Storage rules for thermolabile drugs. Pharmacy storage rules
The organization of drug storage should ensure the separate storage of drugs, grouped according to the following classification criteria: toxicological group, pharmacological group,
Classification signs of drug groups for separate storage
type of application, state of aggregation, physical and chemical properties, shelf life, dosage form.
So, depending on the toxicological group, medicines related to:
List A (poisonous and narcotic substances);
List B (potent);
General list.
Lists A and B are lists of drugs approved for medical use by the State Pharmacological Committee, registered by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and requiring special safety measures and control during storage, manufacture and use of these drugs due to the high pharmacological and toxicological risk.
Taking into account the pharmacological group, it is necessary to store separately, for example, vitamins, antibiotics, cardiac, sulfa drugs etc.
The sign "type of application" stipulates separate storage drugs for outdoor and internal use.
Medicinal substances "Angro" are stored taking into account their state of aggregation: liquid, bulk, gaseous, etc.
According to the physicochemical properties and influence various factors external environment there are groups of drugs:
Requiring protection from light;
From exposure to moisture;
From volatilization and drying;
From exposure to high temperatures;
From exposure low temperature;
From exposure to gases contained in environment;
Odorous and coloring;
Disinfectants.
When organizing separate storage of drugs, it is also necessary to take into account the shelf life, especially if it is relatively short, for example, 6 months, 1 year, 3 years.
An important feature, which should be taken into account when storing separately, is the type of dosage form: solid, liquid, soft, gaseous, etc.
Have a number of drugs that are consonant in name;
Place nearby drugs for internal use, which have very different higher single doses, and also place them in alphabetical order.
Failure to comply with the rules for separate storage of drugs described above can lead not only to a deterioration or loss of consumer properties of drugs, but also to the error of pharmaceutical personnel when dispensing a high-quality, but wrong drug and, as a consequence, to a threat to the life or health of the patient.
During storage, a continuous visual control is carried out over the condition of the container, external changes in drugs and medical devices at least once a month. In the event of a change in drugs, their quality control should be carried out in accordance with NTD and GF.
Depending on the physical and chemical properties medicines, the impact on them of environmental factors, they are divided into drugs that require protection from moisture, light, drying, high and low temperatures, coloring and odorous, disinfectants.
Medicines stored in a dark place - antibiotics, tinctures, extracts, vitamins, corticosteroids, plant materials, nitro compounds, amino and amide compounds, phenol and phenothiazine derivatives.
The above means are stored in containers made of light-protective materials. These are metal containers, aluminum foil, orange glass containers, packaging made of materials painted in black, orange or brown... The storage area for such medications should be dark or with tightly closed doors. These products can be stored in tightly closed drawers with a well-fitting lid.
Preparations especially sensitive to light (prozurin, silver nitrate, etc.) are stored in glass containers, pasted over with black opaque paper.
Protection of medicines from moisture is needed for such hygroscopic substances and preparations as dry extracts, plant materials, nitrogenous, nitrogenous salts, phosphoric acid, antibiotics, enzymes.
These medicines are stored in a dry room in a tight container made of glass, metal, aluminum foil, and plastic. If the hygroscopic properties are pronounced, the container should be hermetically sealed, filled with paraffin on top. Preparations such as burnt gypsum and mustard in powder require special storage, since at high humidity they lose their properties and may be unsuitable for use. Burnt gypsum is stored in a tightly closed container (it is advisable to put a plastic wrap from the inside).
Mustard plasters are stored in bundles wrapped in plastic wrap or parchment paper... These packs are placed in cardboard boxes, pasted over from the inside with plastic foil.
Volatile substances such as alcohol tinctures, thick extracts, liquid alcohol concentrates, essential oils, solutions of ammonia, hydrogen chloride, formaldehyde, carbolic acid, ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, sodium bicarbonate, chloramine B.
In order to protect them from drying out and volatilization, drugs must be stored in a sealed container made of glass, metal, aluminum foil in a cool place. Crystalline hydrates are stored in a cool place in a hermetically sealed container made of glass, metal or thick-walled plastic at an air humidity of 50-65%.
Many medications (antibiotics, hormonal drugs, glycosides, vitamins, fat-based ointments, immunobiological preparations). The instructions for use of the drug indicate the storage temperature: room (+ 18-20 ° C), cool (+ 12-15 ° C). Sometimes it takes low temperature storage (for example, for ATP - + 3-5 ° C).
Immunobiological preparations are stored separately by name, series, taking into account their shelf life. The storage temperature of these products is indicated in the instructions. Immunobiological preparations are subjected to visual control at least once a month.
Antibiotic storage is usually done when room temperature in industrial packaging, unless otherwise indicated in the instructions.
Organopreparations are stored in a dry, cool and dark place at a temperature of 0 to ± 15 ° C (unless otherwise indicated on the label).
Insulin solutions, 40% formaldehyde solution, etc. need protection from the action of low temperatures.
Formalin should be stored at a temperature not lower than +9 ° C. Glacial acetic acid is stored at a temperature not lower than +9 ° C. Medical fixed oils it is required to store at + 4-12 ° С (when a sediment appears, oil is not used in medicine). Insulin preparations are destroyed when they freeze.
Medicines that are affected by air gases include morphine and its derivatives, enzymes, sulfur-containing compounds, organopreparations and enzymes, alkali metal salts, aminophylline, caustic soda and caustic potash, magnesium oxide, etc.
These products are stored in a sealed container filled to the maximum with gas-impermeable materials in a dry room.
Salts of barbituric acid require special storage conditions; they are stored in a sealed container made of materials impermeable to water vapor and carbon dioxide.
Coloring and odorous medicines and parapharmaceutical products (such as brilliant green, indigo carmine, methylene blue) are stored in a special cabinet in a tightly sealed container, separately by name. To work with substances of each name, a hotel scale, a spatula, a mortar and other equipment are distinguished.
Storage of finished medicinal products is carried out taking into account the properties of their constituent ingredients.
Finished products are packed in the package with the label facing out. A shelf card is attached to the cabinets and shelves, which reflects the name of the medicine, the series and the expiration date.
Such a card is entered for each newly received series, which allows you to monitor its timely implementation.
The department should have a card index on the expiration dates of drugs.
Expired medicinal products are stored separately and subject to re-testing (after receiving the test results).
Tablets and pills should be stored separately from other products in their original packaging in a dry place and, if necessary, protected from light.
Store injectables in a cool, dark place in a closet or isolated room.
Liquid dosage forms(tinctures, syrups, etc.) are stored in an airtight container filled to the top in a dark and cool place. If a precipitate falls out, the tinctures can be filtered. It is considered suitable for use after being tested for its quality.
Plasma replacement and detoxification solutions are stored separately at temperatures from 0 to +14 ° C in a dark place.
The extracts should be stored in a glass container with a screw cap and a cork with a seal in a dark place at a temperature of + 12-15 ° C.
Liniment and ointment should be stored in a cool and dark place in a well-sealed container.
Storage temperature is individual.
Store suppositories in a dark and cool place.
Means in aerosol containers are stored mainly at temperatures from +3 to 20 ° C in a dry and dark place, away from heating appliances.
These drugs must be protected from shock and mechanical damage.
Herbal raw materials are stored in a dry, well-ventilated room in a well-closed container.
The cut raw materials should be in fabric bags, powders - in double bags (multilayer paper - inner, fabric - outer), in cardboard packages. Sometimes packing of polymer materials.
Foxglove leaves, kidney tea and other hygroscopic herbs and fruits are stored in a glass or metal tightly sealed container.
Herbal medicinal raw materials are periodically controlled in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmalogy.
If the raw material is affected by mold, pests or loses its normal color and odor, it is either rejected or (after processing) used.
The terms of storage and control of plant materials containing cardiac glycosides are more stringent.
Disinfectants are stored in a cool, dark place, in a hermetically sealed container, away from the storage of plastic, metal and rubber products, from the premises for obtaining distilled water.
