Groups (smg) in schools are still seriously lagging behind the requirements of the time - Document. Guidelines for organizing classes in special medical groups in a secondary school
Belyaev Andrey Nikolaevich,
Yaroslavl, 2015
REGULATORY DOCUMENTS FOR TEACHING PHYSICAL EDUCATION IN SHG GROUPS
- Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 329 “On Physical Culture and Sports”, dated December 4, 2007
- Letter"On the evaluation and certification of students referred for health reasons to a special medical group for physical education." Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2003, No. 13-51 / 123
- Letter"On holding physical culture minutes in general educational institutions areas. Department of Education of the Yaroslavl Region, dated April 18, 2007, No. 037/01-10
- Letter"On exemption from physical education, organization of work and certification of students assigned to a special medical group for health reasons." Department of Education and Department of Health and Pharmacy of the Yaroslavl Region dated February 14, 2008 No. 612/01-11 and No. 745/02.
- Letter“On attestation in the subject “Physical Education”, students assigned to a special medical group for health reasons. Department of Education of the Yaroslavl Region, December 18, 2001 No. 01-10/167
- Letter"On methodological recommendations on the organization of physical education classes with students with deviations in state of health". Department of Education of the Yaroslavl Region, 09.02.2000, No. 01-10/155
A. N. Belyaev, teacher the highest category

A.N. Belyaev, teacher physical education the highest category
- Order No. 701-1 dated 06.06.2011 “On improving the organization of the provision of medical care during physical education and sports events in the Yaroslavl region"
- Letter of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation dated September 1, 2014 “Recommendations for the provision of medical care to students. Monitoring compliance with sanitary and hygienic requirements for conditions and organization physical education in educational organizations"
- Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, Research Institute of Hygiene and Health Protection of Children and Adolescents, FGBU " Science Center health of children" RAMS, M - 2012 "Medical and pedagogical control over the organization of physical education classes for students with health problems
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

FEDERAL LAW RF No. 329 "ABOUT PHYSICAL CULTURE AND SPORT FROM 4.12.2007", article number 28
- Conducting compulsory physical education classes within educational programs in volume, educational standards, as well as additional classes exercise within the extra educational programs.
- Creation of conditions, provision sports equipment and classroom equipment.
- Formation of physical culture skills in students, taking into account individual characteristics and health status.
- Implementation of physical activities during training sessions.
- Holding medical control for the organization of physical education.
- Formation of a responsible attitude of parents to the health of children and their physical education.
- Carrying out annual monitoring physical fitness.
- Assistance in the organization and holding of sports events with the participation of students
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

Health groups
MAIN
PREPARATORY
SPECIAL GROUP "A"
SPECIAL GROUP "B"
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

MAIN HEALTH GROUP
The main medical group for physical education includes:
- students without deviations or with minor deviations in the state of health, a favorable type of reaction of the cardio-respiratory system to dosed physical activity and the level of AF corresponding to age and gender.
- with functional disorders that did not lead to lagging behind peers in physical development and physical fitness.
Juveniles assigned to the main medical group classes are allowed in full according to the curriculum of physical education using preventive technologies, preparing and passing tests of individual physical fitness.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category
PREPARATORY GROUP
The preparatory medical group for physical education includes:
- without deviations or with minor deviations in the state of health, a favorable type of cardio-respiratory system for dosed physical activity and a level of AF that does not correspond to age and gender;
- with minor deviations in the state of health, a satisfactory or unfavorable type of response of the cardio-respiratory system to dosed physical activity;
- frequently ill(3 or more times a year);
- children, having morphofunctional disorders or physically poorly prepared;
- at risk for developing diseases(pathological conditions);
- With chronic diseases (conditions) in the stage of stable clinical and laboratory remission, lasting at least 3-5 years.
Minors assigned to this group are allowed to take classes in physical education curricula, subject to a more gradual mastery of a set of motor skills and abilities, especially those related to the presentation of increased requirements to the body, more careful dosing of physical activity and exclusion of contraindicated movements .
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

IN THE PREPARATORY GROUP :
- Tests, passing individual standards and participation in mass physical education events are allowed after an additional medical examination / observation at a PE lesson.
- To participate in sports competitions these students are not allowed.
- Additional classes are recommended to improve general physical fitness in an educational institution or at home.
- As tests, only those exercises are possible that, taking into account the form and severity of the disease, are not contraindicated in children.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

SPECIAL SUB-GROUP "A" (III GROUP, HEALTH GROUP)
- with health disorders permanent ( chronic diseases(states), birth defects development, deformities without progression, in the stage of compensation) or temporary;
- with developmental disabilities requiring restrictions physical activity.
Minors assigned to this group are allowed to practice health-improving physical culture according to special programs (preventive and health-improving technologies).
When practicing health-improving physical culture, the nature and severity of health disorders, physical development and the level of functionality of a minor should be taken into account, while speed-strength, acrobatic exercises are sharply limited outdoor games moderate intensity, outdoor walks are recommended. Adaptive physical education classes are possible.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

ORGANIZATION OF THE WORK OF THE SPECIAL GROUP "A" IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTION
- local act OU (adopted on pedagogical council approved by the principal of the school)
- Certificate from a healthcare institution with the indication of the diagnosis and honey. group (certified by the signature of the attending physician, members of the CEC, the chairman of the CEC, the signature and seal of the head physician).
- Special opening order groups And until September 1, indicating the full name. physical education teacher, the payroll of the group, the location of the classes, indicating the person responsible for the students.
- The teacher must have special physical culture education (or pass a special courses, seminars).
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

IN SPEC. GROUP "A"
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

A.N. Belyaev, teacher of physical culture of the highest category
JOURNAL OF CLASSES WITH STUDENTS SPECIALIST. GROUPS A
The journal is included by the order of the director in the nomenclature of affairs of the educational institution.
The journal must have a reference number.
Journal graphs:
- Full date of birth
- Class
- Diagnosis
- Lesson recording of heart rate
- Tasks lessons
- Individual tasks
- Accounting for the readiness of students
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

ATTENDANCE RESPONSIBILITY LESSONS IN SPEC. GROUPS
- Parents (Law on Education, letter from the Department of Education of the Yar. Region 14.02.2008 No. 745/02)
- Physical education teacher (letter from the Department of Education of the Yaroslavl Region on methodological recommendations 09.09.2000 No. 01-10/155)
- Classroom teacher
- Deputy Director for UVR, med. employee
- Deputy director for water resources management who has a student in the contingent (letter of the Ministry of Defense 31.10.2003 No. 13-51-263 / 123)
If the lesson of physical education is 1 or the last in the schedule, then at the request of the parents, on the basis of the order of the director, the student may be absent from it. In all other cases, the child must be in class. The physical teacher is responsible for his life. culture.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

DOCUMENTS OF THE TEACHER WORKING IN SPEC. GROUP A
1. Physical culture program for students,
classified for health reasons to a special medical group "A"
2. Calendar thematic plan on the half a year for each
age group
3. Plan - lesson summary
4. Journal of classes with students
5. Individual card of the student (issued by a medical worker together with the teacher)
6. School administration, it is necessary to develop a mechanism for familiarizing physical education teachers with normative documents, Special attention should pay attention to the familiarization of teachers with the health sheet.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

SPECIAL SUB-GROUP "B" (IV GROUP, REHABILITATION GROUP):
- minors with permanent health disorders(chronic diseases (conditions) in the stage of subcompensation) and temporary, without pronounced disturbances of well-being
- students with severe health problems in the stage of subcompensation.
Juveniles included in this group are recommended to without fail exercise therapy in medical organization, as well as conducting regular self-study at home according to the complexes proposed by the physiotherapy doctor of a medical organization.
When recruiting medical groups of students for physical education, one should be guided by the list of deviations in the state of health
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

