CT of the abdominal cavity with contrast that shows. CT and MSCT of the abdominal cavity
Examination methods based on the physical effect of X-rays on human tissues are widely used in clinical practice for the diagnosis of many pathologies. With the development of technology, there is an improvement in the available diagnostic methods - the examination becomes more comfortable and safe for the patient, and more informative for the doctor. The most popular radiological diagnostic methods at the moment are CT and MSCT - the studies are very similar in terms of the principle of scanning, however, there is a significant difference in the design of the devices.
Multislice computed tomography
Multislice computed tomography(MSCT) is a type of CT. Scanning is carried out on advanced equipment and has a lot of advantages over conventional computed tomography due to an extended list of settings - the specialist has the ability to adjust the scanning parameters, adjusting to each specific clinical case. This allows you to get high-quality images desired organ, which will display the smallest features buildings.
Features of multislice computed tomography
MSCT is based on the ability of X-rays to reflect differently from body tissues depending on their density - physical principle scanning is no different from a conventional CT scan. main feature The device for multispiral tomography consists in the location of X-ray tubes inside the device - sensors that emit ionizing radiation are located around the circumference of the installation. During scanning, the MSCT machine rotates around the couch with the patient, while the couch itself moves horizontally inside the tomograph. If you follow the paths of the sensors around the patient, you get a dense spiral - based on this, the study was called a spiral computed tomography(SKT, or MSCT), and the tomographs themselves are called multidetector.
One turn of the MSCT machine is enough to scan one selected area - this has significantly reduced the examination time. For example, for the study of organs abdominal cavity it only takes a few seconds, unlike a conventional CT scan, which takes at least 15 minutes. This achievement made it possible to significantly expand the list of indications - the study can be carried out in patients who find it difficult long time lie still in an enclosed space, e.g. children, the elderly, claustrophobic patients. The same applies to patients on life support devices, suffering from severe somatic diseases, as well as emergency patients. The modernized device of the tomograph for SCT made it possible to make the examination almost silent, and therefore more comfortable for the patient.
When performing SCT, a specialist can choose the required cut size himself, while modern tomography makes it possible to scan with a minimum cut of up to 1 mm, which makes it possible to identify the smallest pathological formations.
In addition to the above, by reducing the scanning time during MSCT, the radiation load on the patient is reduced - the dose of X-ray exposure during SCT is almost 30% lower than during conventional CT. Given this factor, spiral CT has significantly fewer contraindications - the study can be used in childhood.
The technique of contrasting has also changed - when performing SCT, a smaller amount of contrast agent is required. The introduction of contrast is carried out using an automatic injector built into the machine for tomography and is called bolus contrast. This technique allows better tracking of the dosage of the administered drug and significantly reduces the burden on the patient's kidneys.
When performing CT, the doctor receives more information than with conventional CT, while spending much less time on the study. Due to the fact that the images are taken in different planes, the most accurate images are obtained that convey in detail all the structural features of the organ.
Indications for MSCT
CT scan of the spine
In most cases, CT is prescribed to diagnose the condition of bone structures - the skull, spine, limbs. X-rays are well absorbed by bone tissue, resulting in a clear three-dimensional image that can be viewed from all sides. SCT is prescribed for the diagnosis of traumatic injuries - fractures, microcracks, as part of an oncological examination to detect neoplasms and metastases. In addition, the method allows diagnosing diseases of hollow organs - the stomach, intestines, lungs. In many cases, CT scanning is performed for differential diagnosis in cases where other methods of examination have not shown exact result. Sometimes SCT is prescribed after CT to clarify the location, size and structure of the identified neoplasm.
Compared to conventional CT, CT allows better visualization of:
- Neoplasms of small sizes - up to 1 mm.
- Hemorrhages in the brain, hematomas in soft tissues.
- Diseases of the pancreas, liver, gallbladder.
- Pathology of the aorta and its branches.
Which is better - CT or MSCT?

The multislice computed tomograph has a number of advantages over the tomographs of the previous generations.
Computed tomography is one of the most progressive, rapidly developing diagnostic methods today. Every year more and more modern devices come into operation, new methods of work, subspecies this survey, which help to get rid of the shortcomings of CT, while maintaining the considerable advantages of this method. These include, in particular, spiral and multislice computed tomography. What is the difference between CT and MSCT or CT?
What is SKT?