There are peculiarities in the storage of products medical purpose... So, rubber products must be stored in a dark place at temperatures from 0 to +20 ° C, protected from mechanical damage, aggressive substances (formalin, lysol, etc.). The preservation of the elasticity of rubber is facilitated by ammonium carbonate, the vessels with which it is recommended to place in cabinets and rooms for storing rubber products. To prevent the products from being squeezed, they must not be stacked in cabinets in several layers.
Cabinets for rubber products and parapharmaceutical products should have tight-fitting doors and a smooth inner surface. Bundles, probes are stored suspended on removable hangers located under the cabinet lid. Rubber heating pads, overhead circles, ice bubbles are kept slightly inflated. The removable rubber parts of the devices must be stored separately. Elastic catheters, gloves, bougie, rubber bandages, finger cots are stored in tightly closed boxes, sprinkled with talcum powder. The rubber bandages are sprinkled with talcum powder over the entire surface and stored rolled up.
Separately store rubberized fabric in rolls, horizontally suspended on racks. It can be stored on shelves in no more than 5 rows. Elastic lacquer bougies, catheters, probes are stored in a dry place. Products are rejected if stickiness and softening appear.
When rubber gloves harden, they are placed in a warm 5% ammonia solution for 15 minutes, then they are kneaded and kept for 15 minutes in a 5% water-glycerin solution with a temperature of + 40-50 ° C.
Plastic products are stored in a dark ventilated room at a distance of at least 1 m from heating devices, with a relative humidity of not more than 65%. Switches and electrical appliances must be fireproof.
It is necessary to store dressings and auxiliary materials in a dry ventilated area. Cabinets, racks and storage trays should be painted from the inside with a light oil paint... Periodically, they must be wiped with disinfectant solutions (for example, 0.2% chloramine solution).
Sterile bandages, napkins and cotton wool are stored in their original packaging. Non-sterile dressings are stored on racks packed in thick paper or in bags.
The auxiliary material (paper capsules, filter paper) is stored in its original packaging in separate cabinets in strictly hygienic conditions... After opening the package, the material is stored in paper or polyethylene bags or in kraft paper bags.
Metal products of medical technology, including surgical instruments, are stored in dry rooms at room temperature.
A sharp fluctuation in temperature and humidity in the storage room is unacceptable. The relative humidity should be no higher than 60% (rarely 70%).
Metal products that do not have anti-corrosion grease must be treated with a thin layer of petroleum jelly. Such instruments should be stored wrapped in paraffin paper. You need to take the tools with a gauze napkin or tweezers. Scalpels and knives are stored in special cases of boxes to avoid dullness.
Store surgical instruments by name. This is convenient for their release and control.
Copper (brass), tin products do not require lubrication.
If rust appears on painted iron products, it is removed and the product is painted again.
Silverware and nickel silver tools must not be stored together with sulfur, rubber products, as their surface may turn black.
Medicinal leeches should be kept in a bright and clean room without the smell of medicines and perfumes. Leeches can die due to sudden temperature fluctuations. They are kept in wide-necked glass jars(50-100 leeches require about 3 liters of water). From above, the jar is covered with a dense coarse calico napkin or a double layer of gauze and tied tightly, otherwise the leeches will creep out.
Leeches must be kept in clean water free of chlorine, peroxide compounds, salts of heavy metals. Water must be changed daily, harvesting it 2 days before use.
Before changing the water, it is necessary to rinse the inside of the jar, then drain the water through cheesecloth. The jar is filled with 1/3 of clean water. If the leeches become lethargic, the water must be changed 2 times a day.
The storage of medicines and medical devices with flammable and explosive properties is regulated by Order No. 318 dated 05.11.1997.
Compliance with this Order helps prevent fires and accidents, creates safe conditions labor. This Instruction must be followed by all pharmacy organizations.
Coming to work new employee It is imperative to be familiar with this Manual, with the rules for storing compressed gases and explosive substances. He must observe safety precautions, fire safety and be able to provide first aid in case of an accident. The knowledge of employees on the above issues should be checked at least once a year by a commission of 3 people. The results of the check are documented in a protocol.
In accordance with the requirements of the Rules fire safety RF 01-93, all pharmacies must have and store in the proper place primary means of extinguishing a fire. The storage rooms for flammable substances should have instructions on fire safety measures and plans for the evacuation of people.
Substances that are flammable and prone to spontaneous combustion in contact with air, water, and sunlight should be stored separately. Influence high temperatures and mechanical influences should be completely excluded.
There should be separate storage or compartments for flammable media. The premises must be well ventilated.
The floors of warehouses and unloading areas must be flat and solid.
Racks and pallets for storing flammable and explosive substances must be made of non-combustible material, strong. The width of the shelves should be no more than 1 m, the distance from the floor and walls should be 0.25 m, the aisles between them should be no less than 1.35 m.
Electrical installations are installed in accordance with the regulations.
It is allowed to store in pharmacies no more than 10 kg of flammable liquids in fireproof cabinets. There must be free access to the cabinet.
With special care and thoroughness, it is necessary to receive, pack and dispense drugs with explosive properties.
It is necessary to distribute the goods at the place of main storage immediately upon arrival. The state of the container closure deserves special attention.
It is forbidden to pack several explosive substances at the same time in one room. At the end of the working day, it is necessary to return the remaining substances to the main storage facilities. Rooms are often and thoroughly ventilated.
On the doors of each storage and packaging room, bright indelible inscriptions should be placed: “Explosive”, “Flammable”, “No smoking”, “In case of fire, call…”.
Near the entrance, in a conspicuous place, hang a sign with the inscription: “Responsible for ensuring fire safety, full name” Every day, the responsible person inspects the storage rooms at the end of the working day.
Explosives include nitroglycerin.
Explosive substances include potassium permanganate, silver nitrate.
Flammable substances include alcohol, alcoholic tinctures and solutions, turpentine, ether, chloroethyl, cleol, organic oils, X-ray films.
Flammable substances include glycerin, sulfur, dressings, plant materials, vegetable oils.
Store flammable and flammable liquids separately from other substances in well-closed glass or metal containers.
Heating should be carried out in water baths or on stoves with a closed spiral.
Large bottles, cylinders can be stored on racks in 1 row in height, at a distance of at least 1 m from heating devices.
You can fill the container with a flammable liquid no more than 90% of its volume.
Alcohol in large quantities is stored in metal containers, filling no more than 75% of the volume.
Joint storage of flammable substances with acids (especially sulfuric and nitric), compressed gases, dressings, sulfur, potassium permanganate is prohibited.
Ether for anesthesia and medical ether should be stored in their original packaging in a cool, dark place away from heating appliances.
Particular care should be taken when loading, carrying and packing flammable liquids, the tightness of the container is important.
Containers, freed from liquids, must be left open for a while.
Explosive substances require special storage conditions. Containers with substances must be tightly closed.
Silver nitrate should be stored in isolation in a clean room, no more than 50 g in a pharmacy and up to 5 kg in warehouses.
Potassium permanganate is explosive on contact with sulfur, dust, alcohol, ethers, glycerin, organic substances. It is stored in tin drums in a separate compartment (in warehouses), in rod glasses with ground-in corks.
Store the nitroglycerin solution in small containers in a cool, dark place. Caution must be observed when moving utensils with nitroglycerin and hanging the drug. Small amounts of nitroglycerin on the skin can cause food poisoning (severe headaches).
The storage of explosive substances with acids and alkalis is prohibited.
Cylinders with flammable liquids must be transported together in adapted baskets or crates with serviceable handles.
The storage of nitric and sulfuric acids requires special care: it is necessary to exclude contact with wood, straw and other substances of organic origin.
