Capillary hemangioma: causes, symptoms, treatment. Capillary hemangioma: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment.
A hemangioma formed from capillaries in any organ is a benign focal tumor in the form of a tumor, which is more common than other types of this pathology.
The main difference between a capillary hemangioma and all other similar neoplasms is the specific location of the vascular cells and a highly developed stroma.
The danger of vascular formation lies in the fact that with progression, it is possible to disrupt the functioning of the organ in which it is localized.
V in this case violated functionality liver.
In very rare cases, a tumor can mutate into a malignant neoplasm, so when the first symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from a qualified specialist.
Varieties of liver hemangiomas
According to histological structures, liver hemangioma is divided into two main types:
- Cavernous formation. It is a benign tumor characterized by the development of venous vessels and the formation of plasma-filled cavities.
- Capillary formation. Presented as choroid plexuses small size with possible formation of cavities.
Capillary hemangioma
Experts who study the nature of the occurrence of capillary gamangioma of the liver are inclined to believe that its development begins as early as prenatal period and continues after birth. The causes of this pathology are unknown.
Symptoms of the development of the disease
The majority of patients who had a capillary tumor did not show any complaints or discomfort.

Most often, this pathology is discovered quite by accident during the diagnosis of other conditions.
The developing neoplasm does not cause any discomfort or pain syndrome, localized in the area of the right hypochondrium.
In those cases when the formation begins to progress and grows into an organ, the functionality of the damaged organ is inhibited, and, consequently, the corresponding symptoms appear.
Hemangioma can also make itself felt with the development of any complications.
Predisposing factors for the development of pathology
Since the exact cause of the development of such a pathology as hemangioma has not been identified to date, there are a number of factors, the effect of which can lead to the development of pathology:

When to see a doctor?
For help, a doctor should be consulted immediately after the first incomprehensible and unknown symptoms appear. This may be a signal of the manifestation of a more severe course of the pathological condition.
The best option for any person is to have a yearly whole body exam. It is necessary to identify any pathology that has a latent, asymptomatic course.
This will allow you to protect yourself and, if necessary, get adequate treatment on time.
Diagnostics
To detect vascular neoplasms in the liver, use following methods research:
Treatment
Treatment of liver hemangioma is always a difficult question for doctors, since in most cases, nutrition of the formation occurs from several arterial vessels. And consequently from this, any surgical intervention is accompanied by massive bleeding.
The operation is performed in cases where the neoplasm meets all the evaluation criteria:
For the treatment of hemangiomas, they are most often used radiation therapy... Such treatment is indicated only for adults in exceptional cases, since it is possible to provoke severe complication- radiation sickness.
Medical treatment of vascular neoplasm implies long-term intake hormonal drugs, the action of which is aimed at stopping the development of tumor cells and scarring the affected area. Also, doctors prescribe beta-blockers, which stabilize intravascular pressure.
Forecasts and conclusions
There are three main stages in the formation of hemangiomas:
- Proliferation stage. The tumor is rapidly progressing, as a rule, the duration of this stage does not exceed 10-12 months;
- Rest stage. Most often, it is characterized by minor changes in the neoplasm and it lasts for about a year and a half;
- The stage of involution. During this period, the hemangioma begins to shrink.
Capillary hemangioma is a benign tumor that develops from small vascular capillaries... Most often, such a tumor is congenital, sometimes a neoplasm occurs in the first week of life. How dangerous is the disease? What are the treatments for capillary hemangioma?
Types of capillary hemangioma
- Star view is a small, red, punctate lump that rises above the skin.
- Pineal view is a strongly protruding tumor-like neoplasm bright red.
- Cavernous view is a limited hemispherical tumor.
- Point view manifests itself in the form of small bright red rounded spots.
- Branchy view is a soft and nodular neoplasm.
- Flat view develops as pink or bright red spot... When you press on it, it begins to fade sharply.
- Racemose species is the most dangerous, with it there is a small tumor, which contains many thick veins.
The causes of the appearance of capillary hemangioma
To date, scientists have not yet fully clarified the cause of the development of benign capillary hemangioma, which does not develop into malignant tumor... This is most likely a congenital anomaly.
Occasionally, a capillary hemangioma can form on the liver. The main reason is - hormonal disbalance... The formation is small, although in some situations the hemangioma can grow rapidly.
Capillary hemangioma symptoms
Capillary formation is most often diagnosed in infants. Quite often, within 3 years, the hemangioma may first decrease in size, and then completely disappear. As shows medical practice, the child's self-education disappears by the age of 5. In some situations, the hemangioma begins to grow rapidly and affects adjacent tissues.
Common is capillary, which appears as a vascular birthmark but eventually spreads to half of the face. The stain looks ugly and brings discomfort to the patient.
In newborns, hemangioma may be in different places, but most often appears on the head, neck. How the benign tumor will grow and develop is unknown. It is dangerous when the hemangioma begins to grow actively.
If capillary hemangioma appears in the area of the nose, ear, eyes, mouth, it not only spoils appearance but also leads to serious problems with vision, hearing, breathing. In this situation, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor in order to prevent serious complications.
Diagnostics of the capillary hemangioma
The doctor examines the patient completely and notices any neoplasms. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound scan is performed, on time you can find out for sure:
- Where is the tumor located?
- What is the structure of the tumor?
- How voluminous the tumor is.
In the case of an extensive neoplasm, angiography is performed. If the doctor suspects renal hemangioma, the specialist prescribes an ultrasound scan, X-ray, computed tomography. Also, the patient must be sure to pass a urine and blood test.
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are used to diagnose capillary vertebral hemangioma. You can learn about capillary hemangioma of the liver using scintigraphy.
Important! With capillary hepatic hemangioma, it is forbidden to conduct a biopsy, otherwise everything may end up in the strongest.
To diagnose capillary hemangioma of the liver, it is necessary to monitor the patient's condition for three months. Sometimes hemangioma leads to serious complications.
Methods of treatment and prevention of capillary hemangioma
To prevent the appearance different entities it is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Watch what you eat.
- Are not long time in the sun.
- Consult a geneticist in a timely manner.
If you have a small hemangioma on your skin, you do not need to treat it. The doctor decides on removal in the event of an extensive hemangioma on the face.
Point hemangiomas are removed using electrothermocoagulation. Keep in mind that after the completed procedure, you may have a small cosmetic defect.
If a cavernous hemangioma appears on the face, alcohol sclerosis is used to get rid of it. In the event of a combined hemangioma, cryotherapy is first performed and part of the skin is removed, then sclerotherapy is used for the subcutaneous part.
Capillary hemangioma treatment laser
To delete benign neoplasm use a laser. He is not only efficient procedure, after it there are no scars and scars. Also a plus is that the procedure takes a little time.
What if the capillary hemangioma starts to grow?
- The neoplasm is irradiated with X-rays. It becomes noticeable how the tumor decreases significantly in size, and after a while it dies altogether.
- Embolization is the blockage of blood vessels. After the procedure, the tumor dies.
Please note that only your doctor can select the treatment based on the tests performed.
Attention! There are times when surgical treatment impossible because the capillary hemangioma is extensive. In this case, hormone treatment can be prescribed (Prednisolone is most often prescribed). This method of treatment makes it possible to stop the development of the tumor, dries up the pathological vascular network.
Thus, it refers to a benign neoplasm that does not develop into a malignant tumor. Despite this, pathology violates familiar image life, because it spoils the appearance. In this situation, self-medication is not worth it, consult a doctor immediately. Based on the examination, he will select the necessary course of therapy for you.
Character, differing in structure, structure and tissue from which they are formed. For example, hemangiomas grow from vascular tissues.
Description of what is hemangioma?