SCT, or spiral computed tomography, is a separate area of computed tomography, the peculiarity of which lies in the mechanism of the tomograph itself. The X-ray emitter in it continuously rotates, simultaneously with translational movements the table on which the patient is fixed. When turning, the mechanism describes a spiral segment around the patient. This method explores not a specific slice, but the whole area at once. It has a fairly high speed, and also has a low radiation dose.
A similar method is used to examine patients who have severe injuries, including those that may interfere with holding their breath, with pain syndrome and so on, as well as for children under 12 years old, if it is vital for the child to undergo a CT scan, for virtual endoscopy and other similar manipulations. SCT allows the doctor to obtain an image in any plane, not just the frontal one, and create a three-dimensional image of the examined organ. This method does not have absolute contraindications and has great practical value.
What is MSCT?
MSCT (deciphering - multislice computed tomography) is another type of traditional CT. Multislice CT allows you to quickly assess the prevalence of the pathological process and its localization, even if the patient is in serious condition. A huge advantage of this method is its high speed: the MSCT device allows you to make a diagnosis in a matter of minutes, much faster than a CT scanner.
In addition, MSCT provides a noticeable improvement in the quality of the overall image, both with and without contrast enhancement. This diagnostic method has a large anatomical coverage area and provides minimal radiation exposure. When examining the abdominal cavity, the position of the organs, their size, structure, the presence of pathological formations, the condition of the bile ducts, lymph nodes, the presence of fluid are assessed - which is shown by MSCT of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space. In addition, MSCT of the abdominal aorta makes it possible to assess the state of blood flow in this area.
Are MSCT and SKT harmful?
One of the main reasons why patients are often afraid of CT examinations is the likely harm of this diagnostic method. CT does have Negative influence on the body, although not at all as critical as they sometimes write about it - by no means 500 times more than an x-ray; you can safely undergo 2 examinations on a CT scanner a year without risking anything. However, for this reason, CT is not always available - children under 12 and pregnant women try not to prescribe this method.
However, sometimes it is impossible to replace CT with magnetic resonance imaging or ultrasound, and the study becomes a matter of life and death. In this regard, spiral or multislice tomography has become a real find - they are not completely devoid of radiation exposure, but they significantly reduce it. So the question of how often MSCT / SCT can be done is not so popular - this method allows more frequent use. If necessary, MSCT will be practically not harmful to the child. But during pregnancy, MSCT and SCT still prefer not to prescribe without the most extreme need, when the life of the mother can be in serious danger.
MSCT and CT with bolus contrast
Both methods, with their inherent high accuracy, can be even more efficient. For example, when searching for oncology, maximum power is required to be able to find even the smallest, up to 1 mm, formations or metastases. A picture of MSCT of the abdominal cavity, enhanced with contrast, allows you to view the area under study in great detail, which few other diagnostic methods provide. Deciphering the MSCT image is carried out by a specialist after tomography, it allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and condition internal organs.
Contrast in this case has exactly the same contraindications and limitations as for conventional computed tomography. In particular, the contrast agent is not suitable for patients who are allergic to iodine in any form, as it is essentially an iodine preparation. A relative contraindication may be renal failure (this feature of the body may interfere with the withdrawal of the contrast agent after the examination), thyrotoxicosis (increased levels of thyroid hormones), or diabetes. The price of MSCT of the abdominal cavity with contrast will be slightly higher than usual.
Preparation for the examination
Multispiral computed tomography of the abdominal cavity requires restriction of food intake, which can provoke gas formation - for example, carbonated drinks, bread, legumes, and so on. It is advisable to take a drug before the examination that will help reduce gas formation - for example, it can be a regular Activated carbon, - and an antispasmodic, which will help relax smooth muscles. All this will allow the intestines not to swell and not strain, obscuring the rest of the organs.
Before MSCT of the abdominal cavity with contrast is performed, the patient must wait several hours without eating and drinking, it is highly recommended to exclude smoking. It is also advisable to pre-test for the absence of an allergy to the drug, if there are no such data. How MSCT with intravenous contrast is carried out should be monitored by a doctor so that, if any negative reactions on the drug, give immediately medical care patient.