SPECIAL SUB-GROUP "B". INDICATIONS:
- Congenital heart defects without signs of circulatory failure
- postoperative period after surgical interventions about heart disease
- Overweight
- Violations menstrual cycle during the formation of menstrual function
- Congenital malformations of the kidneys
- Chronic gastritis, gastroduodenitis, enterocolitis, colitis
- Functional stomach disorders
- Myopia, hypermetropia, astigmatism, strabismus
- Chronic rhinitis, nasopharyngitis, chronic pharyngitis
- Otitis chronic
- Chronic bronchitis, simple, mucopurulent, obstructive, emphysematous, unspecified, etc.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category
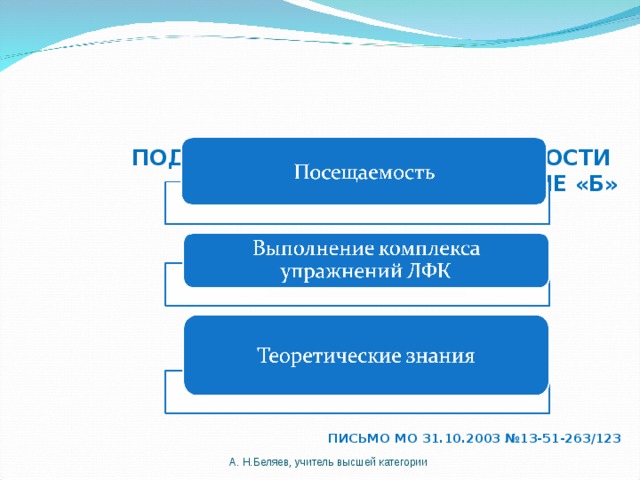
APPROACHES TO ASSESSMENT OF PROGRESS IN SPEC. GROUP "B"
LETTER OF MO October 31, 2003 No. 13-51-263/123
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

FORMATION OF ASSESSMENT. SPECIAL GROUP B
- visit standard. It consists of attending classes 2 times a week / 25 classes per six months.
The medical and health dispensary issues a certificate indicating the number of hours attended by the student.
- If the number of visits exceeds the standard, then for practical part can be rated - 5 (excellent)
- Grade for theoretical part consists of 2-3 essays on topics set by the teacher and a set of exercises for your disease.
- If the standard is not met for a good reason (student's illness), then he can only qualify for an assessment 4 (good).
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

COMPLETING GROUPS. IMPORTANT:
- The recruitment of medical groups is carried out on the basis of a conclusion about the state of health, an assessment of the functional capabilities of the body(according to the type of reaction of the cardio-respiratory system to a dosed physical load) and the level of physical fitness of the student.
- The functional capabilities of the body of students are determined medical worker schools at the beginning school year according to the results of the test with dosed physical activity.
- Attendance at the classes of SMG students is mandatory.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

COMPLETING GROUPS. IMPORTANT :
- To clarify the diagnosis, the student should be sent for additional medical examination.
- Students who have not passed a medical examination are not allowed to engage in physical education.
- The recruitment of medical groups for physical education should be completed by June 1st.
- Health changes(functional disorders, diseases, injuries) and the functional capabilities of the body that have arisen due to summer period, are taken into account when distributed to medical groups for the current academic year based on the results of the survey in September.
- Medical group for physical education of each student is entered into "Health Sheet" cool magazine.
- The second copy of the "Health Certificate" must be handed over physical education teacher.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

COMPLETING GROUPS. IMPORTANT:
- Groups are formed of no more than 12 people, taking into account the nature of the diseases (letter of the Department of Education of the Yaroslavl Region 09.02.2000 No. 01-10 / 155)
- It is desirable to take into account the age of students, 7-9 years old, 10-12 years old, 13-14 years old, 15-16 years old.
- Can create different age groups with a differentiated approach
- Be sure to consider the letter №13-51-263/123 31.10.2003
- Take into account the diagnosis of the disease
- Take into account the data on the functional state of the student
- Take into account the level of physical fitness
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category
WHEN DISTRIBUTING SCHOOLCHILDREN INTO PHYSICAL GROUPS, THE FOLLOWING INDICATORS ARE CONSIDERED:
- The results of the last medical examination comprehensive assessment health status and determination of the medical group of physical education classes
- Past acute and exacerbations of chronic diseases since the last medical examination
- Children with frequent acute illnesses(4 or more times a year) and long-term remission of a chronic disease (2 years or more) need to clarify the physical culture group
- Data on physical fitness provided by the physical education teacher after the final test at the end of the school year
- Indicators of the body's functional readiness for physical activity (the level of physical and puberty, functional tests of cardio-vascular system)
- The results of an in-depth examination of the functional capabilities of the body (express assessment of the level physical health according to G.L. Apanasenko and determination of general physical performance using a two-stage step test)
! THE FACT OF THE PRESENCE OR ABSENCE OF DIFFERENCES IN THE STATE OF HEALTH IS NOT DETERMINING.
! THE BEST FUNCTIONAL TEST - OBSERVATION OF A CHILD DURING THE LESSON OF FC!!!
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

THE MAIN OBJECTIVE OF TRAINING – CHANGING THE MEDICAL GROUP OF STUDENTS FOR PHYSICAL EDUCATION DURING THE ACADEMIC YEAR
A change in the medical group for physical education is established by a pediatrician (paramedic) on the basis of in-depth data medical examination, the dynamics of health indicators (past diseases), as well as on the recommendation of a physical education teacher based on the dynamics of physical fitness indicators.
With a positive dynamics of indicators, it is possible to transfer from the special medical group "A" to the preparatory one and from the preparatory medical group to the main one.
In case of inconsistency of physical activity functionality the student's body should be transferred from the main to the preparatory or from the preparatory to the special medical group "A".
! Data on changing the medical group for physical education should be transferred to the physical education teacher immediately.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

- In the schedule before or after lessons at the rate of 2 times a week for 45 minutes or 3 times a week for 30 minutes (including 2 hour lessons in physical education)
- Zero and double lessons are not allowed
- Most in the open air (taking into account the conformity of the clothes of the students, the air temperature, avoiding hypothermia.)
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

TEACHERS WORKING IN THE SMG SHOULD:
- know anatomical and physiological features children of different age groups;
- know the methods of physiotherapy exercises for patients with various diseases;
- know the indications and contraindications for physiotherapy exercises ;
- know the sanitary and hygienic standards during classes and the rules
- safety and labor protection;
- conduct a systematic in-depth study students in order to identify their individual capabilities and determine directions
- to keep records of the development of general educational programs by students;
- to systematically monitor the reaction of students to the proposed load according to external signs of fatigue;
- determine the physiological curve of the lesson, taking into account the well-being of students in the process of classes;
- have work program, Timetable of classes, journal of progress and attendance, journal of health monitoring of students.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

THE DOCTOR MUST:
The doctor of the educational institution performs three times a year
- medical examination of students of a special medical group with the results recorded in the individual card of the student.
- Together with the teacher of the special medical group, he decides on the transfer of students to the preparatory, basic medical group, analyzes the dynamics of physical development.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

DESIGN OF A COOL MAGAZINE
- Final scores from special magazine(special group A) are transferred to the subject page of the class magazine, as well as to the summary record of progress.
- On the subject page of physical culture ( left side) class magazine, only for students with special gr. B, a footnote is made confirming the assessment.
Letter from the Department of Education
Yaroslavl region 09.02.2000 No. 01-10/155
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

SAMPLE CERTIFICATE CONFIRMING STUDENT RELEASE
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

ORGANIZATION OF CLASSES WITH RELEASED STUDENTS
- The exemption can only be temporary: from 1 week to 1 month
- The student is issued a certificate stating the period of release
- The student is exempted from practical classes
- The student must be present at the physical education class.
- At the request of the parents and the order of the school principal, the student may not be present at the first or last lesson of physical education.
- AT class magazine mark and indicate missed lessons. Other records are not provided by regulatory documents.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