Such formations belong to tumor processes of a non-cancerous nature, due to venous abnormalities of congenital origin... Such a tumor can grow anywhere with a vascular network.
A hemangioma is characterized by a lack of tendency to malignancy, but such tumors are capable of rapidly growing and re-forming after surgical intervention... As a result of uncontrolled growth, self-propagation of damage to neighboring organs and tissue, the formation of extremely dangerous hemorrhages.
Causes of occurrence in children and adults
There is no reliable information about the provoking factors of hemangioma in adults, although there are many assumptions and hypotheses explaining the factors and mechanisms of formation of certain tumor processes.
It has been absolutely proven that there is no connection between mutations and the development of education. The generally accepted theory of the onset of hemangioma is a viral infectious factor that occurs at the time of pregnancy up to 12 weeks.
The bottom line is that during the first trimester, formation occurs circulatory system, and the toxic effect of viruses leads to the formation of intraorganic or superficial hemangiomas already in infancy or in adulthood.
The picture shows a flat hemangioma of the skin of the face in a newborn baby
In adults, such tumor processes are activated due to a traumatic factor or as a result of a thrombus-forming process.
Views
There are several types of hemangiomas. In connection with the location of the tumor, they are divided into:
- Skin formations, which are characterized by their location in the superficial epidermal layers. Similar tumor formations belong to harmless hemangiotic varieties, which is why, as a rule, they are not touched. Although in the case of being close to the visual or auditory organs, on the face, back or in the perineum, removal is necessary in order to avoid irreversible changes and dysfunction of closely located organs;
- Musculoskeletal formations arising on the spine, muscle or joint tissues. These tumors are a little heavier, but not so much that they are removed immediately after detection. As a rule, surgical measures are started when a hemangioma of this nature becomes the culprit of problems with the skeletal formation of children;
- Parenchymal hemangiotic processes concentrate in the testicles, bladder, hepatic, adrenal or renal, cerebral or pancreatic parenchyma. Such tumors require immediate removal, because they are fraught with intraorganic lesions or bleeding.
In accordance with the histological structure, hemangiomas are classified according to morphological characteristics into such varieties as a simple or capillary tumor, combined, venous or mixed formations, etc.
In addition, hemangioma is senile and infantile. Infantile form hemangiomas are most common in newborn girls and are usually located in the head or neck. Outwardly, an infantile hemangioma looks like a reddish spot that disappears autonomously by about 7-9 years.
Senile hemangiomas are also called senile. Such formations look like crimson-red bumps, which are mistaken for moles. But with a mole, senile hemangioma has structural differences, because a hemangiotic tumor consists of venous structures.
Capillary
This hemangiotic form is considered one of the most common tumor processes. Capillary hemangioma is characterized by a shallow location in the upper epithelial layers. The structure of the tumor is represented by the accumulation of many interconnected by walls and intertwined capillaries. Such formations are prone to penetrating germination.
Such tumors are located mainly on the head and neck. They can occupy large areas, causing cosmetic discomfort to the patient.
Photo capillary hemangioma on the scalp
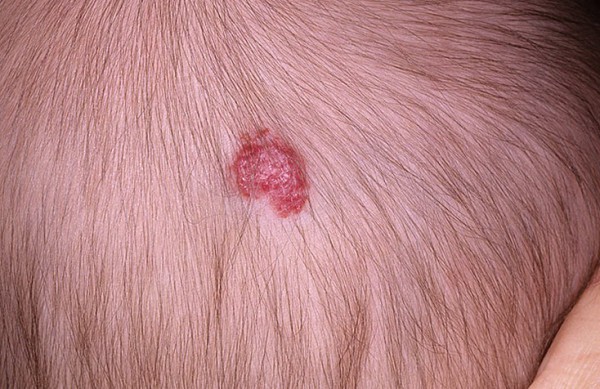
With pressure on such a hemangioma, a rapidly passing blanching of the tumor is traced. This is an asymmetrical spot with jagged edges, which has a purple-cyanotic or reddish-pink tint. Such tumors are prone to ulceration, although they are almost never malignant.
Cavernous
A similar tumor concentrates in subcutaneous tissue, forming from larger vessels than the capillary form of education. It looks like a protruding purple swelling formed from a venous accumulation. Cavernous hemangioma can only grow into subcutaneous tissues, and internal organs or muscle tissues are very rarely affected. Occurs on the skin of the thighs and buttocks.
Photo of cavernous hemangioma on the neck of a child
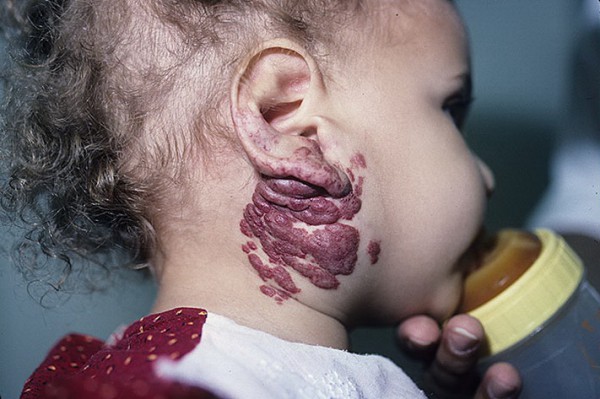
Such formations can be diffuse or limited. Diffuse hemangiomas have blurred edges, occupy a large area in the form of multiple formations of different sizes. Limited tumors are distinguished by a clear demarcation from other areas.
Combined
Hemangiomas of a combined nature represent a cavernous-capillary mixture, such formations are located under the skin in the tissue and in the epidermal layers. Hemangioma is formed on intraorganic surfaces, on the bones of the skull, frontal bone or skin. This tumor is most specific for adult patients.
Racemose
This variety is relatively rare. Racemic hemangioma is also called branched. Most often, such neoplasms are located on the limbs and hairy parts heads. They consist of wriggling and intertwining blood vessels. Such a neoplasm is usually considered by specialists as a cavernous hemangioma.
Mixed
A similar term means a tumor consisting of vascular, nervous, lymphoid and connective tissues. The group of such formations includes angioneuromas, angiofibromas, gemlinfangiomas and other tumors. The clinical data of this kind of formations are due to the type of predominant tissue.
Venous
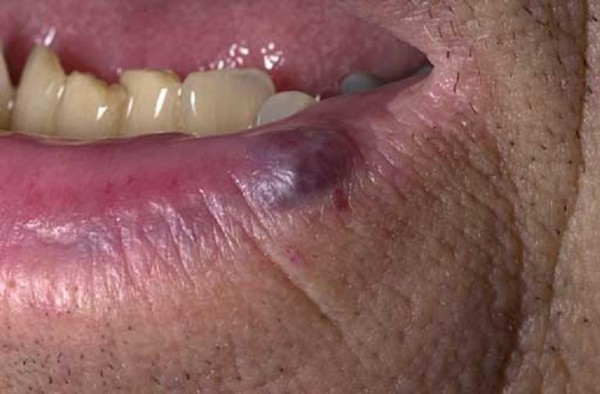
Venous hemangioma is often called a swelling of senile lips or a venous lake, because this formation is usually found on the face of older people. Experts suggest that UV radiation has an important effect on the development of such tumors.
Externally, venous hemangioma looks like a soft dark purple or bluish papule with a diameter of no more than a centimeter. Usually such a formation is located on the lower lip.
