White patches on labia. White plaque on the genitals, causes and principles of treatment
The appearance of white plaque in the folds of the genital organs is a frequent phenomenon, and it is not always the result of inflammatory process. white bloom on the labia due to the fact that a woman during the cycle there are changes in the smell, consistency and structure of the secretions. Just like plaque, discharge similar color do not have a strongly pronounced smell, if the woman’s health is all right. The presence of a slight sour smell depends on the microflora of the vagina and is considered the norm.
anxiety symptoms
White plaque on the labia in itself is not a reason to panic. Particular attention should be paid to the occurrence of concomitant manifestations: burning sensations in the genital area and discomfort in the lower abdomen, the presence bad smell, plaque and secretions. Sometimes these manifestations are accompanied by fever. In this case, in order to identify the causes that caused similar changes worth a visit to the gynecologist.
Other in intimate places plaque appears

A white spot on the labia may occur due to poor-quality treatment of thrush. The process of infection can occur constantly from a sexual partner. In the case of thrush, the formation of plaque is accompanied severe itching. The appearance of secretions and plaque white color on the mucosa reproductive organs can happen not only mature woman, but also in a teenage girl who is not sexually active. Usually they appear in girls at the age of eleven or thirteen and signal that menstruation may soon begin. The reason is the hormonal changes taking place in the body.
Consequences of hormonal changes
At the beginning of sexual activity, when the vaginal microflora changes, plaque on the labia is explained by a reaction to the partner's foreign flora. In the future, these changes cease to disturb the woman. However, in case of prolonged similar condition a specialist should be consulted. Without an examination and consultation with a gynecologist, it is almost impossible to say whether a white coating on the labia that has appeared is evidence of a serious illness, or hormonal changes occur in the body associated with the onset of sexual activity. Don't try to remove plaque as soon as possible. In the absence of diseases, it protects the body, preventing the penetration of pathogenic microbes. Thanks to this, the microflora of the vagina remains healthy.
Hygiene rules
During personal hygiene procedures, white plaque on the labia is recommended to be removed. cotton swab wetted vegetable oil or water. In this case, it is better not to use ordinary shower gels or soaps, as they can only increase irritation. Much more efficient in this case there will be the use of special gels for intimate hygiene. They are based on extracts of calendula and chamomile, which are used in traditional folk medicine to relieve inflammation and irritation of intimate areas.
Appearance in intimate area white pimples
Pimples and white balls on the mucous membrane of the genitals should not be taken too lightly. Their appearance in this area often indicates infection with syphilis. Syphilis, being a common infection of the body, is transmitted mainly through sexual contact or during childbirth to a child from a sick mother.
Leukoplakia is characterized by keratinization and thickening of the stratified squamous epithelium.
Causes of leukoplakia of the vulva
The development of leukoplakia is based on complex neuroendocrine and metabolic processes caused by changes nervous system. Often leukoplakia occurs as a result of dysfunction of the ovaries, adrenal cortex and a number of other glands. internal secretion. The emergence and development of the disease is facilitated by age-related atrophic processes in the vulva, due to the restructuring of the neuroendocrine system.
Although leukoplakia can occur at any age, the disease is most often observed during menopause and menopause. In women with impaired activity of the gonads, the disease occurs more often than in healthy women.
A certain role in the development of leukoplakia is played by a lack of vitamins, especially A-hypovitaminosis.
Signs of leukoplakia of the vulva
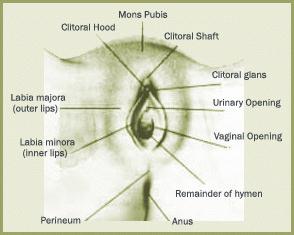
The main sign of leukoplakia is foci of depigmentation - whitish spots, which are usually located symmetrically. Most often they are localized on the labia minora, clitoris and also on inner surface labia majora (the outer surface, as a rule, is not affected), further spreading to the perineum and inguinal folds.
TO characteristics The disease also includes itching of the external genital organs, usually occurring at night. There is also a feeling of numbness, burning, tingling and crawling.
Leukoplakia can be limited, that is, consist of separate plaques, or diffuse - in the form of merged lesions. According to the severity of the thickened layer, 3 forms of the disease are distinguished: flat (simple), hypertrophic (hyperkeratotic) and warty. Hypertrophic and warty leukoplakia are characteristic of limited lesions.
