during the period of forced inactivity, to strengthen the muscles during the recovery and rehabilitation period.
- Fluctuorization... Currents of partially or fully rectified alternating current, low frequency (from 10 to 2000 Hz) are used. When exposed to such currents, irritation and excitement of tissues occurs, lymph and blood circulation increases, the movement of leukocytes is activated, and the work of muscle tissue is stimulated.
Contraindications to the use of pulsed current therapy can be:
- individual intolerance;
- tumors;
- the second trimester of pregnancy, in which it is used very carefully pulse therapy;
- bleeding;
- fresh hemarthrosis.
 The action of current pulses on the body causes irritating, exciting and stimulating effects that can help in the treatment of various diseases, pathologies and complications.
The action of current pulses on the body causes irritating, exciting and stimulating effects that can help in the treatment of various diseases, pathologies and complications.
When the current passes through the tissues of the body, it causes tissue tension, strengthens the work of cell membranes.
Thus, it activates their functionality, excites cells and improves their vital functions, nourishes muscles, restores the work of nerve fibers, blood vessels, joints. A disease such as prostatitis can be effectively treated with impulse currents.
When applying therapy, the patient receives the following results:
- Blood flow improves, and, accordingly, the substances of drugs used to treat prostatitis penetrate faster into the tissues of the prostate gland.
- Decreases congestion in the pelvis.
- The metabolism improves, which strengthens the entire body.
- The synthesis of prostate secretion is improved.
- The permeability of cell membranes increases.
For effective therapy of prostatitis, electrotherapy with different kinds impulse currents. Galvanization allows you to influence the prostate gland with currents of low frequency with continuous action, it relieves inflammation, relieves pain. Medicinal electrophoresis helps to enhance the effect of medicines, as the permeability of tissues at the cellular level increases.
With electrical stimulation, the function of the pelvic muscle tissue increases, which helps in the treatment of pathologies of the genitourinary system. Thanks to this technique, many patients with prostate problems receive high-quality and effective treatment... Feedback from both doctors and patients suggests that complex therapy with current pulses is one of the most effective methods treatment and prevention of prostatitis and many other diseases.
