The result is monitoring of preschoolers in physical culture. Explanatory note
Organization of a monitoring system in a preschool educational institution for physical development
CHARACTERISTIC OF PEDAGOGICAL MONITORING AS A CONTROL METHOD
Creation of monitoring within construction pedagogical process- an urgent need for modern preschool education... The use of this technology as the main method of monitoring the effectiveness of the development, upbringing and education of children allows you to fully implement the most important humanistic principle "Do no harm!" teaching activities, predict it further development... Monitoring as a method of control is ethical, since it does not "look for the guilty", it is psychological, as it helps to increase the level of staff motivation through a clear vision of ways to solve problems and creates a sense of confidence in the success of actions. It is pedagogical, since it helps to unite teachers around the main goals by including them in analytical, diagnostic and design activities, which is one of the most important functions of managing the development of a preschool educational institution. Pedagogical monitoring is a stronger medicine than educational standards. It allows not only to quickly track the process and dynamics educational activities, but also to correct it in a timely manner if possible negative impact on the health and mental development of the child. In addition to health technologies, the use of the monitoring method allows you to approach the goal in the shortest possible way. The main goal of psychological and pedagogical monitoring is the timely correction of educational and health-improving activities, as well as the environmental conditions of a preschool educational institution to prevent possible adverse effects on the health and psychological well-being of children. But, in addition, monitoring allows you to identify the most efficient technologies and methods of physical education wellness work with kids. At the same time, it should be noted that monitoring gives results only in those institutions that have the characteristics of a dynamically developing preschool institution. These characteristics are: high level organizational and pedagogical culture, developed pedagogical self-government and the presence of creative space.
Relevance this issue suggests a result activities of preschool educational institutions as a complex change in the personality of the child.
The purpose of the methodological development is the mechanisms for organizing monitoring at the preschool educational institution for the health and physical development of pupils.
Tasks: Reveal the content of monitoring physical development and raising children in preschool educational institutions; Determine the criteria for assessing the professional competence of teachers in the health and physical development of children in preschool educational institutions; Determine the technology for monitoring health and physical education in a preschool educational institution.
This methodical development involves tracking the mechanisms for organizing monitoring in preschool educational institutions on the health and physical development of pupils, making decisions in the need for its planning, its effectiveness, improvement, as the latest of the achievements of pedagogical science and best practice.
Characteristics of pedagogical monitoring as a control method
It is customary to distinguish between two types of control: control of results and control of the process.
Monitoring results allows you to find out what was done from the planned, what remained unfulfilled, what results were achieved. In this case, the leader and educator gain experience by learning from their mistakes.
Process control makes it possible to identify whether there have been deviations from the activity, whether people and means were successfully selected, how rational the activity is, whether its time parameters are correctly determined.
Controlling a process can be more difficult than controlling results. Therefore, in practice, the latter is often preferred.
Researchers interpret that the control method at the moment it is optimal for assessing the quality and effectiveness of physical culture and recreation activities, because it does not allow to fully find out what led to such results, what and in what time period were observed deviations in activity and what will be the consequences of this activity.
Pedagogical monitoring allows you to achieve the optimal combination of control of the result and the process, contributing to the improvement of activities and its development. Its purpose is not simply to know how an activity is carried out and what its results are. It consists in creating a project for a new activity that expands the scope of the capabilities of the teacher and the preschool institution as a whole.
Thus, monitoring as a control method is not only saturated to the limit with knowledge about controlled objects, but also clearly includes research. It allows you to achieve the desired reflective result and, on this basis, develop guidelines for new practice.
Monitoring can be described as a path to accuracy in assessing performance. The choice of criteria and indicators largely depends on the degree of qualification of the personnel, the level of their professionalism, as well as on the level of organizational culture of the institution, the most important indicator of which is the ability of the team to adequate assessment their activities.
1 health conditions of children
2 diagnostics physical fitness preschoolers
3 professional competence of educators
4 quality of physical culture and health improvement work
5 continuity in work with parents
creating conditions for the physical development of children in preschool educational institutions
The purpose of monitoring physical education and development of children in preschool educational institutions:
Improving the quality of physical education and health-improving work with children.
At the first stage
Analyze and evaluate the effectiveness of work on the physical development of children, the incidence of children; evaluate the effectiveness of the educational process in terms of state standards of physical education of children; identify problems in the activities of a teacher for the physical development of children; to determine the level of pedagogical competence of educators in the use of health-improving and health-preserving support. In the second step: predict next steps teaching staff (on the methodological council, pedagogical council);
to develop measures to improve the quality of physical education and development of children, to strengthen their health. To do this, it is necessary to involve proactive teachers in this, create a creative problem group;
develop a work plan for the team, outline activities with teachers;
determine the effectiveness of the work done.
At the third stage:
implement planned activities;
carry out the correction of the pedagogical process;
eliminate the reasons that inhibit the reduction of morbidity and improve the health of children and their physical development.
At the fourth stage (intermediate diagnostic):
to compare the indicators of the physical development of preschoolers with the state standard;
to compare the incidence rates of children with the initial ones;
compare the analysis of the effectiveness of ongoing activities;
make management decisions to eliminate deficiencies in work.