Pharmacy
Sale of medicinal products to the population according to doctor's prescriptions (except for narcotic drugs, psychotropic, potent and poisonous substances) and without a doctor's prescription; sale of prepackaged medicinal plant materials in factory packaging, medical products, personal hygiene items (means);
· Manufacturing of medicinal products according to the doctor's prescriptions, manufactured intra-pharmaceutical preparations in accordance with the approved prescriptions and packaging of medicinal products with their subsequent sale;
Dispensing medicines free of charge or at a discount to certain groups of the population in accordance with the current legislation Russian Federation and on the basis of contracts concluded with territorial bodies management of healthcare, medical institutions and insurance companies;
Providing the population necessary information on the proper use and storage of medicinal products at home; providing advice to ensure responsible self-medication;
· Providing medical professionals health care institutions, education, social security the necessary information about the drugs available in the pharmacy, as well as about new drugs;
Pharmacy kiosk
It can carry out the following functions:
· Sale of medicinal products to the population without a doctor's prescription; sale of prepackaged medicinal plant materials in factory packaging, medical products, personal hygiene items (means);
· Providing the population with the necessary information on the proper use and storage of medicinal products at home;
Rendering the first medical care.
Pharmacy shop
The same as a pharmacy kiosk, the differences from which the regulatory documentation does not establish.
Distance selling pharmacies
Distance selling (home delivery) pharmacies are often referred to as Internet pharmacies. This is inaccurate: until now, a noticeable part of distance pharmacies does not have their own website; customers place orders there by phone. Many regular customers make an order by phone even if the pharmacy has a website. However, an efficient Internet interface is essential for a distance pharmacy as it facilitates the selection process and stimulates impulse demand. When ordering medicines remotely, you can often get advice from a pharmacist.
Pharmacy storage rules
Compliance with the approved Instruction allows you to ensure the preservation of High Quality drugs and create safe working conditions for pharmacists when working with them. Special attention pay to the storage, prescribing, accounting and dispensing of poisonous and narcotic drugs. Correct storage drugs is based on the correct and rational organization of storage, strict accounting of its movement, regular monitoring of the shelf life of drugs. It is also very important to maintain optimal temperature and air humidity, observe the protection of certain drugs from light. Violation of the rules for storing medicines can lead not only to a decrease in the effectiveness of their action, but also harm health. Overly long-term storage drugs (even if the rules are followed) is unacceptable, since the pharmacological activity of the drugs changes. An important condition storage is the systematization of drugs by groups, types and dosage forms. This avoids possible mistakes due to the similarity of the names of drugs, to simplify the search for drugs and control of their expiration date. Narcotic drugs (List A) should be stored in safes or iron cabinets with secure constipation. A printed list of poisonous medicines is kept in a closet with an indication of the highest single daily doses. It is recommended to record the taking of drugs and their remainder. Rooms and safes with narcotic and especially poisonous substances must have an alarm, and there must be metal bars on the windows. The stock of poisonous and narcotic drugs should not exceed the general standard of stocks established for this pharmacy. Medicines from list B are stored in lockers with an indication of the list of drugs and higher single and daily doses. The instructions for organizing the storage of medicines and medical products apply to all pharmacies and pharmacy warehouses. The equipment of the storage rooms should ensure the safety of medicines. These rooms are provided with fire-fighting equipment, the required temperature and air humidity are maintained in them. The parameters of humidity and temperature are checked once a day. Thermometers and hygrometers are fixed on the inner walls away from heating devices at a distance of 3 m from the doors and 1.5 m from the floor. To register the parameters of temperature and relative humidity, an accounting card is created in each department. An important role is played by the cleanliness of the air in the premises for storing medicines, for this they must be equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation or, in extreme cases, with vents, transoms, and lattice doors. Heating of the room should be carried out by central heating devices, the use of gas appliances with an open flame or electrical appliances with an open spiral is excluded. If pharmacies are located in climatic zones with sharp fluctuations in temperature and humidity, they are equipped with air conditioners. The drug storage rooms should be enough cabinets, shelving, pallets, etc. The racks should be located at a distance of 0.5-0.7 m from the outer walls, at least 0.25 m from the floor and 0.5 m from the ceiling. The distance between the shelves should be at least 0.75 m, the aisles should be well lit. The cleanliness of the premises of pharmacies and warehouses is ensured by wet cleaning at least 1 time a day using permitted detergents... Medicines are placed according to toxicological groups. Poisonous, narcotic drugs - list A. This is a group of highly toxic drugs. Their storage and use require special care. Poisonous drugs and drugs that cause drug addiction are stored in a safe. Especially poisonous agents stored in the inner compartment of the safe, locked with a padlock. List B - potent drugs. Medicines of list B and ready-made funds containing them are stored in separate lockers with the inscription “B”. The storage of drugs depends on the way they are used (internal, external), these funds are stored separately. Medicines are stored in accordance with the state of aggregation: liquid drugs are kept separate from bulk, gaseous, etc. It is not recommended to keep nearby drugs that are consonant in name, drugs for internal use with very different higher doses. It is necessary to store plastic products, rubber products, dressings, and medical equipment separately in groups. At least 1 time a month, it is necessary to carry out control external changes medicines, container condition. If the container is damaged, its contents must be transferred to another package. On the territory of the pharmacy or warehouse, if necessary, measures are taken to combat insects and rodents.
About writing prescriptions and dispensing medicines
Analysis of inspection materials legal entities of all forms of ownership, carrying out medical and pharmaceutical activities, organized and carried out by the Ministry of Health in 2007, showed that up to now there are violations of medical and pharmaceutical workers the requirements of regulatory legal acts in terms of compliance with the rules for prescribing and dispensing medicines to the population.
Earlier, by letters dated 24.10.2005 No. 12-1-13 / 3767 "On prescribing and dispensing medicines" and dated 20.01.2006 No. 02-3-04 / 738 "On measures to improve the availability of medical care", the Ministry of Health indicated the need to ensure the availability of medical care, including the issues of prescribing prescriptions by doctors of outpatient clinics, ambulance teams and hospitals of hospital organizations, as well as the need for strict observance of the Rules for Prescribing Medicines and the Rules for Dispensing Medicines to the Population, approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Health of the Republic Belarus of December 6, 2000 No. 53, and the requirements of the decree of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus of May 13, 2005 No. 11 "On approval of the list of medicines dispensed without a doctor's prescription."
However, until now, doctors of health care organizations of all forms of ownership and various departmental affiliations, independently practicing doctors, if indicated, do not always issue prescriptions for medicines to patients, but make recommendations orally or in the form of notes on paper. In turn, for these "appointments" of an unidentified form, drugstore specialists dispense medicines.
The Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus requires strict implementation of the above-mentioned regulations and draws attention to the need to use prescription forms of the established forms for a doctor to contact a pharmacist.
The doctor who wrote the prescription, the pharmacist and the pharmacist who made and dispensed the medicinal product are liable for the consequences established by law for the consequences that occur in the event of an incorrect prescription or incorrect dispensing of the medicinal product.
In connection with the above, the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus instructs:
the chairman of the health committee of the Minsk city executive committee, heads of regional health departments, general directors of trade and production republican unitary enterprises "Pharmacy", "BelFarmatsiya", "Minskaya Pharmacy", heads of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs licensed for medical or pharmaceutical activities, to re-train specialists on the Rules for Prescribing for Medicines and the Rules for Dispensing Medicines with subsequent verification of knowledge of this topic, as well as by order of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus dated May 13, 2005 No. 11 “On approval of the list of medicines dispensed without a doctor's prescription "(As amended by the Resolution of the Ministry of Health of January 7, 2006 No. 1;
heads of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs licensed for medical and (or) pharmaceutical activities to ensure strict compliance with the Rules for Prescribing Medicines, Rules for Dispensing Medicines to the Population and the List of Medicines Dispensed without a Doctor's Prescription, paying special attention to compliance with their standards vacation;
heads of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs licensed for pharmaceutical activities in terms of works and services for the retail sale of medicines, place in trading halls pharmacies information for the public on the list of medicines dispensed without a doctor's prescription, in new edition;
heads of higher and secondary medical educational institutions Ministry of Health, including postgraduate education, in the process of training students and cadets, pay special attention to the issues of studying the rules for writing prescriptions and the rules for dispensing medicines from pharmacies and their practical consolidation.