Often, leukoplakia precedes atrophy of the integumentary stratified squamous epithelium.
With sclerotic changes in the vulva, the clitoris and labia minora are deformed, the labia majora become significantly flattened and thickened, the skin and mucous membranes intimately grow together with the underlying tissue, they narrow the entrance to the vagina, and also (less often) the external opening urethra. The glossy-pearl shade of the integumentary tissues that have lost their elasticity resembles a crumpled parchment sheet (a symptom of parchment). The presence of cracks and ulcerations favors tissue infection, the occurrence of an inflammatory reaction, which is accompanied by pain, swelling and redness.
Prolonged itching of the vulva contributes to the emergence of a number of emotional and neurotic disorders in the form of insomnia, increased irritability, depression, and decreased ability to work. To this are added difficult or painful urination, the inability to have a sexual life.
Diagnosis of leukoplakia of the vulva
Areas of leukoplakia are visible to the naked eye. However, the apparent ease of diagnosis is dangerous in cases where leukoplakia is combined with vulvar cancer. That is why the doctor supplements the visual examination of the vulva with its examination using a colposcope. In doubtful cases, he may resort to a biopsy of a suspicious area of \u200b\u200btissue with subsequent histological examination.
Treatment of vulvar leukoplakia
Most effective complex therapy, which is selected strictly individually.
Non-surgical treatment of leukoplakia includes the following components: psychotherapy, hydrocortisone phonophoresis on the vulva area, intramuscular injections 5-10% solution of tocopherol acetate in oil, 1 ml, reception ascorbic acid. It is also recommended to perform daily subcutaneous injections of biogenic stimulants (aloe extract, FiBS, suspension or placenta extract - all 1 ml) in order to activate the hormonal function of the adrenal cortex. The course of treatment (30 injections) is repeated after 3-4 months. Simultaneously with the use of biostimulants, folliculin ointment (20,000 units) and aloe liniment can be used as a local therapeutic agent.
For the treatment of leukoplakia, ointments containing glucocorticoids are used. They have anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties, as well as eliminate or reduce the sensation of itching. The most appropriate use of hydrocortisone (1% and 2.5%), prednisolone (0.5%), fluorocortic (contains 0.1% triamcinolone acetonide) ointments.
An indispensable prerequisite for the success of treatment is a thorough systematic toilet of the external genitalia, perineum. For washing, only boiled water is used, adding sodium bicarbonate, infusion of chamomile or calendula to it. Use for washing solutions of potassium permanganate and boric acid, like various soaps, undesirable, so cat. they dry and irritate the tissues, exacerbating the discomfort.
Lingerie should be made of natural fabrics, it should not fit snugly against the external genitalia, otherwise itching may increase.
It is necessary to exclude smoking and drinking alcohol. The basis of the diet should be dairy products, boiled meat (especially the liver and kidneys), boiled fish, vegetables, berries and fruits. Dry food, spices, spicy dishes, smoking, strong tea and coffee.
Traditional medicine offers its methods of treatment of vulvar leukoplakia - acupuncture, water procedures using herbs and plants. For example, lying down before going to bed and immediately after waking up, it is useful to drink a glass of boiled water room temperature.
Having found a white coating on the genitals, you should not immediately panic. In principle, this is a fairly common phenomenon, and it is not always based on pathological factors.
But how to distinguish the norm from the pathology? What causes this phenomenon, how to diagnose and treat it? This will be discussed in our article.
The essence and causes of the appearance of white plaque on the genitals
The appearance of plaque on the genitals can be both natural, physiological basis and be a sign of various diseases.
Often, white plaque is formed as a result of the development sebaceous glands a secret that mixes with scales of dead epithelial cells and moisture. This mixture called smegma. When inappropriate, smegma accumulates in the clitoris, labia in women, and in the area foreskin in men.
This phenomenon occurs regardless of age. You can even see a white coating on the genitals of a girl from 0 to 2 months old. Thus, the newborn organism is cleansed and adapted to environment. It is not uncommon for plaque to occur during the time when the body builds protection against the penetration of various infections.
If the white plaque does not have a pronounced odor and does not cause discomfort, then it does not pose a threat to health.
But if, in addition to white bloom, you find a number of other uncharacteristic signs, then this can already become a problem. In this case, the presence of plaque indicates the possibility of a number of diseases.