At the fifth stage (final - diagnostic)
identify the assessment of the state of the monitoring objects. Namely: the state physical health children, morbidity assessment;
analyze the professional knowledge and skills of educators;
analyze methodical work(efficiency);
identify the effectiveness of management decisions;
to analyze the assessment by parents of the activities of preschool educational institutions for the physical development and upbringing of children.
All functions and stages of the monitoring process, that is, all its elements are structurally and functionally interconnected and represent a single cycle of pedagogical monitoring. The loss of any of these components makes monitoring ineffective.
Data collection for monitoring physical education
To monitor physical education and track the impact of its technologies on children's health, it is necessary for teachers to have an idea of the dynamics of physical development, development physical qualities and physical fitness, the quality of motor skills development, morbidity. (Based on the recommendations of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation).
Assessment of the physical development of children
The physical development of children is an important indicator of the state of health, which is characterized by a set of morphological and functional parameters caused by hereditary factors and environmental conditions.
When assessing the physical development of children, the following are taken into account:
Body length and weight, circumference chest, and in children under 3 years of age and head circumference;
Functional indicators: vital capacity of the lungs, endurance coefficient, muscle strength of the hands, etc.;
The degree of development of the subcutaneous fat layer, tissue turgor, muscle development, muscle tone, posture and musculoskeletal system.
The physical development of children is particularly affected by the influence external environment: unsatisfactory living conditions, lack of air, lack of sleep, inadequate nutrition, climatic features, improper daily routine, restrictions on physical activity. In this regard, the level of physical development is considered to be a vivid indicator of their health, living conditions and upbringing. The pace of physical development is influenced by hereditary factors, type of constitution, individual characteristics central nervous system, metabolic rate, etc. The physical development of children naturally changes throughout life.
Indicators of weight and body length increase unevenly, not only in different age periods but also in different seasons... A more intensive increase in body weight in children is observed in late summer and autumn, to a lesser extent - in spring and early summer. This is due to the improvement in metabolism due to the increase in the time children spend on fresh air greater motor activity, varied diet with inclusion enough fresh vegetables and fruits. The rate of increase in body length is more pronounced in spring and early summer, when increased ultraviolet radiation increases calcium-phosphorus metabolism and promotes intensive growth bones. An individual assessment of physical development is carried out by comparing anthropometric indicators child with regional standards. This allows you to identify deviations in physical development and take the necessary measures to improve their health. The use of standards makes it possible to conduct a group assessment of the physical development of a group of children in preschool and track the dynamics of indicators, as well as conduct comparative studies of children attending and not attending preschool institutions. In addition, the group assessment method allows you to determine the degree of effectiveness of various health and fitness technologies. Physical assessment can be done different methods... The most practiced is the method of determining biological age children.
Children are examined by medical workers at least twice a year.
Practitioners use tables of physical development, in which indicators correlate with the growth of children. People are not all the same: there are big, medium and small. There are formulas with which to determine future growth person. Knowing the future growth of the child (errors of no more than 3 cm in one direction or another), it is possible with a high degree of accuracy to attribute it to a certain group of children: large, medium, small.
When examining a child, for example, it may turn out that the indicators of physical development correspond to the average, and according to the data of his future growth, the child should have indicators corresponding to the column "large". Perhaps there is a delay in physical development. But in any case, such a conclusion can only be made by a pediatrician.
Standard average growth rates can be calculated using the following formulas:
Boy's height = 6 x age + 77;
Girl's height = 6 x age + 76.
Physical development data allow us to determine the number of harmoniously developing children, as well as children who have problems.
The results of the survey are discussed at a medical and pedagogical meeting. The data allow us to develop special health programs for children with deviations from the norm. For example, for children with low stature in the complex physical exercise swimming, jumping, hanging should be included, and their menu should include a lot of dairy products, carrots. If the child has excess weight body and at the same time no chronic pathology was found in him, that is, it makes sense to organize a special diet food with the introduction of gradually increasing physical activity. When he loses some weight, then you can include in the complex and strength exercises strengthening muscle mass... Of course, all this should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations and under the supervision of a physician. About condition cordially- vascular system can be judged by functional tests and indicators of physical performance. It is advisable that parents support the recommendations of the doctor and caregivers.
The proportionality of physical development is measured using the Pignet index (PI).
PI = Height (cm) - [Weight (kg) + Amb. gr. cl. (cm)]
The data obtained is verified against the indicators.
Standard indicators of the Pignet index in children preschool age
Age of children Boys Girls 3 years
31.1 31.0 4 years
34.2 34.7 5 years
36.5 37.0 6 years
The lower the Pignet index in children compared to the standard, the stronger their physique. Conclusion: using the indicators of the Pigne index, it is possible to draw certain pedagogical conclusions about the quality of physical culture and health improvement work and safely say that children have grown stronger, or, on the contrary, the quality of physical education leaves much to be desired.
The state of the cardiovascular system can be judged by functional tests and performance indicators.
When carrying out functional tests in children 4 - 7 years old normal performance are:
1. Increase in heart rate after 20 squats for 20 seconds by 25 - 40% of the initial data.
2. Increased breathing rate by 5 - 6 units.
By these indicators, we can also judge the degree of effectiveness of physical education in relation to the health of children. If at the beginning of the year the pulse rate of children increased by 45% under load, then, in principle, it corresponds to the norm. But three months have passed, and the indicators of functional tests are still the same. The conclusion suggests itself: purposeful activity on physical education children in this group or preschool educational institution as a whole are not conducted.