Application
to the order of the Ministry of Health and social development Russian Federation
I. General Provisions
1.1. These Rules for the storage of medicinal products establish requirements for the premises for storing medicinal products for medical use and to the storage of these medicinal products, including those with flammable and explosive properties (hereinafter referred to as the Rules).
1.2. The rules apply to drug manufacturers, drug wholesalers, pharmacy organizations, individual entrepreneurs holding a pharmaceutical license or a medical license, medical and other organizations involved in the circulation of drugs (hereinafter referred to as organizations, individual entrepreneurs).
1.3. All employees of organizations and individual entrepreneurs must know and comply with the requirements set forth in these Rules. Responsibility for the fulfillment by the employees of organizations of the requirements of these Rules rests with the heads of these organizations.
1.4. Each employee of the organization entering work must be instructed at the workplace on the storage of medicines requiring special storage conditions (flammable, explosive substances, compressed gases), according to safety and fire safety rules, as well as the rules for providing first aid to the victim when accident.
II. General requirements for the design and operation of premises for storing medicines
2.1. The device, composition, dimensions of areas and equipment of the premises for storing medicinal products must meet all the requirements of the current regulatory and technical documentation.
2.2. The device, operation and equipment of the premises for storing medicines must ensure their safety.
2.3. In order to preserve the quality of medicines, certain temperature and humidity must be maintained in the storage rooms of medicines.
2.4. To maintain the cleanliness of the air in the drug storage rooms in accordance with the current regulatory and technical documentation, they are equipped with supply and exhaust ventilation with mechanical induction. If it is impossible to equip storage rooms with supply and exhaust ventilation, it is recommended to equip vents, transoms, second lattice doors, etc.
2.5. In organizations and individual entrepreneurs working in a climatic zone with large deviations from the permissible standards of temperature and relative humidity, drug storage rooms should be equipped with air conditioners or other equipment that provides the necessary conditions storage of medicines.
2.6. Premises for storing medicines should be provided with the required amount racks, wardrobes, pallets, podtovoy and other devices.
2.7. Decoration of premises for storing medicines ( inner surfaces walls, ceilings) must be smooth and allow for wet cleaning. The floors of medicinal products storage rooms should have a dust-free coating that is resistant to the effects of mechanization and wet cleaning with the use of disinfectants, while the use of unpainted wooden surfaces is not allowed. The materials for finishing the premises for storing medicinal products must comply with the requirements established for them.
2.8. Premises for storing medicines must be kept clean; the floors of the premises should be periodically (but at least once a day) cleaned wet way using approved detergents.
III. General requirements for premises for storing medicines and organizing their storage
3.1. Premises for storing medicines should be equipped with special equipment, allowing to ensure their storage, taking into account the physicochemical, pharmacological and toxicological properties, as well as the requirements of the quality standards of medicines and the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation and their proper preservation.
3.2. Persons authorized in accordance with the established procedure have access to the premises for storing medicinal products. Access of unauthorized persons to these premises is excluded.
3.3. Storage rooms for medicines should be equipped with devices for recording air parameters (thermometers, hygrometers or psychrometers), which are located on the inner wall of the storage room, away from heating devices at a height of 1.5-1.7 m from the floor and at a distance of at least 3 m from the doors. The readings of these devices must be recorded daily in a special journal (map), which is kept by the responsible person of the organization or an individual entrepreneur for a year and stored for a year, not counting the past. Control devices must be certified, calibrated and verified in accordance with the established procedure.
3.4. Medicines in storage rooms should be placed taking into account the most full use area of the room, creation best conditions labor for workers, the possibility of using means of mechanization and ensuring pharmaceutical order.
3.5. In storage rooms, medicines are placed separately:
in strict accordance with toxicological groups;
narcotic and psychotropic drugs;
potent and poisonous medicinal products, other medicinal products subject to quantitative accounting;
according to pharmacological groups;
depending on the method of application (internal, external);
in accordance with the state of aggregation of pharmaceutical substances (liquid, bulk, gaseous, etc.);
in accordance with the physicochemical properties of drugs and the influence of various environmental factors;
taking into account deadlines storage for medicinal products with limited shelf life;
taking into account the nature of the various dosage forms;
using computer technology (alphabetically, codes, etc.).
3.6. It is not recommended to place nearby medicines that are consonant in name, medicines for internal use with very different higher doses, and also to arrange them in alphabetical order.
3.7. Shelves (cabinets) for storing medicinal products in the premises for storing medicinal products should be installed as follows:
the distance to the outer walls is not less than 0.6 - 0.7 m;
the distance to the ceiling is not less than 0.5 m;
the distance from the floor is not less than 0.25 m;
aisles between racks not less than 0.75 m;
on all racks, cabinets, shelves, a rack card is attached indicating the name of the drug, series, expiration date, number of storage units.
3.8. In organizations and at individual entrepreneur records of medicines with a limited shelf life must be kept on paper or in in electronic format with archiving on hard media. The archiving mode is established by the head of the organization or an individual entrepreneur.
3.9. If medicines with an expired shelf life are identified, they should be activated and stored separately from other groups of medicines.
IV. Requirements for storage facilities for flammable and explosive medicinal products and organization of their storage
4.1. Flammable medicines, medicines capable of forming explosive mixtures, and also prone to spontaneous combustion when in contact with air, water, flammable substances or upon action sun rays should be stored isolated from other medicinal products in conditions that completely exclude the possibility of such contact, as well as the influence of high temperatures and mechanical stress.
4.2. The storage rooms for medicinal products related to the list of flammable or explosive substances, in accordance with the appendix to these Rules, (hereinafter, respectively - flammable medicinal products, explosive medicinal products) must fully comply with the current regulatory documents.
4.3. Flammable medicines and explosive medicines should be stored according to the principle of homogeneity in accordance with their physicochemical, fire hazard properties and the nature of the packaging. For this purpose, fire-resistant storage rooms for pharmacies and medical organizations, storage rooms of drug wholesalers and drug manufacturers (hereinafter - warehouse) are divided into separate rooms (compartments) with a fire resistance limit of building structures of at least 1 hour.
4.5. The required (per work shift) amount of flammable medicines for the current consumption is allowed to be kept in the filling rooms of warehouse premises and storage rooms of pharmacies and medical organizations, but with strict adherence to fire safety measures. The remaining amount of flammable medicines at the end of work at the end of the shift is returned to the main storage site.v 4.6. The floors of warehouses and unloading areas should have a hard, even surface, excluding potholes and other irregularities. It is forbidden to use boards and iron sheets for leveling the floors. Floors must provide a comfortable and safe movement people, cargo and vehicles, have sufficient strength and withstand the loads from the stored materials, ensure the simplicity and ease of cleaning the warehouse.
4.7. Warehouses for storing flammable and explosive drugs should be equipped with non-combustible and stable racks and pallets designed for the appropriate load. The racks are installed at a distance of 0.25 m from the floor and walls, the width of the racks should not exceed 1 m and have flanges of at least 0.25 m. Longitudinal aisles between the racks should be at least 1.35 m.
4.8. V pharmacy organizations for the storage of flammable and explosive drugs, isolated rooms are provided.
4.9. The storage room for flammable and explosive medicinal products must be equipped with automatic fire protection and alarms in accordance with the current regulatory documents.
4.10. Pharmacy organizations allow storage of pharmaceutical substances with flammable and combustible properties, up to 10 kg in built-in fireproof cabinets with doors at least 0.7 m wide and at least 1.2 m high. and have free access to it.
4.11. In pharmacy organizations built into a building for another purpose, the amount of stored flammable medicines in bulk should not exceed 100 kg.