Indications of MSCT of the abdominal cavity
For MSCT and SCT, the following factors are indications:
- injuries that may affect the abdominal organs;
- urolithiasis disease;
- anomalies in the development of organs;
- adrenal hyperplasia;
- kidney damage;
- diseases of the urinary and biliary tract;
- abscesses, cysts;
- fatty degeneration or cirrhosis of the liver;
- pancreatitis, other lesions of the pancreas;
- diseases of the spleen;
- hepatomegaly;
- other diseases of unknown etiology.
Where can I do MSCT and SKT in St. Petersburg and Moscow
Clinics that perform spiral and multislice computed tomography are not present in every district of St. Petersburg and Moscow. These include the medical centers "TsMRT", "Road Clinical Clinic" and some others. Where to undergo MSCT of the abdominal cavity in St. Petersburg / Moscow time, you can find out in the appointment service, as well as how to clarify prices, the age of patients received or sign up for an examination.
Modern methods diagnostics involve the use of devices that allow, without a negative impact on a person, to recognize the disease even at initial stage its development.
More recently, magnetic resonance imaging was considered the most popular. However, today more than new technique, which is not yet very popular, but quite informative and safe. This is a spiral computed tomography (SCT).
The principle of this method
What is SKT. This method at first glance is a conventional computed tomography.
Spiral computed tomography is divided into two types:
- single-cut, giving only one layer;
- multilayer, allowing to reconstruct simultaneously up to 64 tomographic layers.
First of all, this technique is aimed at determining the problems associated with the human bone-articular system - the skull, limbs,.
It is rarely used to detect pathologies in soft tissues.
Operating principle this method Diagnosis is based on scanning the body using x-rays. They, in turn, after the stage of conversion into electrical impulses, are fed to a computer monitor for further study.
In this examination, a special table is used, on which the patient must be in a supine position. At the time of the study, the table moves synchronously relative to the course of the tube, which performs rotational actions in relation to the body. The speed of rotation of the table will directly depend on the goal of diagnosing. Such an CT scanner makes it possible to visualize neoplasms up to one millimeter in size. This is enough important indicator in the presence of cancer. It is necessary for the timely elimination of the lesion.
Within three to five minutes, one area of the body can be examined. On average, the entire procedure can take up to thirty minutes. The results are then printed as snapshots.

Physiotherapy
The order of the procedure
4 hours before the start of the process, it is necessary to exclude food and water from the diet.
When examining certain organs, the patient is encouraged to undergo training. Its essence lies in the intake of urographin by patients. In more detail, how to prepare for the procedure, the specialist appointed to conduct the study will tell.
Dinner should be light, and it is better to use liquid porridge and juice as breakfast.

The patient is placed on a table that drives into a special tunnel - a scanning device. To make the patient more comfortable, the table is equipped with special pillows and belts. They are designed to limit movement during the procedure. This will allow you to take clear, high-quality pictures.
- the ability to obtain ultra-thin sections, due to this, the quality of the images increases;
- diagnostics takes little time, which is important, especially in emergency situations when the fastest possible diagnosis is important;
- the degree of security at a high level;
- you can get three-dimensional images and design pictures;
- the method provides more information than conventional computed tomography.
- small, but harmful exposure to the body; its level can be compared with the dose that a person receives from environment for three to five years;
- possible allergic reactions to a contrast agent that contains iodine;
- SCT examination for children can be carried out only from the age of seven;
- the method is not acceptable during pregnancy, and also prohibits breastfeeding within a day after the use of a contrast agent.
- liver;
- gallbladder;
- pancreas;
- kidneys;
- spleen;
- pelvic organs.
- The patient is intolerant to the contrast agent.
- The patient cannot for a long time hold breath.
- There is no possibility for taking a prone position.
- Large body weight.
- The child is under seven years of age.
- Claustrophobia.
- Pregnancy period.
- Effusion in the pleural cavity.
- dizziness
- Do you sometimes see goosebumps in your eyes?
- Pain in the back of the head or just presses
- Neck pain or heaviness

If the patient cannot be motionless for a long time (for example, children) or suffers from claustrophobia, he is given a sedative.
In the office next to it is a computer station, where a doctor-technologist works. It is he who controls the scanner, conducts a conversation with the patient and says what needs to be done at one time or another.
The SCT procedure is considered quite safe, despite the fact that the patient receives a small fraction of radiation. But because of its insignificance, it does not harm the body. There may be a risk when using a contrast agent or sedative medication. If there is an allergy to drugs or iodine, the patient should without fail notify the doctor.