PROGRAM ON F.K. WITH STUDENTS OF SMG.
Ministry of Education Russian Federation
Programs for students of a special medical group
Physical education grades 1-11
Approved by the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation as
educational programs in physical culture for students in grades 1-11 of educational institutions 2nd edition stereotypical
Physical Culture. Programs for students of a special medical group of educational institutions. 1-11 cells. / ed. - comp. A. P. Matveev, T. V. Petrova, L. V. Kaverkina.
The collection includes exemplary programs for students of a special medical group of educational institutions (grades 1-11). These programs are the first to be developed for this category of students. based on the Mandatory Minimum Education Content and Minimum requirements for the level of training of students in the field of physical culture.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category

- L.N. Kodaneva, M.A. Joke "Methodology physical education classes in special
medical group of a general education institution: Practical guide/ Under
general ed. V.N. Fursova. – M.: ARKTI, 2006. – 64 p.
Teachers who create work programs are required to supplement the missing blocks with topics and didactic units that are not in the author's program in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard - 2010 and the FCSC - 2004.
Students assigned to a special medical group for health reasons are certified based on the results of fulfilling the requirements of the SHG curriculum.
A. N. Belyaev, teacher of the highest category
Organization of work in the SHG HEALTH AND IMPROVEMENT PHYSICAL CULTURE Organization of work in the SHG Practice shows that the organization of the work of special medical groups (SHG) in schools is still seriously lagging behind the requirements of the times. This is due to the fact that the process of physical education of weakened children is very difficult. If the physical exercises of healthy children, adolescents and youth are based on a single methodology common to all students, then classes in the SHG should be based on completely different methods. Profound differences in the etiology and pathogenesis of past diseases, various localizations, the nature and severity of those developed under the influence of pathological process violations require different approach to the classes being held. Principles of SHG training methodology First of all, it is a health-improving therapeutic and prophylactic orientation of physical culture means. A teacher of physical education should know the peculiarities of the influence of physical exercises and hardening means on a sick or weakened child's body, be able to choose the means and methods of physical culture necessary for the treatment of a disease, and be able to evaluate the effectiveness of their effect on the body. The approach to the use of physical culture means should also be differentiated, depending on the nature and severity of structural and functional disorders in the student's body caused by a pathological process. In the preparatory period, the means and methods of physical education are used exclusively in recreational purposes. In the main period, as the adaptation of the organism of students to the conditions of muscular activity improves and the functional state disturbed by the disease is restored, they gradually move to professional-applied physical training. On the final stage classes provide an increase in general and especially special work capacity, strengthening the body's defenses. Completion of groups The main criterion for the inclusion of a student in the SHG is the establishment of a diagnosis with the obligatory indication of the degree of impairment of body functions. For a more differentiated approach to prescribing motor modes SHG students are recommended to be divided into two subgroups - "A" and "B" (according to the severity and nature of the disease). Subgroup "A" includes those who have deviations of a reversible nature, i.e. weakened due to various diseases. Subgroup "B" includes schoolchildren with irreversible changes in organs and systems (damage to the cardiovascular, urinary systems, liver; a high degree of refractive error with changes in the fundus, etc.). The division into subgroups allows you to determine the mode of employment. At the same time, the most accessible criterion in the selection of appropriate loads is the pulse mode. In cases of especially pronounced dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal and neuromuscular apparatus and significant health disorders that prevent group lessons in conditions educational institution, students are sent to physical therapy classes in medical institutions. Transfer from one medical group to another is made after additional examination. The main form of physical education for SHG students are lessons that are held twice a week for 45 minutes. or three times a week for 30 minutes. Usually in a group of up to 12 people. In order to increase the effectiveness of classes, it is extremely important correct selection students in groups that are completed by the nature of the disease: cardiovascular system; endocrine systems s; digestive, endocrine systems and metabolic disorders; spine and musculoskeletal system; organs of vision and hearing; urinary system; CNS and peripheral nervous system(cerebral palsy, poliomyelitis, etc.). The relative small number of students with similar diseases does not allow them to be grouped according to the form of the disease. The following grouping is acceptable: a) chronic pathology of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, b) pathology of the musculoskeletal system and refractive error. Practice shows that it is most expedient to complete these groups according to grades (for example, from students in grades 1–4, 5–8, 9–11). If the number of students is not enough to complete the group, then it is advisable to combine students in three or four grades: 1–4, 5–8, 9–11. It should be emphasized the need for a strictly differentiated load, taking into account individual approach to students. Organization educational process In the SHG classes it is advisable to adhere to the generally accepted structure of physical education classes. But there is a peculiarity in the method of conducting them: the lesson consists not of three, but of four parts. Introductory part (3-4 min.): monitoring the pulse rate, breathing exercises. Preparatory part (10-15 min.): general developmental exercises, performed first at a slow and then at an average pace. Each exercise is repeated from 4-5 times to 6-8 times. Particular attention should be paid to correct breathing. Exercises that require large muscle efforts and make breathing difficult are not recommended. With the help of general developmental exercises in the preparatory part of the lesson, it is possible to ensure the sequential (according to the principle of "dispersing" the load) inclusion in the work of all large muscle groups. In this case, the load should not increase sharply. Special breathing exercises used after the most tiring physical exertion can reduce the degree of functional stress experienced by the body. Main part (15–18 min.): training and training. It teaches new physical exercises, trains breathing skills, develops motor qualities. The greatest physical activity should fall on the second half of the main part of the lesson. To do this, the educational material is distributed so that the initial period of the main part is filled with lighter physical exercises. As a rule, in this part of the lesson, one new exercise is taught. At each lesson, it is also necessary to repeat several exercises that have been mastered before. It is very important to avoid fatigue during the repetition of monotonous movements. To do this, as in the preparatory part of the lesson, it is necessary to “disperse” the load on different muscle groups. The development of gymnastics, athletics, basketball, ski training, volleyball provided for by the physical education program is provided mainly at the expense of the main part of the lesson. But for the development of individual sections of sports training, it is advisable to use its preparatory part. Conducting classes in each of the sections of sports training, it is necessary to take care of the development of motor qualities, endurance training, strengthening the muscular structure of the body. The final part of the lesson (5 minutes) includes breathing and relaxation exercises. the main task this part of the lesson is the restoration of the functional state of the body of students after physical exertion. Here, exercises for those muscle groups that were not involved in the lesson are advisable. The intensity of these exercises, providing leisure tired muscle groups, should be lower than in the main part of the lesson. In order to control the correct distribution of the load during the lesson, students should be able to independently measure the heart rate, which, at the signal of the teacher, they determine within 10 seconds. Such a calculation is made 4 times: before the lesson, in the middle - after the most tiring exercise of the main part (in the first 10 seconds), after the lesson and after 5 minutes. recovery period. The practical sections of the physical education program for students of the main and special medical groups are significantly different. SHG students are exempted from fulfilling any practical standards. But the requirements for certain sports that are mandatory for them include: - gymnastics - performing drill exercises, posture exercises, basic movements of the arms, torso, dance steps, acrobatic elements, balance, vaults; lifting and carrying small weights, exercises on gymnastic equipment and with equipment; - Athletics- technique of running for short and medium distances, methods of throwing grenades, long jumps; - skiing training - the technique of mastering certain ways of skiing, climbing and descending mountains, turning on the spot and when moving (on the instructions of the teacher); – swimming – correct execution movements with arms and legs, the ability to stay on the water