Flammable pharmaceutical substances in quantities over 100 kg must be stored in a separate building in glass or metal containers, isolated from the storage rooms for flammable drugs of other groups.
4.12. It is strictly forbidden to enter the premises for storing flammable and explosive medicines with kerosene lamps and candles; you should only use flashlights.
V. Peculiarities of the organization of storage of medicines in the warehouses of drug wholesalers and drug manufacturers
5.1. Medicines stored in warehouses, should be placed on racks or on pallets with a height of at least 14.5 cm. It is not allowed to place medicines on the floor without a pallet.
Each name and each batch of medicinal products should be stored on separate trays. Pallets can be located on the floor in one row or on racks in several tiers, depending on the height of the rack. It is not allowed to place pallets with medicines on top of each other without racks.
5.2. It is not allowed to load the storage space by more than 1/3. At manual way for unloading and loading operations, the height of the stacking of medicines should not exceed 1.5 meters.
When using mechanized devices, medicines should be stored in several tiers, the height of their stacking on the shelf of the rack should not exceed 1.5 meters. Wherein total height placement of medicines on racks should not exceed the capabilities of mechanized loading and unloading facilities (lifts, autocars, hoists, etc.)
Vi. Features of storage of certain groups of medicines, depending on the physical and physicochemical properties, the impact on them of various environmental factors
All medicines, depending on the physical and physical and chemical properties, the impact on them of various environmental factors, are divided into:
requiring protection from light,
requiring protection from moisture,
requiring protection from volatilization and drying,
requiring protection from exposure to high temperatures,
requiring protection against low temperatures,
requiring protection from the effects of gases contained in the environment,
odorous and coloring;
disinfectants.
6.1 Storage of medicines requiring protection from light
6.1.1. Medicines requiring protection from light include: antibiotics, herbal preparations (tinctures, extracts, concentrates from herbal raw materials), herbal medicinal raw materials, organic preparations, vitamins and vitamin preparations; corticosteroids, essential oils, fatty oils, dragee preparations, salts of iodic and hydrobromic acids, halogenated compounds, nitro and nitroso compounds, nitrates, nitrites, amino and admido compounds, phenolic compounds, phenothiazine derivatives.
6.1.2. Pharmaceutical substances requiring protection from light should be stored in containers made of light-shielding materials (glass containers of orange glass, metal containers, packaging made of aluminum foil or polymer materials painted in black, brown or orange colors), v dark room or cabinets painted black inside with tight-fitting doors or tightly knit drawers with a tight-fitting lid.
For storage of drugs that are especially sensitive to light (silver nitrate, proserin, etc.), glass containers are pasted over with black opaque paper 6.1.3. Medicines requiring protection from light, packed in primary and secondary packaging, should be stored in cabinets or on racks, provided that measures are taken to prevent direct sunlight or other strong directional light from entering the medicinal products (use of reflective films, blinds, visors, etc. etc.).
6.2. Storage of medicines requiring protection from moisture
6.2.1. Medicines requiring protection from moisture include: hygroscopic substances and preparations (for example, potassium acetate, dry extracts, herbal medicinal raw materials, hydrolyzing substances, salts of nitric, nitrous, hydrohalic and phosphoric acids, alkaloids, sodium organometallic compounds, glucosides, antibiotics, enzymes, dry organopreparations), medicinal substances characterized in the State Pharmacopoeia as "very easily soluble in water", as well as medicinal substances, the moisture content of which should not exceed the limit established by the State Pharmacopoeia and other regulatory and technical documentation, and medicinal substances oxidized by atmospheric oxygen.
6.2.2. Pharmaceutical substances requiring protection from atmospheric water vapor should be stored in a cool place, in a tightly sealed container made of materials impermeable to water vapor (glass, metal, aluminum foil, thick-walled plastic containers).
6.2.3. Pharmaceutical substances with pronounced hygroscopic properties should be stored in a dry room in a glass container with an airtight seal, filled with paraffin on top. When closing the container with such drugs, it is necessary to thoroughly wipe the throat and cork.
6.2.4. Pharmaceutical substances requiring protection from moisture, obtained in plastic film packaging and intended for supply to pharmacies, should be stored in industrial packaging or transferred to glass or metal containers.
6.2.5. In order to avoid spoilage and loss of quality, special storage of the following medicines should be organized:
burnt gypsum should be stored in a well-closed container (for example, in tightly knit wooden boxes or barrels, preferably lined with plastic wrap from the inside);
mustard powder should be stored in hermetically sealed cans, varnished from the inside;
mustard plasters are stored in packs, packed in parchment paper or plastic wrap, which are placed in tightly sealed containers (for example, cardboard boxes pasted over from the inside with plastic film).
6.3. Storage of medicines requiring protection from volatilization and drying
6.3.1. Medicines requiring volatilization protection include:
volatile matter proper;
Medicines containing a volatile solvent (alcohol tinctures, liquid alcohol concentrates, thick extracts);
solutions and mixtures volatile matter(essential oils, solutions of ammonia, formaldehyde, hydrogen chloride over 13%, carbolic acid, ethanol various concentrations, etc.);
medicinal plant materials containing essential oils;
medicinal products containing crystallization water - crystalline hydrates;
medicinal substances that decompose with the formation of volatile products (iodoform, hydrogen peroxide, chloramine B, sodium bicarbonate);
medicinal substances with a lower limit of moisture content established by regulatory and technical documentation (magnesium sulfate, sodium paraaminosalicylate, sodium sulfate, etc.).
6.3.2. Pharmaceutical substances that require protection from volatilization and drying out should be stored in a cool place, in a hermetically sealed container made of materials impermeable to volatile substances (glass, metal, aluminum foil). The use of polymer containers, packaging and closures is allowed in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia and other regulatory and technical documentation.
6.3.3. Crystalline hydrates, depending on the relative humidity of the air, can exhibit the properties of both hygroscopic and weathering substances. Therefore, they should be stored in a hermetically sealed glass, metal and thick-walled plastic containers at a relative humidity of 50-65% in a cool place.
6.4. Storage of medicines requiring protection from exposure to high temperatures
6.4.1. Medicines requiring protection from exposure to elevated temperatures (hereinafter referred to as thermolabile medicines) include: medicinal substances requiring protection from volatilization and drying; low-melting substances;
immunobiological drugs;
antibiotics;
organopreparations;
hormonal drugs;
vitamins and vitamin preparations;
preparations containing glycosides;
medical fats and oils;
fat-based ointments and other substances.
6.4.2. Thermolabile medicines should be stored at room temperature (+15 - +25 degrees C), cool (cold) temperature (+8 - +15 degrees C). In some cases, a lower storage temperature is required (for example, for adenosine triphosphoric acid - +3 - +5 degrees C), which should be indicated on the label or in the instructions for use of the medicinal product.
6.4.3. Immunobiological medicinal products should be stored in industrial packaging separately by name, at the temperature indicated for each name on the label or in the instructions for use.
6.4.4. Immunobiological drugs of the same name are stored in batches, taking into account their shelf life.
6.4.5. During storage, immunobiological medicinal products should be visually inspected at least once a month.
6.4.6. Antibiotics should be stored in industrial packaging at room temperature, unless otherwise indicated on drug labels.
6.4.7. Organopreparations should be stored in a dark, cool and dry place at temperatures from 0 - +15 degrees. C, unless otherwise indicated on the labels or in the instructions for use.
6.4.8. Burov's fluid must be stored in a cool place. In case of turbidity, the solution is filtered and checked for compliance with all the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia. Opalescence of the solution is allowed.
6.5. Storage of medicines requiring protection from exposure to low temperatures
6.5.1. Medicines requiring protection from exposure to low temperatures include those whose physicochemical state changes after freezing and is not restored upon subsequent warming to room temperature (40% formaldehyde solution, insulin solutions, etc.).
6.5.2. A 40% formaldehyde solution (formalin) should be stored at a temperature not lower than + 9 degrees C. When a precipitate appears, it is kept at room temperature, then the solution is carefully drained and used in accordance with the actual formaldehyde content.