The photo clearly shows how it looks venous hemangioma of the skin in an adult
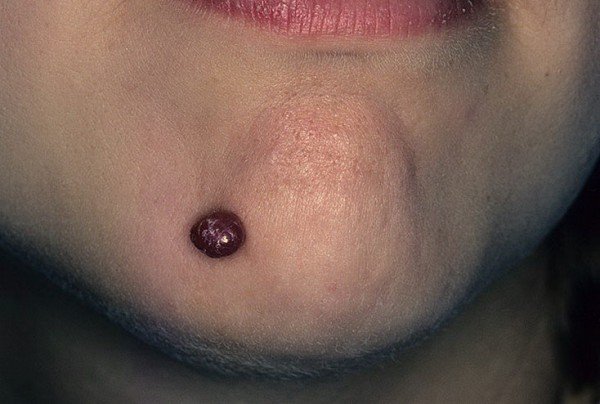
The tumor causes only cosmetic discomfort. When pressed, the venous hemangioma becomes almost colorless, because it has a thin-walled cavity structure and is filled with blood.
The size of the vascular tumor
Hemangioma parameters vary according to the type of tumor formation. There are venous tumors several millimeters or centimeters in size.
Symptoms and localization
The clinical picture of vascular hemangiomas depends on many factors such as age criteria, the location of the hemangioma and the depth of its infiltration into the tissue.
Hemangioma of the skin
Such a venous tumor is located on any part of the body, therefore symptomatic manifestations do not depend on whether the tumor is located on the facial zone or on the gluteal zone. In general, the neoplasm can be characterized by the following features:
- On the surface of the skin cover there is a slight elevation, which can be of any shade of the red palette (from light pink to purple). The tint hemangiotic characteristics are influenced by the number of vessels that make up the tumor;
- With the infiltration of tumors in depth on the skin, different kinds pathological changes caused by insufficient blood supply to tissues - increased hairiness or ulceration, microcracks or hyper-perspiration. Any of these signs can cause hemangioma bleeding;
- At the location of the tumor, there is a slight swelling of the surrounding tissues and pain syndrome;
- When pressed, the formation has a dense consistency, which indicates the absence of a tendency to malignancy. Soft structure indicates a predisposition to increase in size in the near future;
- Around the hemangioma, the formation of paresthesia areas is possible, on which numbness or goosebumps are felt.
When the vascular mass is located near the visual or auditory organs, the nasal cavity or the trachea, the risk increases functional disorders or dysfunction of these organs.
Body
The clinical picture of vascular tumors of the body is almost identical to skin tumors. Its symptoms are also associated with swollen red tones, which cause painful discomfort.
Such formations can be localized in areas where they will be injured (shoulder area, armpits, mammary glands, fingers, belt, etc.). Such damage is fraught with a violation of the integrity of the tumor, cracks, bleeding and the formation of ulcers on their surface.
If the formation is of a rapidly growing nature, then it may undergo infiltration into the region of the ribs, muscle tissue, which will lead to disturbances in these organs.
On the face, head, leg, lip and nose
Such localization of vascular tumors in clinical practice is observed quite often. The main symptomatology of such formations is swelling, reddish tint, soreness in the area of the tumor.
Photo of vascular hemangioma on the lip in an adult
Such localization is dangerous because the formations are too close to the most important organs such as the brain, the orbit of the eyes, ears, eyelids, etc.
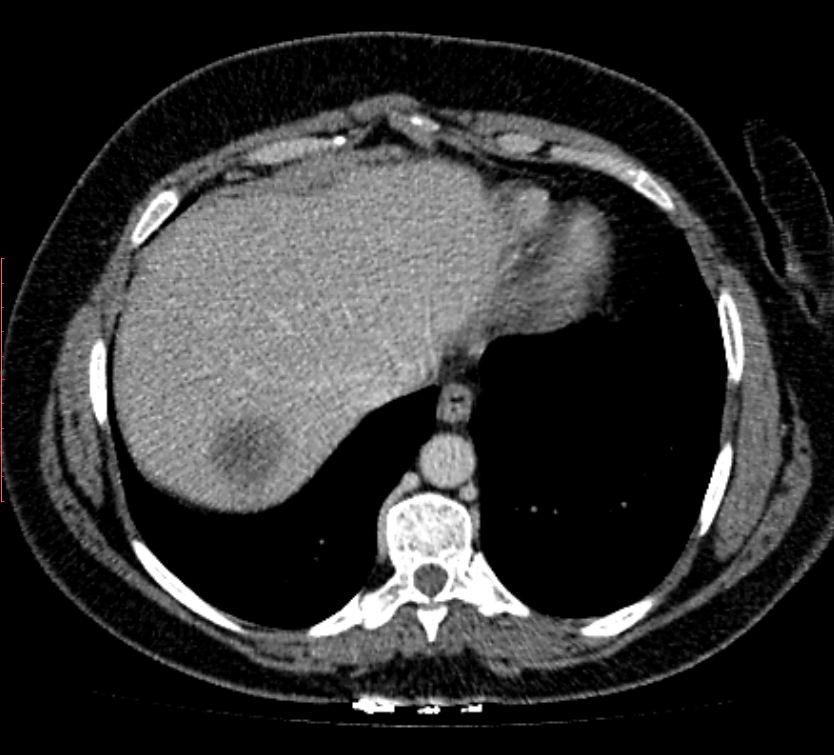
Liver
Usually, such a localization of hemangioma remains unnoticed for a long time, developing asymptomatically. Usually, the gallbladder is also detected by chance during ultrasound, MRI or CT of the liver. A similar tumor is more often found in women 35-50 years of age.
Spine
General principles of treatment
The same therapeutic approach is applied to patients of any age, depending only on the location and properties of the hemangioma. If education does not belong to the group with high risk complications, then it is being monitored, because such tumors are prone to self-elimination.
In general, treatment is indicated:
- When located near the eyes or with a negative effect on vision;
- In the presence of ulceration;
- When the tumor is located in respiratory system or in the immediate vicinity of it, etc.
The tumor is predominantly monitored. If it starts to get complicated, then they resort to vigorous action. Treatment of a tumor is possible with several methods of a conservative and surgical nature.
Among the conservative techniques used:
- Taking funds based on propranolol or timolol - Propranobene, Anaprilin
- Lubrication of the tumor with freshly squeezed celandine juice. Course - 2 weeks;
- Wetting the hemangioma with a solution copper sulfate(1 tbsp. L. Per glass of water). Course - 10 days;
- Daily kombucha compresses. The course is 3 weeks.
How to get rid of a tumor in the spleen
Traditional treatment of hemangioma localized in the spleen area is splenectomy, which leads to absolute recovery.
How to treat diseases in the tongue
Hemangiomas of the tongue are eliminated in several ways:
- Moxibustion;
- Laser treatment;
- Cryotherapy;
- Sclerotherapy;
- Traditional surgical removal.
In most clinical cases, hemangioma in the tongue does not cause concern.
Can the neoplasm pass by itself?
With childhood growth and development, the reverse development of hemangioma is possible with its subsequent self-elimination. If a cavernous tumor is not prone to growth, then it can pass by about 5-7 years of age, so it is better to choose a wait-and-see tactic in such a clinical case. If the tumor begins to grow rapidly, then surgical treatment is necessary.
Which doctor to contact
Therapeutic tactics are selected by specialists: pediatrician, surgeon, dermatologist, etc.
What are the reasons for the development of hemangioma and its treatment, this video will tell:
Did you like the article? Share with your friends on social networks:
In contact with
classmates
And subscribe to site updates in
Capillary hemangioma is a benign neoplasm consisting of interlacing capillaries. There are cavities between the vessels, which are also filled with blood.
This type of tumor occurs quite often, but the reasons for its formation have not yet been clarified. Most often, hemangioma forms on the skin. Also found on the walls internal organs which have a wide capillary network (heart, liver, brain).
In most cases, capillary hemangioma is a congenital defect, however, there are variants of acquired hemangiomas.