and swim, on the instructions of the teacher, a segment of the distance in the studied way, the ability to combine the movements of the arms and legs with breathing when studying the technique of swimming in one of the ways. On contraindications to classes With relatively the same functional state of SHG students, one should take into account contraindications to practicing certain types of exercises, characteristic for each group of diseases. Diseases of the cardiovascular system suggest a group method of training (preferably on fresh air, in a park or square). The lesson is structured so that cyclic exercises prevail ( different kinds walk, ski trips, ice skating, etc.). Exercises with holding the breath, straining, with static tension, with a sharp acceleration of the pace are excluded. General developmental exercises covering all muscle groups are performed in the prone position, sitting, standing. In the process of training, it is necessary to control heart rate and breathing, skin color and general condition child. In case of respiratory diseases, the lesson includes walking, dosed running in combination with walking and breathing exercises, skiing, skating, games, relay races. In cold and windy weather, classes should not be held outdoors, especially for those suffering from bronchial asthma. When conducting classes in the hall, it is necessary to develop correct rhythmic breathing, as well as breathing with an emphasis on exhalation (especially for patients with bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis, etc.). Exercises performed on exhalation through the mouth with the simultaneous pronunciation of vowels [a], [y], [e], [i], [o] and consonants [p], [g], [w], [ u], [h], [s] or combinations thereof (for example, bre, bra, bru, etc.). These exercises should be recommended to be performed at home 3-5 times a day; dosage for one exercise - 2-3 times, the number of exercises - 3-4. After 2-3 months of systematic physical exercise, swimming is advisable. In case of obesity, the training program includes: long walking over rough terrain, running combined with walking, skiing, training on simulators, swimming and playing in water, dumbbell gymnastics, etc. In classes with students with kidney disease (nephritis, pyelonephritis, nephrosis), physical activity is significantly reduced, jumping is excluded, hypothermia is not allowed. When conducting general developmental exercises, special attention is paid to strengthening the muscles of the anterior wall of the abdomen. When swimming, the time spent in the water is limited (5-10 minutes - the first year of study, 10-15 minutes - the second year of study). The permission of the doctor for swimming lessons for this contingent of children is negotiated additionally. For schoolchildren with disorders of the nervous system, exercises that cause nervous overstrain (in balance on an elevated support) are limited, the time of games is reduced, etc. In diseases of the organs of vision, jumping, somersaults, exercises with straining, headstands and handstands are excluded. For chronic diseases gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, liver, the load on the muscles decreases abdominals, limited jumps. As experience shows, for children of the younger age group, it is advisable to include outdoor games in the lessons, for the older - elements of dancing. The activities of children with disorders of the musculoskeletal system include exercises at the gymnastic wall, with stuffed balls, a gymnastic stick, rubber shock absorbers, traction exercises, exercises on simulators. The task is to stop the progression of the disease through physical exercises, and in case of functional posture disorders, to normalize it. Pedagogical control over students is carried out by the teacher at each lesson. In the first fifteen or twenty lessons, signs of fatigue (sweating, reddening of the skin, etc.) should not be allowed to appear. Later on, when good health you can use short-term loads, evocative pleasant fatigue. The criterion for the correct dosing of the load is the change in heart rate during both one lesson and a series of lessons. The pulse of the bulk of the children after the lesson should return to the original data within 15–20 minutes. In addition to monitoring the level of physical fitness of students, the teacher, as the material progresses, evaluates the correctness of the exercises, the improvement in strength, flexibility, and endurance. Homework Logical continuation academic work in the lesson are homework assignments that will help increase the volume motor activity students, improve their physical fitness, improve their health, introduce physical education into everyday life. The teacher must first show the exercises given at home, clarify the load. Total time fulfillment homework should not exceed 15-20 minutes. Most often, homework includes the following exercises: 1. Walking in place with correct posture, lifting the hips high and moving the arms (at the mirror). 2. Jumping in place (height 20-30 cm) with a soft landing. 3. Keeping the balance of the bent and straightened leg. 4. Exercises from ip: lying on your stomach, arms bent in elbow joints and divorced to the sides, brushes - one on top of the other under the chin, feet together. Raising the head and arms back or to the sides; raising the head and arms bent at the elbow joints (elbows back, shoulder blades connected); raising the head and torso, hands on the belt. 5. Exercises from ip: lying on your back, arms along the body: raising the head with simultaneous bending feet alternating leg raises different angles), cyclist movements; lifting the body with the support of hands on the floor, the same - hands on the belt. 6. Exercises to relax the arms and legs alternately, performed from the SP: standing. 7. Exercise from SP: standing, arms to the sides: touch the left knee with the heel of the right foot, fix this position, maintaining balance. The same with eyes closed. 8. Squats on full foot stretching arms forward. Squats on toes, hands in front. The same - hands on the belt. 9. Exercises for the muscles of the foot: grasping light objects (a small ball, a box of matches, etc.) with your toes, bending the foot in a sitting position. 10. Walking on the gymnastic bench (lines on the floor) with the ball tossing up, hitting it on the floor and catching. 11. Exercises with a gymnastic stick: tilt forward, stick horizontally up, behind the head, behind the shoulder blades (in one motion, bring the stick held in front of you with both hands behind your back). 12. Balance on the left (right) leg ("swallow"). 13. Jumping rope on one and both legs with a soft landing on the toes. 14. From a kneeling position, sit on the floor on the side (right, left) and return to SP. 15. Learning hand movements in a certain way of swimming from a standing position, the same with legs, but in a sitting position. 16. Mastering the coordination of movements in a certain way of swimming. To increase the effectiveness of homework, it is useful to hold meetings, talks with parents, invite them to lessons, explain to them how to stimulate and encourage children to complete the given exercises. Carrying out sports and outdoor games Particular attention is required to the methodology of the games. Outdoor games and elements included in the program material sports games require strict dosage. Increased emotional condition during outdoor and especially sports games, it can cause imperceptible fatigue of students, so the teacher should closely monitor its first signs, finish the game in a timely manner, preventing the occurrence of overwork. At each lesson, it is recommended to conduct no more than one game, and you should always start with simpler ones. 1. Race balls (volleyball or basketball). It is carried out in video relay races: a) passing the ball over the head (2 times); b) passing the ball between the legs (2 times); c) passing the ball to the right, to the left (2 times each); d) passing the ball under the feet, over the head, on the right, on the left (2 times each). 2. Passing a volleyball and its varieties: a) tossing the ball over oneself, catching it and passing it to a friend. The game is played when building in 2 lines, facing each other, at a distance of 4–6 m (3–5 times each); b) the same, but when building in 2 columns, facing to each other, after the transfer the player goes to the end of the opposite column (2 times each); c) throwing the ball over the net: 2.1. Two balls - simultaneous throwing on a signal. Two halves of 3 minutes; 2.2. With one ball - whoever catches it throws it. One half 3 min. 3. Passed - sit down: a) the captain passes the ball (the captain stands facing the column at a distance of 1-3 m) to each player. The student, having received the ball and giving it to the captain, sits on the floor (1-2 times); b) the same, but the last one in the column, having received the ball, says: “Gop!”, Everyone gets up and passes the ball to the right or left, between the legs, over the head (by agreement) (1–2 times). 4. Basketball techniques. Schoolchildren are built in 2 lines facing each other: a) passing the ball with two hands from the chest (5 times); b) passing the ball from the chest with a hit on the court (5 times); c) dribbling (5 strokes right hand, 5 hits left) (3 times); d) imitation of throwing the ball into the ring (5 times); e) dribbling and throwing it into the ring (3 times); f) a combination of dribbling and passing the ball (3 times). 5. Game "Ball to the captain": a) change of players after 3 minutes; b) change of players after 5 minutes. 6. Relay race with elements of basketball: a) the duration of the relay race is up to 3 minutes; b) the duration of the relay is up to 5 minutes. The team consists of 6-8 players. 