The positive influence of physical education on the development of physical performance can be tested using a step test. Children are offered two loads of increasing power.
climbing a step with a frequency of ascent 22 times per minute;
climbing a step with a frequency of ascent of 30 times per minute.
The duration of each load is 2 minutes, the rest between them is 3 minutes.
The amount of work performed by the child is calculated by the formula: W = P x n x h,
where P is the weight of the child, n is the number of steps per step per minute, h is the step height in meters. The norm is an increase in heart rate by 15 - 20% at the first load and by 45 - 60% at the second in relation to the initial level. A decrease in these indicators tells us about the health-improving level of physical culture and health-improving work and its correct organization.
Conclusion: functional tests are carried out only in a children's clinic in the direction of medical preschool workers... According to their results, the doctor recommends a mode of exercise intensity in physical education.
An important indicator of the state of the cardiovascular system is the calculation of the endurance coefficient (CV) and its comparison with standard indicators.
The endurance coefficient is calculated by the formula: KV = P x 10 / PD, where P is the pulse, PD is the pulse pressure (pulse pressure is determined by the difference between the maximum and minimum blood pressure). With the development of endurance, the numerical values of CV decrease
Development respiratory system musculature can be traced using a pneumotometer. It is a U-shaped glass tube, half filled with mercury and equipped with a scale, to which a rubber tube with a mouthpiece is attached. To take measurements, first inhale, then exhale deeply. Then they take the mouthpiece into their mouth and produce the maximum inhalation, trying to raise the mercury in the tube of the device as high as possible and keep it at this level for 2 seconds. Inspiratory force will increase as children train. It should be noted that children really like to work with various devices and they rejoice when they are convinced of how the capabilities of their body are increasing.
An important indicator reflecting functionality the respiratory system is the vital capacity of the lungs. It is measured using a spirometer device. The vital capacity of the lungs (VC) is measured in cubic centimeters. The obtained indicators are compared with the proper (by age and sex) VC (VC), which can be calculated using the equations of A.F. Sinyakov.
Equations for calculating JEL (according to A.F. Sinyakov)
Boys JEL = (31 x height in cm) = (32 x weight in kg) - (20 x age) = 2950 (15)
Girls JEL = (25 x height in cm) + (26 x weight in kg) - (15 x age) = 2150 (15)
Knowing the vital capacity of the lungs and body weight, it is possible to determine the vital index (LI) of the child. It is determined by the formula: ZhI = VC / R, where VC is the vital capacity of the lungs, in ml; Р - body weight, in kg. An increase in vital index indicators from 5 to 15 ml / kg will indicate the effectiveness of physical culture and health improvement work.
The presence of baseline data on physical development at each age is not yet a monitoring of physical development. Taking indicators twice a year, as is customary in preschool institutions, is nothing more than monitoring the results. Monitoring involves tracking the dynamics of physical development and correlating its indicators with other parameters, for example, physical fitness or functional state organism. Therefore, indicators of physical development should be taken quarterly. This allows you to see the results of pedagogical influences on each child and a group of children as a whole and accordingly adjust the process of physical development of children.
Assessment of the physical qualities of children The development of physical qualities is assessed by the dynamics of indicators of strength, endurance, flexibility, agility, speed. It should be noted that the degree of development of physical qualities also speaks of the level mental development, as well as the presence of certain inclinations in the child. For example, agility indicates a developing ability to learn quickly.
Speed is assessed by running at a speed of 100 meters.
The strength of the hands is assessed using a hand-held dynamometer, the strength of the shoulder girdle - according to the indicators of throwing a medicine ball weighing 1 kg into the distance from behind the head with both hands, strength lower limbs- on the long jump from the spot.
Agility is assessed by the difference in the time of running a distance of 10 m in a straight and shuttle way (run 5 m, turn around and run back).
Dexterity can be measured by running time on an obstacle course. The child should run on a gymnastic bench 5 m long, roll the ball between six objects (pins, cubes, other objects) located at a distance of 50 cm from each other, crawl under an arc 40 cm high.
Flexibility is measured by the degree of torso bend from the main stance without bending the knees. The exercise is performed on a gymnastic bench 20-25 cm high, to which a special measuring ruler is attached. It's better to highlight its divisions in different colors... For example, the first centimeter is red, the second is green, etc. The child should stand on the bench so that the tips of their toes are flush with the edge of the bench. On command, he leans forward without bending his knees, trying to touch the edge of the bench with his fingertips, and fixes this position for 5 seconds. This indicator is considered the norm (nominal). If the child could not hold this position for 5 seconds or does not reach the edge of the bench without bending his knees, the result is considered unsatisfactory (pessimal). The optimal result is the result in which the child's fingers fall below the edge of the bench (for example, by 0.5 cm, 1 cm, 2 cm, etc.). Evaluation Criteria-P(pessimal); N - nominal; O-optimal (for example, O, if the fingertips are 1 cm below the edge of the bench, etc.). Endurance is measured by continuous running. For preschool children, the following approximate indicators are used: 4 years - 100 m; 5 years - 200 m, 6 years - 300 m, 7 years - 1000 m. The test is considered completed if the child has run the entire distance without stopping.
During the year, indicators of physical qualities may change. This is due to natural growth children, the growth of their physical activity, purposeful work on physical education.