The main feature of the disease is its unpredictability. The tumor can dissolve on its own or begin to progress to a gigantic size, affecting adjacent tissues and organs.
Causes
Most experts agree that capillary hemangioma is intrauterine pathology... Its reasons may be:
- hormone therapy for mom during pregnancy,
- mom's infectious disease during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy,
- hypoxia caused by various pathologies of a pregnant woman,
- birth and postnatal injuries.
In children, the formation of acquired hemangiomas is possible. They develop for the following reasons:
- severe bruises and injuries,
- uncontrolled treatment,
- long course of infectious and viral diseases,
- inadequate hormone treatment,
- autoimmune disorders
- pathology of cardio-vascular system,
- exposure to carcinogenic factors.
Symptoms
In children under 3 years of age, a rapid growth of a benign neoplasm most often occurs.
Young parents can independently determine the presence of superficial hemangiomas. By external changes skin, depending on the type of tumor on children's skin, the following may appear:
- spider veins with a smooth red spot in the middle,
- multiple flat bright spots that turn pale on pressure,
- pineal tumors of bright red color, reaching significant sizes,
- sharply outlined cave-like neoplasms of pink or red color,
- points round shape different shades red and pink.
With the development of hemangiomas of internal organs in babies, it can be observed:
- capriciousness
- loss of appetite,
- bad dream,
- an enlarged liver
- nausea, vomiting,
- weakness,
- increased body temperature.
At an older age, children may complain of pain.
Diagnostics of the capillary hemangioma in a child
To confirm the diagnosis or to identify the pathology of internal organs, it is necessary to carry out a number of diagnostic procedures.
- anamnesis of the mother's pregnancy and childbirth,
- external examination of the baby's skin,
- palpation of the liver, other internal organs,
- Ultrasound of internal organs,
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography,
- biopsy of the damaged area of the skin or mucous membrane.
Complications
Hemangioma is a benign tumor, for this reason, in the case of its timely treatment the forecast is the most favorable. However, with delayed or inadequate treatment, a number of complications are possible:
- damage to many tissues and organs,
- the transition of a tumor from benign to malignant with the ensuing consequences,
- cosmetological problems,
- psychological difficulties due to appearance,
- deterioration in the functioning of individual organs and systems,
- internal bleeding
- sepsis,
- peptic ulcer diseases of the affected organs and tissues,
- death.
Treatment
What can you do
Parents should carefully monitor their behavior and general condition your baby. In the event of the appearance of neoplasms, and even more so with their increase, it is necessary to consult a pediatrician.
In no case should you self-medicate and try to remove the tumors that have appeared.
When making a diagnosis for effective treatment and to minimize the consequences, parents should:
- fully comply with all medical recommendations,
- do not use traditional medicine methods,
- keep breastfeeding as long as possible,
- protect the baby from stressful situations,
- minimize the risk of injury,
- strengthen immunity in all possible ways.
What the doctor does
Most often, during the period from birth to 3 years, either the rapid development of the disease or its self-removal occurs. For this reason, doctors choose a wait and see approach. Treatment is prescribed only with a sharp increase in the tumor.
The treatment course can consist of one or more points:
- taking corticosteroids,
- a course of cytostatic drugs,
- hormone therapy,
- applying pressure bandages,
- the use of topical gels and creams,
- removal of the neoplasm.
The exact same therapy can be indicated at an older age if the existing neoplasms are extensive and are a noticeable cosmetic defect.
Prophylaxis
To prevent hemangioma in her baby, a mother during pregnancy must follow a number of recommendations:
- lead healthy image life,
- treat all existing diseases in a timely manner and under the supervision of doctors,
- take vitamins
- protect the child from stressful situations,
- not be under the influence of carcinogenic factors.
After the birth of a child, in order to avoid the development of pathology or its appearance, it is important:
Arm yourself with the knowledge and read a useful informative article about capillary hemangioma in children. After all, to be parents means to study everything that will help maintain the level of health in the family at the level of "36.6".
Find out what can cause an ailment, how to recognize it in a timely manner. Find information about what are the signs that can identify ailment. And what tests will help identify the disease and make the correct diagnosis.
In the article, you will read all about the methods of treating such a disease as capillary hemangioma in children. Clarify what effective first aid should be. How to treat: choose medications or folk methods?
You will also learn what the danger of untimely treatment of the disease of capillary hemangioma in children can be, and why it is so important to avoid the consequences. Everything about how to prevent capillary hemangioma in children and prevent complications.
A caring parents will be found on the service pages full information about the symptoms of capillary hemangioma disease in children. What is the difference between the signs of the disease in children at 1, 2 and 3 years old from the manifestations of the disease in children at 4, 5, 6 and 7 years old? What is the best way to treat capillary hemangioma in children?
Take care of the health of loved ones and be in good shape!
Hemangioma Is a benign pediatric one that develops from cells of vascular tissue, and is a volumetric neoplasm, consisting of many smallest vessels ( capillaries). The child is either born with hemangioma ( in 30% of cases), or it develops in the first weeks of life.
Most intensive growth observed in the first six months of a child's life, after which the growth processes slow down or stop altogether, and the process of reverse development can begin. In more severe cases, the hemangioma may continue to grow at an older age, increase its size and grow into nearby organs and tissues, followed by their destruction. This leads to both a serious cosmetic defect and functional impairment. various bodies and systems that can have the most adverse consequences.
Hemangioma is quite common and occurs in every tenth newborn. It appears three times more often in girls than in boys. The most commonly affected areas of the face, neck and scalp ( up to 80% of all skin hemangiomas).
Interesting Facts
- The number of hemangiomas in a child can vary from one to two to several hundred.
- They occur as small hemangiomas ( 2 - 3 mm) and huge ( up to several meters in diameter).
- Hemangiomas in adults are extremely rare and are the result of incomplete cure in childhood.
- Small hemangiomas may disappear on their own by the age of five.
- Hemangioma is characterized by the most aggressive growth among all benign tumors.
Causes of hemangioma
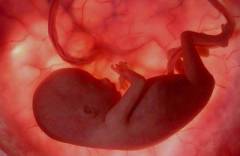 To date, science has no unequivocal opinion about the causes of hemangioma. It is known that the development of this tumor is associated with a violation of the process of vascular formation during the period.
To date, science has no unequivocal opinion about the causes of hemangioma. It is known that the development of this tumor is associated with a violation of the process of vascular formation during the period. Fetal vascular formation
During the growth of the fetus in the womb, the first blood vessels begin to form at the end of 3 weeks of embryo development from a special embryonic tissue - the mesenchyme. This process is called angiogenesis.Depending on the mechanism of vascular development, there are:
- primary angiogenesis;
- secondary angiogenesis.
It is characterized by the formation of primary capillaries ( the smallest and thinnest blood vessels) directly from the mesenchyme. This type of vascular formation is characteristic only for early period embryonic development... Primary capillaries do not contain blood and are a single layer of endothelial cells ( in an adult organism, endothelial cells line the inner surface of blood vessels).
Secondary angiogenesis
It is characterized by the growth of new vessels from the already formed ones. This process is genetically determined and also controlled by local regulatory factors.
So, with the development of an organ and an increase in its mass, the deeper sections begin to experience a lack of oxygen ( hypoxia). This triggers a number of specific intracellular processes, the result of which is the release of a special substance - vascular endothelial growth factor ( VEGF, Vascular endothelial growth factor).
This factor, acting on the endothelium of already formed vessels, activates its growth and development, as a result of which new vessels begin to form. This leads to an increase in oxygen delivered to the tissues, which inhibits the production of VEGF. Thus, angiogenesis is controlled for more later stages development of the fetus and after the birth of the child.