7. Playing basketball according to simplified rules: a) change of players after 3 minutes; b) change of players after 5-6 minutes. Games 1–4 are recommended for schoolchildren in grades 4–8 in the first year of study, games 1–5 are already held in the second year, games 1–5 are given for grades 9–10 in the first year of study, and in the second year - 5-7, in addition, add elementary techniques for playing basketball and volleyball according to simplified rules. The dosage of games is given for one-time holding. In the lessons of the second year of study, it is possible to conduct these games with two or even three repetitions, but between them there must be an interval of at least 5 minutes, which is filled with muscle relaxation exercises, walking, breathing exercises and rest for at least 1 minute. One of the criteria for the correct dosage and conduct of the game can be the recovery period of the heart rate, which should be no more than 5–7 minutes. Ski lessons require careful thought and attention. Before starting ski training, students must undergo an additional medical examination. In the classroom, the tasks of learning to ski and hardening are solved in parallel. The main attention should be paid to mastering the technique of movement, turns, ascents and descents. During classes, it is necessary to strictly monitor the implementation of all sanitary and hygienic rules: rational clothing appropriate for the weather, air temperature not lower than -15 degrees, correct mode classes. It is necessary to avoid both overheating and hypothermia involved. Since the speed of movement is low, teachers need to control that students breathe in and out only through the nose, which will avoid hypothermia of the upper respiratory tract. Work with parents From the first days of work on physical education of SHG students, great importance should be given to systematic work with parents. Although all parents want to see their children healthy, strong, slender, hardy, doing well in school, but only in 8% (out of 100 surveyed) families, children with health problems systematically use physical culture to improve it. One of the main reasons for the underestimation of the role of physical exercises is the lack of awareness of parents about their benefits for improving the health and proper physical development of the child. parent meetings, conversations, lectures, no doubt, will make it possible to achieve positive changes in solving this problem. Medical supervision during physical exercises natural conditions in which classes are held, indicators of the intensity and volume of the work done are taken into account physical work. Great importance while, as already mentioned, has the observation of outward signs fatigue during exercise. If students have an unsatisfactory state after the lesson, due to a discrepancy between the regimen physical stress their state of health, the degree of fitness, it is necessary to reduce physical activity, give children rest, and in some cases conduct an in-depth clinical study. The reaction to physical activity in the process of training should be moderate shifts physiological indicators. Depending on the nature and intensity of the loads, the heart rate, arterial pressure blood, the respiratory rate increases, the period of recovery of indicators to the initial level usually does not exceed 5 minutes. Body weight does not change significantly. Vital capacity and muscle strength may increase or decrease moderately, indicating in the latter case the onset of fatigue. A small degree of fatigue in physical exercises with students who have deviations in health status is quite acceptable. The physiological curve of physical activity is determined by counting the pulse immediately before the start and immediately after the end of each part of the lesson. The resulting pulse curve to a certain extent reflects the reaction of the body caused by exercise, and allows you to trace it in dynamics. In classes with students of the SMG, the so-called undulating nature of the curve is recommended. Marina BELOZEROVA, Ph.D. New Urengoy
MOU "Secondary school No. 5 of the city of Kuvandyk, Kuvandyk district, Orenburg region"
Reference
on the organization of work with children of the SMG in the secondary school No. 5
The number of children studying at the educational institution - 507
Of these include:
To the main group (number of students, % of the total) - 474 students (93%)
In the preparatory group (number of students, % of the total) - 15 students (2.9%)
In the special medical group: 20 students (3.9%)
Subgroup "A" (number of students,% of the total) - 17 students (3.3%)
Subgroup "B" (number of students, % of the total) - 3 students (0.6%)
AT recent times our school is faced with the problem of teaching physical education to students with poor health, who require special norms of physical activity and an individual approach to organizing classes. It is necessary to differentiate the student body depending on the state of health of schoolchildren.
A special medical group (SMG) is formed from students with permanent or temporary health problems admitted to group classes, but having contraindications to increased physical activity. The obligatory type of physical education classes for them are classes for special programs with a differentiated approach and individual assessment of their impact on the body. The main criterion for referring a child to SMG is the diagnosis of the disease, however, in this case, the medical group should be appointed taking into account the severity of the pathological process and the adaptive capabilities of the body.
The main tasks of physical education of students from the SHG group are:
Strengthening health, stable compensation of disorders caused by diseases, and sometimes their elimination.
Promoting proper physical development, hardening, increasing the body's resistance.
Improving the indicators of physical development, mastering vital motor skills and abilities.
Increasing the functional level of organs and systems weakened by the disease.
Gradual adaptation of the body to the effects of physical activity.
Mastery of complexes special exercises that have a beneficial effect on the body, taking into account the existing disease.
Teaching methods of self-control and load dosage.
Raising interest in self-study physical education.
Principles of the method of practicing SMG
Health-improving treatment-and-prophylactic orientation of means of physical culture. When conducting a lesson, the influence of physical exercises and hardening means on a sick or weakened child's body is taken into account, the means and methods of physical culture necessary for the treatment of the disease are selected, and the effectiveness of their influence on the body is evaluated.
A differentiated approach to the use of physical culture means, depending on the nature and severity of structural and functional disorders in the student's body caused by the pathological process.
In the preparatory period, the means and methods of physical education are used exclusively for recreational purposes.
In the main period, as the adaptation of the organism of students to the conditions of muscular activity improves and the functional state disturbed by the disease is restored, they gradually move on to professional-applied physical training.
At the final stage of training, an increase in general and especially special work capacity is provided, and the body's defenses are strengthened.
Group recruitment carried out on the basis of the established diagnosis with the obligatory indication of the degree of violation of body functions.
For a more differentiated approach to the appointment of motor modes of SHG students are divided into two subgroups - "A" and "B" (according to the severity and nature of the disease).
Subgroup "A" includes those who have deviations of a reversible nature, i.e. weakened due to various diseases.
Subgroup "B" includes schoolchildren with irreversible changes in organs and systems (damage to the cardiovascular, urinary systems, liver; a high degree of refractive error with changes in the fundus, etc.).
The main form of physical education for SHG students are lessons that are held twice a week for 45 minutes. or three times a week for 30 minutes.
There are 9-12 people in a group. Groups are completed according to the nature of the disease:
of cardio-vascular system;
endocrine system;
digestive;
spine and musculoskeletal system;
organs of vision and hearing;
urinary system;
CNS and peripheral nervous system (cerebral palsy, poliomyelitis, etc.).
The small number of students with similar diseases does not allow them to be grouped according to the form of the disease. The following grouping is acceptable: a) chronic pathology of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, b) pathology of the musculoskeletal system and refractive error.
Groups are formed by grade (for example, from students in grades 1–2, 3–4, 5–8, 9–11). If the number of students is not enough to complete the group, then they are united from students of three or four grades: 1–4, 5–8, 9–11. The load, strictly differentiated, taking into account the individual approach to students.
Training sessions in the SMG are organized in the following way:
building in the lesson not by height, but by the degree of physical fitness: on the right flank are more prepared children, on the left - less prepared;
Before each lesson, students determine the heart rate. Children whose heart rate is above 80 beats per minute stand on the left flank;
during the relay, the more prepared stand at the beginning of the column, start and finish the relay, if necessary, making two repetitions, the less prepared - one;
during games, poorly trained students are replaced every 2 minutes;
The most important requirements for the lesson:
providing a differentiated approach to students, taking into account their state of health, physical development and motor fitness;
achievement of dynamism, emotionality, educational and instructive orientation of training sessions;
the formation of students' skills and abilities of independent physical exercises.
Data is recorded in a self-control diary (weakness, fatigue, dizziness, pain, sweating, decreased performance, sleep patterns, appetite), as well as heart rate at the beginning and end of the session. Diaries are checked at least once a month, their data is used in determining the load. The teacher receives objective data on the state of health of students during medical examinations.