If you have conditions such as asthma, diabetes, kidney failure, heart problems, or thyroid gland, the patient is also obliged to tell the doctor about it.

X-ray diagnostics
Advantages and disadvantages
Such a technique as spiral computed tomography has the main predominant advantage - it is high efficiency and speed of diagnostic testing. However, it also has a number of disadvantages.
WE RECOMMEND!
For the treatment and prevention of BACK PAIN, our readers use the increasingly popular a method of fast and non-surgical treatment recommended by leading Orthopedists of the country. After carefully reviewing it, we decided to offer it to your attention.
Advantages of SKT:
Despite the range of important positive qualities, SKT has a number of certain disadvantages with risks, among which are:
The minus of the procedure is its low accessibility. Not in all yet medical institutions it is possible to propose such a method. In addition, it is an expensive diagnostic.


Pain in the chest and chest
Diagnostic options
Spiral computed tomography received its wide application when examining organs such as:
The advent of SCT provides more opportunities to determine the presence of stones, for example, in the kidneys and makes it as easy as possible to make the correct diagnosis.
This diagnostic method is also indispensable in the study of ongoing changes in sclerosis and tuberculosis.
The procedure is also used in situations where it is necessary to scan the eye areas, fragments of the face and sinuses. The tomograph makes it possible to detect with great accuracy violations of these organs and the presence of foreign bodies in them.
Among ENT doctors, this procedure is also quite common. It allows to detect pathology temporal bones, paranasal sinuses and auditory canals. This is one of best practices examination of these organs of the human body.
It should be noted that SCT is always used by traumatologists. This allows you to quickly visualize complex injuries of bone tissues or internal organs, as well as in the diagnosis of cranial injuries and cerebral hemorrhage.
Diagnosing the spine with this method helps to determine the presence of even the most minor deviations in the structure of the bones.
It is important to remember that the determination of the need for an SCT study should only be determined by an experienced physician who is able to see the overall picture of the state of health.
Results
After completing the diagnosis with spiral computed tomography, the radiologist begins to study the analysis data and decipher them. All information received as a result of the survey is processed along with the available medical documents. Big Picture compared with the obtained results of SCT, a diagnostic report is written and scans are printed.
The time taken by these events ranges from thirty minutes to several hours. After completing the complete processing of the data, the radiologist issues a conclusion with his signature.
Significant contraindications
The use of spiral computed tomography is contraindicated in the following cases:
Before the study is carried out, it is necessary to consult a specialist. This is necessary so that the doctor can determine the presence of any other individual contraindications that the patient may not be aware of.
However, at the same time, there are no absolute prohibitions for the procedure, so it can be applied to each patient.
In order to prevent SCT, in no case is it carried out by pregnant women and children under the age of sixteen.
This method opens up new opportunities for modern medicine and allows you to take diagnostics to the next, higher level.
If you have symptoms such as:
With a probability of 99.9% you have NECK OSTEOCHONDROSIS, here's what about it says Professor Bubnovsky in his interview. Until you treat the cause of your suffering, all these symptoms will continue to increase over time until they lead to more grave consequences, because all this happens due to a violation of the blood supply to the head, which means that the consequences can be deadly.
If necessary, assess the condition of the structures nervous system, doctors are increasingly prescribing CT scans of the brain.
Spiral computed tomography is fast, safe and exact way detection of various pathologies. In emergency cases, it is used to quickly assess the extent of internal injuries and bleeding, often this is what saves lives.
 Spiral computed tomography has been known since the late 80s of the XX century, when the first spiral tomographs well-known company Siemens began to be used in medical diagnostics. Over the past three decades, hardware systems have been significantly improved. The diagnostic result largely depends on the number of detectors, and the first devices had only two sensors. Tomographs of the second generation were already equipped with 30-50 sensors. In order for them to simultaneously receive a signal, a new volumetric form of the X-ray beam in the form of a wave fan was also developed.
Spiral computed tomography has been known since the late 80s of the XX century, when the first spiral tomographs well-known company Siemens began to be used in medical diagnostics. Over the past three decades, hardware systems have been significantly improved. The diagnostic result largely depends on the number of detectors, and the first devices had only two sensors. Tomographs of the second generation were already equipped with 30-50 sensors. In order for them to simultaneously receive a signal, a new volumetric form of the X-ray beam in the form of a wave fan was also developed.