It is important to note that fetal tissues have a pronounced ability to recover from various kinds of injuries and injuries. As a result of any, even the most insignificant injury ( squeezing, tearing shallow vessel and hemorrhage) healing processes are activated, including secondary angiogenesis with the possible subsequent development of hemangiomas.
Theories of the occurrence of hemangioma
To date, there are more than a dozen theories trying to explain the mechanisms of the appearance and development of hemangiomas, but none of them is able to independently cover all aspects of this disease.The most plausible and scientifically grounded are:
- lost cells theory;
- fissural ( crevice) theory;
- placental theory.
The most modern and scientifically based theory, according to which hemangioma occurs as a result of impaired development of capillaries from the mesenchyme. In the process of embryogenesis, clusters of immature blood vessels ( capillaries), which then turn into veins and arteries. At the end of the formation of the organ, a certain amount of unused immature vascular tissue may remain in it, which disappears over time.
Under the influence of certain factors this process is disturbed, as a result of which involution of capillaries is not observed, but, on the contrary, activation of their growth is noted. This can explain the birth of children with hemangioma, or its appearance in the first weeks of a child's life. It also becomes clear the possibility of the formation of this tumor in almost any tissue of the body.
Fissural theory
At the initial stages of development of the embryo in the region of the skull, the so-called embryonic slits are distinguished - the places of the future location of the sensory organs ( eyes, ear, nose) and the mouth opening. At week 7, blood vessels and nerves that take part in the formation of organs grow into these cracks.
According to the fissural theory, hemangioma occurs in the fetus as a result of a violation of the development of vascular primordia in these areas. This explains the more frequent location of these neoplasms in the area of natural openings of the face ( around the mouth, eyes, nose, ears), however, the mechanism of the development of hemangiomas in other areas of the skin remains unexplained ( on the trunk and limbs) and in the internal organs.
Placental theory
It is assumed that placental endothelial cells enter the fetal bloodstream and remain in its organs and tissues. During the period intrauterine development maternal factors inhibition of angiogenesis do not allow vascular tissue to grow actively, however, the field of birth, their action ceases and intensive growth of hemangioma begins.
The mechanism of occurrence of hemangioma
Despite the variety of theories, they have in common the presence of immature embryonic vascular tissue in the skin and in other organs, where it should not normally be. However, this is not enough for the development of hemangioma. The main factor triggering the process of capillary growth and tumor formation is tissue hypoxia ( lack of oxygen).Therefore, various pathological conditions leading to impaired oxygen delivery to the fetus or newborn baby are potentially risk factors for hemangioma. This data has been confirmed by many scientific studies.
The appearance of a hemangioma can be promoted by:
- Multiple pregnancy. With development in two or more fetuses, the likelihood of having children with hemangioma is increased.
- Placental insufficiency. Characterized by insufficient oxygen delivery ( and other substances) to the fetus due to a violation of the structure or function of the placenta.
- Injury during childbirth. When the child passes through the birth canal, the tissues of the head are compressed quite strongly, which disrupts the normal circulation of blood in them. Long ( or, conversely, too fast), narrow birth canal or big size the fetus can provoke the development of local hypoxia with the subsequent formation of a hemangioma in the scalp and face.
- Eclampsia. This state develops during or during childbirth and is characterized by a pronounced rise in the mother with possible loss of consciousness and, as a result, the delivery of oxygen through the placenta to the fetus is impaired.
- Smoking during pregnancy. When part of the lungs are filled with tobacco smoke, as a result of which the amount of oxygen entering the body decreases. If the mother's body is able to tolerate this condition relatively easily, then hypoxia in the fetus can cause increased growth capillary tissue and the development of hemangioma.
- Intoxication. Impact of various occupational hazards and alcohol abuse during pregnancy increases the risk of having a baby with hemangioma.
- Mother's age. It is scientifically proven that childbirth after 40 years is associated with increased risk the presence of various developmental anomalies in the fetus, including vascular neoplasms.
- Prematurity. Starting from 20-24 weeks of pregnancy, a surfactant is produced in the lungs of the fetus - a special substance, without which pulmonary respiration is impossible. A sufficient amount of it accumulates only by the 36th week of pregnancy, therefore, the breathing processes in premature babies violated, which leads to tissue hypoxia.
Development of hemangioma
Distinctive feature of these neoplasms is a clear staging of their course.In the process of development, hemangiomas are distinguished:
- A period of intense growth. It is characteristic of the first weeks or months after the onset of hemangioma and, as a rule, stops by the end of the first year of life ( possible exceptions). Outwardly, the tumor is bright red, constantly increasing in diameter, as well as in height and in depth. The growth rate varies within various limits - from insignificant to very pronounced ( a few millimeters a day). This period the most dangerous in terms of the development of complications ( ulceration of the tumor, germination into neighboring organs and their destruction).
- Growth stagnation period. In most cases, by the end of the first year of life, the growth of the vascular neoplasm stops, and up to 5-6 years it increases slightly, corresponding to the growth of the child.
- Reverse development period. In about 2% of cases, there is a complete spontaneous disappearance of the hemangioma. Some time after the growth has stopped ( in months or years) the surface of the tumor becomes less bright, may ulcerate. The capillary network gradually disappears, which is replaced either normal skin (with small, superficially located hemangiomas), or scar tissue ( in the case of masses growing into the deep layers of the skin and subcutaneous tissue).
Types of hemangiomas
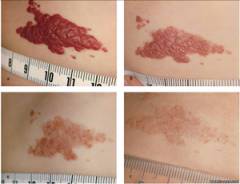 Depending on the nature of the growth, structure and location of the hemangioma, the method of its treatment is chosen, therefore, when establishing the diagnosis, it is also necessary to determine the type of tumor.
Depending on the nature of the growth, structure and location of the hemangioma, the method of its treatment is chosen, therefore, when establishing the diagnosis, it is also necessary to determine the type of tumor. Depending on the structure, they are distinguished:
- Capillary ( simple) hemangiomas. They occur in 96% of cases and represent a dense capillary network of bright red or dark crimson color, towering above the surface and growing into deep layers. This form counts initial stage development of the disease and is characterized by the intensive formation of new capillaries, prone to germination in the surrounding tissues, destruction of the latter.
- Cavernous hemangiomas. Are the result further development capillary hemangiomas. In the process of growth and increase in size, as a result of the overflow of capillaries with blood, some of them expand and rupture, followed by hemorrhage into the hemangioma tissue. The consequence of this process is the formation of small, blood-filled cavities ( cavern), inner surface which is lined with endothelial tissue.
- Combined hemangiomas. Combined hemangioma is referred to as a transitional stage from capillary to cavernous form. It is a tumor in which there is an alternation of immature capillary tissue with cavities filled with blood ( caverns). The increase in the size of the tumor occurs mainly due to the formation of new capillaries, which subsequently also undergo transformation into cavities, up to the complete replacement of the hemangioma.
- Hemangiomas of the skin. They occur in 90% of cases. They can be single or multiple, capillary or cavernous type.
- Hemangiomas of internal organs. Almost always accompanied by multiple hemangiomas of the skin. May vary depending on structure and shape. The most common and dangerous is damage to the liver, bones and muscles.
What do hemangiomas look like on the skin?