The main documents for planning educational work are:
annual plan for the passage of program material;
fourth plan;
notes and plans for individual lessons;
register of classes with schoolchildren.
Additional Documents:
plans for medical and educational activities;
student's health passport;
rules for conducting corrective outdoor games;
thematic plan for conducting conversations with schoolchildren;
thematic plan for conducting conversations with parents;
Organization of the educational process
SHG classes adhere to the generally accepted structure of physical education classes. But there is a peculiarity in the method of conducting them: the lesson consists not of three, but of four parts.
Introductory part (3-4 min.): monitoring the pulse rate, breathing exercises.
Preparatory part (10-15 min.): general developmental exercises, performed first at a slow and then at an average pace. Each exercise is repeated from 4-5 times to 6-8 times. Particular attention should be paid to correct breathing. Exercises that require large muscle efforts and make breathing difficult are not recommended. With the help of general developmental exercises in the preparatory part of the lesson, it is possible to ensure the sequential (according to the principle of "dispersing" the load) inclusion in the work of all large muscle groups. In this case, the load should not increase sharply. Special breathing exercises used after the most tiring physical exertion can reduce the degree of functional stress experienced by the body.
Main part (15–18 min.): training and training. In it, new physical exercises are studied, breathing skills are trained, and motor qualities are developed. The greatest physical activity should fall on the second half of the main part of the lesson. To do this, the educational material is distributed so that the initial period of the main part is filled with lighter physical exercises. As a rule, in this part of the lesson, one new exercise is taught. At each lesson, it is also necessary to repeat several exercises that have been mastered before. It is very important to avoid fatigue during the repetition of monotonous movements. To do this, as in the preparatory part of the lesson, it is necessary to “disperse” the load on different muscle groups.
The development of gymnastics, athletics, basketball, ski training, volleyball provided for by the physical education program is provided mainly at the expense of the main part of the lesson. But for the development of individual sections of sports training, it is advisable to use its preparatory part.
The final part of the lesson (5 minutes) includes breathing and relaxation exercises. The main task of this part of the lesson is to restore the functional state of the body of students after physical exertion. Here, exercises for those muscle groups that were not involved in the lesson are advisable. The intensity of these exercises, which provide active rest for tired muscle groups, should be lower than in the main part of the lesson.
The practical sections of the physical education program for students of the main and special medical groups are significantly different. SHG students are exempted from fulfilling any practical standards. But the requirements for certain sports that are mandatory for them include:
– gymnastics– performance of combat exercises, posture exercises, basic movements of the arms, torso, dance steps, acrobatic elements, balance, vaults; lifting and carrying small weights, exercises on gymnastic equipment and with equipment;
– Athletics- technique of running for short and medium distances, methods of throwing grenades, long jumps;
– ski training- the technique of mastering certain ways of skiing, climbing and descending from mountains, turning on the spot and when moving (on the instructions of the teacher);
Homework
The logical continuation of the educational work in the lesson is homework, which will help increase the amount of physical activity of students, improve their physical fitness, improve their health, and introduce physical education into everyday life. The teacher must first show the exercises given at home, clarify the load. The total time for completing homework should not exceed 15–20 minutes. Most often, homework includes the following exercises:
1. Walking in place with correct posture, high hips and arm movement (at the mirror).
2. Jumping in place (height 20-30 cm) with a soft landing.
3. Keeping the balance of the bent and straightened leg.
4. Exercises from ip: lying on the stomach, arms bent at the elbow joints and spread apart, hands - one on top of the other under the chin, feet together. Raising the head and arms back or to the sides; raising the head and arms bent at the elbow joints (elbows back, shoulder blades connected); raising the head and torso, hands on the belt.
5. Exercises from ip: lying on your back, arms along the body: raising the head while bending the feet; alternating leg raises (at different angles), cyclist movements; lifting the body with the support of hands on the floor, the same - hands on the belt.
6. Exercises to relax the arms and legs alternately, performed from the SP: standing.
7. Exercise from SP: standing, arms to the sides: touch the left knee with the heel of the right foot, fix this position, maintaining balance. The same with closed eyes.
8. Squats on a full foot, stretching your arms forward. Squats on toes, hands in front. The same - hands on the belt.
9. Exercises for the muscles of the foot: grasping light objects (a small ball, a box of matches, etc.) with your toes, bending the foot in a sitting position.
10. Walking on the gymnastic bench (lines on the floor) with the ball tossing up, hitting it on the floor and catching.
11. Exercises with a gymnastic stick: tilt forward, stick horizontally up, behind the head, behind the shoulder blades (in one motion, bring the stick held in front of you with both hands behind your back).
12. Balance on the left (right) leg ("swallow").
13. Jumping rope on one and both legs with a soft landing on the toes.
14. From a kneeling position, sit on the floor on the side (right, left) and return to SP.
15. Learning hand movements in a certain way of swimming from a standing position, the same with legs, but in a sitting position.
16. Mastering the coordination of movements in a certain way of swimming.
Carrying out sports and outdoor games
Particular attention is required to the methodology of the games. The outdoor games and elements of sports games included in the program material require strict dosage. An increased emotional state during outdoor and especially sports games can cause imperceptible fatigue of students, so the teacher should closely monitor its first signs, finish the game in a timely manner, preventing the occurrence of overwork.
At each lesson, no more than one game is played, and you should always start with simpler ones.
1. The ball race is held in the form of relay races:
a) passing the ball over the head (2 times);
b) passing the ball between the legs (2 times);
c) passing the ball to the right, to the left (2 times each);
d) passing the ball under the feet, over the head, on the right, on the left (2 times each).
2. Passing a volleyball and its varieties:
a) tossing the ball over oneself, catching it and passing it to a friend. The game is played when building in 2 lines, facing each other, at a distance of 4–6 m (3–5 times each);
b) the same, but when building in 2 columns facing each other, after the transfer the player goes to the end of the opposite column (2 times each);
c) throwing the ball over the net: 2.1. Two balls - simultaneous throwing on a signal. Two halves of 3 minutes; 2.2. With one ball - whoever catches it throws it. One half 3 min.
3. Passed - sit down:
a) passing the ball by the captain (the captain stands facing the column at a distance of 1-3 m) to each player. The student, having received the ball and giving it to the captain, sits on the floor (1-2 times);
b) the same, but the last one in the column, having received the ball, says: “Gop!”, Everyone gets up and passes the ball to the right or left, between the legs, over the head (by agreement) (1–2 times).
4. Basketball techniques. Pupils are built in 2 lines facing each other:
a) passing the ball with two hands from the chest (5 times);
b) passing the ball from the chest with a hit on the court (5 times);
c) dribbling (5 hits with the right hand, 5 hits with the left) (3 times);
d) imitation of throwing the ball into the ring (5 times);
e) dribbling the ball and throwing it into the ring (3 times);
f) a combination of dribbling and passing the ball (3 times).
5. The game "Ball to the captain":
a) change of players after 3 minutes;
b) change of players after 5 minutes.
6. Relay race with elements of basketball:
a) the duration of the relay is up to 3 minutes;
b) the duration of the relay is up to 5 minutes. The team consists of 6-8 players.
7. Playing basketball according to simplified rules:
a) change of players after 3 minutes;
b) change of players after 5-6 minutes.
Games 1–4 are held for schoolchildren in grades 4–8 in the first year of study, in the second year games 1–5 are already held, for grades 9–10 in the first year they give games 1–5, and in the second year - 5-7, in addition, add elementary techniques for playing basketball and volleyball according to simplified rules. The dosage of games is given for one-time holding. In the lessons of the second year of study, it is possible to conduct these games with two or even three repetitions, but between them there must be an interval of at least 5 minutes, which is filled with muscle relaxation exercises, walking, breathing exercises and rest for at least 1 minute.
Before the start of ski training, schoolchildren undergo an additional medical examination. In the classroom, the tasks of learning to ski and hardening are solved in parallel. The main attention is drawn to mastering the technique of movement, turns, ascents and descents. During classes, they strictly monitor the implementation of all sanitary and hygienic rules: rational clothing appropriate for the weather, the air temperature is not lower than -15 degrees, the correct mode of training. It is necessary to avoid both overheating and hypothermia of those involved, to control that schoolchildren inhale and exhale only through the nose, which will avoid hypothermia of the upper respiratory tract.