The analysis of the growth rates of physical qualities, developed by V.I. Usakov, is used to assess the effectiveness of the physical education system.
Conclusion: if the growth rate of physical qualities is, for example, no more than 8% per year, then there is no system of physical education in a preschool institution. Moreover, physical activity under the guidance of an adult leaves much to be desired, and the natural physical activity of children is clearly limited. Assessment of the work of a preschool institution in this case is unsatisfactory.
With an increase in physical qualities from 9 to 10%, we can conclude that, although purposeful work on physical education is not carried out in a preschool institution, at least teachers do not limit independent motor activity children. The assessment is satisfactory. If the indicators of the increase in physical qualities were from 11 to 15%, then this indicates the presence of a purposeful system of physical education in the preschool institution. But this system still falls short of perfection. The score is good. Growth rates of 15% and more speak not only about a purposeful system of physical education, but also about the active use of the natural forces of nature: the sun, air and water, i.e.
hardening procedures. The score is excellent. The growth rates of physical qualities are calculated according to the formula of V.I. Usakova: W = 100 [(V2 - V1), S x (V1 + V2) where W - growth rates of physical qualities, V1 - initial indicators, V2 - final indicators.
For example, a child's result in long jump from a spot at the beginning of the year was 75 cm, and at the end of the year his result was 79 cm. According to V.I. Usakov we will get the result: W = 100 [(79 - 75), S x (75 + 79) we will make calculations and get 5%. Let's analyze the result.
The level of physical fitness of children is assessed by high-speed running, throwing at a vertical target and long jump from the spot. These indicators are quite enough to assess the level of preparedness of children, but it does not mean at all that children should be taught only these movements. If you do not teach children to climb, balance, slow running and other movements, the optimal results of physical fitness cannot be obtained.
A more accurate assessment of the physical fitness of children can be obtained in relation to the coefficient motor development children, but you can use standard age indicators... Children of the same age, however, differ in height and body weight. Therefore, the indicators of their physical fitness within the same age may be different. How to assess the indices of physical fitness in accordance with the coefficient of motor development. For example, Vitya is 113 cm tall, and Sasha is 98 cm. Most likely, Vitia's long jump performance is 98 cm. It is most likely that Vitia's long jump performance will be higher, for example. But for some of the boys, the indicators can be considered nominal, and for some optimal. Viti's jump - 102 cm, Sasha's jump - 101 cm.
In accordance with the coefficient of motor development, the result of a jump above one is considered optimal. The unit is the length of the body. The nominal result is 0.8 - 1; pessimal - below 0.8. Consequently, the result of Sasha's jump is higher than the length of his body, and the result of Viti's jump is nominal, since his coefficient is 0.9.
Thus, Viti's result can be attributed to the category of the norm, and Sasha's result - to the “optimal” category. Assessment of the quality of movement mastering The quality of motor skills is assessed by how children perform basic movements.
Each movement is divided into specific phases. For example, in a long jump from a run, they distinguish: starting position, takeoff, push, flight, landing, return to the starting position. There are 6 elements in total. Of these, it is critical to obtain good result have: takeoff speed, push force, body position in the flight phase. If we evaluate the performance of the exercise on a five-point system, then these phases should be assigned a greater number of points: starting position - 0.5 points, takeoff - 1 point, clean and jerk - 1 point, flight - 1 point, landing - 1 point, return to the initial position. position - 0.5 points. Control lessons should be carried out at least once every two months, tracing the dynamics of improving the quality of movements. At the end of the year, the results for each age group are summed up by the physical education instructor. The average score is displayed individually, then for the group of boys, for the group of girls, then the average score for the entire group. This form of work gives a fairly complete idea of how the quality of movement performance corresponds to the norm for each specific child and the group as a whole. this work allows the teacher to direct his attention to the most important aspects work and plan accordingly. At the end of the year, an assessment is given for the preschool institution as a whole.
Estimation of morbidity in children
The assessment of the incidence of children is carried out monthly, quarterly, based on the results of the academic and calendar year. Methods for assessing morbidity are agreed with health workers preschool and educational administration. The main thing that should be done in a preschool institution is the differentiation of diseases by types: somatic, colds, infectious, etc. Data should be collected on the incidence of each specific child, each age group and the entire institution as a whole. This makes it possible to trace the dynamics of morbidity throughout the year, as well as to correlate its level with the quality of physical culture and health-improving work.
This approach to assessing morbidity will allow us to single out a group of healthy children (children who practically do not get sick) and correlate their health status with the conditions and lifestyle of the family. The experience of these families in keeping their children healthy should be a subject for discussion.
Quite often, children get sick due to insufficient attention and negligence of their parents. Such a group of parents should be the subject of special care of the preschool institution in terms of their sanitary, pedagogical and social education.
But the purpose of monitoring the incidence is to identify the most bottlenecks in the service of children by personnel. If, for example, there are two parallel groups in a preschool institution, but the incidence of children in one is much higher, then this fact quite definitely indicates shortcomings in the activities of teachers and service personnel. The morbidity data should be known not only to the team, but also to the parents. This not only disciplines the staff, but also the parents. For example, in parent corner the screen of the incidence of children is posted. In it, cases of diseases are marked with multi-colored icons (in red - colds, etc.). From this screen it is easy to judge whether the infection spread, how many children were sick due to neglect of adults (injuries, bad teeth, etc.), whether there were exacerbations chronic diseases... If on the whole the picture is normal, but Vasya Ivanov, as they say, “does not crawl out of illness,” then the guilt of the parents is significant. And they, looking at such a screen, understand this, begin to worry and listen to the advice of experts. But this does not mean at all that, by shifting the blame for the poor health of the child onto the parents (which in this case is quite fair), educators should not take care of this child. On the contrary, an individual health-improving program should be developed for him with the involvement of the parents themselves in its implementation.