Third-generation SRCT devices already used from 300 to 500 sensors, and in subsequent years, in the fourth generation, their number increased to 5000.
Later, improved methods of multilayer computed tomography (MSCT) appeared, where many detectors are located in several rows, which significantly improved the resolution of the device and accelerated the examination.
The development and creation of devices for spiral CT is extremely expensive and high technology. From the very beginning until today, Siemens has been a leader in the development and implementation of helical tomographs.

Any CT scanner uses x-rays to scan. The most significant advantage of helical CT is that many more 3D images of the scanned area can be obtained per unit of time.
The table on which the patient is placed slowly slides along the scanning axis. At the same time, a round coil, in which an X-ray source is mounted, rotates around the subject. The tissues of the human body have different densities and therefore absorb x-rays differently. Sensors installed in the scanner register these differences, and computer program immediately processes the data and displays the result as a picture (snapshot).
The size of the area of the body that can be scanned depends on the speed of the movement of the table on which the patient lies motionless. With spiral tomography, this speed can be very high. It can be adjusted depending on the objectives of the survey. Thanks to this, CT allows for high-quality diagnostics in a very short time.
Is SKT safe? Certainly yes. Conventional X-ray examination is associated with a much higher radiation dose. How newer device for scanning, the safer it is for the subject.
Application of SCT in clinical practice
What is SCT in medicine and how is it used in clinical practice? Since a modern multilayer computed tomography device can produce 64-layer images with high speed and accuracy, doctors actively use this diagnostic method when it is necessary to quickly locate and assess the size of a pathology focus, for example, in the lungs. SCT is able to detect even small neoplasms in internal organs that will not be visible on other tomographs.
This makes it possible to detect pathology in as soon as possible and immediately start treatment even at those stages of the disease when not all symptoms are visible. Time may be the deciding factor for successful multiple therapy serious pathologies(eg lung cancer).
SCT is used in the diagnosis of diseases of almost all internal organs and systems, including the nervous system.
Spiral computed tomography of the brain can be performed with contrast. In this case, before the examination, the patient should drink special solution to improve the quality of imaging, or contrast is injected into a vein.
After the injection, the patient may experience a feeling of heat throughout the body, but this is not at all dangerous and passes quickly. Tomography is carried out without the introduction of a contrast agent (screening method). If there is no suspicion of a tumor and an urgent examination of a patient is necessary, for example, one who has received a head injury, then contrast is not used. Further screening can be used to track the dynamics of development pathological changes, evaluating the effectiveness of drugs.
Contrast may be required in the detection of brain cancer, blood vessel malformations, or the diagnosis of an aneurysm.
The use of the technique in certain pathological conditions
A neurologist may refer you for a spiral CT scan of the brain in the following cases:
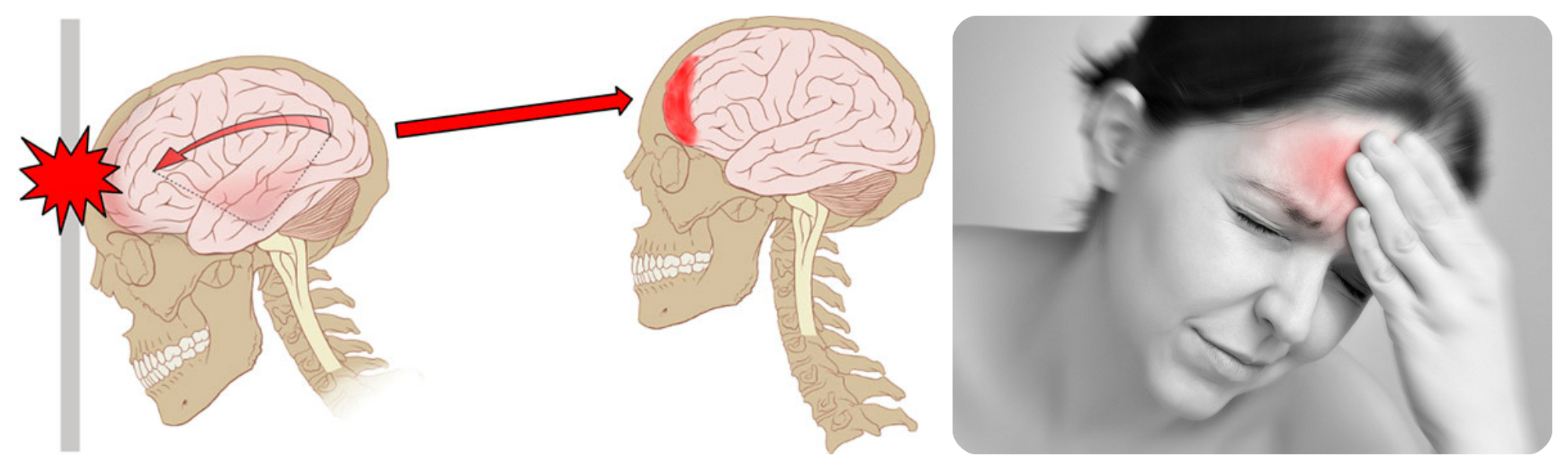
- headaches of unclear etiology, tinnitus, dizziness at rest and when turning the head;
- concussions, bruises of the brain, other craniocerebral injuries;
- suspected neuroinfection;
- neoplasms of the lungs, eyes and ENT organs;
- problems with cerebral circulation, vascular pathology;
- developmental disorders of the nervous system.