6.5.3. Glacial acetic acid should be stored at a temperature not lower than +9 degrees C. When a precipitate appears, the acid is kept at room temperature until the precipitate dissolves. If the precipitate does not dissolve, the liquid part of the acid is drained and used in accordance with the actual content acetic acid in the preparation.
6.5.4. Medical fatty oils must be stored at temperatures ranging from +4 to +12 degrees C. When a precipitate appears, they are kept at room temperature, decanted and checked for compliance with all the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia. When sediment appears, oils are not used in medical practice.
6.5.5. Freezing of insulin preparations is inadmissible.
6.6. Storage of medicines requiring protection from exposure to gases contained in the environment
6.6.1. The group of drugs that change under the influence of gases in the environment include:
substances reacting with atmospheric oxygen: various compounds of the aliphatic series with unsaturated intercarbon bonds, cyclic with side aliphatic groups with unsaturated intercarbon bonds, phenolic and polyphenolic, morphine and its derivatives with unsubstituted hydroxyl groups; sulfur-containing heterogeneous and heterocyclic compounds, enzymes and organopreparations;
substances that react with carbon dioxide in the air: salts of alkali metals and weak organic acids (for example, barbital sodium, hexenal, etc.), preparations containing polyatomic amines (for example, aminophylline), magnesium oxide and peroxide, sodium hydroxide, caustic potassium, etc. ...
6.6.2. Pharmaceutical substances requiring protection from exposure to gases should be stored in a hermetically sealed container made of materials impermeable to gases, if possible filled to the top.
6.6.3. Pharmaceutical substances that are easily oxidized by atmospheric oxygen should be stored in a dry room in a glass container with a hermetic seal.
6.6.4. Particular attention should be paid to the creation of storage conditions for sodium salts of barbituric acid, which must be stored in a hermetically sealed container made of materials impermeable to atmospheric water vapor and carbon dioxide.
6.7. Storage of odorous and coloring medicines
6.7.1. Odorous medicines include medicines that are both volatile and practically non-volatile, but have a strong odor.
6.7.2. Dyeing drugs include drugs that leave a colored mark that cannot be washed off by ordinary sanitary and hygienic processing on containers, closures, equipment and inventory (brilliant green, methylene blue, indigo carmine, etc.).
6.7.3. Odorless medicinal products (pharmaceutical substances) should be stored separately in a hermetically sealed container, impervious to odor, separately according to the names of medicinal products.
6.7.4. Coloring drugs (pharmaceutical substances) must be stored in a special cabinet in a tightly sealed container, separately by name. To work with coloring drugs for each item, it is necessary to allocate special scales, a mortar, a spatula and other necessary equipment.
6.8. Features of storage of disinfectants
Disinfectants (chloramine B, etc.) should be stored in a hermetically sealed container, in a cool place protected from light, in an isolated room, away from storage rooms for plastic, rubber and metal products, from rooms for obtaining distilled water.
6.9. Features of storage of medicines
6.9.1. Storage of medicinal products must meet the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia and the requirements of regulatory and technical documentation, taking into account the properties of the ingredients that make up their composition.
6.9.2. When stored in cabinets, on racks or shelves, medicinal products in industrial packaging should be placed with the label (marking) outward. A shelf card must be attached at the place of storage of the medicinal product, which indicates the name of the medicinal product, series, expiration date, quantity.
6.9.3. Storage of medicinal products in the form of a dosage form of tablets and dragees should be carried out in a dry and / or protected from light place.
6.9.4. Dosage forms for injection should be stored in a cool, dark place in a separate cabinet or isolated room, taking into account the particular container (fragility), unless otherwise indicated on the packaging of the medicinal product.
6.9.5. Liquid dosage forms (syrups, tinctures) should be stored in a hermetically sealed container in a cool, dark place.
6.9.6. Plasma-substituting and detoxifying solutions are stored in isolation at temperatures ranging from 0 - + 40 degrees. C in a dark place. In some cases, freezing of the solution is allowed, if this does not affect the quality of the drug.
6.9.7. Medicinal preparations in the form of extracts are stored in a glass container sealed with a screw cap and a stopper with a seal in a place protected from light. Liquid and thick extracts are stored at a temperature of +12 - +15 degrees. WITH.
6.9.8. Ointments, liniment are stored in a cool, dark place in a tightly sealed container. If necessary, the storage conditions for medicinal products are combined depending on the properties of the ingredients included in it. For example, preparations containing volatile and thermolabile substances are stored at a temperature not exceeding +10 degrees. WITH.
6.9.9. Storage of suppositories should be carried out in a dry, cool and dark place.
6.9.10. Storage of medicinal products in aerosol containers should be carried out at temperatures from +3 to +20 degrees. C in a dry, dark place, away from fire and heating appliances (unless otherwise indicated on the packaging of the medicinal product or in the instructions for its use).
Aerosol packages of medicinal products should be protected from shock and mechanical damage.
6.10. Storage of medicinal plant materials
6.10.1. Unpackaged medicinal plant materials should be stored in a dry, well-ventilated room in a well-closed container, in pharmacy organizations - glass, metal, in boxes with a lid, in warehouses - in bales or closed boxes on racks.
Cut unpackaged medicinal plant raw materials are stored in fabric bags, powders - in double bags: inner - paper, multilayer, outer - fabric, cardboard packages. Depending on the physicochemical properties of medicinal plant raw materials, packaging from polymeric materials is allowed. 6.10.2. Unpackaged medicinal plant materials containing essential oils are stored isolated in a well-closed container.
6.10.3. Some hygroscopic herbs, leaves and fruits must be stored in a sealed glass or metal container (foxglove leaves, kidney tea, etc.).
6.10.4. When storing unpackaged dried juicy fruits, in order to prevent damage to them by barn pests, it is recommended to place a bottle of chloroform in the fruit boxes, into the cork of which a tube is inserted to evaporate chloroform vapors. Chloroform is added as it evaporates.
6.10.5. Packaged medicinal plant raw materials are stored in pharmacies and warehouses on racks or in cabinets.
6.10.6. Unpackaged medicinal plant materials should be subject to periodic control in accordance with the requirements of the State Pharmacopoeia. Grass, roots, rhizomes, seeds, fruits that have lost their normal color, smell and the required amount active ingredients, as well as those affected by mold, granary pests, depending on the degree of damage, are either rejected, or after processing and control are used further.
6.10.7. During storage, special attention should be paid to unpackaged medicinal plant materials containing cardiac glycosides. For them, the State Pharmacopoeia has established stricter storage times and repeated re-control for the content of biological activity.
6.10.8. Unpackaged medicinal plant materials included in the lists of potent and poisonous substances approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 29, 2007 No. 964 "On approval of lists of potent and toxic substances for the purposes of Article 234 and other articles of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation, as well as large the size of potent substances for the purposes of Article 234 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation "(Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2008, No. 2, Art. 89; 2010, No. 28, Art. 3703) (hereinafter - Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 29, 2007 No. 964) is stored in a separate room or in a separate cabinet under lock and key.
6.11. Storage medicinal leeches
6.11.1. Premises for storing medicinal leeches should be light, without the smell of drugs. Sharp temperature fluctuations are not allowed, as this causes the death of leeches.
6.11.2. It is necessary to keep leeches in a pharmacy organization in wide-necked glass vessels at the rate of 3 liters of water for 50-100 individuals. To prevent leeches from spreading, the vessel is covered with a double layer of gauze and tied tightly with twine or elastic band.
6.11.3. Water for keeping leeches must be clean, free of chlorine, peroxide compounds, heavy metal salts, mechanical impurities, and have room temperature. The water in the vessels must be changed daily, preparing it in advance, two days before use. When changing the water, the walls of the vessel are washed from the inside, then the throat of the vessel is covered with gauze and the water is drained through it. The vessel is filled with clean water for 1/3 of the can. When keeping leeches, maximum purity is required, their proximity to odorous and toxic substances is not allowed. In case of leech disease (lethargy), the water is changed twice a day.