Work on physical education in a preschool educational institution should be based on diagnostics, which is carried out by a physical education instructor with the participation of medical and pedagogical workers. The results are recorded in the child's development chart and used by educators when planning work with children. The results of the work are discussed at medical and pedagogical meetings and are reflected in the health passport issued in each group.
Conclusion: an analysis of the health and physical development of pupils is given, problems are identified, ways of managerial decisions are outlined.
One of the areas of monitoring is the assessment of the professional competence of teachers. The following methods can be used to assess professional competence:
analysis of documentation, conducting control and assessment classes, interviews with teachers, parents, game test tasks. All monitoring results should be submitted to technological map... The map is compiled in accordance with Appendix No. 1 to the order of the RF Ministry of Education. dated August 22, 1996. “The form and content of self-examination (introspection) in the process of attestation of a preschool educational institution: criteria for assessing the activities of a preschool educational institution.
Conclusions: the professional competence of teachers is undergoing continuous research in order to support their self-development and improve the quality of educational activities.
The following tasks are set:
1. To create a monitoring model for organizing a system of work in a preschool educational institution, aimed at preserving and strengthening the health of pupils, educating children of value orientations on the priority value of health; 2. To unite the efforts of all teaching staff around the task of preserving and strengthening the health of pupils. 3. To contribute to ensuring the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of pupils by improving the quality of services in preschool educational institutions.
Working with parents
In Concept preschool education it is emphasized: "The family and kindergarten in the chronological order are connected by the form of continuity, which facilitates the continuity of the upbringing and education of children. The most important condition continuity is the establishment of trusting business contact between the family and the kindergarten, during which the educational position of parents and teachers is adjusted. "
We can say with confidence that not a single, even the best physical culture and health program can give full results if it is not implemented in collaboration with the family.
The level of professional skill of teachers is determined by the family's attitude to kindergarten, to the teachers themselves
Explanatory note …………………………………………….… 3
Diagnostics of physical development ………………………………… .... 5
Indicative indicators of physical fitness ... ... ... 6
Using diagnostic tests ……………………………… .7
Diagnostics of psychophysical qualities (tests) ……………… .. …… ..8
Test to determine the increase in indicators of psychophysical
qualities …………………………………………………………………… 12
References …………………………………………………… 14
Protocol of examination of basic movements (appendix) …… ..… 15
Explanatory note.
The acuteness of the issue of the quality of upbringing and development of preschool children continues to persist. Effective leadership that ensures quality involves the attraction and rational use of various means. To do this, you need to be able to plan and evaluate your actions, to have reliable and objective information at your disposal.
There is a problem of obtaining high-quality information about the level of development of pupils in a preschool educational institution in all sections of the program, in particular on physical development. This is due to the fact that new generation programs do not offer criteria for assessing the quality of education, do not provide tests to determine the level of development of a preschooler. This is the case with the complex educational program "Childhood" according to which our preschool institution operates.
The program for the section "Raising children healthy, strong, cheerful" gives a characteristic of the age characteristics of the pupils, the levels in mastering the content of program tasks (high, medium, low), minimum results are proposed, but there are no test tasks, so it became necessary to systematize work in this direction.
We have developed a program for physical examination of preschoolers, which consists of two parts, characterizing:
physical development (measurement of body length and weight, chest circumference);
development of psychophysical qualities:
dimensionstrength: lifting the body in a sitting position, raising the legs while lying on the back;
speedy strength qualities: standing long jump, throwing a medicine ball with two hands from behind the head, throwing a light ball at a distance;
rapidity: running at a distance of 10 meters of descent and 30 meters; "Shuttle run" 3X10 m;
endurance: running at a distance of 90, 120, 150, 300 m (depending on the age of the children);
agility: zigzag running, jumping rope;
flexibility: torso bending forward on the bench.
Diagnostics of the physical development of preschoolers
The examination of children is carried out both indoors (gym, music hall) and on the sports ground. On the sports ground, following tests: throwing the ball at a distance, running at a distance: 10, 30, 90, 120, 150, 300 m, "shuttle run" 3 x 10 m.
The survey must be carried out over several days, in spring and autumn, during the warm season. Clothing should be comfortable, lightweight and clean (not synthetic). It is better for children to engage in a suit outdoors, shoes should be rubber-soled, indoors the uniform is different - sports shorts, a T-shirt, sports shoes.