In oncological practice, spiral CT is indispensable for:
- confirmation of the oncological diagnosis;
- cancer staging;
- clarification of the localization of formations before the biopsy procedure;
- evaluating the possibility of radiotherapy or surgery;
- treatment control;
- detection of disease recurrence.
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity and chest area is also widely used.
The accuracy of the tomograph is enough to detect even minor pathological processes in bone tissue, ligaments, intervertebral discs.
Spiral CT has proven to be effective in diagnosing:
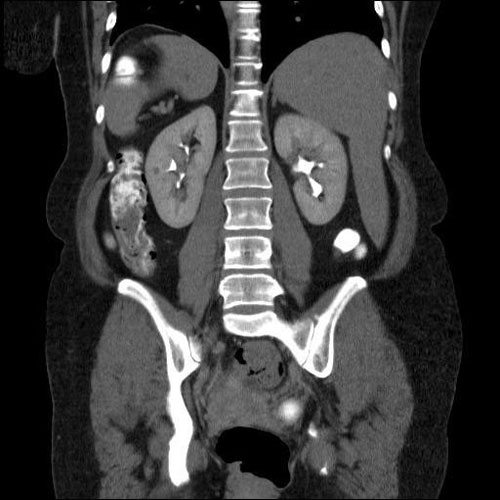
- rupture of the spleen and other abdominal organs;
- urolithiasis;
- congenital anomalies of the retroperitoneal space;
- pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lungs).
Pathological processes in bone tissue are also successfully visualized using SCT, which is why it is used in the diagnosis of diseases of the spine and other parts of the skeleton.
Since CT has a very high resolution, such an examination will help to see the pathology that will go unnoticed when using conventional methods tomography.
Preparation and contraindications
Preparation for the study is quite simple.
- do not eat or drink at least 3 hours before the study;
- do not drink alcohol for 24 hours;
- stop smoking 4-5 hours before the start of the examination, especially with CT of the lungs;
- if the study is carried out with contrast, it is necessary to take in advance special blend, which you will be given or told to purchase at a pharmacy. In some cases, contrast is injected into a vein just before the procedure;
- first of all, undergo an ultrasound or MRI (depending on the recommendations of the doctor) and take the conclusions with you;
- Notify staff of existing allergies to medical preparations or signs of claustrophobia;
- dress comfortably, you may also be asked to wear a hospital gown;
- leave at home or remove all metal objects, including jewelry, glasses, dentures, before the examination, as they may affect the operation of the scanner.
There are also a number of contraindications:
- pregnancy;
- the presence of pacemakers;
- schizophrenia, depression and other psychopathologies;
- inability to ensure immobility;
- age up to 4 years;
- intestinal hyperpneumatization, effusion into the pleural cavity;
- allergy to iodine or other components of the contrast agent;
- overweight.
For children and patients who find it difficult to remain still during the scan, the doctor may prescribe sedative medications before the examination begins.
What Happens During an Examination
skt is pretty simple procedure. The patient is placed on the scanner table. When the examination begins, the table moves smoothly and progressively inside the round coil, where the sensors and the emitter are located. Depending on the goals and object of the study, the patient may be asked to take a certain position on the table.