When organizing work on the physical education of students in educational institutions, the the following recommendations which are presented in the table:
Principles of physical education of children with disabilities in the state of health
|
Medical groups |
Compulsory activities |
Featured additional types classes |
|
Main(Children and adolescents with no health problems or with minor disabilities who have sufficient physical fitness) |
Classes in the curriculum of physical education in full. Passing control standards with a differentiated assessment |
Sports |
|
preparatory(children and adolescents with minor deviations in health status without sufficient physical fitness) |
The same, but subject to the gradual development of exercises that place increased demands on the body. Some limitation of loads and more gradual development of motor skills and abilities. |
Additional training to increase the level of physical fitness. |
|
SMG(children and adolescents with significant deviations in the state of health of a permanent or temporary nature, admitted to group classes in an educational institution) |
Classes in special programs with a differentiated assessment |
The use of available types of physical exercises in the school day (OS) and at home. |
|
Medical groups for FC classes |
Characteristics of the contingent |
Goals |
Technology |
|
Main group |
Prosperous children (1 and 2 health groups) |
Health promotion, training |
health-forming technologies |
|
preparatory group |
Children of the "risk group" - violations of adaptation in the team, reduced performance, functional disorders (2 and partially 3 health groups) |
health preservation, comfortable conditions, individual pace of learning. |
health-saving technologies |
|
Special medical group "A", Corrective exercises |
Children with chronic diseases in the stage of stabilization and recovery, after illnesses (health group 3) |
Rehabilitation by means of FC and medicine |
health-restoring technologies |
|
Special medical group "B", |
Children with manifestations of the disease (health group 3 with incomplete remission, health group IV). |
Treatment |
medical technologies |
Classes with SMG are necessarily held separately from healthy children. However, only a physical education teacher can release a child studying in the SHG from attending physical education lessons according to the class schedule, subject to the mandatory coordination of this with the child's parents and the administration of the educational institution. Usually, for exemption from attending a lesson, parents write an application on which the headmaster puts his visa. Otherwise, the child should be at the lesson, although he does not participate in the process of physical education, he plays the role of an extra.
The time of the classes is not strictly regulated. There are recommendations to conduct physical education lessons for SMG children with a zero lesson or lessons are planned for the afternoon.
Methodology for organizing work in a special medical group in a general education school
Today, in the situation of modernization of education and the transition to 12-year education, the creation of specialized classes, the imperfection of the education system adversely affects the health of schoolchildren and organization of the entire educational process. The conditions of upbringing and education are the environment in which a child aged 3 to 18 is forced to be. It is during these years that intensive growth and body development young man, its biological and social maturation takes place, a worldview is formed, readiness for a variety of labor and creative activity.
The proportion of healthy children is steadily declining. This is especially true for children school age. An analysis of the reports of the school doctor of the MOU “Secondary School No. 7” reflected the following situation. So, for example, according to the results of a medical examination conducted in September 2000, it can be seen that 32% of children in the fifth grade have developmental disabilities. musculoskeletal system, and in the 11th grade there are 61% of such children. Disappointing results were also obtained in the study of visual acuity of students. In grade 5, there is a decrease in visual acuity in 23% of students, and in grade 11, 37% of children need vision correction. As for other diseases, the picture is no better: children diagnosed with VVD in 5 cells. - 28%, in 11 cells. 34%, the number of TB-infected children increases every year by an average of 40%. When examining children in 2001, it was found that the percentage of growth in the incidence of children increased by an average of 37%. Thus, there is a discrepancy between modern requirements necessary for the process of formation and self-determination of schoolchildren in a constantly evolving socio-cultural environment and the level of physical and mental health children.
Taking into account the data of medical examinations and the fact that during the academic year 63% of students systematically miss classes due to illness, in our school the entire educational process was focused on the use of health-saving technologies.
There is currently a large number of health-saving programs used in educational institutions. Consider the program "Health" used in the MOU "Secondary School No. 7".
The program was developed for 2002-2007. During the development of conceptual approaches, the problem, goal and objectives of the program were formulated. Within the framework of the program, a special medical group was created, in which children with poor health are treated under a sparing regimen.
Students with a satisfactory state of health belong to the main medical group. Students with insufficient physical development and low physical fitness, or with minor deviations in health status, belong to the preparatory medical group. This category of students is allowed to engage in physical culture according to the program for the main group, subject to some restrictions in the amount of intensity of physical activity (including temporary ones).
Students who, on the basis of a medical report on their state of health, cannot engage in physical education under the program for the main group (10-15% of the total number of students) belong to a special medical group (SMG).
The special medical group can be conditionally divided into two subgroups: subgroup “A” (students with reverse diseases who, after medical and recreational activities, can be transferred to preparatory group). Subgroup "B" (teaching with pathological deviations (irreversible diseases)).
When completing groups according to similar methods, students are united according to following principle: group 1 - diseases of the cardiovascular system, respiratory organs, myopia; 2- gastrointestinal diseases, gynecological, pyelonephritis. ODA diseases can be connected to any of the groups. When practicing, strictly observe the restrictions in the exercise.
The main criterion for the inclusion of a student in the SHG is the establishment of a diagnosis with the obligatory consideration of the degree of impairment of body functions.
For the purpose of a differentiated approach to the organization of physical education lessons All students of general educational institutions, depending on the state of health, are divided into three groups: basic, preparatory and special medical. Classes in these groups differ in the curriculum, the object and structure of physical activity, as well as the requirement for the level of development educational material.
The next criterion is to determine the degree of physical fitness, tk. should be considered individual characteristics child. Particular attention is paid to this assessment functional state of cardio-vascular system. The next criterion is a functional examination of students with disorders of the central nervous system, on the activity of which the features of motor reactions largely depend. An important criterion selection of children in the SMG is an assessment external factors in which they are: living conditions, dietary habits, psychological climate.
In special medical groups, children should be conscious of their health and be able to use all the means and methods of physical education to restore lost health. Physical education classes enable a sick child to master physical exercises that help him overcome the disease. Overcoming one's own weakness forms the will, character; transforms the personality: stiffness, fear, inferiority complex disappear. The unity of upbringing, health-improving and educational tasks for SHG students is the key to success in the process of adapting them to school conditions in particular and, in general, to later life.
In the classroom in the SMG, they adhere to the generally accepted structure of the lesson. But there is one feature: the lesson consists of four parts.
Introduction(3-4 min) is counting the pulse rate, breathing exercises. The preparatory part (10-15 minutes) begins with outdoor switchgear, performed first at a slow pace, and then at an average pace. Each exercise is repeated 4-5 times, and in the future 6-8 times. One of the first preparatory exercises is sipping, which facilitates the implementation of subsequent physical exertion, improving the adaptation of the cardiovascular system to the conditions of muscular activity. In this part of the lesson, special attention should be paid to breathing, special breathing exercises, which allow you to reduce the degree of functional stress experienced by the body.
![]()
Main part The lesson is 15-18 minutes and is dedicated to learning and training. It masters the main educational tasks. The physiological curve of training should have the greatest rise in the second half of the main part. It is very important to avoid fatigue during this time. It is important to select complexes of physical exercises taking into account the specifics of diseases.