Measurement of physical fitness is carried out by the educator together with the physical education instructor. All survey data are entered into the diagnostic card for each age group separately
Diagnostics of the physical development of preschoolers
|
Newspaper number |
|
|
Lecture number 1. The subject of "physical culture" and its importance in the comprehensive assessment of the quality of education. |
|
|
Lecture number 2. Factors, concepts and terms that determine the quality of education in the field of physical culture. |
|
|
Lecture number 3. Methodology for monitoring studies of physical development, physical and functional fitness as critical indicators health of students. Test № 1 |
|
|
Lecture number 4. The technology of large-scale testing of health indicators at physical culture lessons and physical culture and sports events. |
|
|
Lecture No. 5. From testing practical skills and abilities - to testing the level of knowledge in the subject of "physical culture". Test work number 2 |
|
|
Lecture number 6. Various methodological approaches to assessing health indicators. |
|
|
Lecture number 7. An example of monitoring studies analyzing the results of schoolchildren's educational achievements in the subject of "physical culture". |
|
|
Lecture number 8. Scientifically grounded management decisions made by the education system authorities based on the results of monitoring the physical development and physical fitness of schoolchildren. Final control work |
Lecture number 3
Methodology for monitoring studies of physical development, physical and functional fitness as the most important indicators of students' health
“The most difficult and noble goal of medicine is
not in the treatment of the sick, but in the desire to teach people to stay healthy. "
A. Cornelius Celje
Effective management of the child's development process presupposes possession of information about the dynamics of health indicators and the level of knowledge. The proposed technique for simple and effective technicians self-control, with their regular and systematic use, will ensure tracking in monitoring of the most important indicators of physical development, physical and functional fitness, as well as the level of knowledge on the subject of "physical culture". It does not require separate explanations for its potential addressees (teachers, schoolchildren, students, parents, coaches), despite their dissimilarity in age and educational level. This technique has been tested in educational institutions Kazan.
First, the group of test takers gets acquainted with the methodology and parameters characterizing physical development, physical and functional fitness. Explains how to perform trials and tests, and how to operate the instruments and tools used. Calculation formulas and evaluation criteria are explained in detail.
For integrated assessment health indicators can be used: physical education lessons, classes in sports sections and health groups, an additional hour per week for sports and recreation activities (first introduced since September 1998 in all schools of the Republic of Tatarstan), lessons in "Fundamentals of Life Safety" and "Fundamentals of Military Training", as well as specially organized Days and health hours, electives or extracurricular activities.
Along with physical education teachers, coaches, health workers, teachers of the basics of life safety and the basics of military training, curators and class teachers, teachers of informatics (for the introduction of computer technologies) and students with a propensity for active creative, experimental research and scientific work.
It is advisable to begin the assessment of health indicators by taking into account heredity (genetic history: life history, diseases of relatives, primary diagnosis of risk factors), then proceed to obtaining initial data through actual measurements, performing tests and tests characterizing, among other things, the adaptation of the organism to physical activity, and the level physical condition the subject, then - to the calculation of the proper values of various indicators, their qualitative and quantitative assessment. Measurements, tests and sampling should be varied and systematic (eg 2-3 times a year), which will help maintain and increase the interest of students in the assessment. own health and tracking the dynamics of its indicators. A wellness program can be considered optimal, in which a regime and massage are provided, breathing exercises and physical load, hardening and auto-training, as well as exercises for the development of flexibility, muscle strength and endurance.
Physical education testing is for students an exciting game, where you can compete using the simplest devices (dynamometer, spirometer, measuring tape, stopwatch, etc.), in strength, lung capacity, chest development, breath holding, in the development of physical qualities, etc., and most importantly, in monitoring by tracking the dynamics of these indicators in the learning process.
The physical usefulness of a person is characterized by:
harmony of development;
normal functioning of the cardiovascular, respiratory, musculoskeletal and other systems of the body.
Assessment of indicators of physical development, functional and physical fitness will help in the prevention of morbidity by means of physical culture, sports, tourism and hardening.
This seems to be one of the directions in solving the problem of improving the nation's health.
The state and prospects of children's health are seriously influenced by the content and forms of organization learning activities... It is supposed to monitor the dynamics of the development of the morphofunctional systems of the child's body within the framework of the norm and proactive preventive action that increases the adaptive potential of children. The creation and implementation of functional testing technology, including periodic measurement of functionally significant parameters, presupposes the availability of methodological support and a hardware complex. Methodological support includes a detailed description of the testing procedure (the procedure for examining an individual student and the principles of organizing a mass examination of the class and the entire school). A special section of the methodology is the interpretation of test results for corrective interventions. The hardware complex should provide the ability to measure functional parameters, be compact enough, reliable and have an acceptable cost. A computer - important element a hardware complex that allows you to take into account the results of the survey and form recommendations for a student, a teacher of physical education, class teacher about the current physical condition of the student and its dynamics.
The purpose of the technique- to give knowledge, skills and instill the skills necessary to assess the health indicators of both those who go in for physical culture, sports and tourism, and those who do not.
Tasks:
1. Mastering by students of methods of measurements, calculations and testing.
2. Training in the analysis of the results obtained.
3. Introduction of information and diagnostic computer technologies for the collection, processing and storage of data on the assessment of health indicators.
Actual measurements
The values measured at the first stage are entered into the health indicators testing chart, which consists of a general part and three sections. Table 1 provides an example of the structure of a health scorecard. An individual test card is comprehensive and versatile. It can be used across a wide age range for different population groups. We have applied the technique in practice for preschoolers, schoolchildren, and students.