Among the factors that affect the appearance of white plaque on the genitals, the following can be distinguished:
- (thrush). A disease caused by yeast-like fungi.
- Vaginitis and other inflammatory diseases of the genital organs.
- Genital. It has a viral etiology, is caused by types 1 and 2 of herpesvirus.
- Other infectious and inflammatory diseases (including venereal) of the reproductive and urinary systems.
- Changes in the microflora of the vagina. They are promoted by hormonal disruptions, disorders of the nervous system, long-term use medicines, reaction to sexual partner.
- Teenage changes (often before the onset of the first period).
- Not balanced diet and shortage.
- Reaction to the use of alkaline agents for intimate hygiene.
- Tight, unnatural underwear.
Associated symptoms
The formation of white plaque caused by pathogenic etiology is not a separate disease, but one of its symptoms. As a rule, its occurrence is accompanied by a number of other signs that help diagnose the disease.

To the number accompanying symptoms, include the following:
- Feeling of constant discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- Pain and cutting when emptying the bladder.
- Periodic body enhancement.
- It appears clearly bad smell secretions.
- Redness of the external genitalia, individual cases swelling occurs.
Causes white plaque itching of the genitals, burning sensations in the perineum.
Depending on the nature of the disease, purulent pimples, uncharacteristic formations on the skin and genital mucosa may also appear ( this feature characteristic of infection with syphilis).
All of the above symptoms may indicate the presence of infectious, inflammatory or other diseases in the body.
If you find at least one of the symptoms together with white plaque, then you should not waste time contacting a specialist gynecologist or venereologist. It is not necessary to diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment on your own, this can cause irreparable harm to the body (up to infertility).
Diagnosis and principles of treatment
Various diseases, both infectious and inflammatory, may have similar clinical symptoms. Therefore, without carrying out diagnostic measures, passing all the required tests, it is very difficult to determine the exact diagnosis, and as a result, prescribe adequate therapy.

When a white plaque is detected on the genitals of a woman, the following diagnostic methods are used:
- Ultrasound examination of the genital organs;
- Submission of smears for microflora;
- A smear for the presence of genital infections (STDs);
- Colposcopy;
- General examination of blood and urine.
After the results are obtained, the specialist doctor makes a conclusion and prescribes treatment.
From the nature and specifics of the disease, are prescribed medical preparations oral (tablets), vaginal ( vaginal suppositories) and external (creams, ointments) applications. In especially severe, critical cases, hospitalization is recommended.
Also, remedies can be used to alleviate some symptoms. traditional medicine. For example, a decoction of plants that have anti-inflammatory properties can be used for douching, or as a compress. This will help soothe the inflamed mucosa, and relieve itching for a while.
Important, treatment folk remedies can be carried out only after consulting a doctor, so as not to complicate the course of the disease.
If, after the behavioral diagnosis, it turned out that the whitish plaque does not pose any threat to health and does not need treatment, then it can be “removed” in simple ways.
First of all, it is necessary to keep the genitals clean. Abandon conventional alkaline products (soap) and switch to special balanced hygiene products. Wear underwear made from natural fabrics, balance your diet.
The main thing to remember is that neglect of your health can lead to undesirable consequences which are easier to prevent than to cure.
On the necessary measures for hygiene of the genital organs - on the video:

The periods of menopause and menopause are always associated with hormonal changes body of a woman and are often complicated by the appearance of various unpleasant symptoms and diseases. One of these gynecological ailments related to precancerous conditions is vulvar leukoplakia. At first, this disease can be completely asymptomatic, and in the absence of timely treatment, it can lead to the development of an oncological process.
Leukoplakia of the vulva (or lichen sclerosus) is a degenerative disease of the vulva with manifestations of squamous cell hyperplasia of the stratified squamous epithelium lining the vulva. With this disease, the appearance in the tissues of the vulva of normally absent horny and granular layers is observed, which lead to the development, para- and hyperkeratosis. This disease can be combined with vulvar kraurosis, and such clinical cases in last years are increasingly observed in the practice of gynecologists. With vulvar leukoplakia, cell malignancy and the development of vulvar cancer are observed in 13-30% of patients, and when combined with kraurosis, the risk of occurrence increases. Unfortunately, doctors also note the fact that this gynecological disease becomes “younger” and is increasingly detected in young women.