As with x-rays, the doctor may ask you to hold your breath for a while so that the images are not blurry. The computer that processes information from the scanner is installed in a separate room behind glass, where the staff is located during scanning. The doctor and patient communicate using a public address system. If examined small child, the parent may be allowed to be present in the test room if they wear a lead protective apron.
In very rare cases, CT contrast agents may cause allergic reactions. Some people may experience slight itching or hives (small red bumps on the skin). More serious symptoms allergic reaction include shortness of breath and swelling of the throat or other parts of the body.
The patient should inform the staff immediately if any of these symptoms appear. Very rarely, contrast media can cause kidney problems in some patients. CT is a painless procedure. Inconvenience can only be caused by a long stay in a fixed position.
The duration of the CT scan depends on the size of the scanned area and usually takes from a few minutes to half an hour. Some patients fear that they will experience claustrophobia while in the scanner. However, most modern tomographs do not surround the entire body, but only part of it.
The radiologist who conducted the study issues and describes the results of the study. And the attending physician who sent for this examination is responsible for interpreting the data, making the final diagnosis and prescribing treatment. Usually detailed description v paper form and a picture on a CD is given to the patient within a short time (from 1 hour to 2-3 days).

Despite all the advantages, SCT has a number of disadvantages. This safe procedure, but it is still associated with some exposure. According to medical estimates, exposure in one diagnostic session is approximately equal to the dose that a person receives in 3-5 years in the natural environment.
To control exposure, the doctor performing the tomography should make a note on the patient card about the dose received during each scan, indicating the date of the procedure.
The contrast agent can adversely affect the development of the fetus and newborn, so the use of SCT for pregnant and lactating mothers is limited.
The contrast mixtures used contain iodine, which can cause allergies. The need to remain still during the study makes it difficult to use for children under 6 years of age. Another limitation is the impossibility of using SCT for people weighing more than 150 kg (the maximum load on the movable table of the scanner depends on the type of tomograph).

These two methods are based on completely different physical phenomena. When scanning, an MRI machine generates an electromagnetic field around the patient, while CT uses X-rays. MRI is suitable only for studying soft tissues, and spiral tomography is also suitable for diagnosing diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
These methods differ in cost. average cost SCT in Russia is 5,000 rubles, and an MRI will cost a little more. The price depends on the qualifications of the staff, the level of services provided, the type and age of the equipment. When contrast is used, the price of the procedure increases.
Thus, today SCT is an indispensable technique for visualizing neoplasms and other foci of pathologies with a high degree detail. At the end of the examination, the patient receives high-contrast images of organs and systems on a CD, according to which the doctor can diagnose not only the type, but also the extent of disorders and prescribe treatment.
Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify pathological processes and changes in human body in the early stages, which means that they increase the effectiveness of treatment. Among the high-precision methods of research include spiral computed tomography. What is it, and when is this procedure indicated, what are the contraindications for diagnosis? How is it different from conventional computed tomography and MRI?
What is SCT in modern medicine?
In medicine, this type of study, like MRI, is used for a relatively short time - less than 30 years. When conducting a spiral computed tomography, the patient's body is scanned using x-rays. The latter are transferred to the monitor for analysis after being converted into electrical impulses. The main feature is that both the table on which the patient lies and the tube rotate during the scan. This technique allows to detect neoplasms up to 0.1 cm in size.
What organs and systems are examined?
Spiral computed tomography - effective diagnostic method, which can be used in the study of almost any human organs and systems. Due to the minimum thickness of the section, it reveals the most insignificant pathological changes in the body, allowing you to make a diagnosis on early stage and start therapy promptly. Not always effective when examining soft tissues.

It should be borne in mind that, from a theoretical point of view, helical computed tomography can be used to examine any patient, since it has no absolute limitations.
However, there is a list of conditions in which its implementation is not recommended and is possible only after an assessment by the attending physician of the ratio of potential benefit and probable risk. These contraindications to SCT include:
- effusion in the pleural cavity;
- pregnancy (in this case, it is better to conduct an MRI);
- fear of closed space;
- children's age up to 7 years;
- body weight exceeding that specified by the manufacturer of the device as acceptable;
- absence physical ability to take a lying position;
- the patient cannot hold his breath for a long time;
- there are mechanical devices in the human body (for example, a pacemaker is installed in the heart);
- with individual intolerance to the contrast agent.