Hemangiomas can affect any area of the skin, but are most common in the face, neck, and scalp. Their appearance differs depending on the structure.| Hemangioma on the skin | Detailed description | Photo |
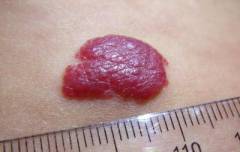
| Capillary hemangioma | It is a painless volumetric formation of elastic consistency, rising above the surface of the skin by a few millimeters. The edges are uneven, clearly demarcated from healthy skin, which is practically unchanged. The surface is bumpy, lobed, bright red or dark crimson. When pressed, the tumor may fade slightly, restoring its original color after the pressure is removed. | 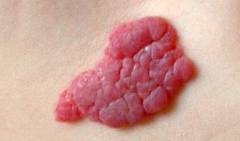 |
| Cavernous hemangioma in the face | A volumetric, painless formation, which completely or partially protrudes above the surface of the skin ( often the hemangioma is located deeper, and only a small part of it rises above the skin). The edges are uneven, clearly demarcated from intact skin. The surface is swollen, rough. When pressed, the formation subsides and may fade slightly. With the cessation of pressure, a gradual restoration of the original size and color of the tumor is noted. | 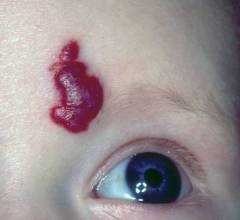 |
| Cavernous hemangioma of the leg (subcutaneous form) | The bulk of the tumor is located in deeper tissues ( in subcutaneous fat, in muscles) and reaches significant sizes. The affected area is enlarged ( in comparison with a symmetrical healthy area of the body). Numerous capillaries are visible on the surface of the skin. When pressed, the elastic, elastic consistency of the tumor is determined. | 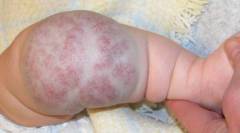 |
| Combined hemangioma of the hand (cutaneous form) | It is characterized by a widespread volumetric formation of a bright red color, towering above the surface of the skin. The affected areas do not have clear boundaries, in some places the transition to the deeper layers of the skin is determined. The surface is uneven, bumpy. In some places, there are more prominent dark crimson tubercles, which fall off when pressed ( caverns). | 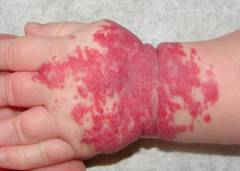 |
Diagnostics of the hemangioma
 Despite the fact that the hemangioma belongs to benign tumors, its intensive growth may be accompanied by a serious cosmetic defect ( when located in the area of the face, head, neck). In addition, when located in internal organs, this neoplasm can lead to their destruction, posing a danger to health and even human life.
Despite the fact that the hemangioma belongs to benign tumors, its intensive growth may be accompanied by a serious cosmetic defect ( when located in the area of the face, head, neck). In addition, when located in internal organs, this neoplasm can lead to their destruction, posing a danger to health and even human life. A pediatric surgeon is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of hemangiomas, who, if necessary, can involve other specialists.
The diagnostic process includes:
- examination by a doctor;
- instrumental research;
- laboratory research;
- consultations of other specialists.
Examination by a doctor
If at birth or in the first weeks of life a red spot is found on the baby's skin, rapidly increasing in size, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since hemangiomas are often characterized by very rapid, destructive growth.What questions will the surgeon ask?
- When did education appear?
- Does the tumor size change ( how much and for what period of time)?
- Was any treatment used and was it effective?
- Did the child's parents, grandparents have hemangiomas, and if so, what was their course?
- Carefully examine the neoplasms and surrounding areas.
- He will study in detail the structure of the tumor under a magnifying glass.
- Determines the consistency of the formation, the nature of the changes when pressed.
- Will change the size of the tumor ( to determine the intensity of growth on subsequent visits).
- He will carefully examine all the skin of the child in order to identify previously undetected hemangiomas.
Instrumental research
Usually, there are no difficulties in diagnosing hemangioma, and the diagnosis is made on the basis of a survey and careful examination. Instrumental diagnostic methods are used to identify lesions of internal organs, as well as when planning surgical removal of a tumor.In the instrumental diagnosis of hemangiomas, the following are used:
- thermometry;
- thermography;
- ultrasound procedure;
- biopsy.
A research method that allows you to measure and compare the temperature of certain areas of the skin. For this purpose, a special device is used - a thermocouple, which is made up of two electrodes connected to an electrical sensor. One of the electrodes is placed on the surface of the tumor, the other - on a symmetrical, but unaffected area of the skin. The sensor allows you to set the temperature difference with an accuracy of 0.01 ° C.
Hemangioma, which is a dense network of capillaries, is supplied with blood better than normal skin, therefore, the temperature in the area of this tumor will be slightly higher. An increase in temperature by 0.5 - 1 ° C in comparison with unaffected skin indicates active growth tumors.
Thermography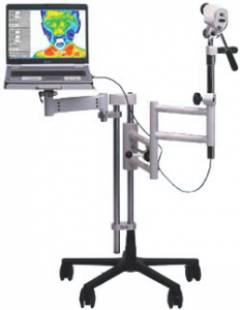 Safe, fast and inexpensive research method that allows you to identify areas of the skin with elevated temperature... The principle of the method is based on the same phenomena as thermometry.
Safe, fast and inexpensive research method that allows you to identify areas of the skin with elevated temperature... The principle of the method is based on the same phenomena as thermometry.
The patient sits down in front of a special infrared camera, which, for a certain time, registers heat radiation from the surface of the skin. After digital processing of the information received, a heat map of the investigated area appears on the monitor, on which warmer foci are displayed in red, and relatively cold ones in blue.
Unlike thermometry, which allows to determine the temperature only on the surface of the tumor, thermography gives more accurate information about the spread of hemangioma and allows you to more clearly define its boundaries, which are often located deep in soft tissues.
Ultrasound procedure (Ultrasound)
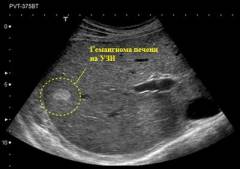 Ultrasound examination is a safe, non-contraindicated method that allows you to determine the presence of masses in the internal organs, as well as to reveal the presence of cavities in cutaneous and subcutaneous hemangiomas. Modern ultrasound machines are quite compact and easy to use, which allows you to carry out a diagnostic procedure right in the doctor's office.
Ultrasound examination is a safe, non-contraindicated method that allows you to determine the presence of masses in the internal organs, as well as to reveal the presence of cavities in cutaneous and subcutaneous hemangiomas. Modern ultrasound machines are quite compact and easy to use, which allows you to carry out a diagnostic procedure right in the doctor's office.
The method is based on the principle of echogenicity - the ability of various body tissues to reflect sound waves, while the degree of reflection will be different depending on the density and composition of the fabric. The reflected waves are recorded by special sensors, and after computer processing, an image of the examined organ is formed on the monitor, reflecting the density and composition of its various structures.
The indications for an ultrasound scan are:
- determination of the structure of the hemangioma ( cavernous or capillary);
- determination of the depth of the location of the hemangioma;
- suspicion of hemangiomas of internal organs ( liver, kidney, and other localization).
- clarification of the size of the tumor when planning a surgical operation.
- The capillary component of the hemangioma. Represents small areas of medium or increased echogenicity ( a dense network of capillaries reflects sound waves to a greater extent than the surrounding tissue), with an inhomogeneous structure and fuzzy contours.
- Cavernous component. A cavern is a cavity filled with blood. The density of blood, and, consequently, its ability to reflect sound waves, is less than that of a dense capillary network, therefore, on ultrasound, caverns are determined as areas of reduced echogenicity ( against the background of a hyperechoic capillary network), rounded or oval, sizes from 0.1 to 8 - 10 millimeters.
CT scan ( CT scan)
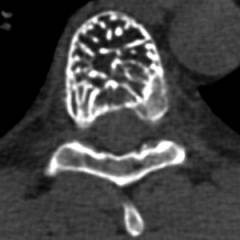 A modern high-precision method that allows you to identify tumors of internal organs with sizes from a few millimeters.