In this article, we will introduce you to the causes, symptoms, methods for diagnosing, treating and preventing vulvar leukoplakia. This information will allow you to start treatment on time and prevent the development of serious complications.
Bye modern medicine cannot give an exact answer about the cause of the development of vulvar leukoplakia in each specific clinical case, but doctors are well aware of the factors that can lead to changes in the cellular composition of the vulvar epithelium. These include:
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- erosion and dysplasia of the cervix;
- genital trauma;
- hormonal imbalance;
- infection;
- neglect of the rules of personal hygiene;
All these factors become especially dangerous after the age of 40 or during menopause.
Psychiatrists consider leukoplakia as a psychosomatic disease, which is provoked by a whole range of psycho-emotional disorders and can be corrected by changing the way of thinking. As a rule, women with such a diagnosis experience constant dissatisfaction with themselves and the actions of the people around them, make increased demands on themselves and a deep distrust of their loved ones and relatives.
Much less frequently, vulvar leukoplakia develops in childhood. However, all of the above factors can cause changes in the vulvar mucosa in girls. That is why regular preventive examinations at this age acquire important role, and when the first signs of the disease appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms
Sometimes vulvar leukoplakia long time is asymptomatic and women learn about its development during a routine or preventive examination by a gynecologist. Pathology can be detected by chance when examining the clitoris and labia minora. Small, usually multiple, spots appear on their mucous membrane off-white. Over time, they thicken, keratinize, slightly rise above the surface of the mucosa and acquire gray white color from pearl shade. Foci of the changed mucosa can increase in size, merge and spread to a significant surface of the vulva. Often, patients experience paresthesia in the form of numbness or tingling in the area of keratosis.
When leukoplakia zones are infected or sclerosed, a woman may pay attention to the sudden appearance of swelling and complain of dryness, tension and tightness of the mucous membrane and skin in the genital area, intense, which increases at night or during movement, intercourse and urination. Prolonged itching of the vulva leads to the appearance of psycho-emotional disorders, exhaustion of the nervous system and disability.
In areas of leukoplakia, multiple subepithelial hemorrhages may appear. On the late stages hyperkeratosis and sclerosis diseases reach their maximum. The mucocutaneous integument becomes rigid, folded, glossy-pearl in color. Telangiectasias and subepithelial hemorrhages appear on their surface. The labia majora become like thickened ridges, the labia minora are almost not defined, and the entrance to the vagina becomes sharply narrowed.
Classification of forms of leukoplakia
According to the severity of hyperkeratosis, leukoplakia can be:
- Flat. Flat spots appear on the vulva whitish spots no signs of inflammation. After removal with a swab, they reappear. Spots may be present in limited areas of the vulva, and with a generalized course, they capture a vast surface of the mucosa.
- Hypertrophic. Foci of mucosal changes look like gray-white spots with clearly defined contours, they rise above the surface and sometimes merge with each other, they are not removed with a swab.
- Warty. The lesions are significant and look like warty growths. May be complicated by ulceration, inflammation, swelling and the appearance of redness, ulcers, cracks and erosions. This form of leukoplakia is considered a precancerous condition.
Leukoplakia of the vulva and pregnancy
In some cases, vulvar leukoplakia can also develop during pregnancy. With the help of timely and well-appointed drug therapy it is usually possible to achieve a stable state without progression of symptoms during gestation and in early postpartum period. In such cases, women are shown delivery naturally. In the presence of severe dryness, thinness, the presence of long-healing ulcers, cracks and extensive foci of leukoplakia, a caesarean section is recommended for delivery.
Diagnostics

To establish a diagnosis, patients are assigned the following types of examination:
- history taking and gynecological examination;
- general blood analysis;
- smear on the flora from the urethra, vagina and cervix;
- analysis by PCR for the presence of human papillomavirus with the establishment of the type of virus;
- biopsy and histological examination;
- cytological examination of scrapings from the cervix and cervical canal on atypical cells;
- vulvoscopy (simple and extended with the use of dyes);
- colposcopy;
- aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity and / or cervical canal, followed by a histological examination of the material;
- immunogram.
On the early stages vulvar leukoplakia is a differential diagnosis of this disease with such diseases as:
- neurodermatitis - itching also manifests itself in other parts of the body, the epithelium is compacted, dry and thickened, the skin is reddened, with inflamed pink-brown papules and has an enhanced pattern;
- - with this disease, there are no areas of pigmentation, itching is mild, there are no atrophic changes in the changed areas of the skin;
- diabetes mellitus - the tissues of the vulva are inflamed, swollen, pasty, itching is severe;
- lichen planus - with this disease, the rashes are papular, multiple and prone to grouping, after opening the papules, areas of atrophy or sclerosis form on the skin with the formation of cicatricial changes.