Vii. Features of storage of flammable medicines
7.1. Flammable medicines include medicines that are flammable and flammable.
7.2. Flammable medicinal products should be stored separately from other medicinal products.
7.3. Flammable medicines (collodion, ethyl alcohol, turpentine, ether, etc.) are stored in tightly sealed strong, glass or metal containers to prevent the evaporation of liquids from the vessels.
7.4. Bottles, cylinders and other large containers with flammable and flammable drugs should be stored on the shelves in one row in height. It is forbidden to store them in several rows in height using various cushioning materials. The storage of the indicated medicinal products near heating devices is not allowed. The distance from the rack or stack to the heating element must be at least 1 m.
7.5. The storage of bottles with flammable and flammable drugs (pharmaceutical substances) should be carried out in a container that protects against impacts, or in balloon tilters in one row.
7.6. At the workplaces of production facilities in pharmacy organizations, flammable and flammable drugs can be stored in quantities not exceeding the replacement requirement. In this case, the containers in which they are stored must be tightly closed.
7.7. Storage of flammable and flammable medicines in a fully filled container is not allowed. The filling degree should be no more than 90% of the volume. Alcohol in large quantities is stored in metal containers, which fill no more than 75% of the volume.
7.8. Joint storage of flammable medicines with mineral acids (especially sulfuric and nitric acids), compressed and liquefied gases, flammable substances ( vegetable oils, sulfur, dressings), alkalis, as well as with inorganic salts that give explosive mixtures with organic substances (potassium chlorate, potassium permanganate, potassium chromate, etc.).
7.9. Medical ether and ether for anesthesia are stored in industrial packaging, in a cool dark place away from fire and heating appliances.
7.10. Calcium hydrochloride is not a highly flammable drug, but upon contact with liquid oily organic products can cause them to ignite, and with ammonia and ammonium salts - an explosion, therefore, its storage should be carried out in isolation, taking into account the described properties.
VIII. Features of storage of explosive drugs
8.1. Explosive medicinal products include medicinal products with explosive and intrinsically explosive properties.
8.2. When storing explosive medicinal products, measures should be taken to prevent dust contamination, which can cause an explosion.
8.3. Containers with explosive drugs (barbells, tin drums, flasks, etc.) must be tightly closed to prevent vapors of these agents from entering the air.
8.4. Unpackaged potassium permanganate in contact with dust, sulfur, organic oils, ethers, alcohol, glycerin, organic acids and other organic substances - explosive.
It should be stored in warehouses in a special compartment in tin drums, and in pharmacy organizations - in bars with ground-in corks separately from the aforementioned means. Joint storage with flammable and flammable medicines is not allowed. Tin drums and bars with potassium permanganate are promptly freed from dust, carefully, avoiding friction.
8.5. Unpackaged nitroglycerin solution (has an explosive property) should be stored in pharmacies or warehouses in small well-sealed vials or metal containers in a cool dark place, taking precautions against fire. You should be very careful when moving dishes with nitroglycerin and weighing this drug, as the evaporation of spilled nitroglycerin threatens an explosion. Even small amounts of contact with the skin can cause poisoning (severe headaches).
8.6. When working with diethyl ether, shaking, shock, friction, etc. are not allowed.
8.7. It is strictly forbidden to store explosive medicines with acids and alkalis.
8.8. When storing nitric and sulfuric acids, measures must be taken to prevent their contact with wood, straw and other substances of organic origin.
IX. Features of storage of narcotic and psychotropic drugs
Narcotic and psychotropic medicines are stored in organizations in isolated rooms specially equipped with engineering and technical means of protection, and in places of temporary storage, subject to:
the rules for the storage of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances established by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 31, 2009 No. 1148 (Collected Legislation of the Russian Federation, 2010, No. 4, Art. 394);
special requirements for the storage conditions of narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances registered in the prescribed manner as medicines intended for medical use in pharmacies, medical institutions, research, educational institutions and drug wholesalers established by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated August 2, 2010 No. 590n (registered by the Ministry of Justice of Russia _____________).
X. Features of storage of potent and poisonous medicines, other medicines subject to quantitative accounting
10.1. Potent and poisonous medicinal products include medicinal products containing potent and toxic substances included in the lists of potent substances and poisonous substances approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 964 dated December 29, 2007, in combination with pharmacological inactive ingredients.
10.2. Storage of strong and poisonous drugs under international control in accordance with the UN Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 and the UN Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances of 1988 (hereinafter - strong and poisonous drugs under international control) , is carried out in premises equipped with engineering and technical means of protection, similar to those provided for the storage of narcotic and psychotropic drugs.
10.3. It is allowed to store in one technically fortified room strong and poisonous medicines under international control, and narcotic and psychotropic medicines.
In this case, the storage of potent and poisonous drugs and narcotic and psychotropic drugs should be carried out (depending on the volume of reserves) on different shelves of the safe (metal cabinet) or in different safes (metal cabinets).
10.4. Storage of potent and poisonous medicines not under international control is carried out in metal cabinets, sealed or sealed at the end of the working day.
10.5. Medicines subject to quantitative accounting, with the exception of narcotic, psychotropic, potent and poisonous medicines, are stored in metal or wooden cabinets, sealed or sealed at the end of the working day.
Information about the author
Konstantin Sokolov
General manager engineering and technical center "TECHNOVIK", an expert in the field of security of warehouse logistics and equipment.
Member of the Association of Manufacturers of Shelving and Warehouse Equipment (Russia), FEM (European Association of Handling Equipment and ERF (European Federation of Shelving Equipment).
Co-author of the unique patented technology of fragmentary repair of racks "Robusto".
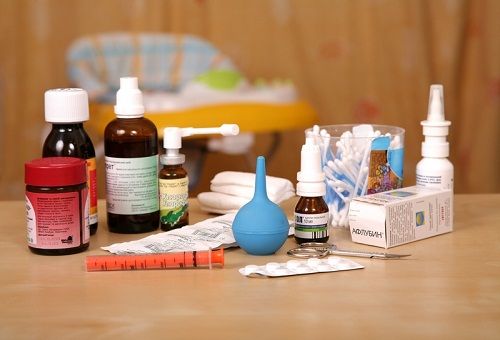
If an ordinary average person is asked whether he complies with the rules for storing medicines and asked to name at least one, he is likely to be confused. Many are sure that it is the lot of retirees to understand medicines and to know the terms and conditions of their storage. However, it is not. Every sane person at home should have a first aid kit with essential drugs. And if there are children, elderly and sick people at home, then there should be more than one first-aid kit. Let's figure out how to place medicines at home so that they are stored in optimal conditions and decide on the composition of the home first aid kit.
What the instruction will tell you about
Arriving home from the pharmacy with an arsenal of purchased pills, the first step is to study the section of the instructions explaining the conditions under which it is necessary to organize the storage of medicines.
In this case, one should focus on the following points:
- storage temperature;
- storage temperature after opening the package;
- shelf life after opening the package;
- humidity;
- storage away from sunlight;
- storage in places inaccessible to children.
As a rule, the instructions for any drug contain a phrase about storage in a place inaccessible to the child. It is very important to follow this rule! Many tablets look like candy, not to mention capsules with multi-colored "polka dots" inside, and the bottle of nasal drops resembles a doll's feeding bottle.

It's scary to imagine what could happen if the daughter not only feeds the doll from such a bottle, but also drinks herself. So the medicines that are used, as they say, here and now, should be stored so far away that children will never get to them. The storage of medicines in the first-aid kit should also be organized out of the reach of children.
On medications that may lose their healing properties under the influence of moisture, it is worth noting: store in a dry place. This means that these types of medicines must be stored in places with constant air humidity. In the instructions for some drugs, the humidity is directly indicated, for example, not higher than 70%. If the specific humidity is not indicated, it should be considered a dry place in which it does not exceed 50-60%.