Final part(5 min) includes relaxation and breathing exercises. The main task of the final part is relaxation and correct breathing.

Students should be able to measure the pulse rate at the teacher's signal for 10 seconds. Such a calculation is made 4 times during each session: before the session, in the middle of it - after the most tiring exercise of the main part, - directly (in the first 10 s) after the session and after 5 minutes of the recovery period.
The curriculum for the subject provides for students of the special medical group to master the test requirements for the theoretical section, which is common for students of the main medical group. The result of mastering the program of students of the special medical group is their transfer to the preparatory group.
A special medical group was organized for children suffering from diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
From the first days of classes in the SHG, anthropometric data were taken from the students, control tests were carried out, which were drawn up in the form of tables.
Table 1.
Anthropometric data
| FULL NAME. | Age | Growth | Head | Breast |
||
Table 2.
Tests
| Squat 1 stage | Squat 3 stage | Throws catching tennis. ball | Throws catching tennis. ball | Romberg test (1) 1 stage | Romberg test (1) Stage 3 | Romberg test (2) 1 stage | Romberg test(2) Stage 3 | Romberg test stage 1 | Romberg test stage 3 | Jumping rope stage 1 | Jumping rope stage 3 |
Squats performed at an arbitrary pace to fatigue, allow you to evaluate strength endurance;
Throwing and catching a tennis ball with two hands from a distance of 1 meter from the wall for 30 seconds at a maximum pace - this indicates coordination of movements, dexterity, speed motor reaction;
Romberg test;
Jumping rope on two legs helps to assess the coordination of movements, agility, speed of motor response, speed endurance, leg muscle strength.
Diagnosis of deviations in the development of the musculoskeletal system junior schoolchildren on medical records showed the following result.
![]()
Tests conducted at the beginning of the school year and at the end showed that there is a significant increase in the physical development of children of primary school age.
Table 3
The effectiveness of the use of classes in the group "Health" of younger students
| Beginning of the school year | The end of school year | Average annual growth in % |
|
| Squats (to exhaustion) | |||
| Throwing and catching the ball | |||
| Romberg test | |||
| jumping rope |
Creation of a valeological educational environment, contributing not only to the preservation, correction, but also to the development of physical health, contributes to the formation of creative abilities and provides high potential creativity every student.
There is also an increase in the performance of schoolchildren, both in physical education lessons and in other subjects, and the adaptive ability of students to the impact of the environment increases.
Accepted Approved
at the Pedagogical Council of the school Director of the MAOU Lyubokhonskaya secondary school
Protocol No. ____ ______________ Kononov K.V.
from "___" ___________ 20___ Order No. dated "__" __________ 20___
Position
about special medical groups
Municipal Autonomous Educational Institution
Lyubokhonsk secondary school
named after A.A. Golovachev
Dyatkovsky district of the Bryansk region
1. General Provisions
1.1 These Regulations have been developed in accordance with Order No. 337 dated August 20, 2001 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation "On measures to further development and improvement of sports medicine and physical therapy”, Letter of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation of October 31, 2003 No. 13-51-263 / 13 “On the assessment and certification of students classified for health reasons to a special medical group for physical education”, instructive letter of the Ministry of Education of the USSR dated May 27, 1982 No. 34-M “On reducing the occupancy rate in special medical groups for physical education classes”
1.2 This Regulation is approved by the Pedagogical Council of the school, which has the right to make its own changes and additions to it.
1.3 This provision is a local normative act regulating the activities of a teacher and students involved in a special medical group (hereinafter SHG).
1.4 Education in the SHG is organized for students who, for health reasons, are contraindicated to attend traditional physical education lessons. For such students, the medical and preventive healthcare institution recommends classes in groups with the least physical exertion.
1.5 The following definitions are used in these Regulations:
To special medical group (MGG) includes persons who have deviations in the state of health of a permanent or temporary nature, which allow them to perform normal training loads, but are a contraindication to classes in the curriculum of physical education.
Depending on the severity and nature of the disease, students referred to SMG are recommended to be divided into subgroups - "A" and "B", in order to have a more differentiated approach to the appointment of motor modes.
Subgroup "A"- schoolchildren with deviations in the state of health of a reversible nature, weakened by various diseases.
Subgroup "B"- schoolchildren with severe irreversible changes in the activity of organs and systems ( organic lesions cardiovascular, urinary systems, liver, a high degree myopia with changes in the fundus, etc.)
2. Main tasks
physical education of students classified as SMG for health reasons in secondary schools are:
health promotion, restoration of functional readiness for physical activity, promotion of proper physical development and hardening of the body;
increase in physical and mental performance;
increasing the body's defenses and resistance;
learning rational breathing, restoring correct posture, and in necessary cases its correction;
mastering the basic motor skills and abilities;
education of moral and volitional qualities;
fostering interest in independent physical exercises and their introduction into the student's daily routine;
creating the prerequisites for the future labor activity students.
3. Organization of classes for a special medical group
3.1 Groups of students assigned to a special medical group are completed for physical education classes at the conclusion of a pediatrician and are issued by order of the school principal by the beginning of the new academic year.
3.2 When forming the SHG, age groups should be distinguished: 7-9, 10-12, 13-14 and 15-16 years old. If the number of students is not enough to complete a special medical group according to age, then groups of different ages are created. Group size up to 12 people.
3.3 In the absence of conditions for the formation of groups of students with the same diseases, it is possible to combine students with a different nature and severity of the disease, carrying out intra-group division into subgroups A and B;
3.4 The movement of children by health groups during the school year (from the SHG to the preparatory, then to the main one and vice versa) is carried out on the basis of a certificate from the pediatrician of the children's clinic. Based on this document, the school director issues an order to transfer the student to another health group. The class teacher together with the teacher of physical education in the class journal on the page "Health Sheet" opposite the student's name make a note: "on the basis of an order from ... transferred to ... .. group."
3.5 The time of the event has been moved from the general schedule to another shift. Zero lessons (in 1 shift) and double lessons in such groups are not allowed.
3.6 Attendance at classes by students of the special medical group is mandatory. Responsibility for attending them rests with the parents, the teacher who conducts these classes, and the class teacher, and is controlled by the deputy director for educational work and the doctor.
3.7 Conducted classes are recorded in a separate register of classes with students, reflecting general information: (full name, year of birth, class, disease diagnosis, duration of a break in physical exercises). The final marks from a separate journal are transferred to the final sheet of the class journal.
3.8 Physical education classes in this group are held according to special curricula.
3.9 When choosing means and methods, it is necessary to strictly observe the basic principles of physical education: gradualness, systematicity, accessibility, versatility.
3.10 Most outdoor activities are recommended. When conducting outdoor exercises, special attention should be paid to the combination of movements with breathing, to avoid long stops. The preparatory and final part of the lesson in cool weather can be held indoors
4. Aboutevaluation and assessment of students
4.1 The current assessment of the progress of students of the special medical group is set on a five-point system.
4.2 The final mark is set taking into account theoretical and practical training, as well as taking into account the dynamics of physical fitness and diligence.
4.3 The main emphasis in the assessment should be placed on the persistent motivation of students to engage in physical exercises and the dynamics of their physical capabilities;
4.4 If the student is present at all lessons, all of the above requirements are met, the physical education teacher has the right to certify the student for grades "good" and "excellent".
4.5 A positive mark should also be given to a student who has not shown significant changes in the formation of skills, abilities and development physical qualities, but regularly attended classes, diligently completed the tasks of the teacher, mastered the skills available to him.
4.6 In certificates of basic general education and secondary (complete) general education, a mark in physical culture is required.
4.7 Possible forms of knowledge control of students assigned to a special medical group for health reasons:
interview on theoretical questions;
oral communication on theoretical issues;
an abstract, as a rule, on a topic according to the profile of the disease;
practical implementation of therapeutic exercises according to the profile of the disease.
5. Documentation
Lists of students referred for health reasons to a special medical group
Order for the school "On the organization of the SMG"
SMG class schedule
Journal of attendance, progress and passage of program material.
Present position.
Basic Documents planning of educational work are:
annual plan for the passage of program material in the academic year;
fourth plan;
notes and plans for individual lessons;
register of classes with schoolchildren.
Additional Documents for the organization of the educational process in physical culture for children of the SHG are:
plans for medical and educational activities;
student's health passport;
rules for conducting corrective outdoor games;
thematic plan for conducting conversations with schoolchildren;
thematic plan for conducting conversations with parents;
programs of special courses for children and parents on adaptive physical culture.