If a skin disease is suspected, a woman is advised to consult a dermatologist.
With the development of psychoneurological disorders in a woman, a consultation with a psychotherapist is prescribed.
Treatment
All patients with vulvar leukoplakia are subject to dispensary dynamic observation by a gynecologist or oncologist (in the presence of a malignant lesion). To monitor the condition of leukoplakia sites, such examination methods as cytological analysis and colposcopic examination are mandatory.
The tactics of treating vulvar leukoplakia depends on the degree and nature of changes in the vulvar mucosa and is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease and preventing the degeneration of plaques in. On the early stages disease, the patient is prescribed long-term complex conservative therapy, which requires constant medical supervision and monitoring of its effectiveness (according to the results of the tests).
Conservative therapy
For conservative treatment of vulvar leukoplakia, the patient is recommended:
- taking medications;
- proper hygiene measures;
- dieting;
- physiotherapy procedures.
Medical therapy
To eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease are prescribed:
- local preparations to eliminate inflammation: Baneocin, Elidel cream, Beloderm ointment, Dermovate ointment, Clobetasol propionate, etc .;
- local preparations to eliminate itching: Akriderm, Sinaflan ointment, Beloderm, Triderm, Celestoderm, Progesterone cream, etc .;
- : Tavigil, Loratadin, Clarisens, Fenkarol, etc.;
- local hormonal preparations: Estriol cream, Progesterone cream, Testosterone propionate ointment, etc.;
- antibacterial agents for local application(for secondary infections): Levomikol, oil solution Chlorophyllipta, 5% Synthomycin liniment, Synthomycin suppositories, Chlorhexidine emulsion, etc.
For general strengthening body and improve the condition of the mucous membrane, it is recommended to take vitamin-mineral complexes.
If it is impossible to eliminate itching of the vulva medications for external use, novocaine vulvar blockades and radio wave puncture are prescribed skin vulva.
At severe inflammation and secondary infection, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs in the form of tablets or injections can be prescribed. If necessary, drugs for immune correction are prescribed.
Patients with psychoneurological disorders are assigned psychocorrection classes and taking antidepressants and tranquilizers.
Hygiene measures

- Avoid overheating of the body.
- Do not wear synthetic or tight-fitting underwear.
- Avoid sun exposure.
- Refuse to take hot baths, saunas and baths.
- For washing, do not use antiseptic solutions and soap that dry out the skin, but use boiled water with the addition of soda (to soften) and decoctions of herbs (chamomile, calendula, nettle, sage).
- Do not douche.
- Avoid using synthetic pads and tampons.
Diet
- drinking alcohol and smoking;
- intake of fatty smoked, spicy dishes, black tea and coffee.
IN daily diet Vitamin-rich (especially vitamin A) and mineral-rich vegetables, fruits, lean meats, cereals, and dairy products should be included.
Physiotherapy
For anti-inflammatory and desensitizing effect are prescribed:
- phonophoresis with drugs;
- modulation of brain rhythms;
- radio wave treatment;
- magnetophoresis;
- sonophoresis;
- laser phoresis;
- darsoval;
- balneotherapy;
- transcutaneous laser blood irradiation;
- physiotherapy.
Surgery
Need surgical treatment determined by the indicators of analyzes and the effectiveness of conservative therapy. To eliminate foci of leukoplakia, the following can be used:
- excision of areas of leukokeratosis of the vulva with a scalpel or radioknife;
- removal of foci of leukokeratosis using cryodestruction;
- removal of foci of leukokeratosis using laser ablation;
- extirpation of the vulva (performed with signs of degeneration into cancer).
With signs of degeneration of the tumor into a cancer patient after surgery, courses of radiotherapy are prescribed.
Prevention
Prevention of leukoplakia consists in regular preventive examinations And timely treatment inflammatory diseases, hormonal disruptions and metabolic disorders.
Which doctor should I contact?
When the first signs of vulvar leukoplakia appear, you should consult a gynecologist. If necessary, the doctor may recommend consultations with a dermatologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist and oncologist.