Conducting spiral computed tomography is acceptable in the diagnosis of pathological changes in almost any human organs and systems. If the patient complains of headaches, visual disturbances, loss of sensation in the limbs, clouding of the mind and consciousness, or unexpected paralysis occurs, then a spiral CT scan is recommended. CT scan of the brain is indicated in the following cases:
- vascular damage;
- pathology of the lymphatic system;
- suspicion of pathological processes in the structure of the lungs;
- assessment of brain damage in case of suspected acute stroke;
- pathology of the auditory canals, temporal region of the skull, nasal sinuses;
- increased ICP;
- to confirm / refute a brain tumor;
- traumatic brain injury;
- neurotic disorders;
- anomalies in the development of the child are also a reason to conduct an CT scan of the head;
- deformation inner ear, which provoked a decrease in the level of hearing;
- epilepsy (epileptic seizures are also an indication for an CT scan of the brain).
Differences between spiral computed tomography and MRI and CT
SCT and MRI are methods for examining internal organs and systems that differ in 3 important features:
- principle of operation - an electromagnetic field is used in MRI diagnostics, X-rays are used in CT;
- informative - MRI is used to study soft tissues, SCT - in most cases, to examine solid bone structures;
- the time of the procedure - MRI can last up to one and a half hours, a spiral study lasts a few minutes on average.
Both CT and conventional computed tomography are types of x-rays. The basic principle of operation is almost the same - a layer-by-layer scan of the body or a separate organ is carried out. However, there is a difference between them. The main difference is in the thickness of the cut. While CT has a minimum thickness of 10 mm, CT allows a more accurate picture due to the thickness of the layers of about 3 mm. This is achieved due to the fact that the table with the patient enters the apparatus smoothly (with CT this happens step by step, while the “step” is 1 cm), and the radiation source rotates around it in a spiral.
Research stages
 Conducting spiral tomography, taking into account the time spent on the preparation, processing of data, the formation of prescriptions and recommendations by the radiologist, takes no more than 4 hours. No special preparation is required. The patient is recommended to undergo preliminary MRI and ultrasound, and 4 hours before the study, you can not eat, drink and smoke.
Conducting spiral tomography, taking into account the time spent on the preparation, processing of data, the formation of prescriptions and recommendations by the radiologist, takes no more than 4 hours. No special preparation is required. The patient is recommended to undergo preliminary MRI and ultrasound, and 4 hours before the study, you can not eat, drink and smoke.
Stages of CT diagnostics:
- administration of contrast (intravenously or orally);
- placing the patient on a mobile table (since it will be necessary to lie still, in some cases the doctor prescribes sedative medications);
- the table drives inside the gantry - “pipes” (the radiation source rotates along a spiral path);
- a scan is performed (usually the procedure takes from 5 to 30 minutes);
- information is displayed on a computer monitor (if desired, it can be recorded on a portable device);
- the radiologist deciphers the result of the diagnosis and issues a referral for a consultation with narrow specialists.
An CT examination is completely painless and may cause minimal discomfort associated with being in a confined space.
If an abdominal examination is performed or chest the patient will need to hold their breath for a while.
In order for the interpretation of the results of the study to be as accurate and reliable as possible, you need to provide the radiologist with your medical card or the conclusion of the attending physician indicating the preliminary diagnosis. Then the doctor will be able to take into account all previous diseases and injuries, individual characteristics structure of the patient's body.
What does the picture show?
What does the picture that the doctor receives as a result of the procedure show? It allows you to visualize injuries to bones and internal organs, determine the state of lymphoid tissues, identify a tumor, and diagnose pathological processes of both acute and chronic course. The study also makes it possible to monitor the patient's condition in dynamics and thus evaluate the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
For example, when examining the kidneys, it is possible to identify not only malignant or benign formations in their structure. Polycystic kidney disease, abscesses, developmental anomalies are also diagnosed. Renal tomography is indicated in postoperative period(if a transplant or removal was performed), as well as with an organ biopsy.
How much does SKT cost?
The average cost of a spiral computed tomography in Russian clinics is 5 thousand rubles. For scanning one organ, you will have to pay from 4 thousand rubles, while the diagnostics of the whole body costs three times as much - about 13 thousand rubles. The price may vary depending on the region, the qualifications of the specialist and the equipment itself - the results of the study on the latest generation tomograph will be more accurate, but it is more expensive.