Table 1
Test card structure
Some explanations for filling out the test card. The first column of the common part contains the number in order, or the code of the test taker, if anonymity is required. A feature of the general part of the table is that the columns "Full name", "Gender", "Date of birth", filled in once, can accompany a person throughout his life (from 1st to 11th grade and further). There you can add the column "Type of institution". It indicates the class, letter (for schools), junior, middle, senior group(for preschool educational institutions), course, group, faculty, specialty (for a university). The information in this column can be shown in the title of the table or immediately below it. The continuation of the general part are three autonomous blocks of well-known, standard, easily measured indicators.
The program for computer processing of initial information provides for the autonomous execution of calculations for indicators of physical development, physical and functional readiness, but it will not start work without filling in the first columns "Full name", "Sex", "Date of birth". The age of the test taker is determined by the computer by the date of birth. For example, 7 years old - age from 6.5 to 7.5, 8 years old - from 7.5 to 8.5, etc. This accuracy is sine qua non the correctness of the collection of anthropological material in studies containing biomedical methods. In Fig. 1 shows some of the proof tests.
Physical development. Physical development studies are carried out using anthropometric techniques:
1) somatometric - body length (height), body weight (weight), circumference and chest excursion;
2) physiometric - vital capacity of the lungs, muscle strength of the hands, back strength;
3) somatoscopic - the shape of the chest (physique), type of posture, etc.
Comprehensive assessment of physical development included for each tested:
determination of the group of physical development using centile tables (group I - healthy children, group II - "risk group", group III - children with significant deviations in physical development);
determination by weight and height indices of deficiency or excess body weight, body weight corresponding to the norm.
Summing up the individual values of the indicators, computer program calculates rating values for a class, school, group or course, answering the questions: “What percentage of students belong to groups I, II, III? How many percent of students are underweight? " etc.
Height is measured using a wooden stadiometer or a folding metal anthropometer. A person stands with his back to the digital markings and the interscapular region, buttocks, heels, touches the vertical stand of the stadiometer. His head is in a position in which the lower edge of the orbit and the upper edge of the ear tragus are at the same level. Do not touch the stadiometer with the back of the head. The movable bar of the stadiometer is lowered onto the subject's head (without pressure).
The metal anthropometer is placed strictly vertically. The horizontal ruler of the anthropometer extends 15–20 cm and is located on the very high point heads. The position of the head is the same as when measuring with a stadiometer.
Body weight is determined by weighing on a medical scale. The balance must be checked before use.
The chest circumference is measured with a measuring tape, which is applied horizontally in the front under the nipples for women, along the nipples for men, and at the back at the angle of the scapula. Measurements are taken at rest (pause between inhalation and exhalation), during inhalation and exhalation. The circumference of the waist (abdomen) is measured at the narrowest point (usually at the level of the navel) when calm breathing... The circumference of the hand is measured at the wrist.
Right and left hand strength is measured with a wrist dynamometer. The straight arm is set aside to the shoulder level, the dynamometer in the hand with a scale inward squeeze without jerking with maximum effort. The hand does not touch the body. This measurement is repeated at intervals of 30 seconds. three times, the highest value corresponds to the strength of the hand.
Lung vital capacity - the largest number air that can be exhaled after maximum inhalation. The vital capacity of the lungs is an indicator of the mobility of the lungs and chest, highly dependent on height, age and gender.
The vital capacity of the lungs is measured in a standing position with an SSP spirometer. Rest for 3-5 minutes is recommended before taking measurements. After the maximum inhalation, you should pinch your nose with your fingers, clasp the mouthpiece with your lips and exhale evenly, as deep as possible into the spirometer, trying to stay straight without stooping. From two or three measurements with pauses of 15–20 sec. fix the greatest result.
Physical fitness. Usually, the following mandatory simple tests are used, reflecting the level of development of six vital physical qualities:
1) high-speed (running 30 m or 100 m);
2) coordination (running 3 × 10 m, jumping rope);
3) high-speed power (long jump from a place, lifting the body in 30 seconds);
4) power (pull-up, push-up, hanging on the bar);
5) endurance (running 1000 m, 2000 m, 3000 m);
6) flexibility (tilt of the trunk forward characterizes the ability of flexibility in spinal column). This quality characterizes the functional capabilities of the musculoskeletal system, the degree of mobility of its links and is determined by the maximum range of motion when bending forward from a standing position (legs straight) by measuring the distance from the support to the tips of the fingers lowered down with a ruler. If they are below the support, the flexibility is positive (+), if they are above the support, it is negative (-). Flexibility can be measured from a sitting position (Fig. 1). Distinguish between active flexibility, when movements are performed due to muscle contractions, and passive, when movements are performed using weights.
Additionally, using the simplest exercises, you can assess jumping ability (Abalakov's test), the work of the vestibular apparatus (Ozeretsky's test), and the speed of reaction (see Fig. 1).