A modern high-precision method that allows you to identify tumors of internal organs with sizes from a few millimeters.
The essence of the method lies in the ability of tissues to absorb X-rays passing through them. To conduct the study, the patient lies down on a special retractable computer tomograph table and is placed inside the apparatus. A special device begins to rotate around it, emitting X-rays, which, when passing through the tissues of the body, are partially absorbed by them. The absorption rate depends on the type of fabric ( the maximum ability to absorb X-rays is noted in bone tissue, while they pass through the air spaces and cavities almost completely).
The rays passed through the body are registered with a special device, and after computer processing, a detailed and clear image of all organs and tissues of the investigated area appears on the monitor.
It must be remembered that holding computed tomography combined with the receipt of a certain dose of radiation, in connection with which the appointment this study must be strictly justified.
The indications for CT are:
- suspicion of hemangioma of the liver and other organs;
- inaccurate data on ultrasound;
- planning of surgical removal of hemangioma ( in order to clarify the size of the tumor and the involvement of neighboring organs).
- Hemangioma of the liver ( and other internal organs). Represents education reduced density, rounded or oval in shape with uneven edges and a heterogeneous structure.
- Hemangioma of the bones. Since bone tissue absorbs X-rays as much as possible, its normal CT image will be the densest ( white ). When the hemangioma grows, the bone tissue is destroyed and replaced by a capillary network, as a result of which the bone density decreases, in their projection there are darker areas corresponding to the prevalence of the tumor. Can be recorded resulting from the destruction of bone tissue.
- early childhood (due to high radiation exposure);
- claustrophobia ( fear of confined spaces);
- the presence of tumor diseases ( Maybe Negative influence CT for their course);
- the presence of metal structures ( prostheses, implants) in the field of research.
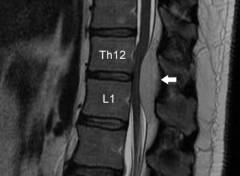 Modern high precision diagnostic method, allowing you to study in detail the structure of the spine and spinal cord... MRI is absolutely safe and harmless, the only contraindication is the presence of metal parts in the human body ( implants, prostheses).
Modern high precision diagnostic method, allowing you to study in detail the structure of the spine and spinal cord... MRI is absolutely safe and harmless, the only contraindication is the presence of metal parts in the human body ( implants, prostheses).The principle of performing magnetic resonance imaging is the same as for CT, only instead of X-rays, the phenomenon of nuclear resonance is used, which manifests itself when the human body is placed in a strong electromagnetic field. As a result, the nuclei of atoms release certain kind energy, which is registered by special sensors, and after digital processing is presented on the monitor in the form of an image of the internal structures of the body.
The main advantages of MRI over CT are the absence of radiation and a clearer image of the soft tissues of the body ( nerves, muscles, ligaments, blood vessels).
The indications for MRI of the spine are:
- Suspected spinal cord compression by a tumor. Such suspicions may be caused by the presence of multiple hemangiomas on the skin in combination with gradually developing clinical symptoms spinal cord injury ( impaired sensitivity and motor functions arms, legs and other parts of the body).
- Planning surgery to remove the tumor.
- Inaccurate data with other research methods.
- Germination of hemangioma into the vertebral bodies. Moreover, their bone structure is disturbed, partially or completely replaced by capillary tissue.
- The degree of compression of the spinal cord by the tumor. A vascular formation is determined that protrudes into the lumen of the spinal canal and squeezes the spinal cord, or grows into it ( in this case, the tissue of the spinal cord at the level of the lesion is not determined).
- The degree of tumor invasion into the ligamentous apparatus of the spine.
This method allows you to most accurately determine the structure and size of the hemangioma, to assess the involvement of neighboring organs and tissues.
The essence of the method is to inject a special contrast agent into a vein or artery from which the tumor is supplied with blood. This procedure performed under the control of CT or MRI, which makes it possible to assess the speed and intensity of the spread of the contrast agent in the capillary network of the hemangioma.
Angiography is a rather dangerous diagnostic method, therefore, it is prescribed only in extreme cases, when it is necessary to determine the size of the tumor as accurately as possible ( when planning surgical operations in the area of the face, head, neck).
Absolute contraindications for angiography are:
- for contrast agent;
- and / or.
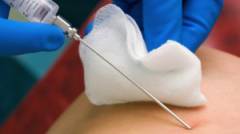 This study includes intravital sampling of body tissues for the purpose of subsequent examination under a microscope of their structure and cellular composition.
This study includes intravital sampling of body tissues for the purpose of subsequent examination under a microscope of their structure and cellular composition. There are risks associated with biopsies, the most dangerous of which is bleeding. In addition, the diagnosis can be confirmed without this study, therefore the only reasonable indication for a biopsy is a suspicion of a malignant degeneration of the hemangioma.
Early signs of malignant hemangioma can be:
- Changes in the surface of the tumor - violation of the usual structure, intense growth in height and depth, ulceration or peeling.
- Consistency change - the structure becomes heterogeneous, denser areas appear.
- Color change - darker areas of brown or black appear.
- Changes in nearby skin areas - signs of inflammation appear ( redness, swelling, soreness, local fever).
- Incisional biopsy. It is most commonly used to sample skin hemangiomas. Under sterile conditions after treatment of the tumor and surrounding tissues ethyl alcohol local anesthesia is performed on the site from which it is planned to take material. A certain area of the skin is excised with a scalpel, which must necessarily include the tumor tissue and the intact skin adjacent to it.
- Puncture biopsy. It is more often used to collect material from internal organs ( liver, spleen, muscles and bones). Under ultrasound control, a special hollow game with sharp edges is injected directly into the tumor tissue, while both peripheral and central sections of the neoplasm enter the needle.
Biopsy material ( biopsy), is placed in a sterile test tube and sent to the laboratory, where, after specially processing and staining, microscopic examination the structure and cellular composition of the tumor, as well as comparison with intact skin areas.
All hemangiomas removed surgically, should also be sent for histological examination without fail.
Laboratory research
Laboratory methods studies are not very informative in the process of diagnosing hemangiomas and are more often used to identify complications of the disease, as well as to monitor the patient's condition during treatment.The most informative is ( UAC), although its changes are nonspecific and can occur in other diseases.
Blood sampling is done in the morning on an empty stomach. After pretreatment with alcohol, the skin ring finger it is pierced with a special needle to a depth of 2 - 4 mm, after which several milliliters of blood are drawn into the pipette.
Typical changes in the UAC are:
- Thrombocytopenia. A condition characterized by a decrease in the amount in the blood due to their increased destruction in the tissue of the hemangioma, which is clinically manifested by increased bleeding of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Anemia. Decrease in the amount and in the blood. is a consequence of bleeding and hemorrhage caused.
Consultation of other specialists
To help in establishing a diagnosis, as well as when various complications hemangiomas, pediatric surgeon consultation with specialists from other areas of medicine may be needed.The diagnostic process may involve:
- Oncologist - with suspicion of malignant degeneration of the tumor.
- Dermatologist - with ulceration of hemangiomas or in the presence of concomitant skin lesions.
- Infectionist - with the development of an infectious process in the area of hemangioma.
- Hematologist - with the development of complications from the blood system ( severe thrombocytopenia and / or anemia).
Hemangioma treatment
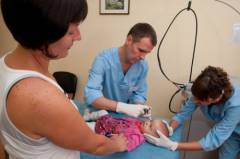 Previously, in relation to hemangiomas in children, it was recommended wait and see tactics, however, the data of recent studies suggest the opposite - the earlier the treatment of the disease begins, the fewer complications and residual effects may develop.