Failure to comply with the rules for protection from direct sunlight can lead to photodegradation of the drug components, which is caused by the ultraviolet component of sunlight.
It is especially worth mentioning the temperature and shelf life. Distinguish the storage temperature of the drug in:
- unopened packaging;
- after opening the package, preparing a solution, etc.;
The same applies to the shelf life. These temperature and time characteristics must be known and distinguished. For example, the powder for the preparation of the "Regidron" solution is stored for 3 years at room temperature, and the solution itself is stored in the refrigerator for no more than a day. Many eye drops in unopened containers are stored for 2 years, and after opening - no more than 30 days.
Moreover, some drugs cannot be stored after opening. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully study the instructions and note whether there are any restrictions on the temperature and storage time of the drug after opening. If the storage periods before and after opening do not coincide, the rules for storing medicines are advised to mark the opening date on the container and from it to count the shelf life "after opening" specified in the instructions.
Reading the instructions for a particular drug, you can find specific temperature ranges at which it is advisable to store it. But sometimes you can find such phrases related to storage:
- at room temperature;
- in a cool place;
- in fridge.
If everything is clear with the refrigerator, then a cool place should be understood as a place where the temperature ranges from + 8 ° С to + 15 ° С. The room temperature is considered to be + 15- + 25 ° С. So the choice of storage location for a particular medicine should be based on this information. The inscription in the instructions: store at a temperature not higher than + 15 ° С, should be interpreted in the interval + 2 ° С - + 15 ° С. And the inscription: store at a temperature not lower than + 8 ° С should be understood as an interval of + 8 ° С - + 25 ° С. That is, with such instructions, the lower limit is + 2 ° С, and the upper limit is + 25 ° С.
Advice: do not forget that in summer the temperature in the room rises above + 25 ° C, so medicines, the storage temperature of which is limited to room temperature, should be transferred to the refrigerator. The storage of medicines organized in this way will be correct.
How to choose a place to store medicines
Now let's talk about the place where the storage of medicines will be the most convenient, safe and will allow medicines to keep their medicinal properties... As a rule, medicines are not stored in one place. This follows primarily from the fact that different medicines have different temperatures at which they are stored. There are medications that cannot be refrigerated, such as Valocordin. It is kept at room temperature.
In addition to the difference in temperature, there are other criteria on the basis of which many medicines are not kept together in one medicine cabinet. For example, medicines are stored separately:
- for indoor and outdoor use;
- liquid and tableted;
- medical devices such as Esmarch's mug, tonometer, heating pads, syringes, thermometers, etc.
Thermometers, especially mercury ones, need to be stored in a separate case in a secluded place: where children will not find it, and where it will not be accidentally touched or dropped. By the way, by 2020 Russia plans to completely abandon medical devices containing mercury, including thermometers. Therefore, it is already possible to switch to alternative devices for measuring temperature: electronic, tympanic thermometers and others. They are safer, allow faster temperature measurements, which is especially important if the family has small children.
Separately, I would like to dwell on herbal preparations. They should be kept in dry, dark places at temperatures up to 25 ° C. As a rule, a closet often becomes such a place. If packs with dried flowers and leaves are not opened, they can be safely stored there. But if cardboard box opened, it is better to pour its contents into an airtight jar, for example, from glass.
If this is not done, there is a high probability of infection. herbal preparations home bugs. They love bright aromas and attract them like a magnet. strong odors... For the same reason, open bags with mustard plasters should be stored wrapped in plastic.
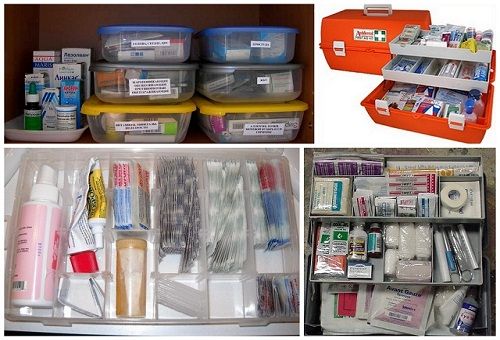
Thus, having sorted the available medicines into boxes, we get several first-aid kits. Where is the best place to organize the storage of medicines? Acceptable places in the house for this would be:
- fridge;
- wardrobe in the corridor (its upper shelf).
The refrigerator is suitable as a storage place for medicines due to the possibility of maintaining constant temperature within the range from + 5 ° С to + 7 ° С. It should be remembered that the temperature on the door is 1-2 ° C higher. To properly store medicines in the refrigerator, you need to place them in a tightly closed box or plastic bag. If there are children in the house, the first aid kit, which will be in the refrigerator, must be securely closed.
The closet in the hallway - the best place in order to place a first aid kit in it. The corridor has the smallest fluctuations in humidity and temperatures, there is no direct sunlight. The top shelf of the cabinet is the most suitable place for storing medicines that are kept at room temperature. Children won't get there.
Advice: the first aid kit should be located in a place where there is no access not only for children, but also for mentally unhealthy family members (if any) and pets.
It is worth noting that such popular places for storing medicines as the kitchen and bathroom are not the best choice. This is due to the fact that in these rooms, due to the specifics of their use, temperature and humidity often change, which can reach 80%. It is worth putting to cook something on long time- and the scale of the thermometer will show 30-33 ° С, and the hygrometer - 70%.
High humidity coupled with heat can lead to decomposition of the active medicinal components - as a result, the medicine will deteriorate before the expiration date. Also elevated temperatures and humidity can cause evaporation of the connecting drug components and, as a result, an increase in the concentration of active substances. Thus, it will be impossible to calculate the exact dosage of the medicine, and not knowing that this process occurred, to a large extent exceed it, which can even cause poisoning.
How to assemble a home first aid kit
In addition to the fact that the rules for storing medicines provide for their maintenance in a "working" condition, subject to the correct storage conditions, medicines should be readily available, that is, if necessary, a specific drug should be in its place so that you do not have to look for it.
To do this, every home should have several types of first aid kits:
- general home first aid kit;
- children's first aid kit;
- separate first aid kit for an elderly person.
Tip: the correct first aid kit should be a box, the cavity of which is divided into compartments. According to them, preparations similar in action should be decomposed. This will make it easier to find them. It is not allowed to store medicines in the first-aid kit without specifying their name (for example, without labels or remnants of tablets in a soft paper packaging, the name of which is torn off) and the expiration date. It is also helpful to keep the drug instructions.
A general household first aid kit should at least contain medications for emergency... It:
- bandages, cotton wool, plaster;
- hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green, iodine;
- antipyretic drugs;
- antihistamines;
- cough remedies;
- pain relievers;
- antidiarrheals, powder for oral rehydration solution.
If there are small children or elderly people in the house, personal first aid kits should be collected for them. In a children's first-aid kit, there should be the same types of medicines as in an adult, only allowed for use in children. If the child is given pills, the dose of which is calculated by weight, it is convenient to put a small piece of paper with the calculation in the package. If the baby falls ill suddenly, with an abundance of symptoms that frighten the mother, in her upset feelings it will be difficult for her to concentrate and calculate necessary for the child dose. This may concern, for example, paracetamol tablets, activated carbon etc.
It is convenient for an elderly person to collect all the medicines they use and place them in a separate box. So, if necessary, he himself can find what is in him this moment you need, among the relatively small number of your own vials and pill boxes. A person knows well how they look, and will not confuse them with anything else. As if the drugs he needed were in the general medicine cabinet.
When deciding where to put a particular medicine, you should always rely on the period and storage conditions before and after opening the package. Medicines should be stacked neatly, as they say, on the shelves. Then it will be easy to find them. Buy for future use only the products that are part of the home first aid kit and are necessary for first aid. Do not forget to carry out a "revision" in the first-aid kit from time to time, throwing out unusable medicines. Be healthy!
Details Here