The creation of a single universal form for physical fitness indicators led to an increase in the number of test physical exercises from 6 (the standard of education for schoolchildren) to 10. Now the initial information on physical fitness meets, along with the educational standard, the requirements of the Presidential Competitions of Russian Schoolchildren. In addition, with an increase in the number of tests for physical fitness, we provide an opportunity to freely choose those exercises that are better for the trainee, in the performance of which he can achieve greater success. This is the focus of the control standards for six physical qualities (see Table 2) included in the Draft federal component of the State Educational Standard general education.
table 2
Requirements for the subject "physical culture" to the individual level of physical fitness of schoolchildren (at the choice of students)
From the draft of the federal component of the State educational standard of general education (parts 1 and 2) of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation (Moscow, 2002)
|
Physical qualities |
Physical exercises |
Primary school |
|||
|
Boys |
Girls |
Young men |
Girls |
||
|
Rapidity |
Running 60 meters (sec.) |
||||
|
Jumping rope in 30 seconds. (time) |
|||||
|
Raising the body from a supine position, hands behind the head in 30 seconds. (time) |
|||||
|
Standing long jump (cm) |
|||||
|
Endurance |
Cross run 2 km (min., Sec.) |
||||
|
Skiing 2 km (min., Sec.) |
|||||
|
Swimming 100 m (min., Sec.) |
excluding time |
1.45 |
excluding time |
2.05 |
|
|
Agility |
Shuttle run 3x10 m (sec.) |
||||
|
6 throws of a small ball into a 1 x 1 m target from a standing position at a distance: - 12 m (number of hits on the target); |
|||||
|
Profile level |
|||||
|
Rapidity, |
Running 100 meters (sec.) |
13,0–14,3 |
15,3–17,0 |
||
|
Flexion and extension of the arms in support lying on the floor (times) |
|||||
|
Pulling up the torso from a hang on the arms (times) |
|||||
|
Standing long jump (cm) |
|||||
A feature of the new requirements for the individual level of physical fitness of schoolchildren is a free choice from the proposed physical exercises that characterize certain physical qualities. This applies, first of all, to preschoolers and schoolchildren, who need to be captivated by a variety of physical activity, manifested in physical culture, health-improving, sports and other activities. The fulfillment of these test exercises characterizes the initial level of development and controls the success of improving physical qualities during each academic year.
Functional readiness. The heart rate is measured in 15 seconds, and the result is multiplied by 4. To get more accurate result heart rate measurement is recommended to be done in 1 min. Resting heart rate is measured after 5-7 minutes. rest lying on your back or sitting. The starting position for measuring heart rate while standing is to lean your back against the wall, so that your feet are at a distance of your feet from the wall, stand for 1-2 minutes before measuring. Heart rate after 30 squats in 30 sec. measured in a standing position immediately after loading. After that, sit down, completely relax, try to restore your breathing. The heart rate is measured after 1 min. recovery.
Blood pressure is measured with a tonometer according to the method of N.S. Korotkov on right hand in a sitting position after 5-10 minutes of rest. The cuff is placed in the middle of the bare shoulder 1–2 cm above the elbow bend. The subject's hand should be comfortably placed on the table and turned with the palm up. The moment of appearance of tones corresponds to systolic pressure, and their disappearance corresponds to diastolic pressure. Modern tonometers of semi-automatic and automatic type can be used.
Respiratory rate is calculated in 1 minute. at rest while sitting. In this case, breathing should be natural, normal, without delays or increased frequency. To calculate the breathing rate, put your palm on lower part chest and upper part belly.
The breath holding time on inspiration (Stange test) is measured after 3-5 minutes of rest. The test person takes three deep breaths and, at an incomplete fourth breath, holds his breath, pinching his nose with his fingers. The stopwatch is used to determine the breath holding time. To determine the time of holding the breath during exhalation, the measurement technology is similar. The interval between measurements of the breath holding time during inhalation and exhalation is not less than 5–7 minutes.
During the research, the following instruments and equipment are used:
stopwatch- for measuring heart rate, respiration rate, breath holding, time of performing samples, tests and physical exercises;
medical tonometer- for measurement blood pressure(systolic pressure / diastolic pressure / pulse pressure);
spirometer SSP- to measure the vital capacity of the lungs;
hand dynamometer- to measure the strength of the right and left hand (scale from 25 to 120 kg);
stadiometer- to measure growth;
tape measure- to measure the circumference of the chest, waist circumference, hand, jump length;
metric ruler- for measuring flexibility, performing a speed test;
Libra- to determine body weight;
mats, gymnastic bench, crossbar, parallel bars, mini-stepper- to perform exercises that characterize physical fitness;
a computer- to collect, store and process the results obtained.
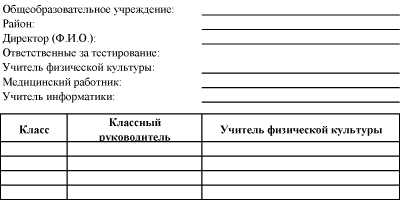
The results of the actual measurements are entered into the health indicators testing card (Table 3).
Table 4
Cover page for health metrics testing card
The methodology for calculating and evaluating the results of actual measurements will be discussed in lecture 5.
Questions and tasks for independent work
1. What parameters characterize the physical usefulness of a person?
2. What tests, samples, indices can be used to measure indicators of physical development, physical and functional fitness?
3. Give examples of quality and quantify health indicators.
1. Izaak S.I. Monitoring of physical development and physical fitness: theory and practice. - M .: Soviet sport, 2005.
2. Semenov L.A. Conditioned physical fitness monitoring in educational institutions. - M .: Soviet sport, 2007.
3. Landa B.Kh. Methodology for a comprehensive assessment of physical development and physical fitness // Tutorial... - M .: Soviet sport, 2006 .-- S. 208.
4. Draft federal component of the State educational standard of general education (parts 1 and 2) of the RF Ministry of Defense. - M., 2002.