Previously, in relation to hemangiomas in children, it was recommended wait and see tactics, however, the data of recent studies suggest the opposite - the earlier the treatment of the disease begins, the fewer complications and residual effects may develop. This statement is due to the unpredictable and often rapid growth of the tumor, which is relatively short time can grow several times and grow into adjacent organs and tissues. In favor early start treatment is also evidenced by the data of statistical studies, according to which only 2% of skin hemangiomas undergo complete independent reverse development, and in more than 50% of cases visible cosmetic defects remain on the skin ( scarring).
In the treatment of hemangiomas, the following are used:
- physical methods of removal;
- surgical removal method;
- drug therapy.
Physical methods for removing hemangiomas
V this group includes methods of physical impact on the hemangioma tissue, resulting in its destruction and subsequent removal.TO physical methods relate:
- cryodestruction;
- laser irradiation;
- sclerotherapy;
- electrocoagulation;
- close-focus X-ray therapy.
It is used to remove superficial or shallow skin hemangiomas, the size of which does not exceed 2 cm in diameter. The essence of the method lies in the effect on the tumor with liquid nitrogen, the temperature of which is -196 ° C. In this case, the tumor tissue freezes, its death and rejection, followed by replacement with normal tissue. Removal of large tumors can lead to the formation of extensive scars, representing a serious cosmetic defect.
The main advantages of this method are:
- high-precision destruction of tumor tissue;
- minimal damage to healthy tissue;
- relative painlessness;
- minimal risk bleeding;
- quick recovery after the procedure.
The whole procedure takes several minutes, after which the hemangioma area is treated with a solution of potassium permanganate, and the patient can go home. Usually 2 - 3 sessions of cryotherapy are required with intervals of 3 - 5 days. After the end of the treatment, the area where the hemangioma used to be must be treated with brilliant green for 7 to 10 days until a dense crust forms. Complete healing takes place within a month.
Laser irradiation
Modern method removal of superficial and deeper skin hemangiomas with a diameter of up to 2 cm using a laser.
The main effects of laser radiation are:
- thermal destruction of irradiated tissues ( charring and evaporation);
- coagulation of blood in vessels exposed to the laser ( prevents bleeding);
- stimulation of the process of restoring normal tissue;
- prevention of scar formation.
A dense crust forms at the site of exposure, which is rejected on its own after 2 - 3 weeks. A small scar may form under it ( at large sizes removed hemangioma).
Sclerotherapy
This method can be used to remove larger hemangiomas located on the skin or in internal organs. The principle of the method is based on the cauterizing and coagulating ability of some chemical substances, which are introduced into the tissue of the hemangioma, causing the destruction of blood vessels and cavities, followed by their replacement with scar tissue.
Currently, for the purpose of sclerosing hemangiomas, 70% alcohol is used. The procedure should be performed by an experienced surgeon under sterile conditions. The skin area around the hemangioma is injected with a solution of novocaine ( for the purpose of pain relief), after which 1 to 10 ml of alcohol ( depending on the size of the neoplasm).
After 2 - 3 hours, inflammation and swelling of the tissues appears at the injection site, and after 2 - 3 days the area of the hemangioma becomes denser and becomes painful. The procedure is repeated several times with a break of 7 to 10 days. The complete disappearance of the hemangioma is noted in the period from 3 months to 2 years after the end of treatment.
Electrocoagulation
The method of destruction of tumor tissue through the action of high-frequency pulsed electric current... When exposed to current on living tissues, rapid rise their temperatures are up to several hundred degrees, followed by destruction, charring and rejection of dead masses.
The main advantage of this method is the minimal risk of bleeding, since high temperatures lead to blood clotting in the vessels feeding the hemangioma and sclerosis ( scarring) of their lumen.
With the help of an electric knife, superficial and intradermal hemangiomas can be removed, and electrocoagulation can be used as an auxiliary method in surgical removal tumors.
Close focus X-ray therapy
It consists in the local impact of X-rays on the tissue of the hemangioma, which leads to the destruction of the capillaries of the tumor. X-ray therapy is rarely used as independent method treatment of hemangioma and is more often used in the preoperative period in order to reduce the size of the neoplasm, which will reduce the volume of surgery.
The impact of X-rays on the body, especially children, is associated with a number of side effects, the most dangerous of which is the possibility of developing a malignant neoplasm. In this regard, close-focus radiography is used in extremely rare cases when other methods of treatment are ineffective.
Surgical method for removing hemangiomas
As an independent method of treatment, it is used for small superficial skin formations located in areas of the body where postoperative scar less significant in cosmetic terms ( in men in the back, legs).During the operation, under general anesthesia the entire tumor and 1 - 2 mm of the surrounding healthy skin are removed. When the hemangioma is located in deeper tissues and in internal organs, the volume of the operation is determined by the size of the tumor and the degree of invasion into the affected organ.
Quite often in the preoperative period, conservative methods of treatment are used ( drug therapy, ), as a result of which there is a decrease in the size of the tumor, which makes it possible to reduce the volume of the operation and to a lesser extent injure the nearby organs ( muscles, bones).
Drug treatment of hemangiomas
Until recently, drug therapy was practically not used in the treatment of hemangiomas. but Scientific research recent years found that some drugs have a beneficial effect on the course of the disease, slowing down the growth process and reducing the size of the tumor.However, the complete disappearance of the hemangioma as a result of only drug therapy observed only in 1 - 2% of cases, therefore this method treatment is more often used as preparatory stage before surgical or physical removal of the tumor.
| Name of the medication | Mechanism of action | Method of administration and dosage |
| Propranolol | The drug blocks certain vascular receptors ( B2-adrenergic receptors), which affects the hemangioma. The action of propranolol is due to:
| It is taken internally. The initial dose is 1 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into two doses ( in the morning and in the evening). With no effect ( manifested in a slowdown in the growth of hemangioma and a decrease in its size) the dose can be increased to 3 mg / kg / day. The course of treatment is from 6 months. During treatment, it is necessary to monitor the performance of the cardiovascular system weekly ( to measure blood pressure, heart rate, conduct). |
| Prednisone | Steroid hormonal drug, the action of which is due to the activation of the formation of scar tissue in the area of the hemangioma. As a result, the capillaries are compressed, the blood flow through them stops, they are desolate and destroyed, being replaced by scar tissue. The effects of prednisolone are:
| It is taken orally, after a meal, with a glass of water.
|
| Vincristine | An antineoplastic drug, the action of which is due to blocking the processes of cell division, as a result of which the growth of hemangioma slows down and stops. The drug has a mass side effects, and therefore it is prescribed only if other medicines are ineffective. | Introduced intravenously, once a week, at a dose of 0.05 - 1 mg per square meter body surface. During treatment, it is necessary to regularly monitor the composition of peripheral blood ( conduct general analysis blood at least 2 times a month). |
Consequences of hemangioma
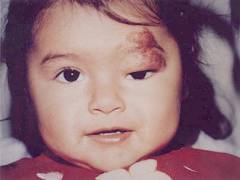 With the wrong and untimely treatment of hemangioma, a number of complications can develop that pose a threat to human health and life.
With the wrong and untimely treatment of hemangioma, a number of complications can develop that pose a threat to human health and life. The most formidable complications of hemangioma are:
- germination and destruction of nearby organs;
- destruction of muscles, bones, spine;
- compression and / or destruction of the spinal cord ( with the development of paralysis);
- destruction of internal organs ( liver, kidney, spleen and others);
- hemangioma ulceration and attachment;
- malignancy;
- thrombocytopenia and anemia;
- cosmetic defect ( untreated hemangiomas and their scars can persist throughout life).
- the initial location of the tumor;
- the speed and nature of growth;
- time of initiation of treatment;
- the adequacy of therapeutic measures.
